Students can Download Basic Maths Chapter 17 Straight Lines Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, 1st PUC Basic Maths Question Bank with Answers helps you to revise the complete Karnataka State Board Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Karnataka 1st PUC Basic Maths Question Bank Chapter 17 Straight Lines
Question 1.
Find the slope of the line joining the points (3, -4) and (-7,3).
Answer:
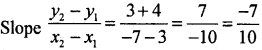
Question 2.
Show that the line joining points (2, -3) and (-5,1) is parallel to the line joining the points (7, -1) and (0,3) and perpendicular to the line joining the points (4,5) and (0, -2).
Answer:
Let m1 be the slope of the lien l1 joining points (2, -3) and (0, 3)
![]()
Let m2 be the slope of the line l2 going (7, -1) and (0,3)
![]()
⇒ m1 = m2
∴ L1 and L2 are parallel to each other.
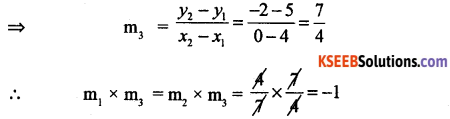
![]()
Question 3.
L1 and L3 or l2 l3 are perpendicular to each other. The slope of a line is double the
slope of another line. If the tangent of the angle between the is \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\). Find the slope of the lines.
Answer:
If slope of one line is m, then the slope of the other is 2m.
Let the angle between them θ then tan θ = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\)
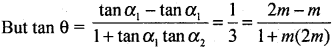
⇒ \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) = \(\frac{m}{1+2 m^{2}}\)
⇒ 1 + 2m2 = 3m
⇒ 2m2 – 3m + x = 0
⇒ (2m – 1)(m – 1 ) = 0
∴ 2m – 1 = 0 and m – 1 = 0
m = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) m = 1
∴ Slope are \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\), and 1.
On standard form of straight lines:
Question 1.
Find the equation of line passing through (-3, 5) with slope \(\frac { -1 }{ 5 }\)
Answer:
Let (x1 y1) = (-3, 5). slope m = \(\frac { -1 }{ 5 }\)
The equation of line is y – y1 = m(x – x1)
= y – 5 = \(\frac { -1 }{ 5 }\) (x + 3)
⇒ 5y – 25 = -x – 3
⇒ x + 5y – 22 = 0
![]()
Question 2.
Find the equation line passing through (-3, 2) and (11, -1).
Answer:
Let (x1, y1) = (-3,2), (x2, y2) = (11,-1)
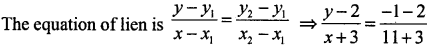
⇒ \(\frac{y-2}{x+3}=\frac{-3}{14}\)
⇒ 14y – 28 = -3x – 9
⇒ 3x + 14y – 19 = 0 is the equation
Question 3.
Find the ratio in which the line join (1, 2) and (4, 3) is divided by the line joining the points (2,3) and (4, 1).
Answer:
Let A = (2,3) B = (4, 1)
∴ the equation of line is a given by \(\frac{y-3}{x-2}=\frac{1-3}{4-2}\)
⇒ \(\frac{y-3}{x-2}=\frac{-2}{2}\) = -1
⇒ y – 3 = -x + 2
∴ x + y – 5 = 0 is the equation of line
Let c = (1,2) and D(4,3) cut the line AB at P(x ,y) is the ratio 2 : 1 then
![]()
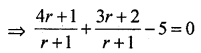
⇒ 4x + 1 + 3r + 2 – 5(r + 1) = 0
⇒ 2r – 2 = 0
⇒ r = 1
∴ the required ratio is 1 : 1
Question 4.
Express 9x – 4y – 13 = 0 in the intercept from
Answer:
Consider 9x – 4y = 13 = \(\frac{9}{13} x-\frac{4}{13} y\) = 1
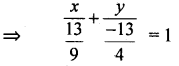
∴ x – intercept = \(\frac{13}{9}\)
y – intercept = \(\frac{-13}{9}\)
![]()
Question 5.
If P ¡s the length of the perpendicular from the origin on a line, whose x and y intercepts are respectively a and b then show that = \(\frac{1}{p^{2}}=\frac{1}{a^{2}}+\frac{1}{b^{2}}\)
Answer:
Let the line any the axis at A and y – axis at B
Then by data OA = a and OB = b from the figure
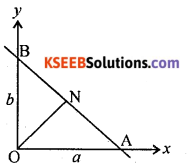
Area of OAB = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) (O.A) (O.B) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) ab
or = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) (AB).P
⇒ \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) ab = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) (AB).P ⇒ a2b2 = (AB)2. p2
Also AB2 = OA2 + OB2 ⇒ AB2 = a2 + b2 (∴ because a2b2 = (a2 + b2) . p2
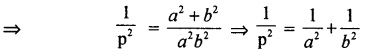
Intersection of two lines and Concurrency of Lines
Question 1.
Find the equation of line parallel to the y-axis and drawn through the point of intersection of x – 7y + 5 = 0 and 3x + y – 7 = 0.
Answer:
The equation of line through the point of intersection of the given lines is of the form x – 7y + 5 + k(3x + y – 7) = 0
∴ (1 + 3k)x + (k -7)y + 5 – 7k = 0 (1)
Since the lines are parallel to y-axis, coefficient of y = 0
i.e., k – 7 =0
∴ k = 7 substitute in (1) we get
22x – 44 = 0
∴ x – 2 = 0 is required equation
Question 2.
Find the equation of the line through the intersection of 5x – 3y = 1 and 2x + 3y – 23 = 0 and perpendicular to the line whose equation is 5x – 3y -1 = 0 and perpendicular to the line whose equation is 5x – 3y – 1 = 0.
Answer:
We have 5x – 3y – 1 = 0 ….. (1)
and 2x + 3y – 23 = 0 ….. (2) .
∴ the equation will be in the form
(5x – 3y – 1) + k(2x + 3y – 23) = 0
⇒ (5 + 2k)x + 3(k – 1)y – (23k + 1) = 0 …… (3)
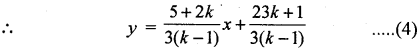
∴ Slope of line = \(\frac{5+2 k}{3(k-1)}\)
Also 5x – 3y – 1 = 0
⇒ y = \(\frac{5}{3} x \frac{1}{3}\) …….. (1)
∴slope = \(\frac{5}{3}\)
Given (4) and (5) are perpendicular
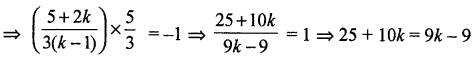
⇒ k = -34. Substituting the value of k in (3), we get
(5x – 3y – 1) -34 (2x + 3y – 25) = 0
⇒ 5x – 68x – 3y – 102y – 1 + 782 = 0
⇒ 63x + 105y – 781 = 0
![]()
Question 3.
If lines whose equation are y = m1 + c1y = m2x + c2 and y = m5x + c3 meet is a point then prove that m1( (c2 – c3) + m2 (c3 – c1) + m3(c1 – c2) = 0
Answer:
The equation of the given lines are
m1x – y + c1 = 0 ……. (1)
m2x – y + c2 = 0 …… (2)
m3x – y + c3 = 0 .. (3)
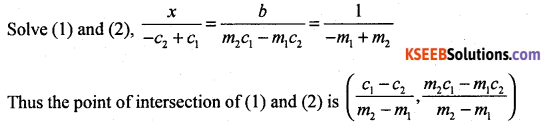
The three lines will be concurrent if the point of intersection of (1) and (2) lies on (3)
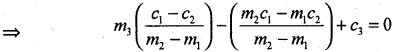
⇒ m3(c1 – c2) – (m2c1 – m1c2) + c3 (m2 – m1) =0, simplify,
⇒ m1(c2 – c3) + m2(c3 – c1) + m3(c1 – c2) =0
Question 4.
For what values of k are the lines x – 2y + 1 = 0, 2x – 5y + 3 = 0 and 5x – 9y + k = 0 are concurrent.
Answer:
consider
x – 2y + 1 = 0 ……. (1)
2x – 5y + 3 = 0 ….. (2)
5x – 9y + k = 0 …….. (3)
Solve (1) and (2) \(\frac{x}{-6+5}=\frac{-y}{3-2}=1\)
⇒ \(\frac{x}{-1}=\frac{-y}{-1}=\frac{1}{-1}\)
⇒ x = 1, y = 1
point of intersection of (1) and (2) is (1,1),
⇒ (1, 1) lies on (3) = 5 – 9 + k = 0 = k = 4
Angle between the lines, Length of perpendicular
Question 1.
Find the angle between the lines 2x + 3y – 4 = 0 and 3x – 2y + 5 =0
Answer:
By data
2x + 3y – 4 = 0 … (1)
3x – 2y + 5 = 0 …… (2)
∴ Slope of (1) = \(\frac{-a}{b}=\frac{-2}{3}\) = m1
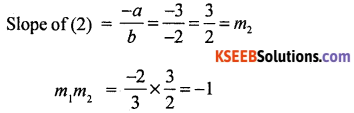
∴ the angle between the lines is 90°
![]()
Question 2.
Determine the position of the points (2, 1) and (-1, 1) w.r.t the line 4x – ly + 1 = 0.
Answer:
4(2) -7(1) = -7 + 1 = 2 > 0
4( -1) – 7(1) = – 4 – 7 + 2 = -10 < 0
Since the two points are opposite in sign the two points lie an either sides of the given line 4x – 7y + 1 = 0
Question 3.
If points (9,8) and (-3,3) are equidistant from the line 5x + 2y + 7 = 0 find ‘a’.
Answer:
Distance from (a, 8) to the line 5x + 2y + 7 = 0
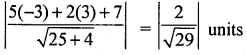
Given that the distance are equal
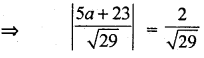
⇒ 5a + 23 = 2
or
5a + 23 = -2
⇒ a = \(\frac{-21}{5}\) and a = -5