Karnataka 2nd PUC Biology Important Questions Chapter 10 Microbes in Human Welfare
Question 1.
Write a note on microbes used in household products? or Explain the role of Microbes in Household products?
Answer:
(a) Curd: One of the examples of fermenting activities of microorganisms. Ans; (1-lj)
(b) Lactic Acid Bacteria (LAB) Ex: L. lactis, L, acidophilus, L. bulgaricus etc. .
MECHANISM
Question 2.
Explain the mechanism of milk turning into curd by LAB?
Answer:
Conversion of lactose of milk into curd. LAB produce acids that coagulate and partially digest milk proteins.
A small amount of curd added to milk as inoculum or starter at suitable temp (50 – 40° c) for 6 to 8 hrs.
Question 3.
Give benefits of curd?
Answer:
Benefits: Improves nutritional quality by increasing Vit. B12. They check disease-causing microbes.
Question 4.
Name the vitamin present in curd?
Answer:
Vitamin B12.
Question 5.
In which food would you fined LAB?
Answer:
Curd
![]()
Question 6.
Give any 2 examples, that microbes evolve gases during metabolism?
Answer:
1. Dosa and Idli – Bacterial fermentation of rice and black gram leads to CO2 evolution, which causes doughing of raw material. Atmospheric bacteria like Leuconostoc mesenteroides, Pseudococcus cerevisiae, Streptococcus faecalis etc. enhance this action.
2. Wheat flour and water is mixed with Baker’s yeast saccharomyces cerevisiae liberate CO2 which results in Dough, which makes the bread soft and porous.
Question 7.
Name the microbe used in production of bread?
Answer:
Saccharomyces ceresvisiae (yeast)
Question 8.
What is Toddy?
Answer:
A traditional drinks prepared by fermenting sap, obtained from toddy palm in florescence (spadix) is tapped for toddy. [Note: Neera obtain from Coconut plant is a refreshing drink, when heated produce palmsugar and jaggery],
Question 9.
Name the source of Toddy?
Answer:
Toddy (Phoenix dactylifera).
[Note: Fermented fish, soyabean, Bamboo shoots are used as food].
CHEESE: Oldest food items, prepared by activities of microbes. Different varieties of cheese are known for their texture, flavor, taste etc.
Ex: (a) Swiss Cheese – with special flavour and large holes.
Question 10.
Write the role of microbe’s in house hold food products.
Answer:
(a) CURD: One of the examples of fermenting activities of microorganisms.
Lactic Acid Bacteria (LAB)
Ex: L. lactis, L. acidophilus, L, bulgaricus etc.
Benefits: Improves nutritional quality by increasing Vit. B12.
(b) They check disease-causing microbes. Vitamin B12
- Swiss cheese by propionibacterium
- Roquefort cheese
(c) DOUGH for making foods:
Ex: Idli, Dosa, Bread, Jalebi Prepared by the fermentation process.
Saccharomyces cerevisiae (yeast).
(d) Toddy is a fermented drink from palms.
![]()
Question 11.
Why large holes are seen in Swiss cheese? or Mention the bacteria responsible for the large holes seen in Swiss Cheese.
Answer:
Large holes are due to large amount of CO2 released by the thermophilic bacteria Propionibacterium shamanic.
Question 12.
Which Species of penicillium produces Roquefort cheese?
Answer:
(b) Roquefort Cheese: Prepared by sheep’s milk and is ripened by growing a fungus Penicillium Roquefort. [Note: This cheese has- Green blue mottling colours with particular flavour,.These living microorganisms are probiotics, which influence intestinal microflora, which cure intestinal disorders]
Question 13.
Explain the role of microbes as industrial products?
Answer:
A number of powerful industries are* based on beneficial activities of microbes. They aim towards growing microbes in very large scales in a specialised vessel called Fermentors or Bioreactors.
Examples: 1. Fermented beverages: prepared by using yeast – Saccharomyces cervisiae.
Bread making, Alcoholic drinks, Undistilled Wine, Beer, Whisky, Brandy, Rum and distilled hard liquors
Question 14.
Give one appliction of Brewer’s yeast?
Answer:
Brewer’s yeast, Saccharomyes cerevisiae is used for Fermenting purpose using malted cereals and fruit juices to produce ethanol and Grape-wine.
Question 15.
What are Antibiotics, give one example?
Answer:
These are the chemical substances which are produced by some microbes and can kill or retard the growth of other micro organisms (disease-causing) Ex: Penicillin
Question 16.
How was Penicillin discovered?
Answer:
Pencillin was discovered by Alexander flemming. He experimented on Staphylococcus bacteria. Which could not grow on unwashed culture plates, he concluded that it was due to chemical produced by fungi Penicillium notatum.
Question 17.
Name two scientists who experimented the role of penicillin as an antibiotic?
Answer:
Ernst chain and Howard Florey – Experimented using this antibiotic in world war II to treat American soldiers. They got Nobel prize 1945.
[Note: Most of the antibiotics are from 3 groups of microorganisms.
- Eubacteria – Bacillus.
- Ramified bacteria – Streptomyces
- Fungi – Pencil, Aspergillus, Cephalosporium.
Question 18.
Name the source of Penicillin?
Answer:
Penicillium notatum Chemicals, Enzymes and other Bioactive molecules
Question 19.
Name the microorganism which produces butyric acid.
Answer:
Clostridium butylicum.
![]()
Question 20.
Write a note on microbes application as chemical, enzymes and bioactive molecules?
OR
Mention any 5 microbes and their commercial or industrial products.
Answer:
Microbes are also used for the commercial and industrial production of chemicals like organic acids, alcohols, and enzymes.
Acid producers are:
- Aspergillus niger (fungus) → Citric Acid.
- Acetobacter aceti (bacterium) → Acetic acid.
- Clostridium bretylium → Butyric acid.
- Lactobacillus → Lactic acid.
Question 21.
Name the sources of Acetic acid and citric acid?
Answer:
Acetobacter aceti and Aspergillus niger.
Question 22.
Name an organism producing pectinase. Mention the use of pectinase?
Answer:
Aspergillus niger produces Pectinases and Proteases → Used for clarification of bottled fruit juices to clarify.
Question 23.
Name any two industrially important enzymes and their uses?
Answer:
- Invertase → Production of ethanol.
- Pectinases → Used for clarification of bottled fruit juices.
Question 24.
Name the enzyme and its source used in detergent?
Answer:
Candida albicans (Fungi) Produces enzyme → Lipases → used in detergent are helpful in removing oily stains
Question 25.
Name the source Clot bluster and its action?
Answer:
Streptococcus produces the enzyme is Streptakinase → modified genetically and used as ‘Clot bluster’ for removing clots from blood vessels of patients of myocardial infarction leading to a heart attack.
Question 26.
Name the source of cyclosporin A? Mention the use of cyclosporin-A.
Answer:
Cyclosporin: A bioactive molecule, which is produced by fungus Trichoderma polysporum., acts as an immunosuppressive agent in organ-transplant patients.
Question 27.
Name the bioactive molecule used in organ transplantation. Who provided an experimental proof for the chemical evolution of life?
Answer:
Cyclosporin A [Stanley Miller and Harold Urey].
Question 28.
Which Bioactive moecule is used as an immunosuppressive agent?
Answer:
Cyclosporin A
![]()
Question 29.
Name the fungus that produce statin? Explain its function.
Answer:
2. Monascus purpereus (Yeast) – Statin → acts as blood Cholesterol lowering agent. Inhibits enzyme synthesis, which is responsible for synthesis of cholesterol.
Question 30.
Mention the use of Statin?
Answer:
Blood cholesterol-lowering agent.
Question 31.
Name the fungus that produces cyclosporin A?
Answer:
Trichoderma polysporum.
Question 32.
Define Sewage?
Answer:
It is municipal wastewater containing domestic water born wastes including human and animal excreta etc.
[This can not be discharged into natural water bodies like rivers and streams, so it is treated in sewage treatment plants (STP) to make it less polluting by using heterotrophic microbes.]
Question 33.
Expand STP?
Answer:
Sewage treatment plant.
Question 34.
Mention two stages of STP?
Answer:
Two stages:
- Primary treatment
- Secondary treatment.
Question 35.
Explain steps involved in sewage treatment? or Explain different stages involved in Sewage treatment.
Answer:
1. Primary Treatment: It is a physical removal of large and small particle from the sewage through filtration and sedimentation. Initially floating debris is removed by sequential filtration. Later-The grit (soil and small pebbles) removed by sedimentation. This concentrated solid material that settles down forms the PRIMARY SLUDGE, supematent forms the Effluent. Effluent is taken for secondary treatment.
2. Secondary treatment/Biological treatment:
The primary effluent is passed into large aeration tanks, and air is pumped into it to make it aerobic, which allows vigorous growth of useful aerobic microbes into “FLOCS”
“Masses of bacteria associated with fungal filaments to form mesh-like structures”.
While growing thege microbes consume the major part of the organic matter in the effluent (by oxidation), so BOD is reduced. After BOD reduction, the effluent is passed into a sedimentation tank, where the microbial floes are allowed to settle down, this settled material ‘Activated Sludge’, a small part of it is pumped back into aeration tank to serve as the Inoculum.
The remaining major part of the sludge is pumped into large tanks called Anaerobic Sludge digester, here
other anaerobic microorganisms start digesting bacteria and fungi in the sludge. During this digestion bacteria produce a mixture of gases such as Methane, H2S, and C02 which are highly inflammable can be used as [Biogas].
[Note: The number of STP is not enough in our country to treat large sewage quantities, so the untreated sewage is often discharged directly into rivers leading to pollution and increase in water bom diseases. The ministry of Environment, Forest has initiated GANGA ACTION PLAN and YAMUNA ACTION PLAN to save these major rivers of our country form pollution, so that only treated sewage may be discharged into the rivers.]
Question 36.
Define BOD?
Answer:
BOD → Biochemical Oxygen Demand → It is the amount of the oxygen, that would be consumed if all the organic matter in one litre of water, were oxidised by bacteria. [BOD is a measure of the organic matter present in the water, greater BOD, more is its polluting potential.]
Question 37.
What is Activated Sludge?
Answer:
After reduction of BOD of effluent in Sewage treatment plant, it is passed into sedimentation tank, where the microbial floes are allowed to settle down, this settled material is Activated Sludge.
Question 38.
BOD is an index of water pollution? Comment.
Answer:
The BOD test measures the rate of uptake of oxygen by micro organisms in a sample of water and thus indirectly BOD is a measure of the organic matter present in the water. The greater the BOD value of wastewater, more the pollution.
![]()
Question 39.
What are FLOCS? Microbial floes?
Answer:
Masses of bacteria associated with fungal elements to form mesh like structure.
Question 40.
Disposal of sewage into water without proper treatment may cause of serious diseases? Give reason.
Answer:
Sewage contains large amounts of organic matter and microbes, many of which are pathogenic.
Question 41.
Define Biogas. Mention the components of biogas?
Answer:
Biogas is a mixture of gases (65% Methane, 30% CO2, and the remaining 5% includes H2, N2, O1, and H1S) produced from degradable organic matter by the activity of ‘Anaerobic bacteria’, which may be used as fuel.
Question 42.
What are Methanogens? Give one example of methanogenic bacteria?
Answer:
Certain anaerobic bacteria which grow anaerobically on cellulosic material produces- Methane, CO, and Hr They are known as Methanogens, Ex: Methanobacterium ruminated.
Question 43.
Mention the role in methanobacterium in cattles?
Answer:
Methanobacterium present in rumen of cattle, break down cellulosic material anaerobically which is present in the food and play important role in the nutrition of cattle.
Question 44.
What is Gobar gas?
Answer:
The excreta of cattle i.e, dung, commonly called gobar is rich in methanobacterium, so this dung can be used for generation of biogas known as gobar gas.
Question 45.
Name the institutes which helped in the development of bio fuel technologies in India?
Answer:
This technology was developed by efforts of Indian Agricultural Research Institute (IARI) and Khadi and Village industries commission (KVIC).
Question 46.
Explain the Mechanism of .Working of Biogas plant?
Answer:
The biogas plant has a concrete tank (10-15 ft deep) in which biowastes and slurry of dung is collected.
The tank has a floating cover which rises on production of gas in the tank, due to microbial activity.
After filling slurry biogas tank is covered by the floating lid. Methanobacterium in the dung act on the biowastes to produce biogas. The biogas plant has an outlet, which is connected to a pipe to supply biogas to nearby houses.
The spent slurry (sludge) is removed through another outlet and may be used as fertilizer.
![]()
Question 47.
Draw a neat labelled diagram of Biogas plant?
OR
Describe the parts of a biogas plant with a labelled diagram?
Answer:
Biogas plant consist of vessel in which dung and water are added it is connected to a dome shaped vessel in which there is another vessel placed which contains methane and C02 gas this is termed as gas holder on the upper side there is a pipe through which the gas escapes. Gas holder is connected to a vessel in which the sludge is placed. The biogas plant is used in rural areas for cooking purpose.
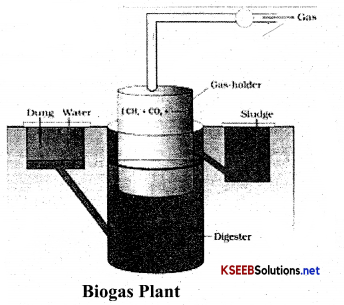
Question 48.
What is Biocontrol?
Answer:
Biocontrol: Use of biological methods for controlling plant diseases and pests.
Question 49.
What are the harmful effects of insecticides and pesticides?
Answer:
- Chemical insecticides and pesticides are extremely harmful to human beings and animals.
- Pollute Environment and plants. Pollute soil through chemical weedicides.
- Create ecological imbalance by disturbing the food chain/food web by the eradication of field fauna and flora (pests).
Question 50.
Explain why biocontrol is considered a holistic approach?
Answer:
Reduce our dependence on toxic chemical pesticides. Familiarity with various life forms inhabiting the field.
Knowledge about the life cycles, patterns of feeding habitat of predators and pests, which help to develop appropriate means to biocontrol.
Question 51.
Explain the role of microbes used as Biocontrol agents with examples?
OR
Name the controlling agents to control aphids and mosquitoes?
Answer:
- Dragonflies and Ladybirds are used to get rid of aphids and mosquitoes.
- Bacillus thuringiensis – control caterpillars of butterfly.
Available in dried powdered form of spores, which is mixed with water and sprayed on plants, which kill caterpillars and leave other insects unharmed.
Bt toxin genes have been introduced into plants to provide resistance to pests, ex: Bt cotton. - Trichoderma (fungus) – present in the root ecosystem is effective on plant pathogens.
Question 52.
Write a note on Baculovirus?
Answer:
Baculoviruses of genus Nucleopolyhedrovirus – attack insects and other arthropods. It is Excellent species-specific narrow-spectrum insecticide. They have negative impacts on plants, mammals, birds, fishes and other non-target insects.
Desirable when beneficial insects are conserved and help in Integrated Pest Management (IPM) programme or when an ecologically sensitive area is treated.
![]()
Question 53.
What are Biofertilizers?
Answer:
Biofertilizers – Organisms that enrich the nutrient quality of the soil.
[Need – Chemical fertilizers are toxic and harmful and pollute the soil and environment.
Approach – Organic farming i.e. usage of bio fertilisers.
Examples: Main sources
(a) Bacteria
(b) Fungi
(c) Cyanobacteria],
Question 54.
Describe the role of microbes as bioferfilizers? or Explain the role of bacteria, Cyanobacteria and of fungi in the enrichment of quality of soil.
Answer:
- Dragonflies and Ladybirds are used to get rid of aphids and mosquitoes.
- Bacillus thuringiensis – control caterpillars of butterfly. Available in dried powdered form of spores, which is mixed with water and sprayed on plants, which kill caterpillars and leave other insects unharmed. Bt toxin genes have been introduced into plants to provide resistance to pests, ex: Bt cotton.
- Trichoderma (fungus) – present in root ecosystem is effective on plant pathogens.
- Baculoviruses of genus Nucleopolyhedrovirus – attack insects and other arthropods. It is Excellent species specific narrow-spectrum insecticides. They have negative impacts on plants, mammals, birds, fishes and other non target insects.
Desirable when beneficial insects are conserved and help in Integrated Pest Management (IPM) programme or when an ecologically sensitive area is treated. - Biofertilizers – Organisms that enrich the nutrient quality of the soil.
[Need – Chemical fertilizers are toxic and harmful and pollute the soil and environment.
Approach – Organic farming i.e. usage of bio fertilizers. Examples: Main sources (a) Bacteria (b) Fungi (c) Cyanobacteria],
Bacteria:
Rhizobium – Fix atmospheric nitrogen, in leguminous plants. Free-living nitrogen-fixing bacteria – Azospirillum and Azotobacter, enrich the nitrogen content of the soil.
Question 55.
Discuss the role of fungi as bio fertilizers?
Answer:
Fungi form symbiotic association with the roots of higher plants called Mycorrhiza.
Ex: Glomus. The fungal hyphae absorbs phosphorus from soil and passes into the plant.
Benefits of Mycorrhiza:
(a) resistance to root bom pathogens
(b) tolerance to salinity and drought
(c) Overall increase in plant growth and development.
Question 56.
How cyanobacteria are useful to plants?
Answer:
Cyanobacteria are autotrophic microbes, widely distributed (aquatic and terrestrial) can fix atmospheric nitrogen fixation. Eg. Anabaena, Nostoc, Oscillatoria etc.
They serve as bio fertilizers in paddy fields. Blue-green Algae add organic matter and increase the fertility of the soil. Regular use of biofertilizers from the market to replenish soil nutrients and reduce dependence on chemical fertilizers.
![]()
Question 57.
Give an account of microbes used as Biofertilizers.
Answer:
1. Rhizobium symbiotic bacteria – Fix atmospheric nitrogen, in leguminous plants. Free-living nitrogen-fixing bacteria – Azospiriullum and Azotobacter, enrich the nitrogen content of the soil.
2. Fungi: Fungi form a symbiotic association with the roots of higher plants called Mycorrhiza. Ex: Glomus.
- The fungal hyphae absorb phosphorus from soil and pass into the plant.
- They serve as biofertilizers in paddy fields.
- Blue-green Algae add organic matter and increase fertility of the soil.
- Regular use of biofertilizers from the market to replenish soil nutrients and reduce dependence on chemical fertilizers.
Question 58.
Write the role of microbe’s in household food products.
Answer:
(a) CURD: One of the examples of fermenting activities of microorganisms.
Lactic Acid Bacteria (LAB).
Ex: L. lactis, L. acidophilus, L. bulgaricus etc.
Benefits: Improves nutritional quality by increasing Vit B12
(b) They check disease-causing microbes. Vitamin B12.
- Swiss cheese by propionibacterium
- Roquefort cheese
(c) Dough for making foods: Ex: Idli, Dosa, Bread, Jalebi prepared by the fermentation process, Saccharomyces cerevisiae (yeast).
(d) Toddy is a fermented drink from palms.
→ Microbes: Microscopic organisms which are not visible with naked eyes and viewed under microscope.
Ex: Bacteria, Viruses, Yeasts etc.
- They are omnipresent.
- Adaptability to the entire biosphere
- They can be grown and multiplied on specific ‘Culture media’ consisting of various nutrients and hormones. Both useful and harmful microbes.
- The close relationship of man and microbes is as early as 5000 B.C. in making Curd, Bread, Wine, Vinegar etc.