Labour 10th Notes KSEEB Social Science
→ Human society is formed on natural inequalities. This natural inequality is based on ‘Division of Labour.’
-‘PLATO’ IN ‘REPUBLIC’
→ A society’s need is fulfilled by different divisions of people. Division of Labour creates less skilled workers.
– KARL MARX
→ Plato has classified Division of Labour into Economic Labour and Social Labour
![]()
→ Division of Economic Labour goes with the technical and people’s co-operation.
→ Divison of Social Labour achieves social control through class, status and stratification.
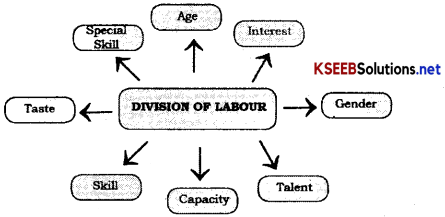
→ “Specialization” creates Division of Labour.
→ “Specialization” – having deeper knowledge and indepth skill in the particular field.
→ “Class System” emerged due to economic interests and division of labour.
→ “Labour” means earning in cash or kind by providing one’s manual or intellectual labour (physical or mental)
→ “Equal labour, Equal Pay”, can be termed inequality in labour.
→ Discrimination in labour occurs if differential payment is given to two individuals who put the same amount of time and effort.
![]()
→ Inequality in labour can also be classified based on “with compensation and without compensation”.
→ “Without compensation” labour is the labour without payment. Eg. Family work, social work, artist etc.
→ “Labour with compensation” is based on offering semi-skilled or skilled labour for “wages” based on total work done in a day, week or month.
→ “Compensation” is an agreement between the worker and the owner.
→ Labour sector is divided into
- Primary
- Secondary
- Tertiary Sectors
→ Labour sector is further divided, into
- Organized &
- Unorganized sectors
→ Organized Sector: The sector of Labour enrolled as per the laws of the Government and provided fixed wages and facilities within the framework of law such as special allowances, provident fund etc.
→ In the organized sector the relationship between the employee and employer is guided by legal provisions.
→ The unorganized labour sector is not guided by any legal provisions.
→ More than 90% of labourers work in unorganized sector.
→ Challenges faced by unorganized sector workers are broadly classified as
- Migration
- Social Security .
- Legal Framework
- Child Labour
- Physical & Mental Exploitation
→ KARL MARX: Karl Heinrich Marx (1818-1883) was a German philosopher, sociologist, historian and economist. He wrote the famous book “Das Capital”.
![]()
→ DICTUM: A short statement that expresses a general truth or principle.
→ SAFAI KARMACHARIS: Workers involved in the work of local civic bodies.
→ COMPENSATION: Money paid to a person in exchange of his labour.
→ NCC: National Cadet Corps
→ ITI: Industrial Training Institute
→ PRIMARY SECTOR: The sector of economy concerned with primary industries Eg. Agriculture.
→ SECONDARY SECTOR: Industry that converts the raw material provided by primary sector into goods and products for the consumer and manufacturing industry.
→ TERTIARY SECTOR: A part of the country’s economy concerned with providing services.
→ MODALITY: The way in which some thing exists.
→ CIRCULAR MIGRATION: Or ‘repeat migration’ is the temporary and usually repetitive movement of migrant workers between house and host areas for the purpose of employment.
→ PAYMENT OF GRATUITY ACT 1971: Law enacted by the Government to ensure that the payment of gratuity to employees throughout the country based on a uniform platform.