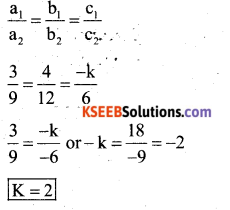
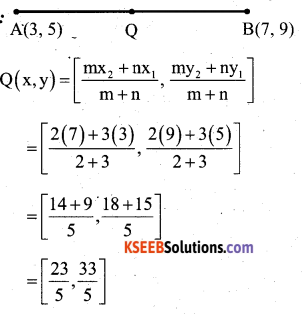
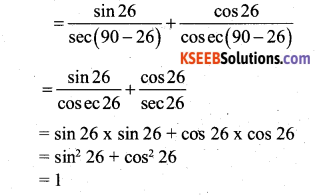
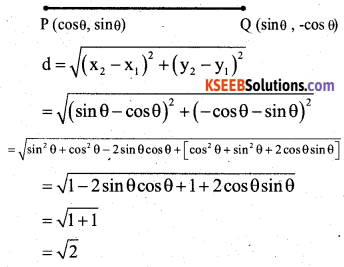
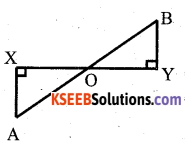
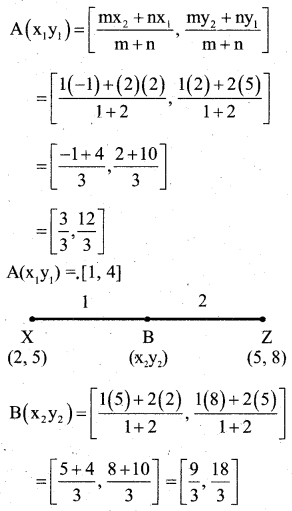
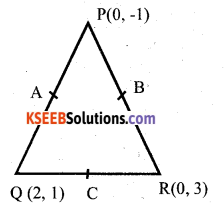
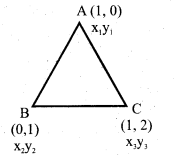
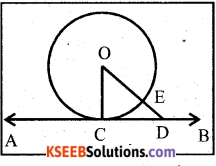
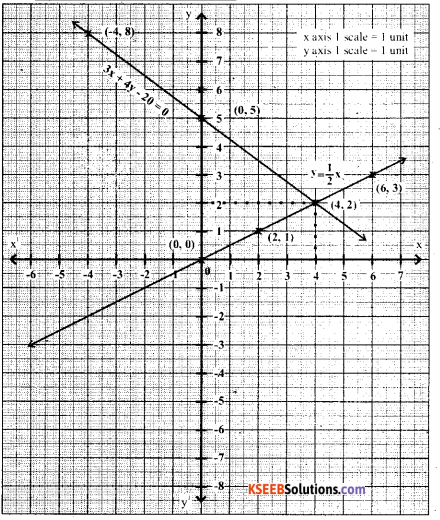
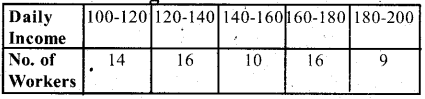
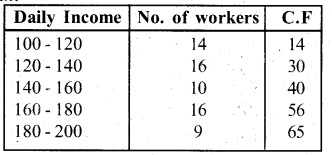
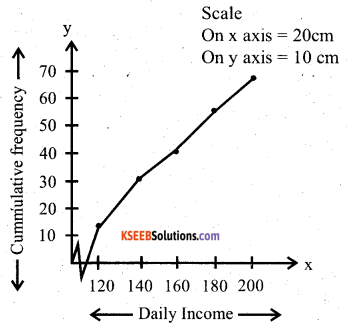
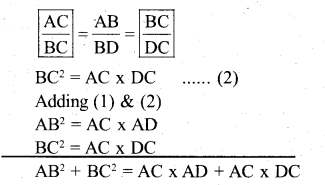
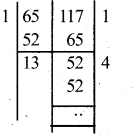
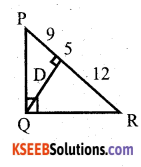
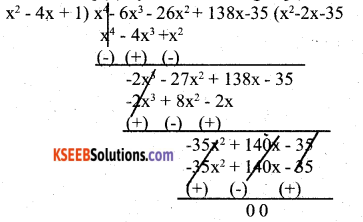
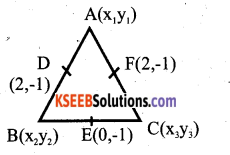
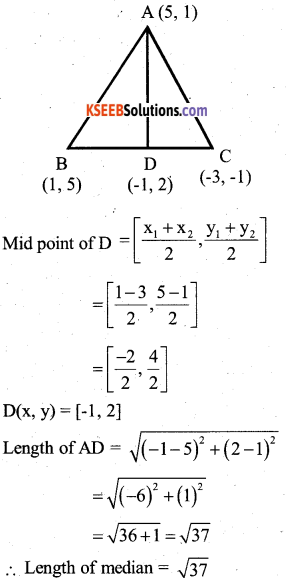
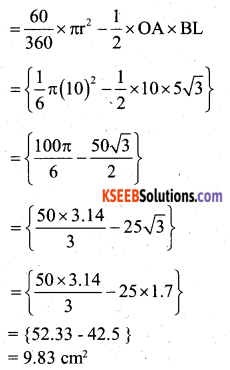
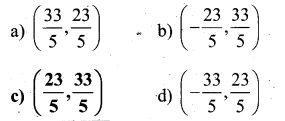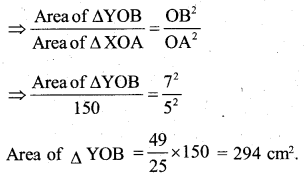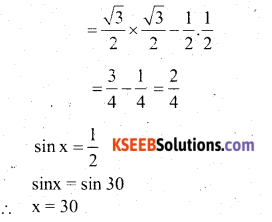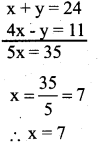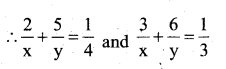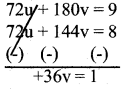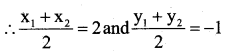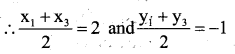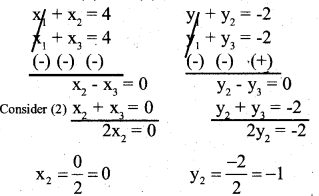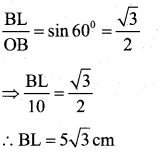You can Download नागरिक के कर्तव्य Questions and Answers Pdf, Notes, Summary Class 10 Hindi Karnataka State Board Solutions to help you to revise complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
नागरिक के कर्तव्य Questions and Answers, Notes, Summary
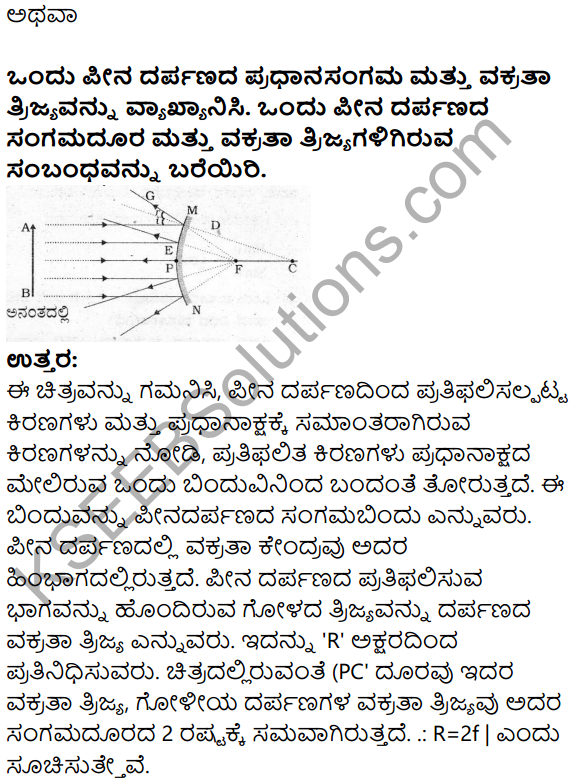
अभ्यास
I. निम्नलिखित प्रश्नों के उत्तर लिखिए :
प्रश्न 1.
मीना मैडम ने कितने दिनों के कार्यशिबिर का आयोजन किया था ?
उत्तर:
मीना मैडम ने पंद्रह दिनों के कार्यशिबिर का आयोजन किया था।
प्रश्न 2.
संभाषण का विषय क्या था ?
उत्तर:
नागरिकों के मूल कर्तव्य यह संभाषण का विषय था।
प्रश्न 3.
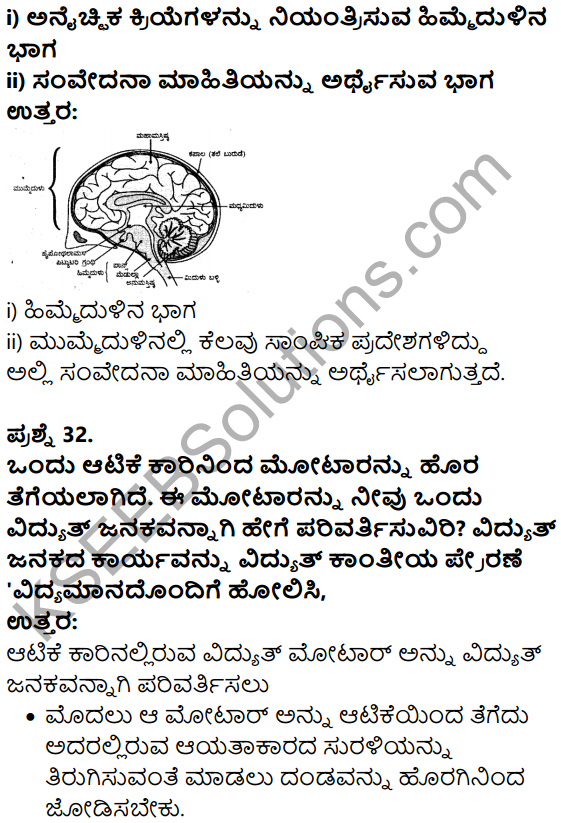
अकुल ने मीना मैडम से क्या कहा ?
उत्तर:
अकुल ने मीना मैडम से कहा, एक नागरिक की है सियत से हमें अपने देश के राष्ट्र\(\square\)ध्वज, राष्ट्र\(\square\)गान र तथा। राष्टी \(\square\)य त्योहारों का आदर करना चाहिए। करना चाहिए।
प्रश्न 4.
सलमा ने क्या कहा ?
उत्तर:
सलमा ने कहा कि प्रकृति हमारी माँ है। इसलिए हमें प्राकृतिक संसाधनों का अपव्यय नहीं करना चाहिए। साथ ही पर्यावरण को स्वच्छ रखना भी हमारा कर्तव्य है।
प्रश्न 5.
अन्वर ने मीना मैडम से क्या कहा ?
उत्तर:
अन्वर ने मीना मैडम से कहा कि देशवासियों के प्रति भाईचारे का भाव रखना जरूरी है। जाति, धर्म, भाषा, प्रदेश, वर्ग पर आधारित सभी भेदभावों से दूर रहना चाहिए।
प्रश्न 6.
मीना मैडम ने छात्रों से अंत में क्या कहा ?
उत्तर:
मीना मैडम ने छत्रों से कहा कि देश की म रक्षा और उत्कर्ष के लिए सतत प्रयत्नशील रहें। अपने कर्तव्यों का पालन करें तभी देश का कल्याण होगा।