Students can Download Karnataka SSLC Social Science Model Question Paper 2 with Answers, Karnataka SSLC Social Science Model Question Papers with Answers helps you to revise the complete Karnataka State Board Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Karnataka State Syllabus SSLC Social Science Model Question Paper 2 with Answers
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 80
I. four alternatives are given for each of the following questions / incomplete statements. Only one of them is correct or most appropriate. Choose the correct alternative and write the complete answer along with its letter of alphabet in your arts wer booklet. (8 ×1 = 8)
Question 1.
Which battle the British as real holders of power over Bengal, Bihar and Odisha?
A. Battle of plassey
B. Battle of Buxar
C. First Carnatic war
D. Third Carnatic war
Answer:
B. Battle of Buxar
Question 2.
The belief of Aryan supremacy gave rise to
A. Fascism
B. Nazism
C. Socialism
D. Communalism
Answer:
B. Nazism
![]()
Question 3.
India adopted ‘Disarmament’ as a basic aspect of it Foreign policy because
A. India is worried that massive scale of arms could lead to Third World War
B. India is a peace loving country
C. India cannot produce arms
D. India fears accidently triggering nuclear destruction
Answer:
B. India is a peace loving country
Question 4.
The state in which ‘Silent valley movement’ started is
A. Karnataka
B. Gujarat
C. Maharastra
D. Kerala
Answer:
D. Kerala
Question 5.
Specialization creates
A. Organised labour
B. Unorganised Labour
C. Class system
D. Division of labour
Answer:
D. Division of labour
Question 6.
The cause of change in the course of rivers is
A. Floods
B. Dams
C. Low ground water level
D. Silting
Answer:
D. Silting
Question 7.
The prime reason for Rural backwardness is
A. Illiteracy
B. Poverty
C. Slow growth rate of agriculture
D. Competition from industries
Answer:
C. Slow growth rate of agriculture
Question 8.
The indiscriminate exploitation of natural resources of a country is due to
A. Industrialization
B. Population explotion
C. Globalization
D. Consumerism
Answer:
C. Globalization
![]()
II. Answer the following questions in a sentence each: (8 × 1 = 8)
Question 9.
According to which land tax system of the British, the farmer was directly linked to East India Company?
Answer:
Ryotwari system
Question 10.
Which incident started the Second World War?
Answer:
Germany’s occupation of Poland on September 01, 1939.
Question 11.
Give one instance of the cordial relationship between India and Russia.
Answer:
Russia has extended its support to India’s quest for permanent seat in the UN security council.
Question 12.
When and where was the first labour union established?
Answer:
‘The international working men’s association’ was the first labour union established in London in the year 1864.
Question 13.
Which industry is the basis of all other industries.
Answer:
Iron and steel industry.
Question 14.
How is density of population different from size of population?
Answer:
Size of population: The total number of people living in a particular area is called the size of population.
Density of population: The number of people per sqkm is called density of population.
Question 15.
When the lending rate of interest by banks increases drastically creating lower credit creation in the economy. What step does RBI take to create credit?
Answer:
It varies the Repo rate.
Question 16.
Per captia income is used as indicator of development instead of national income. Why.
Answer:
- Comparison of economic development between countries with different levels of population is incorrect.
- Higher the population, slower the increase in national Income.
![]()
III. Answer the following questions in three to four sentences each : (8 × 2 = 16)
Question 17.
What were the main aspects in the declaration of the British Queen?
The Queen of Britain passed a declaration in 1858. It had the following aspects :
Answer:
- The agreements entered by the company with the local Kings were accepted.
- Non – pursuance of regional expansion.
- Providing a stable government for Indians
- Equality before the law
- Non-interference of the government in religious issues of Indians and practicing religious tolerance.
Question 18.
How did the Labour Party in England try to find solutions for the political problems of India just before Independence?
Answer:
- The Labour party government seat a cabinet committee to India for disscustion on giving self – rule rights with INC and Muslim League.
- It recommeded for a federal form of government.
- It suggested them to form an interim government.
- It suggested to form a consituent assembley to formulate constitution.
Question 19.
What was India’s contribution in alleviation of economic inequality among third – world countries?
Answer:
- India followed Non – Aligned policy.
- India urged developed countries to provide assistance to developing countries without conditions.
- India helped to chanUalize monetary help to the third – world countries.
OR
How did independent India help solve Bangladesh Crisis?
Answer:
- India helped the liberation of Bangladesh from Pakistan.
- India helped to resettle Bangladesi refugees in-Bengal, Tripura, Meghalaya and Assam.
- In spite of India facing economic crisis, it helped Bangladeshi refugees find new hope of life in India.
Question 20.
There is a need for disarmament. Illustrate.
Answer:
- Arms Race is a dangerous phenomenon.
- Disarmament is the only solution to Arms race.
- Arms Race creates insecurity, fear, instability and threat of war.
- Resources used to produce arms can be usefully used for development.
- Threat of Nuclear War.
OR
Illustrate the relationship between India and USA
Answer:
Relationship between India and USA
- India follows non – aligned policy.
- USA supported many India’s five year – plans.
- USA extended support during Indo-China war in 1965.
- India and USA share interest in controlling terrorism.
- India and USA support each other in trade, science and technology, space science, education.
- India and USA share mutual responsibility to strengthen UNO.
- Go-operate to support global peace.
- India adjusts its foreign policy according to the political party in power in USA.
![]()
Question 21.
What are the major effects of soil erosion?
Answer:
The important effects of soil erosion are :
- Loss of soil fertility and fall in agricultural productivity
- It leads to silting and floods, change of the course of rivers, and reduction of capacity of the reservoirs.
- Ground water level is lowered and there is decrease in soil moisture
- Vegetation covers dries up and drought increase.
- Economy as a whole suffers a great set back.
Question 22.
The Himalayas are a boon for India. How?
Answer:
- Himalayas act as natural frontiers and prevent foreign invasion.
- Prevent cold winds from Central – Asia.
- Obstruct rain bearing winds and cause heavy rainfall.
- Slopes have thick forests, an ideal natural resource.
- Storehouse of minerals.
- Birth – place of many perennial rivers – Ganga, Brahmaputra.
- Have many waterfalls, useful for generation of Hydro – electricity.
Question 23.
What are the objectives of government fiscal policy.
Answer:
- Achieve economic growth
- Maintain economic (price) stability
- Achieve fair distribution of income.
Question 24.
What were the results of Third Carnatic War?
Answer:
- Globalization promotes economic growth, generates wider range of products and services.
- Globalization has made the availability of the similar type of products all over the world.
- Globalization creates competition for local firms and thus keeps the costs down.
IV. Answer the following questions in six sentences each : (9 × 3 = 27)
Question 25.
What are the causes and results of Battle of Plassey?
Answer:
Siraj – ud – Daula ascended the throne of Oudh after the death of his grandfather Aliwardi Khan
Causes :
1. He was fiirions that the Dastakths issued by Faruk Shiara, the Mughal emperor of Bengal were misued by the officials of East India company causing loss to the Oudh treasury.
2. The English repaired the Calcutta fort and placed cannons in it. The Nawab ordered their removal but the British refused.
3. The Nawab conqured Fort William. He imprisoned 146 English soldiers in a small dungeon in the fort.
4. 123 Soldiers died of suffocation. Robert Clive was enraged and attacked Oudh near Plassey.
Results :
-
- Siraj – Ud – Daula was captured and killed.
- Mir Jaffar become the Nawab of Bengal.
- East India comapny gained exlusive trade rights in Bengal.
- The company forced Mir Jaffer to pay seventeen crore and seventy lakh rappees as compensation for the attack on fort.
Question 26.
What was Raja Ram Mohan Roy’s role in the social reforms in India.
Answer:
- Started Athmiya Sabha, in Calcutta to eradicate socio – religious maladies.
- Stared Brahma Samaj in 1828 to purge Hinduism of caste system, superstitions.
- He attempted to rebuild Hindu society based on philosophical foundations of upanishads.
- His efforts led Governor General William Bentinckto implement ‘Prohibition of Sati act’in 1829.
- He published articles to develop rationality among people in his journal ‘Samvada Komudhi’.
Question 27.
What were the causes for the failure of 1857 mutiny?
Answer:
The First war of Indian Independence in 1857 failed due to following reasons:
- The Mutiny did not cover many parts of India.
- They focused on the issues of the dethroned kings and queens rather than the freedom of the country.
- It was not a planned Mutiny
- Disunity among Indian soldiers
- Lack of direction and efficient leadership
- The Indian soldiers lacked military strategies, discipline and organization
- Many Indian Kings supported the British rather than their countrymen.
- The common people lost faith in Indian soldiers because they went about plundering and harassing them.
![]()
Question 28.
Name the factors which influence foreign policy of a country?
Answer:
- To regulate the interaction with other countries.
- To maintain peaceful relations with other countries.
- For cordial trade and commerce.
- National security.
- To develop friendly relations with other countries to check enemy countries.
Question 29.
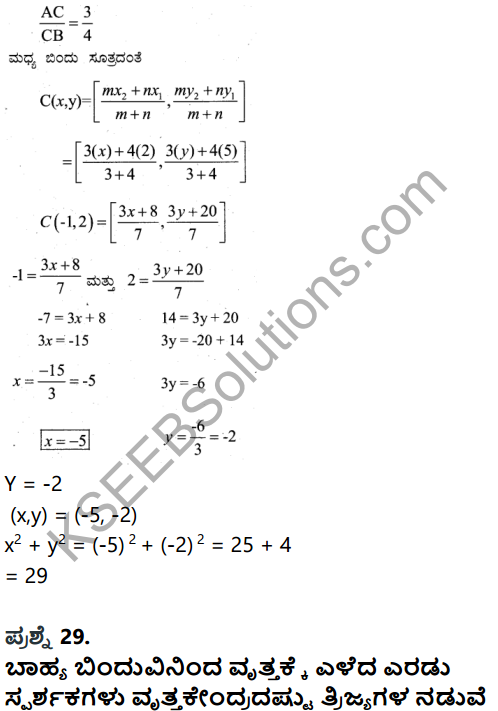
How is Untouchability a social evil? Discuss.
Answer:
Untouchability is a social evil in India. It has its roots in the Vedas and based on the varna system, Brahmana, Kshatriya, Vysya & Shudra. The caste group occupied the lowest position on the caste system and were considered untouchables.
The untouchables were not allowed to lead a dignified life. They were not allowed to touch wells, tanks and cemetery used by upper caste people. They had to do menial jobs like carrying in the night spil dead animals and filthy jobs. They were barred from using the footwear, though footwear made by them were worn by the upper caste people. Untouchables were denied education and social justice. Untouchables were not allowed to own property. This is in human and also the violation of basic human rights.
Question 30.
Rice is the most important food crop of India. Jusify.
Answer:
- Staple food of eastern, southern and south-western India.
- India has largest area under rice cultivation in the world.
- India is second largest producer of rice.
- It the major kharif crop of India.
- Grown in all states of India.
OR
What are the main objectives of Biosphere Reserves.
Answer:
- Biospheres are special protected area of land or coastal enviroments.
- For conservation fo Ecology.
- For research
- For educational purpose
- To spread awarness of ecology among locals.
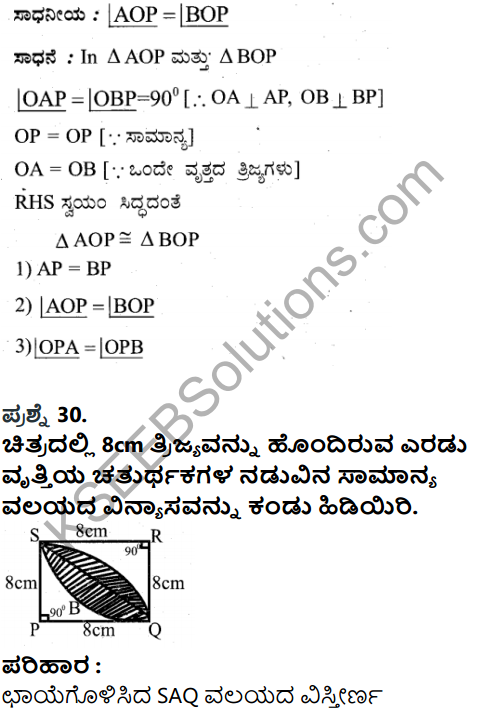
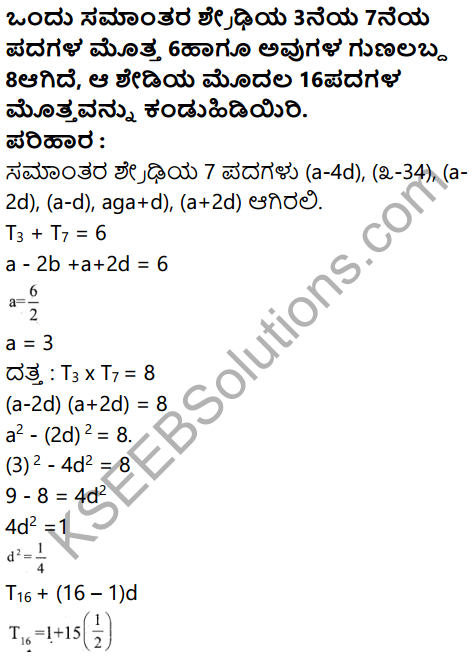
Question 31.
Mention the main causes of soil erosion.
Answer:
The main causes of soil erosion are :
a) deforestation
b) overgrazing,
c) shifting cultivation
d) faulty methods of cultivation
e) use of top soil for making bricks, tiles etc.
![]()
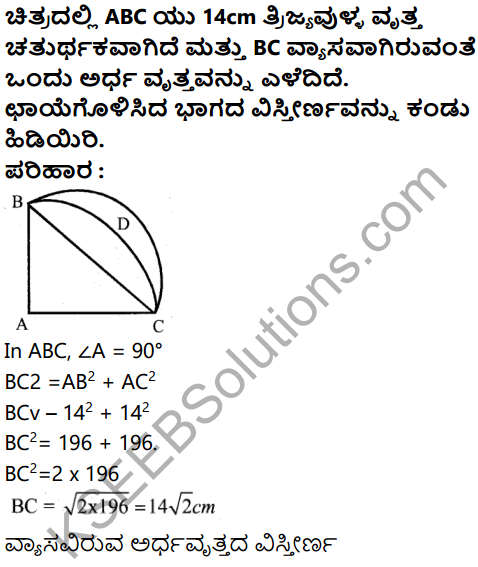
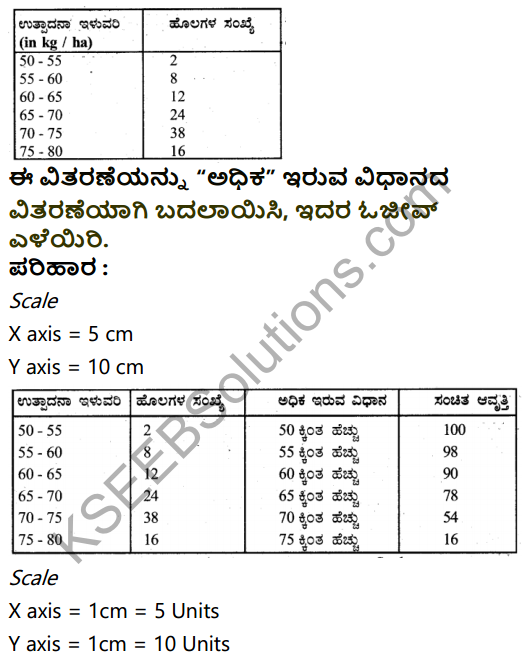
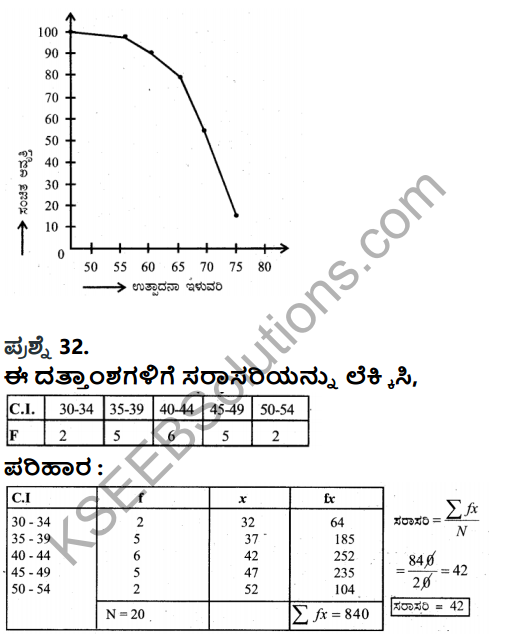
Question 32.
Define development and explain the process of development.
Definition:
Economic development is a process whereby an economy’s real national income increases over a long period of time.
– Prof. Meter and Baldwin Process of development:
- Operation of the forces that bring changes in supply of factors of production in the structure of demand of products.
- Changes in factor supply takes place due to discovery of additional resources, education and skill development.
- Capital accumulation, population as growth, adoption fo better techniques of production.
- Demand for production is proportional in change in size and composition of population level and distribution of income, tastes etc.
- The above changes contribute to an increase in national income.
OR
Explain Gandhiji’s concept of ‘gram swarajya’ in the light of decentralization.
Answer:
- Decentralization is the process of providing power and responsibility of developing their village to people themselves.
- Power sharing occurs and people participate in decision making.
- It aims at planning and development from the village level.
- It reduces exploitation, increases human independence and dignity.
- It nurtures human values such as compassion and co – operation.
- Panchayat Raj system is the form of decentralization in India.
- Panchayat Raj system was implement in 1993 throughout India.
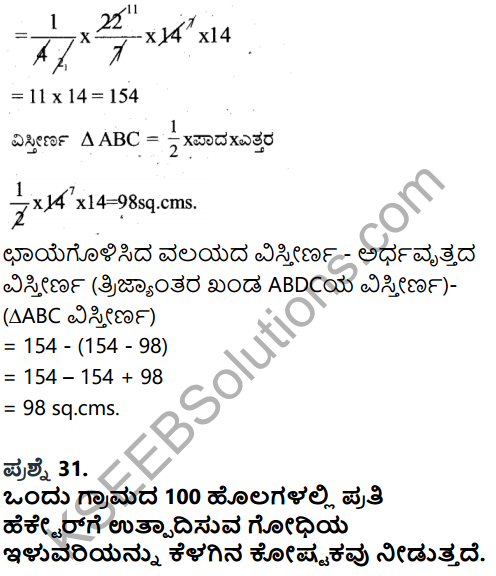
Question 33.
Entrepreneurship is a creative activity. How?
Answer:
- Because it is a process of an action of an entrepreneur takes to establish his enterprise.
- It creates and build something new
- It is a knack of sensing opportunity where others can’t.
- It is an attitude of mind to seek opportunity.
- Hence Entrepreneurship is a creative activity.
OR
Explain the advantages of Globalization.
Answer:
- Globalization promotes economic growth and generates a wider range of products and services.
- Globalization helps to increase the standard of living of the people
- Globalization has made the availability of the similar type of products all over the world.
- Globalization increases the GDP of a country.
- Globalization has helped in increasing the income of the people
- By buying the products from other countries, customers are offered a much wider choice of goods and services.
- Globalization creates competition for local firms and thus keeps the costs down.
- Globalization promotes specialization. Countries can begin to specialist in those products that are best at making.
- Economic interdependence among different countries can build improved political and social links.
![]()
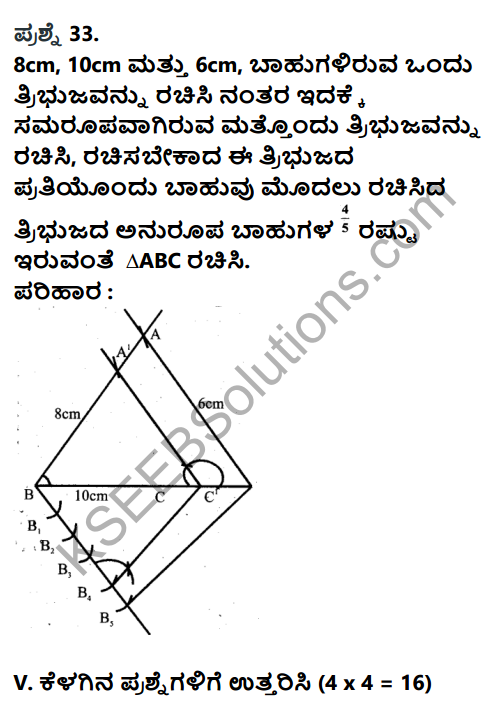
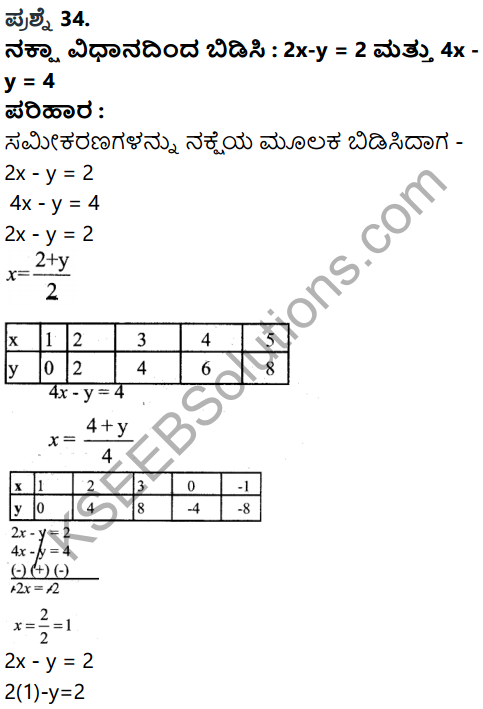
V. Answer the following questions in six sentences each : (4 × 4 = 16)
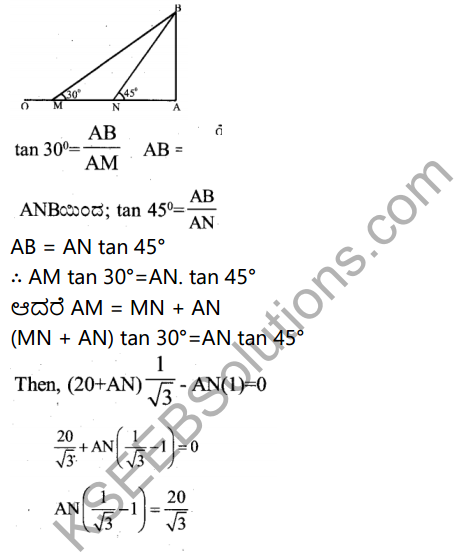
Question 34.
Explain the process of South – West monsoon.
Answer:
- The rainy season in India is known as South – West mons son season.
- Temperature over land rises at the end of summer.
- Low pressure develops over Central India.
- High pressure over the Indian ocean.
- Moisture laden winds blow towards Indian mainland from south – west bringing about 7570 rainfall.
- The Arabian sea branch of S.W Monsoon brings heavy rainfall to the western side of Western ghats.
- Bay of Bengal branch of S.W monsson brings heavy rainfall in the hills of Meghalaya and Assam.
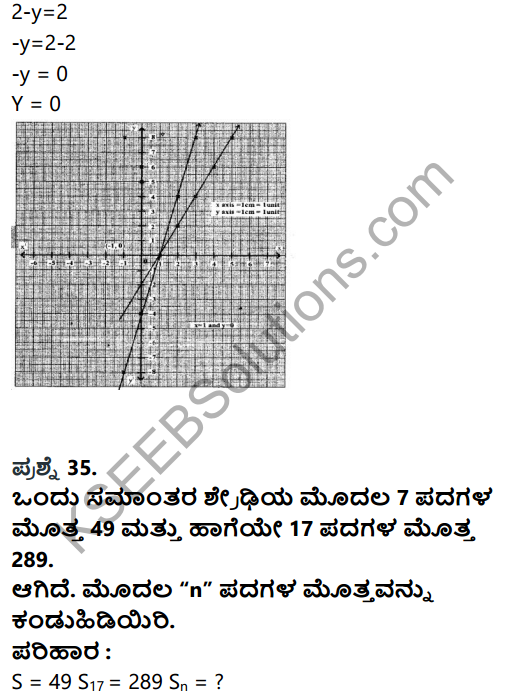
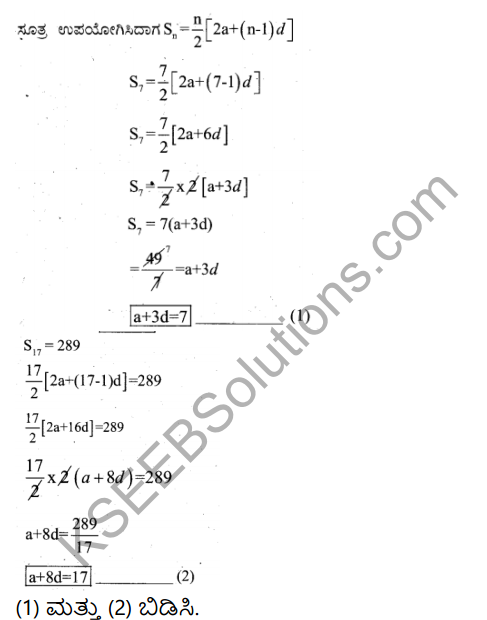
Question 35.
Explain the European Union.
Answer:
It is an institution of 27 European countries. It was founded in 1922 as per the agreement of Matrich among the member countries. It provides for common market, common currency and common agriculture and trade policy. The following are the subdivision of this organization.
1) Committee
2) Commission
3) European Parliament
4) European Court of Justice.
The European Union resembles a federal government structure. As the founders asserted this strives for international peace and democracy in the world. This seems to be the continuation of earlier European Economic Community (EEC). The members states have given away some of their sovereign powers to the union willingly.
Question 36.
Why was Stratford Cripps sent to India. Explain.
Answer:
- British government favoured a federal government at the center and regional governments at the states.
- Third round table conference was organised to discuss the formation of govt.
- Congress did not participate opposing the decisions of the British.
- The British implemented the Government of India Act 1935.
- The act gave political rights for Indians and elections were held.
- Congress formed the government at the center.
- The British took unilateral decision to participate in II World War.
- Congress walked out of the cabinet opposing their decision.
- Gandhiji declared personal Satyagraha.
- The Britain Govt, sent Stratford Sripps to mediate.
OR
The Integration and unity of China became important. Why?
Answer:
- China was controlled by landlords and warlords.
- Parts of China were under colonial rule.
- In 1911, a democractic revolution took place under Kuomintang party’s Sun – Yat – San.
- In 1925, the Communist Party of China took birth to unify China.
- It supported farmer’s and worker’s movements.
- After the death of Sun – Yat – San, Chaig – kai – Shek became the leader of Kuominatang party.
- He joined imperialistic forces and attacked and killed thousands of communist revolutionaries.
- Mae – Tse – Tung started ‘Long – March’ to gamer support for Communist Party.
- Japan invaded China and was defeated by – the Communist Party.
- Japan withdrew and Mao – ze – Tung occupied Japnese colonies in China.
- By 1949, the Communist party gained control of China and established people Republic of China.
![]()
Question 37.
Partition of India had created problems. Explain.
Answer:
- Bloody communal violence broke out soon after partition.
- Millions of people migrated to India which put a great financial stress on the new country of India.
- The 562 princely states had to be integrated into the Indian union.
- Challenge of creating a new constitution
- India had to build its defence forces to protect its newly acquired freedom.
- There was a need to strengthen the social fabric to establish social security and mitigate gender, caste, religious and economic inequality in Indian society.
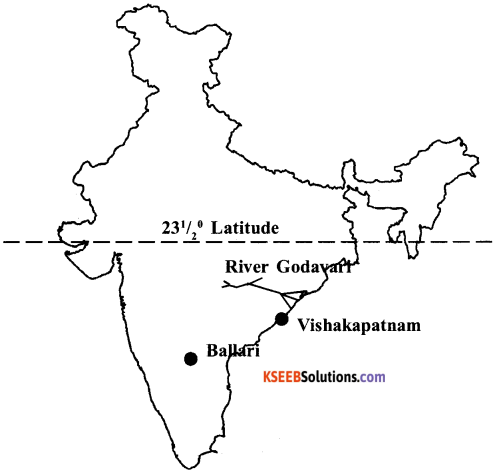
VI. 38. Draw out line map of India and mark the given by naming them (1 + 4 = 5)
A. 231/2° Latitude
B. Ballari
C. Vishakapatnam
D. River Godavari
Answer: