KSEEB 10th English Dr BR Ambedkar Lesson Notes Questions and Answers
Check Your Understanding
Share your responses
(Refer to Text Page No. 69):
Question 1.
Ambedkar spent most of his life by …………..
a. purchasing books
b. attending conferences
c. reading books
d. importing books.
Answer:
c. reading books.
![]()
Question 2.
Pick out the word in the first paragraph which means ‘a quality that makes person or a thing different from another.’
Answer:
Voracious
Question 3.
How did the fourteenth amendment of the American Constitution benefit the Black Americans ?
Answer:
It gave freedom to the Black Americans.
Question 4.
What did Mahatma Phule work for ?
Answer:
He worked for classless society and women’s uplift.
Question 5.
Mookanayak, Bahishkrit Bharat and Samata were
a. Voice mails
b. Newspapers
c. Political parties
Answer:
b. Newspapers.
![]()
Question 6.
Gandhiji termed the depressed classes as
Answer:
Harijans.
Share your responses
(Refer to Text Page No. 71):
Question 1.
Draft is a banking term. How is the word used In the context of this lesson?
Answer:
The word ‘draft’ is used as transitive verb which means to make a version of a document that will need more work In order to be finished.
Question 2.
Dr. Ambedkar was not In the Congress party. Yet he was made the chairman of the drafting committee. Why?
Answer:
The Constituent Assembly understood Dr. Ambedkar’s social philosophy and his undying faith in the dignity of human beings.
Question 3.
He raised It brick by brick’. In this context, what was raised?
Answer:
He drafted Constitution and he raised it which came as Fundamental Rights in the Constitution of India.
![]()
Question 4.
Who were the other notable members of the drafting committee ?
Answer:
Alladi Krishnaswami Ayyar, K. M. Munshi. and N. Gopalswami Ayyangar.
Question 5.
Ambedkar had ‘rare gifts’. What were they ? Can you think of your own ‘gifts’ ? Share them with your class.
Answer:
Dr. Ambedkar had the rare gift of unravelling the most complicated legal concepts in the moss. Simple language which could be understood by common man. He had an insatiable thirst for books. I have the gift of the gab. I can speak on any subject without any problem.
Question 6.
Constitution is a fundamental document to both the ruler and the ruled. How ?
Answer:
It avoids complete tyranny and complete oppression. It limits the individual.
Share your responses
(Refer to Text Page No. 72):
Question 1.
Nehru chose Ambedkar as law minister for three reasons. What are they ? (Paragraph 7)
Answer:
Dr. Ambedkar had a special skill in the field of law. He had a great vision of social justice. He had made campaigns against social injustice.
![]()
Question 2.
Are you aware of the facilities provided by the Social Welfare Department ? Mention any two.
Answer:
The department offers accommodation and scholarships to the depressed class.
Question 3.
After independence, members of the Scheduled Castes have found doors opened to them. How ?
Answer:
The first thing is providing equality of opportunities to all. Today no legal bars exist. They are enrolling themselves in institutes of higher learning and entering public service. Today they are able to occupy high offices of State.
Question 4.
All people should be given equal opportunities to prove themselves. How are the members of the Scheduled Castes proving themselves?
Answer:
They are going for higher studies and they have taken prestigious positions of the state and the centre. They
are working with creditably and looking after responsibility.
![]()
Question 5.
Babasaheb Ambedkar considers public agitation in free india as unconstitutional. Why?
Answer:
Because some public agitations result in the loss of lives and public property.
Question 6.
Social discrimination still exists in India. Debate in the class.
Answer:
Today also we notice discrimination in India because of class. creed, caste and colour. The downtrodden are not properly looked upon. I think untouchability never disappears from this nation. But If we understood that all are human beings, then only we can win all being human.
Share your responses
(Refer to Text Page No. 73):
Question 1.
What were the opinions of the Buddha and Avvai regarding the caste divisions?
Answer:
Buddha never believed caste divisions. Fie only believed In the divisions between noble and ignoble and wholesome
and unwholesome. According to Tamil poetess. there are only two castes In the world namely. the charitable who give and are superior and the misers who do not and are, therefore Inferior.
Question 2.
Caste system In India Is In a strong position because of
(fill in the blank picking the answer from paragraph 11)
Answer:
its power structure.
![]()
Question 3.
Why did the British magnify the caste distinctions ?
Answer:
Because they wanted to rule India under the policy of Divide and Rule. So that they could strengthen their hegemony over us.
Question 4.
The word ‘hegemony’ means
a. distinction
b. control
c. strength
Answer:
b. control.
Question 5.
‘they brought about a veritable revolution in social thought.’
a. Who are they ?
b. What ‘revolution is referred to here ?
c. How did they bring about the revolution ?
Answer:
(a) They are Mahatma Gandhi and Dr. B.R. Ambedkar.
(b) Oneness of Hindu Community.
(c) Gandhiji reminded the higher castes of their duty towards the depressed classes. Dr. B.R. Ambedkar did the same by reminding of their inherent rights to equality with the higher and more powerful castes.
Question 6.
Why did Nehru describe Dr. Ambedkar as ‘a symbol of revolt’ ?
Answer:
Because Nehru could notice the perseverance and persistence of Dr. B.R. Ambedkar. He stressed human rights to be given for the depressed class. He was always active.
Think about the Test :
Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
Ambedkar had a great thirst for books when he was a student. Explain.
Answer:
The former president of India Sri R. Venkataraman speaks about Dr. B.R. Ambedkar. He says that Dr. B.R. Ambedkar had a insatiable thirst for books. [le was a voracious reader and considered books sa more Important than his daily expenses. When he was in New York, he had purchased more than 2,000 books which had been sent to India.
![]()
Question 2.
How did the fourteenth amendment to the U.S constitution and Mahatma Phule influence Ambedkar?
Answer:
When Dr. Ambedkar was in U.S.A., he was drawn to the fourteenth Amendment of the Constitution of the U.S.A. which gave freedom to the Black Americans and saw at once the parallel of the situation for the Depressed Classes in India. He also read the life and works of Mahatma Phule and decided to devote all his time and talents for the amelioration of his underprivileged brethren.
Question 3.
There were great luminaries on the Drafting Committee. Dr. Ambedkar is remembered as the pilot. Give reasons.
Answer:
Dr. Ambedkar explained everything in the convincing way. He had the combination of tact and frankness and utmost patience. He explained clearly the meaning and scope of the different provisions of the Draft Constitution. He had the rare gift of unravelling the most complicated legal concepts in the language which the laymen understood. So he is remembered as the pilot.
Question 4.
Write a short note on Dr. Ambedkar’s idea/perception of the three pillars of State.
Answer:
The three pillars of the State, the Legislature, the Executive and the Judiciary. He told that the jurisdiction of each should be clear and not hampered, so that the welfare of the citizen was safeguarded.
![]()
Question 5.
What are the significant observations of Dr. Ambedkar on the constitution?
Answer:
Dr. B.R. Ambedkar remarked that Constitution is a fundamental document. It defines the power and position of the three organs of the State. The main purpose is not merely to create the organs but to limit their authority to check, so as to avoid tyranny or oppression.
Question 6.
Nehru chose Dr. Ambedkar as the law minister. What might have prompted Nehru to do so?
Answer:
Jawaharlal Nehru noticed Dr. Ambedkar’s skills in the field of Law and Legislation. He also understood his vision of social justice. So he chose Dr. Ambedkar as the First Law minister of Independent India.
Question 7.
What made Dr. Ambedkar describe the methods of Civil Disobedience, Non-cooperation and Satyagraha as the “Grammar of anarchy”?
Answer:
Dr. Ambedkar told that the Constitutional methods to be used to achieve social objectives. He calls it Grammar of Anarchy because it is fine to revolt against a government formed without the consent of the people but not possible but not possible in democracy which is based on free and fair elections,
Question 8.
How did Dr. Ambedkar and Mahatma Gandhi try to wipe out caste discrimination from India?
Answer:
Mahatma Gandhi and Dr. B.R. Ambedkar stressed the oneness of the Hindu community. Gandhiji did this by reminding the higher classes of their duty towards the depressed classes and Dr. Ambedkar reminded the depressed classes their right to equality with higher classes.
![]()
Question 9.
Discuss with your friends and complete the web-chart given below
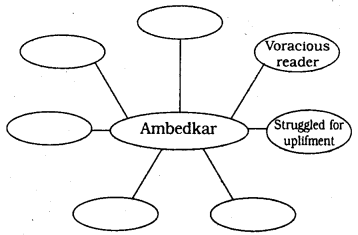
Answer:
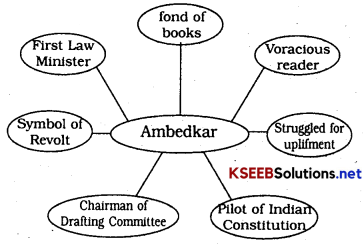
Enrich Your Vocabulary
Task-1:
Read the following paragraph and replace the underlined words appropriately with the words given below in brackets.
Children have special qualities. They can think and imagine in creative ways and are able to understand new things much better than their elders. But just by new ideas, nothing happens. Their ideas must have inborn strengths and stand the test of time. They should not become self-satisfied with their first steps of success.
(complacent, conceive, trait, perceive, inherent]
Answer:
qualities – trait
think and imagine- conceive
understand – perceive
inborn – inherent
self-satisfied – complacent
![]()
Use the Phrases given in brackets in (Task-1) in sentences of your own.
(complacent, conceive, trait, perceive, inherent]
Answer:
(1) Man should have different traits.
(2) I perceive my subjects.
(3) Hew can conceive the problem easily.
(4) Man is a bundle of some inherent qualities.
(5) My friend has complacent nature
Listen and Comprehend
Task-1: Answer these questions orally:
Question 1.
What information is Shreya giving her father ?
Answer:
She is giving information about Republic Day.
Question 2.
Is her father encouraging or discouraging her ?
Answer:
He is encouraging her.
Question 3.
What does father tell her about what a Constitution is ?
Answer:
Constitution is a set of rules and regulations for all people living in India and Republic Day is actually when we Indians got our Constitution. It came into force on 26th January, 1950.
![]()
Question 4.
Should everybody obey the Constitution? How do you know ?
Answer:
Everybody should obey the Constitution because everyone is the citizen of India and it is our duty to obey the rules and regulations.
Speak Well
Expressing gratitude
(A boy goes to a book shop to buy a book on folk tales. The dialogue is given below)
Book Seller: Good afternoon, gentleman. What can I do for you?
Sharieff :Good afternoon, I’d like to buy some books on national leaders.
Book Seller :On national leaders? Sure, sir. If you don’t mind, please have a look at the fourth almirah on your right. Sharieff: (after going through some titles) Could you take them out, please?
Book Seller: Of course (he takes them out and hands them over to Sharieff)
Sharieff: Thank you. Ah! I need these three books. Will you please gift-wrap them?
Book Seller: With pleasure, (he does so)
Sharieff: How much should I pay?
Book Seller: We allow a 10% rebate.
Sharieff: That’s very nice of you. So, I have to pay Rs. 240/ –
Book Seller : Yes. We also give you a diary as a free gift.
Sharieff: Thank you very much, (he pays the money)
Book Seller : You’re Welcome, (hands over the books and the gift)
Answer:
These are the terms used to express gratitude :
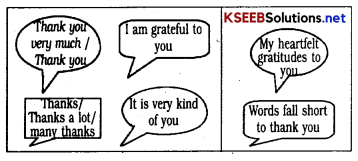
Task-1: Imagine your friend sends you a gift on your birthday. How will you express your gratitude?
Ans: It is very nice of you.
I am very much pleased.
So nice of you.
Read and Respond
Read the following poem.
The Eagle – Alfred Lord Tennyson
He clasps the crag with hooked hands Close to the sun in lonely lands, Ring’d with the azure world, he stands.
The wrinkled sea beneath him crawls;
He watches from his mountain walls,
And like a thunder bolt, he falls
![]()
Meanings:
clasps – holds firmly
crag – a rough mass of rock
azure-blue
crawls – moves with the body in contact with the floor
Task-1:
Read the poem. Note that every line of the poem is either suggestive or evocative, that is, capable of making the readers imagine some pictures in mind. These poetic expressions are given in column ‘A’. Read the poem carefully, read the expressions, and find out the line that evokes or suggests the pictures. Write the line number in column ’B’. One example is given.
Answer:
| Expression/Suggestion | Line | |
| 1. | Exaggerated expression (hyperbole | 2 |
| 2. | What is usually seen as vast and grand is described as nervous or afraid (paradox) | 4 |
| 3. | Comparison describing a sudden attack (simile) | 6 |
| 4. | Repetition of sounds /k/and /h/ (Alliteration) | 1 |
| 5. | Word picture of somebody or something surrounded by the blue sky (Imagery) | 3 |
| 6. | Image or a picture of somebody or something staring long at the prey (Imagery) | 5 |
Self-Assessment
Read the statement and put a tick mark in the appropriate box.
Answer:
| SI. No. | Statement | Yes | No | To some extent |
| 1. | I read the poem ‘The Eagle’ silently. | ✓ | ||
| 2. | I got the pictures in my mind while reading the poem. | |||
| 3. | I found out the line that evokes or suggests the pictures. | ✓ | ||
| 4. | I understood the meaning of different poetic expressions. | ✓ | ||
| 5. | I have got Interest in reading such poems. | ✓ |
Practise Writing
Task-1:
Imagine you are booking a ticket to visit Mumbai. Give the following personal details as furnished below :
Learn Grammar Through Communication
Task-1:
Here are some sentences. Combine them using linkers given in brackets. One is done for you.
e.g. It rained heavily. We reached home in time, (though)
Though it rained heavily, we reached home in time.
1. There is shortage of water. Some people are wasting it unthinkingly, (although)
Answer:
Although there is a shortage of water, some people are wasting it unthinkingly.
![]()
2. There was heavy traffic. We were delayed, (since)
Answer:
Since there was heavy traffic, we were delayed.
3. The students played for an hour. They attended to their studies later on. (and then)
Answer:
The students played for an hour and then attended to their studies later on.
4. We expected a difficult question paper. The questions asked in the examination were easy, (but)
Answer:
We expected a difficult question paper but the questions asked in the examination were easy.
5. The flight was delayed. The weather was cloudy, (as)
Answer:
As the weather was cloudy, the flight was delayed.
6. The student scored less marks. He had not studied properly, (because)
Answer:
The student scored less marks because he didn’t study properly.
Make Reference
Syllabification:
Look at the words given below. The words are split. Read them aloud.
1. con-so-nant
2. fa-ther
3. col-lege
4. pa-per
5. con-ver -sa-tion
6. lIt – tie
![]()
A part of a word with a vowel sound is a Syllable. Of course, there are some exceptions like Little.
Task-1: Refer to a dictionary and split the following words Into their syllables.
Answer:
1. probability pro – ba bi-it-ty
2. determInation de-ter-mi-na-tion
3. accept : ac-cept
4. canteen : can-teen
5. again : again
6. conscience : con-science
7. idea : I-de-a
8. reflection : re-flec-tion
Task-2 :
Look at the word ‘probability’ given in the dictionary: pro-ba- ’bi- li-ty. The syllable ‘bi’ is stressed. Pronounce the words above with proper stress. Verify with the help of the dictionary.
Do the Project
Question 1.
Collect the incidents of great men/ women/children who showed courage and fought for social justice.
Answer:
Chandra Shekhar Azad was born on 23 July 1906 in Bhawra village, in the present-day Alirajpur district of Madhya Pradesh. He was then called Chandra Shekhar Tiwari. His forefathers were from the Badarka village near Kanpur (in present-day Unnao District. His mother, Jagrani Devi, was the third wife of Sitaram Tiwari, whose previous wives had died young. After the birth of their first son, Sukhdev, in Badarka, the family moved to Alirajpur State.
A monument of Chandra Shekhar Azad in his native village Badarka. His mother wanted her son to be a great Sanskrit scholar and persuaded his father to send him to Kashi Vidyapeeth, Banaras to study. In December 1921, when Mohandas K. Gandhi launched the Non-Cooperation Movement, Chandra Shekhar, then a 15-year old student, joined. As a result, he was arrested.
On being produced before a magistrate, he gave his name as ‘Azad’, father’s name as ‘Swatantra’ (independent) and residence as ‘Jail’. From that day onward, having announced his name to be Azad (The Liberated) in court, he was known as Chandra Shekhar Azad among the people.
Revolutionary life:
After suspension of the non-cooperation movement in 1922 by Gandhi, Azad became more aggressive. He committed himself to achieve complete independence by any means. Azad also believed that India’s future lay in socialism. He met a young revolutionary, Pranvesh Chatterji, who introduced him to Ram Prasad Bismil who had formed the Hindustan Republican Association (HRA), a revolutionary organisation. Azad was impressed with the aim of HRA, i.e., an independent India with equal rights and opportunity to everyone without discrimination of caste, creed, religion or social status.
On introduction, Bismil was impressed by Azad, when Azad reportedly put his hand over a lamp and did not remove it till his skin burnt. He then became an active member of the HRA and started to collect funds for HRA. Most of the fund collection was through robberies of government property. He also wanted to build a new India based on socialist principles. Azad and his compatriots also planned and executed several acts of violence against the British.
![]()
Most of his revolutionary activities were planned and executed from Shahjahanpur which was also the hometown of Ram Prasad. He was involved in the Kakori Train Robbery of 1925, in the attempt to blow up the Viceroy’s train in 1926, and at last the shooting of J.P. Saunders at Lahore in 1928 to avenge the killing of Lala Lajpat Rai.