KSEEB SSLC Class 10 Maths Solutions Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Ex 3.6 are part of KSEEB SSLC Class 10 Maths Solutions. Here we have given Karnataka SSLC Class 10 Maths Solutions Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Exercise 3.6.
Karnataka SSLC Class 10 Maths Solutions Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Exercise 3.6
Question 1.
Solve the following pairs of equations by reducing them to a pair of linear equations :
(i) \(\frac{1}{2 x}+\frac{1}{3 y}=2\)
\(\frac{1}{3 x}+\frac{1}{2 y}=\frac{13}{6}\)
(ii) \(\frac{2}{\sqrt{x}}+\frac{3}{\sqrt{y}}=2\)
\(\frac{4}{\sqrt{x}}+\frac{9}{\sqrt{y}}=-1\)
(iii) \(\frac{4}{x}+3 y=14\)
\(\frac{3}{x}-4 y=23\)
(iv) \(\frac{5}{x-1}+\frac{1}{y-2}=2\)
\(\frac{6}{x-1}-\frac{3}{y-2}=1\)
(v) \(\frac{7 x-2 y}{x y}=5\)
\(\frac{8 x+7 y}{x y}=15\)
(vi) 6x + 3y = 6xy
2x + 4y = 5xy
(vii) \(\frac{10}{x+y}+\frac{2}{x-y}=4\)
\(\frac{15}{x+y}+\frac{5}{x-y}=-2\)
(viii) \(\frac{1}{3 x+y}+\frac{1}{3 x-y}=\frac{3}{4}\)
\(\frac{1}{2(3 x+y)}-\frac{1}{2(3 x-y)}=\frac{-1}{8}\)
Solution:
(i) \(\frac{1}{2 x}+\frac{1}{3 y}=2\) ……………. (i)
\(\frac{1}{3 x}+\frac{1}{2 y}=\frac{13}{6}\) ……………… (ii)
From eqn. (i),
\(\frac{1}{2 x}+\frac{1}{3 y}=2\)
\(\frac{3 y+2 x}{6 x y}=2\)
3y + 2x = 12xy
2x + 3y – 12xy = 0
2x + 3y = 12xy …………….. (i)
From eqn. (ii),
\(\frac{1}{3 x}+\frac{1}{2 y}=\frac{13}{6}\)
\(\frac{2 y+3 x}{6 x y}=\frac{13}{6}\)
6(2y + 3x) = 13 × 6xy
12y + 18x = 78xy
18x + 12y – 78xy = 0
18x + 12y = 78xy ……………… (ii)
Multiplying eqn. (i) by 4,
4(2x + 3y) = 4 × 12xy
8x + 12y = 78xy …………….. (iii)
From eqn. (ii) – eqn. (iii),
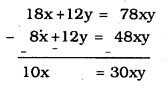
\(x=\frac{30 x y}{10}=3 x y\)
\(\frac{x}{x}=3 y\)
1 = 3y
\(y=\frac{1}{3}\)
2x + 3y = 12xy
\(2 x+3\left(\frac{1}{3}\right)=12 \times x \times \frac{1}{3}\)
2x + 1 = 4x
2x – 4x = 1
-2x = -1
2x = 1
\(x=\frac{1}{2}\)
\(x=\frac{1}{2}, \quad y=\frac{1}{3}\)
(ii) \(\frac{2}{\sqrt{x}}+\frac{3}{\sqrt{y}}=2\) ………….. (i)
\(\frac{4}{\sqrt{x}}+\frac{9}{\sqrt{y}}=-1\) ………….. (ii)
From eqn (i)
\(\frac{2}{\sqrt{x}}+\frac{3}{\sqrt{y}}=2\)
\(\frac{2 \sqrt{y}+3 \sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x y}}=2\)
\(3 \sqrt{x}+2 \sqrt{x y}=2 \sqrt{x y}\) …………… (i)
From eqn (ii),
\(\frac{4}{\sqrt{x}}+\frac{9}{\sqrt{y}}=-1\)
\(\frac{4 \sqrt{y}-9 \sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x y}}=-1\)
\(-9 \sqrt{x}+4 \sqrt{y}=-\sqrt{x y}\)
\(9 \sqrt{x}-3 \sqrt{y}=\sqrt{x y}\) ……………….. (ii)
Multiplying eqn (i) with 2
\(2(3 \sqrt{x}+2 \sqrt{y})=2 \times 2 \sqrt{x y}\)
\(6 \sqrt{x}+4 \sqrt{y}=4 \sqrt{x y}\) ……………….. (iii)
By adding eqn (ii) + eqn (iii)
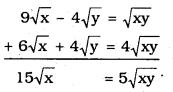
\(\sqrt{x}=\frac{5 \sqrt{x y}}{15}\)
\(\frac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}}=\frac{5 \sqrt{y}}{15}\)
\(1=\frac{\sqrt{y}}{3}\)
\(3=\sqrt{y} \quad \sqrt{y}=3\)
∴ y = 9
Substituting the value of ‘y’ in eqn (i)
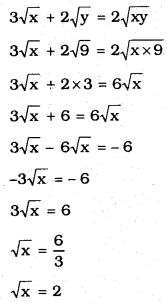
∴ x = 4, y = 9
(iii) \(\frac{4}{x}+3 y=14\)
\(\frac{3}{x}-4 y=23\)
by putting the value of By multiplying eqn. (i) by 4, multiplying eqn. (ii) by 3, and then adding them,
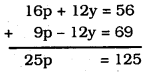
∴ p = 5
\(\frac{1}{x}=p=5 \quad \quad x=\frac{1}{5}\)
Substituting the value of ‘p’ in eqn. (i)
4p + 3y = 14
4 × 5 + 3y = 14
20 + 3y = 14
3y = 14 – 20
3y = -6
∴ y = -2
∴ \(\quad x \cdot=\frac{1}{5}, y=-2\)
(iv) \(\frac{5}{x-1}+\frac{1}{y-2}=2\)
\(\frac{6}{x-1}-\frac{3}{y-2}=1\)
Let \(\frac{1}{x-1}=p \text { and } \frac{1}{y-2}=q\)
\(5\left(\frac{1}{x-1}\right)+\frac{1}{y-2}=2\) ……………. (i)
\(6\left(\frac{1}{x-1}\right)-3\left(\frac{1}{y-2}\right)=1\) …………… (ii)
5p + 1 = 2 …………… (iii)
6p – 3q = 1 …………… (iv)
By solving equation \(\mathrm{p}=\frac{1}{3}, \quad \mathrm{q}=\frac{1}{3}\)
Substituting \(\frac{1}{x-1}\) for p,
\(p=\frac{1}{x-1}=\frac{1}{3}\)
x – 1 = 3
∴ x = 4
Substituting \(\frac{1}{y-2}\) for q,
\(q=\frac{1}{y-2}=\frac{1}{3}\)
y – 2 = 3
∴ y = 5
∴ x = 4, y = 5
(v) \(\frac{7 x-2 y}{x y}=5\) ……………. (i)
\(\frac{8 x+7 y}{x y}=15\) ………………… (ii)
From eqn. (i)
\(\frac{7 x-2 y}{x y}=5\)
7x – 2y = 5xy ………….. (i)
From eqn. (ii)
\(\frac{8 x+7 y}{x y}=15\)
8x + 7y = 15xy ……………… (ii)
Eqm (i) × 7 and Eqn. (ii) × 2, we have
49x – 14y = 35xy ………….. (iii)
16x + 14y = 30xy ……………. (iv)
From eqn. (iii) + eqn. (iv)
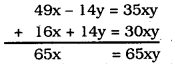
∴ \(\frac{65 \mathrm{x}}{65 \mathrm{x}}=\mathrm{y}\)
1 = y
∴ y = 1
Substituting the value of ‘y’ in eqn. (i)
7x – 2y = 5xy
7x – 2 (1) = 5 × x × 1
7x – 2 = 5x
7x – 5x = 2
2x = 2
∴ x = 1
∴ x = 1, y = 1
(vi) 6x + 3y = 6xy ………………. (i)
2x + 4y = 5xy ………………… (ii)
Multiplying eqn. (ii) by 3
3(2x + 4y = 5xy)
6x + 12y = 18xy ………………. (iii)
From eqn. (i) – eqn. (ii)
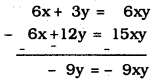
9y = 9xy
\(\frac{9 y}{9 y}=x\)
1 = x
∴ x = 1
Substituting the value of ‘x’ in eqn (i),
6x + 3y = 6xy
6 × 1 + 3y = 6 × 1 × y
6 + 3y = 6y
6y – 3y = 6
3y = 6
∴ \(\quad y=\frac{6}{3}\)
∴ y = 2
∴ x = 1, y = 2
(viii) \(\frac{10}{x+y}+\frac{2}{x-y}=4\)
\(\frac{15}{x+y}+\frac{5}{x-y}=-2\)
Let \(\mathrm{u}=\frac{1}{\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{y}}, \mathrm{v}=\frac{1}{\mathrm{x}-\mathrm{y}}\) then,
10u + 2v = 4 …………. (i)
15u – 5v = -2 …………. (ii)
Multiplying eqn. (i) by 5 and multiplying eqn. (ii) by 2 and then by adding
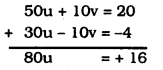
∴ \(\quad \mathbf{u}=\frac{1}{5}\)
Substituting the value of ‘u’ in eqn. (i)
\(10 \times \frac{1}{5}+2 v=4\)
2 + 2v = 4
2v = 4 – 2
2v = 2
∴ v = 1
∴ u = 1/5 , v =1
\(\frac{1}{x+y}=\frac{1}{5} \quad \frac{1}{x-y}=1\)
∴ x + y = 5 x – y = 1
x + y = 5 …………….. (iii)
x – y = 1 …………….. (iv)
From eqn. (iii) + eqn. (iv)
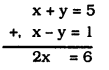
x = 3
∴ Substituting the value of ‘x’ in (iii)
x + y = 5
3 + y = 5
y = 5 – 3
y = 2
∴ x = 3, y = 2
(viii) \(\frac{1}{3 x+y}+\frac{1}{3 x-y}=\frac{3}{4}\) ………….. (i)
\(\frac{1}{2(3 x+y)}-\frac{1}{2(3 x-y)}=\frac{-1}{8}\) ……………. (ii)
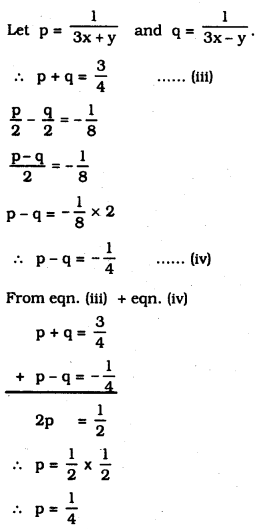
Substituting the value of ‘p’ in eqn. (iii)
\(p+q=\frac{3}{4}\)
\(\frac{1}{4}+q=\frac{3}{4}\)
∴ \(\quad q=\frac{3}{4}-\frac{1}{4}\)
∴ \(\quad q=\frac{1}{2}\)
∴ \(\quad p=\frac{1}{3 x+y}=\frac{1}{4}\)
3x + y = 4 ……………. (v)
\(q=\frac{1}{3 x-y}=\frac{1}{2}\)
3x – y = 2 ……………… (vi)
From eqn. (v) + eqn. (vi)
3x + y = 4
+3x – y = 2
6x = 6
∴ \(\quad x=\frac{6}{6}=1\)
Substituting the value of ‘x’ in eqn. (v)
3x + y = 4
3 × 1 + y = 4
3 + y = 4
∴ y = 4 – 3
∴ y = 1
∴ x = 1, y = 1
Question 2.
Formulate the following problems as a pair of equations, and hence find their solutions :
(i) Ritu can row downstream 20 km in 2 hours, and upstream 4 km in 2 hours. Find her speed of rowing in still water and the speed of the current.
Solution:
Let speed of Ritu
in still water be x km/hr.
in current water be y km/hr
Speed of water while
upstream is (x + y) km/hr,
downstream is (x – y) km/hr,
2(x + y) = 20
x + y = 10 ………… (i)
2(x – y) = 4
x – y = 2 …………… (ii)
By Adding eqn. (i) and eqn. (ii),
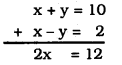
∴ \(\quad x=\frac{12}{2}=6\)
Substituting the value, x = 6 in eqn. (i),
x + y = 10
6 + y = 10
y = 10 – 6
∴ y = 4
∴ Speed of Ritu
in still water, x = 6 km/hr.
in current water, y = 4 km/hr.
(ii) 2 women and 5 men can together finish an embroidery work in 4 days,, while 3 women and 6 men can finish it in 3 days. Find the time taken by 1 woman alone to finish the work, and also that taken by 1 man alone. ‘
Solution:
Number of days required
for women be ’x’
for men be ‘y’
Work done by woman in 1 day \(=\frac{1}{x}\)
Work done by man in 1 day \(=\frac{1}{y}\)
\(4\left(\frac{2}{x}+\frac{5}{4}\right)=1\)
\(\frac{2}{x}+\frac{5}{4}=\frac{1}{4}\) ………….. (i)
\(3\left(\frac{3}{x}+\frac{6}{y}\right)=1\)
\(\frac{3}{x}+\frac{6}{y}=\frac{1}{3}\) ……………… (ii)
Let \(\frac{1}{{x}}={p} \text { and } \frac{1}{y}={q}\)
∴ \(2 p+5 q=\frac{1}{4}\)
8p + 20q = 1 ……….. (iii)
\(3 p+6 q=\frac{1}{3}\)
9p + 18q = 1 ……………. (iv)
By Cross-multiplication
\(\frac{\mathrm{p}}{-20-(-18)}=\frac{\mathrm{q}}{-9-(-8)}=\frac{1}{144-180}\)
\(\frac{p}{-2}=\frac{q}{-1}=\frac{1}{-36}\)
If \(\frac{p}{-2}=\frac{1}{-36}\) then \(p=\frac{-2}{-36}=\frac{1}{18}\)
If \(\frac{q}{-1}=\frac{1}{-36}\) then \(q=\frac{-1}{-36}=\frac{1}{36}\)
\(p=\frac{1}{x}=\frac{1}{18} \quad ∴ \quad x=18\)
\(q=\frac{1}{y}=\frac{1}{36} \quad ∴ \quad y=36\)
∴ Number of days taken by one woman to complete work, x = 18
Number of days taken by one man to complete the work, y = 36.
(iii) Roohl travels 300 km to her home partly by train and partly by bus. She takes 4 hours if she travels 60 km by train and the remaining by bus. If she travels 100 km by train and the remaining by bus, she takes 10 minutes longer. Find the speed of the train and the bus separately.
Solution:
Let speed of the train be x’ km/hr. and Speed of the bus is ‘y’ km/hr.
\(\frac{60}{\mathrm{x}}+\frac{240}{\mathrm{y}}=4\) …………… (i)
\(\frac{100}{x}+\frac{200}{y}=\frac{25}{6}\) …………… (ii)
If \(\frac{1}{\mathbf{x}}=\mathbf{p} \quad \frac{1}{\mathbf{y}}=\mathbf{q}\) then
60p + 240q = 4 ……………… (iii)
\(100 p+200 q=\frac{25}{6}\) ……………….. (iv)
Multiplying eqn. (iii) by 10, Mulitplying eqn. (iv) by 6 and then eqn. (iii) – eqn. (iv), we have
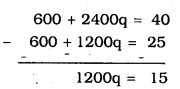
∴ \(\quad q=\frac{15}{1200}\)
∴ \(\quad q=\frac{1}{80}\)
Substituting the value of \(q=\frac{1}{80}\) in eqn. (iii)
\(60 p+240 \times \frac{1}{80}=4\)
60p + 3 = 4
60p =4 – 3
∴ \(\mathrm{p}=\frac{1}{60}\)
∴ \(\quad \mathrm{p}=\frac{1}{60}=\frac{1}{\mathrm{x}}\)
∴ x = 60 km/hr.
∴ \(\quad q=\frac{1}{80}=\frac{1}{y}\)
∴ y = 80 km/hr.
∴ Speed of train, x = 60 km/hr.
Speed of bus, y = 80 km/hr.
We hope the given KSEEB SSLC Class 10 Maths Solutions Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Ex 3.6 will help you. If you have any query regarding Karnataka SSLC Class 10 Maths Solutions Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Exercise 3.6, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.