Karnataka 2nd PUC Economics Important Questions Chapter 6 Non – Competitive Markets
Question 1.
What is monopoly?
Answer:
Monopoly means a market with a single seller.
Question 2.
What is monopolistic competition?
Answer:
Monopolition is a type of imperfect market In which there are many seller selling differentited products but perfect substitutes.
Question 3.
What is an oligopoly?
Answer:
Oligopoly is the market situation in which there are few firms selling homogeneous or differentiated products.
Question 4.
What is meant by product differentiation?
Answer:
Product differentiation refer to the diferences alone in materials by design or colour etc..
![]()
Question 5.
Define profit?
Answer:
The profit refer to the surplus of income over expencess of production.
Question 6.
Define abnormal profit?
OR
Define super normal profit?
Answer:
The abnormal profit refer reffer to when the equilibrium price is greater than the minimum of the AC curve.
Question 7.
Define normal profit?
Answer:
When the equlibrium price becomes equal to minimum point of the AC curve than it is said as the firm is earning normal profits.
Question 8.
Define Price rigidity?
Answer:
Price rigidity implies that price are different to change
Question 9.
From where do you buy electricity for home? What are the characteristicke of that market?
Answer:
We buy electricity from electric office (BESCOM)
The characteristics ofthis market are:
- Single seller
- No close substitutes.
Question 10.
Mention the three forms of imperfectely competitive market?
Answer:
The three forms of imperfectly competitive market are:-
- Monopoly
- Monopolistic competition
- Oligopoly
![]()
Question 11.
In which market form is there product differentiation?
Answer:
Monopolistic competition market and oligopoly market
Question 12.
What is price discrimination?
Answer:
It refers to charging og different price from different consumes for different units of the same product.
Question 13.
What is the shape of MR curve under monopoly?
Answer:
Under monopoly market MR curve from left to right and it lies below the AR curve.
Question 14.
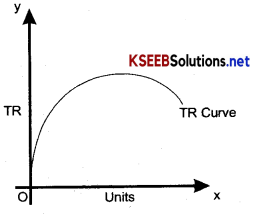
What is the shape of the TR monopoly?
Answer:
TR curve is invese U- shaped as show below in the diagram:
Question 15.
What will you call that market which was characteristics both of monopoly and perfect completion?
Answer:
Monopolistic competition.
Question 16.
Give four examples of product (soap) differentiation?
Answer:
- Medimix
- Santoor
- Lux
- Cintholetc.
Question 17.
Which type of market has full control Over price?
Answer:
Monopoly has full control over price.
![]()
Question 18.
Which type of market has partial control over price?
Answer:
Monopolistic competition has partial control over price.
Question 19.
Which type of market has no control over price?
Answer:
A competitive firm has no control over price
OR
Perfect competition
Question 20.
On what factor does the price depend for the monopoly firm?
Answer:
For the monopoly firm, the price depends on the quantity of the commodity sold.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
How does a monopoly differ from a competitive firm?
Answer:
Monopoly
- Monopoly is a market with single seller
- Produce different product
- Price is determined by individual firm
- Smaller output in higher price.
Competitive firm:
- Competitive firm is market with many seller.
- Produce homogeneous product
- Price is determined by demand & supply
- Large output and lesser price.
![]()
Question 2.
What are selling costs?What is their main objective?
Answer:
Selling costs are those expenses of the producer incurred on marketing of goods produced.
The main objective of the selling costs:
- The selling cost are very important differ our product from the other products.
- The selling costs may be attached to particular consumer & particular brand.
- Give two example of monopolistic competitive industry?
The two example of monopolistic competitive industry
- Soap Industry
- Biscuit Industry
- Paint Industry etc.
Question 4.
Why is the demand curve of monopolistic competitive firm more elastic than that of a monopoly?
Answer:
The demand curve is more elastic in monopotic competition than monopoly because the competition is more than that of monopoly.
Question 5.
Can a monopolist incur loss in the short- run?
Answer:
Yes, monopolist can incure loss, in the situtation where short run average cost exceeds shortrun average revenue i.e SAC > SAR.
Question 6.
Describe the feature of monopoly?
Answer:
The features of monopoly are as follows
- There will be existence of one seller or single seller.
- There will be no close substitutes.
- There will high barriers to entry.
- monopolist is a price maker
- Monopolists have perfect knowledge about the market conditions.
- Monopolist willhave more chance to do price discrimination.
![]()
Question 7.
What is oligopoly market? Write down the charactersties of oligopoly market?
Answer:
Oligopoly is a market situtation in which there are few firms selling homogeneous Or differeneiated products.
Features of oligopoly market:
- There will be existance o few large firms.
- There will be interdependence among firms.
- Ologopoly is market with better group behaviour.
- The only way open to the oligopolist to his sales is either by advertising or improving the quality of the product.
- The firms under oligopoly produce homogeneous or differentiated products.
- Under oligopoly prices do not move freels as per the changes in demand.
Question 8.
Write down the features of monopolistic competition?
Answer:
The features of monopolistic competition
- The number offirms producing a producvt will be large under monopolistic competition.
- There will be free entry and exit of firms.
- The most outstanding features of monopolistic competition is product olifferentiation.
- There will be existence of selling costs.
- Under monopolistic competition a firm fixes its own price of its product.
Question 9.
Difference between monopoly and monopolistic competition?
Answer:
| Monopoly | Monololistic |
| 1. In monopoly there is only one firm. | 1. In monopolistic competition there are many firms. |
| 2. There is no closer substitute of the commodity | 2. There many close substitutes. |
| 3. There is compete restriction on the entry of the firm. | 3. There is freedom of entry. |
| 4. There are homogenous products. | 4. There is product diffienciation. |
![]()
Question 10.
Analyse the effect of firms in price in diffrent markets?
Answer:
1. Perfect competition: In this market, a firm cannot effect the price by the industry because there are large number of buyers and sellers in perfect competition.
2. Monopoly: In this market, firm is the industry. It can effect the price of the commodity to a great extent. The price of the commodity is determined by itself. It can effect the price indirectly by increasing or decreasing the supply of the commodity.
3. Monopolistic competition: In thus market, a firm can effect the price to some extent by changing the brand/size of its product.
Question 11.
Explain the implications of freedom of entry & exit of firms under perfect competition?
Answer:
Implications of freedom and entry and exit of a firm under perfect competition In perfect competition, there is free entry of new firms and exist of existing firms. New firm induced by large profits can enter the industry whereas in case of loss inefficient firm leave the industry. The implication is that no firm can earn abnormal profit in the long run. The firm earns just normal profit i.e minimum profit necessary to remain business.
Question 12.
Giving reason, distinguish between the behaviour of demand curves of firms under perfect competition and monopolistic competition.
Answer:
Under perfect competition, demand curve is perfectly inelastic, whereas under monopolistic competition, demand curve is highly inelastic shown below:
Reason Under perfect competition, a firm is price takes and price of every unit of commodity is the same, on the other hand, more goods can be sold only by lowering the price.
Exercises
Question 1.
What would be the shape of the demand curve so that the total revenue curve is
(a) A Positively sloped straight passing through the origin?
Answer:
The demand curve will be parallel to OX, axis when the total revenue curve is a positively straight line passing through the origin.
(b) A horizontal line.
Answer:
The demand curve will be sloping downward from left to right when the total revenue curve is a horizontal line.
![]()
Question 2.
from the schedule provided below calculate the total revenue, demand curve & the price elasticity of demand?
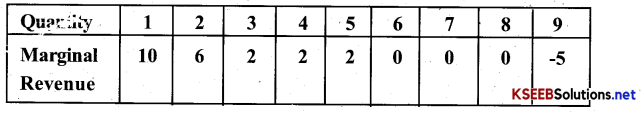
Answer:
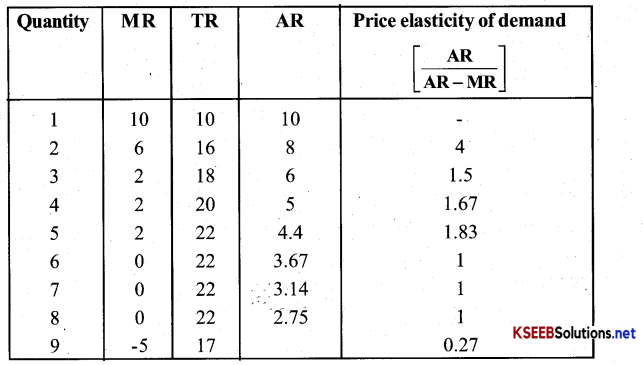
Question 3.
What is the value of MR when the demand curve elastic?
Answer:
Demand curve is elasticity is greater than unity. When price elasticity of demand is more than unity cones, then the value of MR is positive.
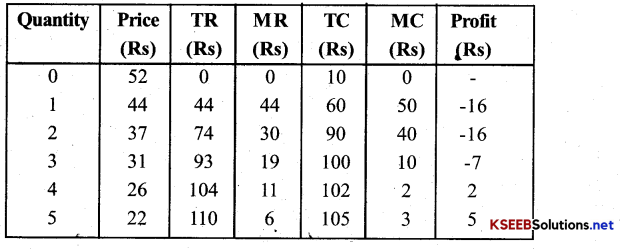
Question 4.
A monopoly firm has a total fixed cost of Rs 100 and has the following demand schedule

Find the short-run equilibrium quantity, price and total print. What would be the equilibrium in the long run? In case the total cost was Rs 1000, Describe the equilibrium in the short run and in the long run?
Answer:
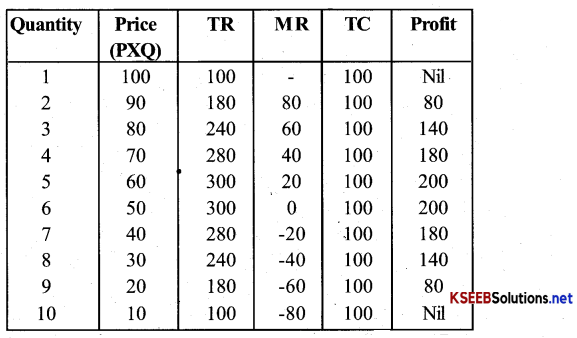
Short-run equilibrium quantity in units, Price is Rs 50 & Print Rs 200
Question 5.
If the monopolist firm of Excercise 3, was a public sector firm. The government set a rule for its manager to accept government fixed price as given (i.e, to be a price taker and therefore behave as a firm in a perfectly competitive Markets), and the government decide to set the price so that demand and supply in the market are equal. What would be the equilibrium price, Quantity & profit in this case?
Answer:
If the government sets a rule for the firm to accept the government fixed price on given the equlibrium price will be equal to Rs 10 Quantity supplied will 10 ad the profit will be zero.
![]()
Question 6.
Comment on the shape of the MR curve is case the TR curve is a
(i) Positively shaped stright line
Answer:
MR curve is a stright line parallel to OX axis when TR curve is a positively shaped stright line.
(ii) Horizontal shaped stright line
Answer:
When TR is horizontal straight line, MR curve is negatively shaped stright line.
Question 7.
The market demand curve for a commodity and the total cost for a monopoly firm producing the commodity is given by the schedule below. Use the information to calculate the following.
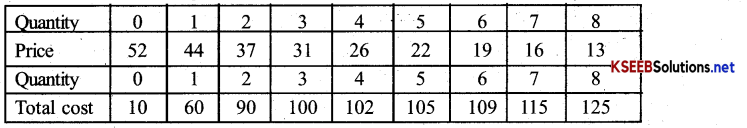
(a) The MR and MC schedules.
(b) The quantities for which the MR and MC are equal.
(c) The equilibrium quantity of output and the equilibrium price of the commodity.
(d) The total revenue, total cost and total profit in equilibrium.
Answer:
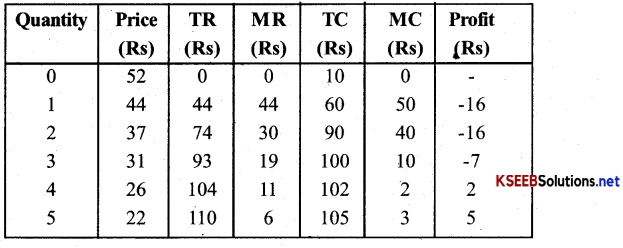
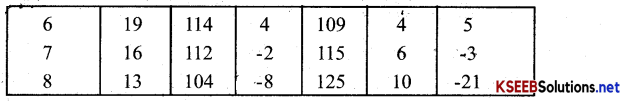
(a) MR and MC schedule are given in the table.
(b) At 6 quantity, MR = MC(=4)
(c) Equlibirum quantity of output = 6 units and equlibrium price is Rs 19.
(d) At equlibrium, profit = TR – TC
= 114 – 109 = 5
Question 8.
Will the monopolist firm continue to produce in the short run if a loss is incured at the best short run level of output?
Answer:
Yes, the monopolist firm continues to produce in the short run if a loss is incurred at the best short run level of output.
![]()
Question 9.
Explain why the demand curve facing a firm under monopolistic competition is negetively shaped?
Answer:
Demand curve facing a firm under monopolistic a difffentiated product. It can influens the price of the commodity to some extent. In this sense it is price maker for its price maker for its product. It can sell more goods at a lower price and less more goods at a higher price. Hence the demand curve facing a firm under monopolistic competition is negetively shape as shown below in the diagram.
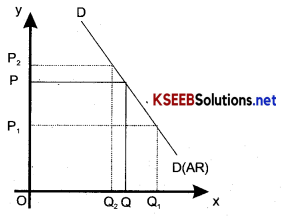
Question 10.
What is the reason for the long run equlibrium of a firm in monopolistic competition to be associated with zero profit?
Answer:
In the long run, there is free entiy and exit of firms. If a firm in monopolistic competition earn abnormal profits. New firm will enter the market resulting into increases in supply. Increase in supply will reduce the price and all the existing firm will be deprived at abnormal profit, in other words there will be normal profit.
On the other hand, if firms rupee loss, in the short run, some of the firms reduce or,stop production and quit the industry. As a result supply will be no profit and no loss. Thus in the long equlibrium, the firms earn only normal profit.
Question 11.
List the three diffrent ways in which oligopoly firms may behaves?
Answer:
Different ways in which oligopoly firms may behave:
Oligopoly firms may behave in the following in different ways.
- Duopoly may collude together and decide not to compete firms together. In such a case, the two firms would behave like a single monopoly firm that has two different factories producing the commodity.
- Each of two firms[in case a duopoly] may deside how much quantity to produce by maximising its ownprofit assuming that the other firms maximising its own profit assuming that the other firms would not change the quantity that it is supplying.
- Oligopoly firms may make the market price ofthe commodity rigid i.e. the market price doesnot more freely in response to change in demand.
![]()
Question 12.
If duopoly behaviour is one that is described by cournot, the market demand curve is given by the equation q = 200 – 4p and both the firms have zero costs, find the quantity supplied by each firm in equilibrium and equilibrium market price.
Answer:
Market demand equation:
q = 200 – 4p
200 – 4p = 0
-4p = -200
p = \(\frac{-200}{-4}\)
q = \(\frac{200}{50}\) = 4
Number of firms = 2
Quantity supplied by each firm = \(\frac{4}{2}\) = 2
Question 13.
What is meant by prices being rigid? How can oligopoly behaviour lead to such an outcome?
Answer:
Rigid Price: Rigid price means that the market price does not move freely in response to changes in demand. In an oligopolistic market, when a firm lowers the price to promote its sale, it effects other firms also. Hence as a reaction, rival firms may also start to reduce their prices. In this situation, the increase in total quantity sold due to lowering of price is shared by all the firms and the firm that had initially lowered the price is able to achieve only a small increase in the quantity it sells. So this firm experiences an inelastic demand curve and its decision to lower price leads to a lowering of its revenue and profit. Therefore any firm finds ot irrational to change the prevailing price.
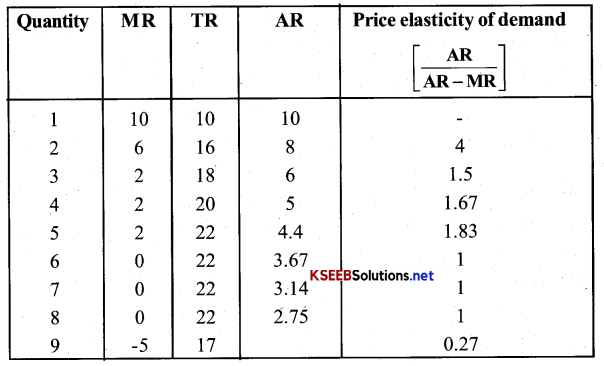
Question 3.
What is the value of MR when the demand curve elastic?
Answer:
Demand curve is elasticity is greater than unity. When price elasticity of demand is more than unity cones, then the value of MR is positive.
Question 4.
A monopoly firm has a total fixed cost of Rs 100 and has the following demand schedule

Find the short-run equilibrium quantity, price and total print. What would be the equilibrium in the long run? In case the total cost was Rs 1000, Describe the
Answer:
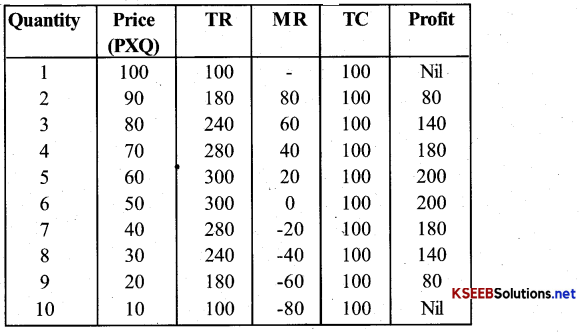
Short-run equilibrium quantity in units, Price is Rs 50 & Print Rs 200
Question 5.
If the monopolist firm of Excercise 3, was a public sector firm. The government set a rule for its manager to accept government fixed price as given (i.e, to be a price taker and therefore behave as a firm in a perfectly compitititve Markets), and the government decide to set the price so that demand and supply in the market are equal. What would be the equilibrium price, Quantity & profit in this case?
Answer:
If the government sets a rule for the firm to accept the government fixed price on given the equlibrium price will be equal to Rs 10 Quantity supplied will 10 ad the profit will be zero.
Question 6.
Comment on the shape of the MR curve is case the TR curve is a
(i) Positively shaped stright line
(ii) Horizontal shaped stright line
Answer:
(i) MR curve is a stright line parallel to OX axis when TR curve is a positively shaped stright line.
(ii) When TR is horizontal straight line, MR curve is negatively shaped stright line.
![]()
Question 7.
The market demand curve for a commodity and the total cost for a monopoly firm producing the commodity is given by the schedule below. Use the information to calculate the following.
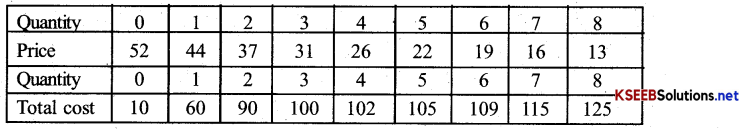
(a) The MR and MC schedules.
(b) The quantities for which the MR and MC are equal.
(c) The equilibrium quantity of output and the equilibrium price of the commodity.
(d) The total revenue, total cost and total profit in equilibrium.
Answer: