Karnataka 2nd PUC Business Studies Important Questions Chapter 10 Financial Market
I. One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Name any one type of financial market.
Answer:
Money market.
Question 2.
Give the meaning of financial market.
Answer:
Financial market is a market comprising of institutions issuing instruments or securities for the purpose of raising funds.
Question 3.
State the minimum and maximum period of maturity in the case of money market instruments.
Answer:
14 days to one year.
Question 4.
Name any one of the Money Market Instruments.
Answer:
Treasury bills.
Question 5.
Name the most important constituent of Indian Money Market.
Answer:
The Reserve Bank of India is the most important constituent of Indian money market.
Question 6.
Name the money market instrument issued by the Government of India.
Answer:
Treasury Bills.
![]()
Question 7.
Name any one capital market instrument.
Answer:
Shares.
Question 8.
State any one component of capital market.
Answer:
Primary Capital Market.
Question 9.
What is Demat Account?
Answer:
It is an account in which all securities are held electronically.
Question 10.
What is dematerialisation of securities?
Answer:
Dematerialsiation or Demat is the process by which the paper documents of an investor are cancelled and credited to Demat Account of the investor maintained in electronic form, with a depository.
Question 11.
What is the biggest advantage of on – line Trading on a Stock Exchange?
Answer:
The biggest advantage of on – line trading is that they charge considerably lower brokerage for stock trading in comparison with the traditional stock broker.
Question 12.
Expand SEBI?
Answer:
Securities Exchange Board of India.
![]()
Question 13.
State any one objectives of SEBI?
Answer:
Development of Securities Market.
Question 14.
Expand NSEI.
Answer:
National Securities Exchange of India.
Question 15.
Expand NASDAQ.
Answer:
National Association of Securities Dealers Automated Quotations.
Question 16.
Expand BSE.
Answer:
Bombay Stock Exchange.
Question 17.
Expand SENSEX.
Answer:
Sensitive Index.
![]()
Question 18.
Name any one speculator in Stock Exchange.
Answer:
Bull
II. Two Marks Question and Answers
Question 1.
What is Money Market?
Answer:
It is a market concerned with buying and selling of short term financial instruments like Treasury bills, Commercial papers etc.,
Question 2.
What is Capital Market?
Answer:
The post of a financial system concerned with raising capital by dealing in shares, bonds and other long term investments.
Question 3.
Write any two Money Market Instruments.
Answer:
(a) Commercial Papers
(b) Commercial Bills
![]()
Question 4.
What are Treasury Bills.
Answer:
It is an instrument of short term borrowing by the government of India maturing in less than one year, it varies from 14 days to 364 days and they are highly liquid in nature.
Question 5.
What are Commercial Papers?
Answer:
It is a short term unsecured promissory note, negotiable and transferable by endorsement and delivery with a fixed maturity period of fifteen days to one year.
Question 6.
What is a Certificate of Deposit?
Answer:
These are short term unsecured negotiable instruments in bearer form issued by commercial banks. It bears a maturity date and fixed rate of interest.
Question 7.
What is a Call Money?
Answer:
It is a method by which banks faced with temporary shortage of cash borrow short term finance from other banks, maturity period varies from one to fifteen days.
Question 8.
What is Bankers Acceptance?
Answer:
A banker’s acceptance is a promised future payment, or time draft, which is accepted and granted by a bank and drawn on a deposit at the bank. It specifies the amount of money, the date and the person to whom the payment is due. After acceptance, the draft becomes an unconditional liability of the bank.
![]()
Question 9.
What is a Primary Capital Market?
Answer:
It is a new issue market which mobilises the funds from investors to organisations, funds are raised by issue of shares, debentures and bonds.
Question 10.
What is a Secondary Capital Market?
Answer:
It is also known as stock market or stock exchange, it is a market for the purchase and sale of existing securities.
Question 11.
Name the two Depositories operating in India.
Answer:
NSDL (National Securities Depository Limited) and CDSL (Central Depository Service Limited)
Question 12.
State any two depository services.
Answer:
- A depository helps in converting physical holding of securities into electronic holding.
- It keeps custody of investor’s holdings.
Question 13.
State any two objectives of SEBI.
Answer:
- Development of securities market
- Protection of Interest of Investors.
Question 14.
Who is Bull speculator?
Answer:
Bulls are speculators on the stock exchange who always expect a rise in the prices of securities. Hence, they go on buying shares in the expectationof selling them at a higher price in future and making profit.
![]()
Question 15.
Who is a Bear speculator?
Answer:
Bears are Speculators on the stock exchange who always expect a fall in the prices of securities. Hence, they go on buying shares in the expectation of selling them at a higher price in future and making profit.
Question 16.
Give the meaning is Spot Delivery?
Answer:
It means securities are delivered to the purchaser immediately on the spot after the payment is made.
Question 17.
What do you mean by Forward Delivery?
Answer:
In this case securities are transferred to the purchaser and payment is received at a later date, generally the period of forward delivery is one month, or it may be more with mutual agreement.
Question 18.
What are Blue Chips?
Answer:
It represents shares with high market capitilisation and also major share included in the main index of stock exchange.
III. Five Marks Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Explain any five Money Market Instruments.
Answer:
(a) It is an instrument of short-term borrowing by the government of India maturing in less than one year, it varies from 14 days to 364 days and they are highly liquid in nature.
(b) It is a method by which banks faced with temporary shortage of cash borrow short term finance from other banks, maturity period varies from one to fifteen days.
(c) These are short-term unsecured negotiable instruments in bearer form issued by commercial banks. It bears a maturity date and fixed rate of interest.
(d) It is a short-term unsecured promissiory note, negotiable and transferable by endorsement and delivery with a fixed maturity period of fifteen days to one year.
(e) They are short-term negotiable and self liquidating money market instruments with low risk. It is a bill of exchange used to finance the working capital requirements ofbusiness organisations.
![]()
Question 2.
Distinguish between Money market and Capital Market Money Market
Answer:
(a) It is a short term market
(b) It involves instruments like Treasury bills, Call money, Commercial bills.
(c) Major players are RBI, Commerical Banks
(d) Instruments are highly liquid.
(e) Rate ofreturn is low
(f) Low risk market
Capital Market
(a) It is a long term market’
(b) It involves instruments like Shares, Bonds, Debentures.
(c) Major players are individual investors, foreign investors.
(d) Instruments are relatively less liquid.
(e) Rate of return is high
(f) High-risk market.
Question 3.
Explain the trading procedure on a Stock Exchange.
Answer:
- 1st Step: Selection of a broker who is registered under SEBI
- 2nd Step: Opening a Demat Account in any of the selected banks.
- 3rd Step: Placing an order with the help broker.
- 4th Step: Giving orders to broker to execute the order.
- 5th Step: Last step in trading is to select the mode of payment for settlement.
Question 4.
State any ten depository services offered by a Depository.
Answer:
Depository services
(a) A depository helps in converting physical holding of securities into electronic holding.
(b) It keeps custody of investors holdings.
(c) It eliminates the risks involved with the physical certificates such as theft, forgery, damage of certificates.
(d) It significantly reduces brokerage charges.
(e) It reduces time required to clear each transaction as there is no paper work involved.
(f) It helps the investor to apply for new issues, as at present public issues are taking place only at demat mode.
(g) All corporate benefits like right issue, bonus shares are paid directly into investors Demat Account.
(h) Company pays dividend to the investors into their bank account registered in the Demat Account.
(i) Stamp duty is not applicable for transfer of securities in demat mode.
(j) An investor can monitor his investment dealings easily in Demat mode as depositories send SMS regarding debits or credits in Demat Account.
IV. Ten Marks Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Explain the different functions of stock exchange.
Answer:
(a) It is a organised market for securities.
(b) It is a deal with second hand or existing securities.
(c) It is a specialised market for purchase and sale of industrial and financial securities.
(d) Only approval and recognised securities of public and government companies are allowed for dealing.
(e) It provides liquidity by bringing together . investors and businesses.
(f) It may be an association of persons or an incorporated company.
(g) It regulates the dealing in securities.
(h) It facilitates free and paid trade of securities.
(i) It allows dealings of only listed companies securities.
(j) All investors have to buy and sell securities through members’of stock exchanges.
(k) Stock exchanges are regulated by SEBI as per Securities Contracts (regulations) Act 1956.
![]()
Question 2.
State any ten functions of SEBI.
Answer:
The principal functions of SEBI are as follows:
(a) Regulating the business in stock exchanges and any other securities market.
(b) Registering and regulating the working of capital market intermediaries (brokers, merchant bankers and so on).
(c) Registering and regulating the working of mutual funds.
(d) Promoting and regulating self-regulatory organisations.
(e) Prohibiting fraudulent and unfair trade practices in securities market.
(f) Promoting investor’s education and training of intermediaries of securities market.
(g) Prohibiting insider trading in securities.
(h) Regulating substantial acquisition of shares and take – over of companies.
(i) Conducting enquiries and audits of stock exchanges.
(j) Levying fees and other charges for carrying out its functions.
(k) Conducting research for the above purposes.
(l) Performing such other functions as may be prescribed by the Act or by the Government.
Question 3.
Mention any 10 Stock Exchanges Operating in India.
Answer:
(a) Bangalore Stock Exchange (Karnataka)
(b) Bombay Stock Exchange (Maharastra)
(c) Madras Stock Exchange (Tamilnadu)
(d) Pune Stock Exchange (Maharastra)
(e) Cochin Stock Exchange (Kerala)
(f) Delhi Stock Exchange (Delhi)
(g) Calcutta Stock Exchange (West Bengal)
(h) Hyderabad Stock Exchange (Andhra Pradesh)
(i) National Stock Exchange (Maharastra)
(j) Canara Stock Exchange (Karnataka)
(k) Jaipur Stock Exchange (Rajasthan)
(l) Ludiana Stock Exfchange (Punjab)
(Hint to remember, relate with IPL Cricket teams)
Question 4.
Name the market where companies Issue new securities.
Answer:
Primary Market.
![]()
Question 5.
How many stock exchatiges are there in India?
Answer:
Three are 22 regional stock exchanges and 2 National level Stock Exchanges- NSEI and OTCE!.
Question 6.
Why secondary market Is considered as market for second hand securities?
Answer:
Because in this market existing and second hand securities are sold between investors.
Question 7.
Which money market security is also known as Zero Coupon Bond?
Answer:
‘Treasury Bill’ is also known as Zero Coupon Bond.
Question 8.
Explain the term: Price Rigging
Answer:
Price Rigging refers to manipulating the prices ofsecunties with the main objectives of inflating or depressing the market price of securities.
Question 9.
‘A’ wants to get his company listed in National Stock Exchange . His company’s paid up capital is Rs. 20,00,000. Can he get it listed? Kindly advise him.
Answer:
No, he cannot get it listed in NSE because to get listed in NSE minimum paid up capital required is Rs. 3 crore.
Question 10.
Distinguish between Capital market and Money Market on the basis of following
(i) Participants
(ii) Duration
(iii) Instruments
Answer:
(i) Participants: The participants in capital market are financial institutions, banks, public and private companies, foreign investors and ordinary retail investors from public whereas in money market, the participants are financial institutions, banks, public and private companies but foreign investors and ordinary retail investors do not participate.
(ii) Duration: The capital market deals in medium and long term securities. Whereas the money market deals with short term securities having maximum tenure of one year.
(iii) Instruments: T,he common instruments of capital market are Equity shares, Debebtures, Pref. Shares, Bonds whereas the common instrument of money market are Treasury Bills, Commercial bills, Certificate of Deposits, Commercial paper.
Question 11.
Nature of ‘Capital market” can be well explained with the help of its features. State any three such features of Capital Market.
Answer:
- Link between saver and investment opportunities.
- Deals in long term investment.
- Utilises intermediaries.
Question 9.
Nature of money Market’can be well explained with the help of its features. State any three such features of money market.
Answer:
- Market for short term funds,
- Deals in monetary assets whose pes k-d of maturity is upto one year,
- Market where low risk, unsecured and short term debt instruments are issued and actively traded everyday.
![]()
Question 10.
State any three objectives of NSE.
Answer:
- Establishing a nationwide trading facility for all types of securities.
- Ensuring equal access to investors all ovet the country through an appropriate communication network.
- Providing a fair, efficient and transparent securities market using electronic trading system.
Question 11.
Explain any three functions of a Stock Exchange.
Answer:
- A Stock Exchange is a reliable barometer to measure the economic condition of a country.’
- It helps to value the securities on the basis of demand and supply factors.
- It provides ready market for sale and purchase of securities.
Question 12.
‘SEBI is the watchdog of security market’. Comment.
Answer:
SEBI was setup in 1988 to regulate the functions ofthe securities market and to protect the interest of investors but SEBI was found ineffective in regulating the activities of stock market. It was able to observe and watch only but failed to take corrective measure that is why it is called as watchdog.
Question 13.
‘Stock market imparts liquidity to investment’. Comment.
Answer:
The Stock market is a place where securities of companies are bought and sold. Generally the securities are long term and get matured only after a long period oftime. These securities can be sold in stock market and can be easily converted into cash. The presence of market is an assurance to investors that their investment can be converted into cash as and when required by them.
Question 14.
State any two methods of issuing securites in Primary Market.
Answer:
The Primary market is also known as the new issues market. It deals with new securities being issued for the first time.
The securities may be issued in primary market by following two methods:
- public issue through prospectus
- Offer for sale.
Question 15.
Explain the terms:
(i) Bulls
(ii) Bears
(iii) Stag
Answer:
(i) Bulls: Abul is a speculator who expects rise in price. He buys securities with a view to sell them in future at a higher price and making profit out of it.
(ii) Bears: A bear is a speculate who expects fall in the price. He sells securities which he does not possess.
(iii) Stag: A stag is a speculator who applies for new securities in expectation that prices will rise by the time allotment and he can sell them at premium.
Question 16.
What function does financial market perform?
Answer:
The financial market performs the function ofbringing together the deficit units (Corporate Sector) and surplus units (investors). It is through financial market that the lender meet the borrowers.
Exercises
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are the functions of a Financial Market?
Answer:
Financial market plays an important role in the allocation of scarce resources in an economy by performing the following four important functions
1. Mobilisation of Savings and channelizing them into the most productive uses. A financial market facilitates the transfer of savings from savers to investors. It gives choice to the saver of different investments and thus, it helps to channelize surplus funds into the most productive use.
2. Facilitate Price Discovery In a financialmarket. the households are suppliers of funds and business firms represent the demand. The interaction between them helps to establish a price for the financial asset which is being traded in that particular market.
3. Provide Liquidity to Financial Assets Financial markets facilitate easy purchase and sale of financial assets. Holders of assets can readily sell their financial assets through the mechanism of financial market.
4. Reduce the Cost of Transactions Financial markets provide valuable Information about securities being traded in the market. It helps to save time, effort and money that both buyers and sellers of a financial asset would have to spend to try or otherwise link each other
![]()
Question 2.
“Money Market is essentially a Market for short term funds:’ Discuss.
Answer:
The money market is a market for short term funds which deals in monetary assets whose period of maturity is up to one year these assets are close substitutes for money. It is a market where low risks, unsecured and short term debt instruments that are highly liquid are issued and actively traded every day. It enables the raising of short term hinds for earning returns. The major participants in the market are the Reserve Bank of India, Commercial Bank. Non-Banking Finance Companies, State Go vernments, Large Corporate Houses and Mutual Funds.
Question 3.
What is a Tteasury bill?
Answer:
A Treasuiy Bill is an instrument of short term borrowing by the Government oflndia Maturing in less than one year. They are also known as Zero Coupon Bonds issued by the RBI on behalf of the Central Government to meet its short term requirement of funds. Treasury bills are issued in the form of a promissory note. They are highly liquid and have assured yield and negligible risk of default. They are issued at a price which is lower than their face value and repaid at par treasury bills are available for a minimum amount of Rs. 25,000.
Question 4.
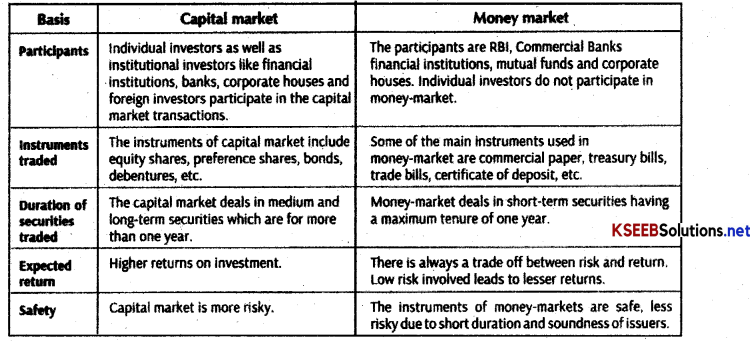
Distinguish between Capital Market and Money Market.
Answer:
Difference between Capital and Money Market
Question 5.
What are the functions of a Stock Exchange?
Answer:
The efficient functioning of a stock exchange creates a conducive climate for an active and growing primary market following are the important functions of a stock exchange
1. Providing Liquidity and Marketability to Existing Securities: The basic function of a stock exchange is the creation of a continuous market where securities are bought and sold. It gives investors the chance to disinvest and reinvest. Thus provides both liquidity and easy marketability to the existing securities in the market.
2. Pricing of Securities: Share prices on a stock exchange are determined by the forces of demand and supply. A stock exchange is a mechanism of constant valuation through which the prices of securities are determined. Such a valuation provides important instant information to both buyers and sellers in the market.
3. Safety of Transactions : The membership of a stock exchange is well- regulated and its dealmgs are well defined according to the existing legal framework which ensures that the investing public gets a safe and fair deal on the market.
4. Contributes to Economic Growth : A ! stock exchange is a market in which existing securities are resold or traded. This process of disinvestment and reinvestment saving get channelized into productive investment avenues. This leads to capital formation and economic growth
5. Spreading of Equity Cult: The stock exchange plays vital role in ensuring wider share ownership by regulating new issues, better trading practices and taking effective steps in educating the public about investments.
6. Providing Scope for Speculation: The stock exchange provides sufficient scope within the provisions of law for speculative activity in a restricted and controlled manner.
![]()
Question 6.
What are the objectives of the SEBI?
Answer:
The overall objective of SESI is to protect the interest of investors, promote the development and regulate the securities in market.
This maybe elaborated as follows
- To regulate stock exchanges and the securities industry to promote their orderly functioning.
- To protect the rights and interests of investors, particularly individual investors to guide and educate them.
- To prevent trading malpractices and achieve a balance between self-regulation by the securities and its statutory regulation.
- To regulate and develop a code of conduct and fair practices by intermediaries like brokers, merchant bankers etc. with a view to making them competitive and professional.
Question 7.
State the objectives of the NSE.
Answer:
NSE was setup with the following objectives:
- Establishing a nationwide trading facility for all types of securities.
- Through an appropriate communication network, ensuring equal access to investors.
- Through electronic trading system, provides a fair, efficient and transparent security market. .
- It enables shorter settlement cycles and book entry settlements.
- Meeting international benchmarks and standards.
Question 8.
What is the OTCEI?
Answer:
The OTCEI is a company incorporated under the Companies Act, 1956. It was set up to provide small and medium companies an access to the capital market for raising finance In a cost effective manner. It is folly computerised, transparent, single window exchange which commenced trading in 1992. This exchange is established on the lines of NASDAQ the OTC exchange in USA. It has been promoted by UTI, ICICI, 1DBI, IFCI, LIC, GIC, SBI, capital markets and can bank financial services. It is a negotiated market place that exists anywhere as opposed to the auction market place, represented by the activity on securities exchange. Thus, in the
OTC exchange, trading takes place when a buyer or seller walks up to an OTCEI counter, taps on the computer screen, finds quotes and effects a purchase or sale depending on whether the prices meet their target.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain the various money Market Instruments.
Answer:
Money Market Instruments
1. Treasury Bill: A treasury bill is an instrument of short term borrowing by the Government of India maturing in less than one year. They are also known as Zero Coupon Bonds issued by Reserve Bank of India on behalf of the Central Government to meet its short term requirements of funds. They are issued in the form of a promissory note. They are highly liquid and issued at a price which is lower than their face value and repaid at par. Treasury bills are available for a minimum amount of Rs.25,000.
2. Commercial Paper: Commercial paper is a short term unsecured promissory note, negotiable and transferable by endorsement and delivery with a fixed maturity period. It is issued by large and creditworthy companies to raise short term funds at lower rates of interest than market rates. It usually has a maturity period of 15 days to one year. The issuance of commercial paper is an alternative to bank borrowing for
large companies that are generally considered to be finally strong. It is sold at discount and redeemed at par.
3. Call Money: Call money is short term finance repayable on demand, with a maturity period of one day to fifteen days, used for inter-bank transactions. Commercial Banks have to maintain a minimum cash balance known as cash reserve ratio. Call money is a method by which banks borrow from each other.
4. Certificate of Deposit: Certificates of deposit are unsecured, negotiable, short term instruments in bearer form, issued by Commercial Banks and development financial institutions. They can be issued to individuals, corporations and companies during periods of tight liquidity when the deposit growth of banks is slow but the demand for credit is high. They help to mobilise a large amount of money for short periods.
5. A Commercial Bill: A commercial bill is a bill of exchange used to finance the working capital requirements of business firms. It is a short term negotiable, self-liquidating instrument which is used to finance the credit sales of firms, when goods are sold on credit, the buyer becomes liable to make payment on a specific date in fiiture.
Question 2.
What are the methods of floatation in Primary Market?
Answer:
The primary market is also known as the new issues market. It deals with new securities being issued for the first time. There are various methods of floating new issues in the primary market
1. Offer Through Prospectus: This involves inviting subscription from the public through issue of prospectus. A prospectus makes a direct appeal to investors to raise capital, through an advertisement in newspapers and magazines. The issues may be under written and also required to be listed on at least one stock exchange. The contents at the prospectus have to be in accordance with the provisions of the Companies Act and SEBI disclosure and investor protection guidelines.
2. Offer for Sale: Under this method securities are not issued directly to the public but offered for sale through intermediaries like issuing houses or stock brokers. In this case, company sells securities unblock at an agreed price to brokers who, in turn, resell them to the investing public.
3. Private Placement: Private placement is the allotment of securities by a company to institutional investors
and some selected individuals. It helps to raise capital more quickly than a public issue. Access to the primary market can be expensive on account of various mandatory and non¬mandatory expenses.
4. Rights Issue: This is a privilege given to existing shareholders to subscribe to a new issue of shares according to the terms and conditions of the company. The shareholder are offered the ‘right’ to buy new shares in proportion to the number of shares they already possess.
5. e-IPOs: A company proposing to issue capital to the public through the on-line system of the stock exchange has to enter into an agreement with the stock exchange. This is called an Initial Public Offer (IPO). SEBI registered brokers have to be appointed for the purpose of accepting applications and placing orders with the company the issuer company should appoint a registrar to the issue having electronic connectivity with the exchange. The issuer company can apply for listing of its securities on any exchange other than the exchange through which it has offered its securities. The lead manager co-ordinates all the activities amongst intermediaries connected with the issue.
Question 3.
Explain the Capital Market reforms in India.
Answer:
The National Stock Exchange is the latest, most modem and technology driven exchange.
NSE has setup a nationwide fully automated screen based trading system.
The NSE was set up by leading financial institutions, banks, insurance companies and others financial intermediaries. It is managed by professionals, who do not directly or indirectly trade on the exchange. The trading rights are with the trading members who offer their services to the investors. The Board of NSE comprises senior executives from promoter institutions and eminent professionals, without having any representation from trading members.
Objectives of NSE
- Establishing a nationwide trading facility for all types of securities.
- Ensuring equal access to investors all over the country through an appropriate communication network.
- Providing a fair, efficient and transparent securities market using electronic trading system.
- Enabling shorter settlement cycles and book entry settlements.
- Meeting international bench marks and standards.. Within a span of 10 year, NST was able to achieve its objectives for which it was set up. It has been playing a leading role as a change agent in transforming the Indian capital market.
![]()
Question 4.
Explain the objectives and functions of SEBI.
Answer:
Objectives of SEBI:
The overall objective of SESI is to protect the interest of investors, promote the development and regulate the securities in market.
This may be elaborated as follows
- To regulate stock exchanges and the securities industry to promote their orderly functioning.
- To protect the rights and interests of investors, particularly individual investors to guide and educate them.
- To prevent trading malpractices and achieve a balance between self-regulation by the securities and its statutory regulation.
- To regulate and develop a code of conduct and fair practices by intermediaries like brokers, merchant bankers, etc. with a view to making them competitive and professional.
Functions of SEBI:
Keeping in mind the emerging nature of the securities market in India, SEBI was entrusted with the twin task of both regulation and development of the securities market.
It has certain functions Regulatory Functions
- Registration of brokers and sub-brokers and other players in the market.
- Registration of collective investment schemes and mutual funds.
- Regulation of stock brokers, portfolio exchanges, underwriters and merchant bankers and the business in stock exchanges and any other securities market.
- Regulation of taken over bids by companies.
- Calling for information by undertaking inspection conducting enquiries and audits of stock exchanges and intermediaries.
- Levying for or other charges for carrying out the purposes of the act.
- Performing and exercising such power under Securities Contracts Act. 1956, as may be delegated by the Government of India.
Development Functions
- Training of intermediaries of the securities market.
- Conducting research and publishing information useful to all market segments.
- Undertaking measures to develop the capital markets by adopting a flexible approach.
Protective Functions
- Prohibition of fraudulent and unfair trade practice like making misleading statements, manipulations, price rigging etc.
- Controlling insider trading and imposing penalties for such practices.
- Undertaking steps for investor protectioa
- Promotion of fair practices and code of conduct in securities market.
Question 5.
Explain the various segments of NSE.
Answer:
NSE provides trading in the following two segments:
1. Whole Sale Debt Market Segment: This segment provides a trading platform for a wide range of fixed income securities that include central government securities, treasury bills, state development loans, bonds issued by public sector undertakings, floating rate bonds, zero coupon bonds, index bonds, commercial paper, certificate of deposit, corporate debentures and mutual funds.
2. Capital Market Segment: The capital market segment ofNSE provides efficient and transparent platform for trading in equity, preference, debentures, exchange traded funds as well as retail government securities.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Primary and secondary markets
(a) compete with each other
(b) complement each other
(c) function independently
(d) control each other
Answer:
(b) Primary Market and Secondary Market complement each other as primary market deals with the issue of new securities and secondary market also helps the fresh Investor to enter in the market
Question 2.
The total number of Stock Exchanges in India are
(a) 20
(b) 21
(c) 22
(d)23
Answer:
(d) There are 23 stock exchanges In India list of stock exchanges in India are Bombay, National, Regional, Ahmedabad, Bengaluru, Bhubaneshwar, Calcutta, Cochin, Coimbatore, Delhi, Guwahati, Hyderabad, Jaipur, Ludhiana, Madhya Pradesh, Madras (Chennai), Magadh, Mangalore, Meerut, OTC Exchange of India, Pune, Saurashtra Kutch, Vadodara.
Question 3.
The settlement cycle in NSE is
(a) T + 5
(b )T + 3
(c) T + 2
(d) T + 1
Answer:
(c) The settlement cycle in NSE is T + 2.
![]()
Question 4.
The National Stock Exchange of India was recognised as stock exchange in the year
(a) 1992
(b) 1993
(c) 1994
(d) 1995
Answer:
(b) NSE was incorporated in 1992 and was recognised as a stock exchange in April 1993
Question 5.
NSE commenced fiitures trading in the year
(a) 1999
(b) 2000
(c) 2001
(d) 2002
Answer:
(b) In 2000. NSE commenced future tradings.
Question 6.
Clearing and settlement operations of NSE is carried out by
(a)NSDL
(b)NSCCL
(c) SBI
(d) CDSL
Answer:
(b) NSCCL carried out the clearing and settlement operations of NSE.
Question 7.
OTCI was started on the lines of
(a) NASDAQ
(b) NYSE
(c)NASAQ
(d) NSE
Answer:
(a) OTCEI (Over The Counter Exchange of India) established on the lines of NASDAQ (National Association of Securities Dealers Automated Quotations).
Question 8.
To be listed on NSE, the minimum capital requirement for a company,
(a) Rs. 5 crores
(b) Rs. 3 crores
(c) Rs.6 crores
(d) Rs. 1 crore
Answer:
(b) In order to have its securities listed the companies should have an minimum of Rs. 3 crores.
![]()
Question 9.
A Treasury Bill is basically
(a) an instrument to borrow short term funds
(b) an instrument to borrow long term funds
(c) an instrument of capital market
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) Treasury Bills are an instrument to borrow short term funds. These are issued by RBI on behalf of the Government of India.
Case Problems:
‘R’ Limited is a real estate company which was formed in 1950. In about 56 years of its existence the company has managed to carve out a niche for itself in this sector. Lately, this sector is witnessing a boom due to the fact, that the Indian economy is on the rise. The incomes of middle class are rising. More people can afford to buy homes for themselves due 10 easy availability of loans and accompanying tax concessions.
To expand its business in India and abroad the company is weighing various Options to raise money through equity offerings in India. Whether to tap equity or debt, market whether to raise money from domestic market or international market or combination of both? When their to raise the necessary finance from money market or capital market. It is also planning to list itself in New York Stock Exchange to raise money through ADR’s. To make its offerings attractive it is planning to offer host of financial plans products to its stakeholders and investors and also expand it’s listing at NSE after complying with the regulations of SEBI,
Question 1.
What benefits will the company derive from listing at NSE?
Answer:
Following are the benefits the company can derive from listing at NSE
- NSE provides nationwide trading facility for all types of facilities.
- The liquidity and best available prices for the securities are ensured by the processing speed ofthe exchange.
- TheNSE network is used to disseminate information and company announcements across the country.
- Enabling shorter settlement cycles and book entry settlement.
![]()
Question 2.
What are the regulations of SEBI that the company must comply with?
Answer:
Following are the regulations of the SEBI for new issue that the company must comply with
- Prospectus has to be attached with every application.
- Objective of the issue and cost ofproject should be mentioned in the prospectus.
- Company’s management, past history and present business of the firm should be highlighted in the prospectus.
- Subscription List for public issue should be kept open for a minimum of 3 days and maximum of 10 days.
- Collections agents are not allowed to collect application money in cash.
- Issue should make adequate disclosure regarding the terms and conditions of redemption security conversion and other relevant features ofthe new Instrument so that an investor can make reasonable determination of risks returns. Safety and liquidity of the instrument the disclose shall be vetted by SEBI in this regard
Question 3.
How does the SEBI exercise control over ‘R’ Limited in the interest of investors?
Answer:
SEBI will exercise control over ‘R’ limited by:
1. Prohibiting fraudulent and uniair trade practices in the securities market, unfair trade practices Include price rigging. Making misleading statements
2. Prohibiting insider trading Le., restricts the persons having access to price sensitive information about the company to take undue advantage of it.
3. Examining that adequate disclosure about the terms and conditions of redemption, security conversion and other relevant features ofthe new Instrument at the time of issue is made so that an investor can make reasonable determination of risks returns. Safety and liquidity of the instrument.
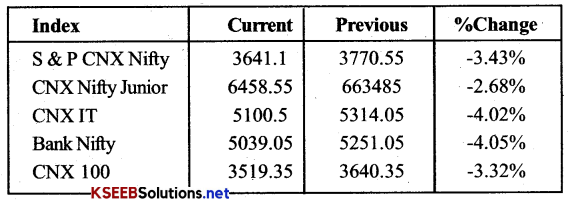
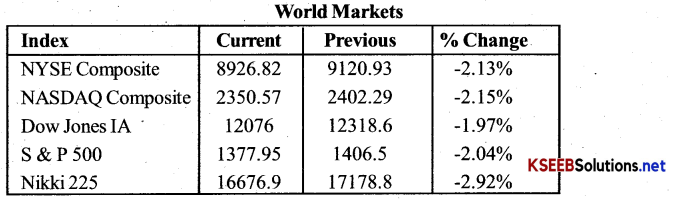
The above figures are taken from the website ofNational Stock Exchange of India. They illustrate the movement of NSE stock indices as well as world stock indices on the date indicated.
![]()
Questions 4.
What do you mean by a stock index? How is it calculated?
Answer:
Stock index refers to the index used to capture the movement of the stock market. It is a barometer which measures overall market trend through a set of stocks which are representatives of the market. An ideal index must represent changes in the prices of securities and also show the price movement of different classes of shares.
Most of the stock market uses the following 3 methods of calculating index:
- Price Weighted Index: An index reflecting the sum of the prices of the sample share in a certain year/month/week/day with reference to abase year.
- Equal Weighted Index: An index reflecting the simple arithmetic average of the price relatives of a sample of shares in a certain period with reference to base year.
- Value Weighted Index: It is an index reflecting the aggregate market capitalisation of the sample shares in certain period in relation to base year.
Question 5.
What conclusions can you draw from the various movements of NSE stock indices?
Answer:
There is a downward swing in the stock market. While comparing the previous and current index of NSE we can say that there is a depression in the market as index is down for all the sectors.
Question 6.
What factors affect the movement of stock indices? Elaborate on the nature of these factors.
Answer:
The fell in the domestic market. As given in the above table, can significantly be attributed to the market sentiments of world market. We can see the world indices and NSE indices are moving in the same direction.
Question 4.
What relationship do you see between the movement of indices in world markets and NSE indices?
Answer:
There is direct relation between NSE indices and world market indices. As there is negative trend in world index, it brings negative trend in NSE index also.