Karnataka Board Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues
KSEEB Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Intext Questions
Question 1.
What is tissue?
Answer:
A group of cells that are similar in structure and for work together to achieve a particular function forms a tissue.
Question 2.
What is the utility of tissues in multi-cellular organisms?
Answer:
In human beings, muscle cells contract and relax to cause movement, nerve cells carry messages, blood flows to transport oxygen, food, hormones and waste material and so on. This is the utility of tissues in multi-cellular organisms.
Question 3.
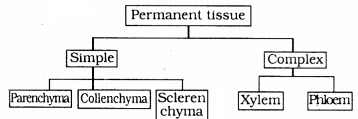
Name types of simple tissues.
Answer:
Parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma are the three types of simple tissues.
Question 4.
Where is apical meristem found?
Answer:
It is present at the growing tips of stems and roots and increases the length of the stem and the root.
Question 5.
Which tissue makes up the husk of coconut?
Answer:
Sclerenchyma tissue makes up the husk of coconut.
Question 6.
What are the constituents of phloem?
Answer:
Phloem consists of sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem fibres and phloem parenchyma.
Question 7.
Name the tissue responsible for movement in our body.
Answer:
Muscle fibre is the tissue that is responsible for movement in our body.
Question 8.
What does a neuron look like?
Answer:
A neuron consists of a cell body with a nucleus and cytoplasm, from which long thin hait like parts arise.
Question 9.
Give three features of cardiac muscles.
Answer:
- Cardiac muscles are cylindrical, branched and uninucleate,
- These work continuously (from birth to death),
- These do not get fatigued.
Question 10.
What are the functions of areolar tissue?
Answer:
- Smooth function and tone of the muscle.
- Concentration and relaxation are easy.
- Transportation is an easy and permeable surface.
- Exchange of gases taken place easily.
KSEEB Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Textbook Exercises
Question 1.
Define the term ‘tissue’.
Answer:
A group of cells that are similar in structure and /or work together to achieve a particular function from a tissue.
Question 2.
How many types of elements together make up the xylem tissue? Name them.
Answer:
Tracheids and vessels, xylem parenchyma and xylem fibre all these make up the xylem tissue.
Question 3.
How are simple tissues different from complex tissues in plants?
Answer:
Simple tissues are made of thin cell walls. Complex tissues are made of more than one type of cells.
Question 4.
Differentiate between parencyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma on the basis of their cell wall.
Answer:
| Parenchyma | Collenchyma | Sclerenchyma |
| It consists of relatively unspecialised living, cells with thin cell walls. They are usually loosely packed. | The cells of this tissue are elongated and irregularly thickened at the corners. There is very little intercellular space. | The cells of this tissue are dead. They are long and narrow as the walls are thickened due |
Question 5.
What are the functions of the stomata?
Answer:
Stomata are necessary for exchanging gases with the atmosphere, transportation (loss of water in the form of water vapour) also takes place through stomata.
Question 6.
Diagrammatically show the difference between the three types of muscle fibres.
Answer:
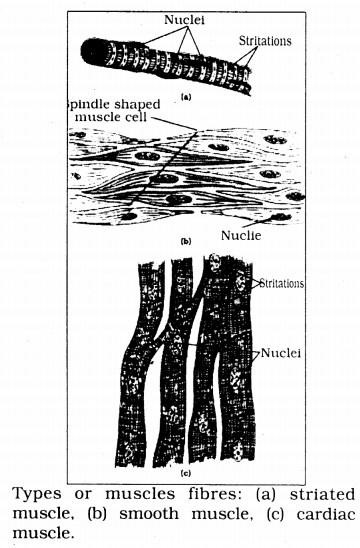
Question 7.
What is the specific function of the cardiac muscle?
Answer:
Cardiac muscles show rhythmic movement throughout our life. This movement helps blood to supply food and oxygen to all parts of our body.
Question 8.
Differentiate between striated, unstriated, and cardiac muscles on the basis of their structure and site/location in the body.
Answer:
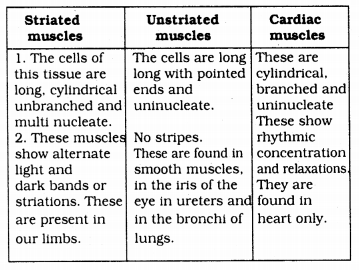
Question 9.
Draw a labelled diagram of a neuron.
Answer:
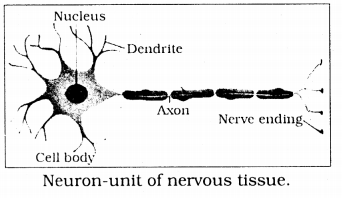
Question 10.
Name the following:
(a) Tissue that forms the inner lining of the cour mouth.
(b) Tissue that connects muscle to bone in humans.
(c) Tissue that transports food in plants.
(d) Tissue that stores fat in our body.
(e) Connective tissue with a fluid matrix.
(f) Tissue present in the brain.
Answer:
(a) Epithelial tissue.
(b) Tendons.
(c) Phloem.
(d) Adipose.
(e) blood.
(f) Forebrain.
Question 11.
Identify the type of tissue in the following: skin, bark of tree, bone, lining of kidney tubule, vascular bundle.
Answer:
- Skin: Areolar tissue.
- bark of tree: Epidermis tissue.
- bone: Tendon tissue.
- lining of kidney tubule: unstriped muscles.
- Vascular bundle: Xylem & Phloem.
Question 12.
Name the regions in which parenchyma tissue is present.
Answer:
Roots and stems.
Question 13.
What is the role of the epidermis in plants?
Answer:
- Epidermis of the leaf contains stomata. Stomata are enclosed by two kidney-shaped cells called guard cells. They are necessary for exchanging gases with the atmosphere.
- Transpiration (loss of water in the form of water vapour) also takes place through stomata.
Question 14.
How does the cork act as a protective tissue?
Answer:
Cells of cork are dead and compactly arranged without intercellular spaces. They also have a chemical called suberin in the walls that makes them impervious to gases and water.
Question 15.
Complete the table. (Answer is filled) Ans:
Answer:
KSEEB Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Additional Questions
Question 1.
Diagrammatically show the longitudinal section of parenchyma and label the parts.
Answer:
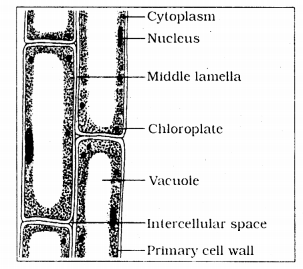
Question 2.
Diagrammatically show the section of collenchyma and label the parts.
Answer:
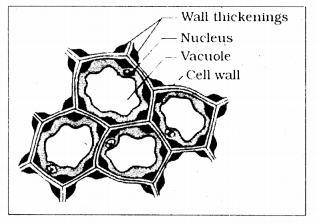
Question 3.
Diagrammatically show the section of phloem and label the parts
Answer:
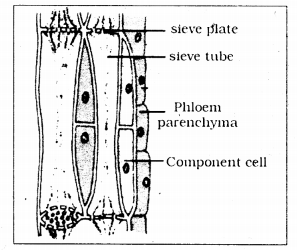
Question 4.
Mention the four type of phloem
Answer :
- Sieve tubes
- Companion cells
- Phloem fibers
- Phocrn parenchyma
Question 5.
Where do you find Aerdar tissue?
Answer :
It is found between and skin and murder around blood vessels of nerves and in the bone marrow it fills the space inside the organ supports internal organs and helps ¡n repair of tissues.
Question 6.
What are tendons?
Answer :
Tendons another tendon strength connect muscles to bones and type of connective tissue are fibrous tissue with great but limited flexibility.