National Income and Sectoral Aspects of the Indian Economy Class 8 Questions and Answers KSEEB 8th Social Science
I. Fill in the blanks with suitable word.
Question 1.
Per capita Income = National Income divided by ________________ .
Answer:
Population
Question 2.
Agency responsible for estimation of National Income of India today is from ________________ Sector.
Answer:
Central Stastical Organisation
Question 3.
The highest share in national income of India today is from ________________ .
Answer:
Primary sector
![]()
Question 4.
Small scale Industries are defined in terms of ________________
Answer:
MSMED ( Micro, small and medium enterprises development)
Question 5.
Indian agriculture is said to be ________________ with monsoons.
Answer:
gamble
Question 6.
Extent of irrigated are a in India is about ________________ percent of cultivated areas.
Answer:
30%
II. Answer the following questions and cuss them in groups.
Question 1.
Define National Income
Answer:
National Income refers to the total value of good and services produced annually in a country.
Question 2.
If the total income of family of 5 members in 2015 was Rs. 567890 Calculate per capital income of the members of the family.
Answer:

Per capita Income is = 1,13, 578.00 Rupees
![]()
Question 3.
State how small industries are helpful for growth of a country like India.
Answer:
Increase in small scale Industries activity is considered as essential for the economic growth and development of the country.
In countries like it is more important for following reasons.* Small scale industries generare huge employment opportunities. Small scale – industries ultilise the natural local resources successfully. Small Scale Industrial Skill from rural and Semi urban areas. Small scale Industries promotes exports and earn foreign money.
Small Scale Industries cover 35% of the gross value of the input in the manufacturing sector, about 80% by the total industrial employment and 40% of total export of the country.
Nearly 488.46 lakh enterprises working in the country in 2013-14, which.employed 11.14 crores of people.
Question 4.
What are the reasons for decline in the size of agricultural holdings in India?
Answer:
Due to increase in population land holdings become reduced by being divided and subdivided to the family members. So it is not possible to undertake scientific and modem agriculture. So, naturally production reduces and leads to farmers becoming poorer.
Question 5.
Examine the reasons for crises in Indian Agriculture.
Answer:
Many factors have reinforced each other to deepen the malady. The major causes of agricultural distress are as follows.
Uneconomic size of cultivated holding. Majority of the people depend on agriculture. Due to divide and sudivision land of holdings, people can’t get division profit in this field.
High population pressure The production and income per head are very low. Rain fed farming and recurrence of droughts. Our agriculture depends on monsoon, but monsoons are uncertain and uneven. Decline in public investments in irrigation and other related manufacturers. Inadequate credit from institutional sources. Inability to get remmunerative prices.
![]()
Question 6.
Discuss the measures to overcome agricultural crisis in India.
Answer:
MEASURES TO OVERCOME AGRICULTURAL CRISIS IN INDIA
The causes of the crisis also point to the remedies, some of which could be:
1. Increasing public investment: There is an urgent need to step up the government investment in drought proofing, water harvesting, research in new varieties of seeds, new cultivation methods that use less water, and retain soil fertility, extension and training of farmers in adoption of efficient crop production practices.
2. Expanding credit availability: The small and marginal farmers, who hesitate to approach a bank or any financial institution, should be ensured greater amount of credit.
3. Marketing reforms: Farmers should be guaranteed remunerative prices for their produce. For this purpose, markets and marketing infrastructure need to be strengthened.
4. Crop Insurance: An insurance scheme that covers and compensates the losses of farmers for all types of risks needs to be put in place.
5. Counseling and moral support: There is a need to set up counseling centres at village level to provide moral support to distressed farmers so that they do not resort to extreme step of committing suicide.
6. Regulating private money lenders: Apart from the above, there is a need to regulate the activities of money lenders so that they do not oppress the poor farmers who have borrowed from them for various purposes.
Additional Questions and Answers
Question 1.
National Income and per capita Income in
Answer:
India 1950-51 to 2014-15
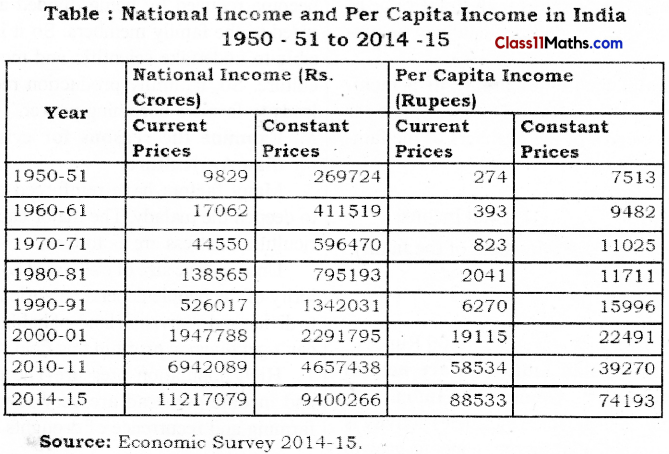
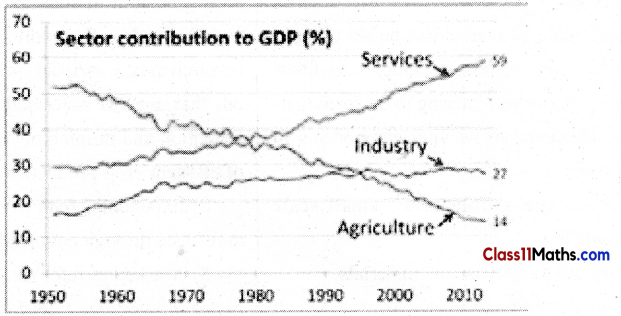
Question 2.
Change in sectoral Shares of GDPin India 1951 to 2013%
Answer:
Question 3.
Average Growth Rate of GDP by Sectors (% Per annum)
Answer:
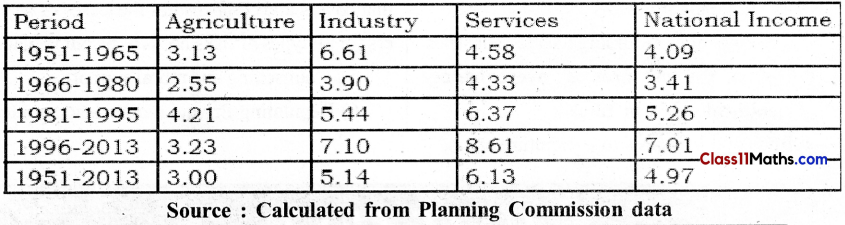
![]()
Question 4.
Mention the measurement of natial Income?
Answer:
The measurement of a Nation’s Income is very difficult and involves complex procedure.
- The rate of economic growth
- Changes in average living standards.
- Changes in the distribution of income.
Question 5.
Explain the primary sector and its important.
Answer:
The primary sector consists of all nature based activities like agriculture, and allied activities like Sericulture, Horticulture, Animal husbandry, Poultry Fishery, Floriculture etc.
Agricultural sector is the predominant and has the largest share in national income.
Question 6.
Which is called as manufacturing sector, why?
Answer:
Secondary Sector is called as manufacturing sector. Hence Converts raw materials into finished products.
Industries contribute nearly 1/3 of national income, has helped in building the basic infrastructure.
Question 7.
Explain tertiary Sector
Answer:
It is also called Service sector. They are hospitals, educational institutions, health centers, hotels telephone services, finance and banking etc.
It contributes major income to national income and provide 28% of Jobs in our country.
Question 8.
Advantages or merits of small scale Industries.
Answer:
Small Scale Industries can be set up any where with simple technology, employing fewer number of people and catering to the local market are considered to be vital components of development
Question 9.
List out the problems of small scale industries
Answer:
(a) non-availability of row materials.
(b) problem of finance
(c) low technical skill
(d) Marketing problems
(e) Competitions from large scale Industries
![]()
Question 10.
Discuss the measures to overcome agricultural crisis in India.
Answer:
Remedial measures to agriculture crisis.
1. Increasing Public Investment. There is an urgent need to step up the government in-vestment in drought proofing, water harvesting, research in new varieties, new cultivation methods that use less water and retain soil fertility, Extention and training of farmers in adoption of efficient crop production practices.
2. Expanding credit availability- Financial assistance through national bank.
3. Marketing reforms: Markets and Marketing infrastructure need to be strengthened.
4. Crop Insurance: An Insurance scheme that covers and compensates the losses of farmers for all types of risks needs to be put in place.
5. Counselling and moral support
6. Regulating Private money lenders etc.