Karnataka 2nd PUC Biology Important Questions Chapter 11 Biotechnology: Principles and Processes
Question 1.
Define Biotechnology.
Answer:
Term coined by Karl Esky (1919). “The utilisation of living organisms or their components for the welfare of mankind.”
Definition: according to European Federation of Biotechnology (EFB). “The integration of natural science and organisms, cells, parts, molecules for products and services”.
Two techniques that established Biotechnology
Question 2.
Define genetic Engineering?
Answer:
- Genetic Engineering: Technique which alters the chemistry of DNA to introduce altered DNA into the host
organisms to change their phenotype. - Sterile Environment: Contamination free environment to enable the growth of the desired microbes, cells, vaccines, enzymes in large quantities for their products.
The technique of G.E includes:
- Creation of Recombinant DNA
- Production of multiple and identical copies of a selected gene – Gene cloning
- Transfer of gene into another cell.
Question 3.
Mention two techniques that established biotechnology?
Answer:
Genetic engineering and sterile environments. [The first Rec-DNA was constructed by Stanley Cohen and Her-best Boyer (1972), by linking an (antR) antibiotic resistance gene with the natural plasmid of salmonella.]
Question 4.
Define plasmid? or What are plasmids?
Answer:
Autonomously replicating, circular, extrachromosomal DNA, found in the cytoplasm of Bacteria.
Question 5.
Mention the basic steps in GMO.
Answer:
Basic steps in Genetically modifying organisms (GMO)
- Identification of gene in DNA with desirable character
- Insertion of that gene into plasmids.
- Introduction of recombinant plasmids into host cells.
- Maintainance of the introduced gene in the desired organism and transfer of DNA into its progeny.
![]()
Question 6.
Who discovered Rec-DNA technology?
Answer:
Stanley cohen it Erbert boyer.
Question 7.
Name the molecular scissor, used in recombinant DNA technology?
Answer:
Restriction Endo Nuclease.
Question 8.
Name the enzyme used to cut DNA strands?
Answer:
Restriction Endo Nuclease.
Question 9.
Mention the tools used in Rec. DNA technology.
Answer:
Restriction on Endo Nuclease, ligases, DNA polymerase.
- Enzymes
- Cloning vectors
- Competent host
- Desired gene
- Bioreactor.
Question 10.
Who isolated REN for the first time?
Answer:
Hamilton Smith (1970), RENHind II from Haemophilus influenzae.
Question 11.
To which group of enzymes REN belongs?
Answer:
REN belongs to a larger class of enzymes – Nucleases.
Question 12.
What are Exo and endonucleases? or classify restriction enzymes. Mention the function of each.
Answer:
- Exonucleases Remove nucleotides from the ends of the DNA.
- Endonucleases Remove nucleotides at specific positions in the middle of the DNA.
Question 13.
How’REN named?
Answer:
Naming REN, Principles:
- Three letter code is given for each REN. The first letter represents the genus name of Bacteria with a capital letter and the subsequent two letters with the small letter will be the species name.
- Ex: Eco, Hin etc., Next letter represents the strain, and the roman number indicates the order in which the enzymes were isolated from the same organism.
- Ex: Hind III Eco RI Bam HI.
Each REN cut DNA at specific 4 to 6 base pairs sequence known as Palindrome Sequences
![]()
Question 14.
What are palindrome sequences. Give an example?
Answer:
Two strands in this region are identical when read both in forward and backward on two DNA strands
Ex:
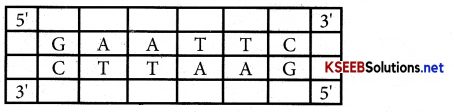
Question 15.
What are sticky ends?
Answer:
REN cut in palindrome site between the same 2 bases on opposite strands which leave single stranded portion at the ends – These single stranded free ends which can join with similar complementary ends of DNA fragment from other source are knows as “Sticky ends”.
Question 16.
Write the function of DNA ligase.
Answer:
Joins DNA fragments.
Question 17.
Give a diagrammatic representation of showing the action of restriction enzyme in the formation of recombinant DNA?
Answer:
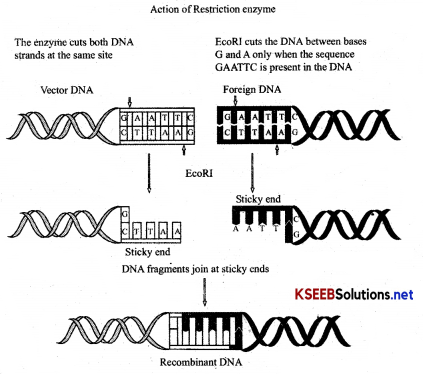
- Steps in formation of recombinant DNA by action of restriction endonuclease + enzyme-EcoRI
- Ligase: Enzyme facilitates the joining of DNA strands catalyzing the formation of an inter-nucleotide ester bond between phosphate and deoxyribose. i.e. phosphodiester bond
- Polymerase: DNA polymerase synthesis new strands of DNA complementary to existing DNA.
Question 18.
Draw a neat labelled diagram of agarose gel electrophoresis?
Answer:
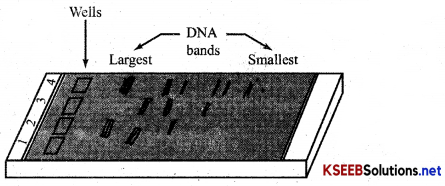
A typical agarose gel electrophoresis showing migration of undigested (lane 1) and digested set of DNA fragments (lane 2 to 4).
Question 19.
Explain in brief the separation and isolation of DNA fragments?
Answer:
The cutting of DNA by REN results in fragments of DNA, which is separated by ‘Gel electrophoresis. Since DNA fragments are negatively-charged molecules, they move towards anode, under an electric field through a medium [Agarose gel].
DNA fragments move according to their size (smaller farther and larger near), eparated DNA fragment can be visualised only after staining DNA with ‘Ethidium bromide. ’ Orange bands of >MA seen only under “EFV light.” The separated DNA fragments are cut out from the agarose gel and extracted am gel piece – Elution. The eluted DNA fragments are purified and used in constructing recombinant DNA by joining them with cloning vectors.
Question 20.
What is Elution?
Answer:
The separated DAN fragments are cut out from the agarose gel and extracted from gel piece
Question 21.
Name the stain used for visualising DNA under UV radiation?
Answer:
Ethidium bromide.
![]()
Question 22.
Mention the technique used to separate DNA fragments in or DNA technology?
Answer:
Agarose gel electrophoresis.
Cloning Vectors:
Cloning Vector: Vectors that are used for the propagation of DNA of interests in a suitable host cell, Eg: Plasmids, Bacteriophage.
Structure of Plasmid:
William Hay and Laderberg (1952) discovered plasmid.
PBR 322 – Naturally occurring plasmid
[Plasmid of Boliver and Rodriquez,’strain 322],
Question 23.
What is plasmid? Mention two sites of plasmid.
Answer:
Plasmids are extra Chromosomal self replicating circular DNA molecules present in the cytoplasm of bacteria
Two sites:
- Origin of replication (ori): Sequence of nucleotides from where replication starts. If any piece of DNA linked to this site, can be made to replicate within host cells.
- Selectable Marker: The vector requires a selectable marker to identify and eliminate non- transformants, and allow the growth of transformants. Transformation is a procedure through which a piece of DNA is introduced into a host bacterium. Ampicillin, Tetracyclin are useful selectable markers.
Question 24.
Describe the structure of the plasmid?
OR
Explain the features of cloning vectors?
Answer:
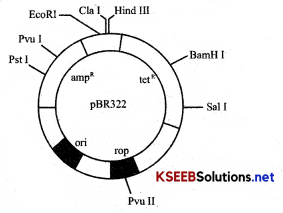
1. Origin of replication (ori): Sequence of nucleotides from where replication starts, if any piece of DNA linked to this site, can be made to replicate within host cells.
2. Selectable Marker: The vector requires a selectable marker to identify and eliminate non- transformants, and
allow the growth of transformants. Transformation is a procedure through which a piece of DNA is introduced into a host bacterium Ampicillin, Tetracycline is useful selectable markers.
3. Cloning sites: The vector should have single or few recognition sites for REN, to insert foreign DN A, which
is ligated at a restriction site present with in the marker gene. Ex: Bam HI or sal I which lie in TetR gene PVU I or Pst I which lie in AmpR gene.
When the genes are inserted into marker gene [eg. TetR gene] the recombinant, plasmids will loose tetracycline resistance, when these plasmids cultured on medium containing Tetracycline will not grow, but grow on medium with Ampicillin.
Therefore recombinants and Non-recombinants can be differentiated.
Above process was time-consuming, so the alternative method was developed, where markers can be differentiated on basis of producing colour in the presence of chromogenic substrate.
Question 25.
What is insertional inactivation?
Answer:
In this process, if a rec-DNA is inserted within coding sequence an enzyme of a plasmid, i.e., p galactosidase
causes inactivation of the enzyme – “Insertional inactivation.”
Thus recombinant -colonies are identified.
i. e. non inserted p – gal produces no blue colour, blue colonies produced are identified as recombinant colonies.
Vectors For Cloning Genes in Plants And Animals:
To deliver genes in Eukaryotic cells. [A agrobacterium tumefacient is a – soil bacteria, pathogen on dicot plants, causes crown gall disease forming Tumours.]
Question 26.
Which in common vector is used for cloning genes in plants?
Answer:
Agrobacterium tumefacians.
Question 27.
Describe the role of Agrobacterium tumefaeians in cloning vectors in plant and animal cells?
Answer:
Agrobacterium tumefacians is able to decliver TDNA which transform normal cells into tumour cells to produce chemicals required by pathogens. So these Tumour inducing plasmids (Ti) are genetically modified and then bacteria is allowed to infect dicot plant cells and induce tumour formation, which indicates transfer of desired gene, and these vectors are made non pathogenic to deliver genes in plant cells.
Question 28.
Define Retroviruses?
Answer:
Retroviruses – RNA viruses, replicate through reverse transcriptase (RNA synthesising DNA), and made non-pathogenic, then used to deliver genes in animal cells.
![]()
Question 29.
“Retroviruses are disarmed before using to deliver desirable genes into animal cells. Why?
Answer:
Retrovirus may cause harm to host cell so disarming helps retrovirus in insertion of desirable genes into animal cell.
Competent Host (Right Host) (Capable):
Since DNA molecules can not pass through cell membrane, host cells are made competent to take up DNA.
Question 30.
Describe methods involved in making a competent host?
or
Mention two techniques or make host competent in r-DNA technology?
Answer:
- By treating with divalent cation, which increases the efficiency of DNA to enter through pores in the cell wall.
- By incubating cells with Rec-DNA on ice-cold CaCl, followed by placing them at 420°C (heat shock) and again back to ice, which developers pores.
- Microinjection: Recombinant, DNA directly injected into the nucleus of animal cell using Microsyringe.
- Gene gun (Biolistics): Suitable plant cells are bombarded with high-velocity microparticles of Gold or tungsten coated with DNA in plant cells.
- Disarmed pathogen vectors, when allowed to infect the cell and transfer the rec- DNA into the host.
Question 31.
What are Biolistics or Gene gun?
Answer:
Plant cells are bombarded with high-velocity microparticles of gold or tungsten located with DNA.
Question 32.
Give diagrammatic representation of processes of Rec. DNA technology?.
Answer:
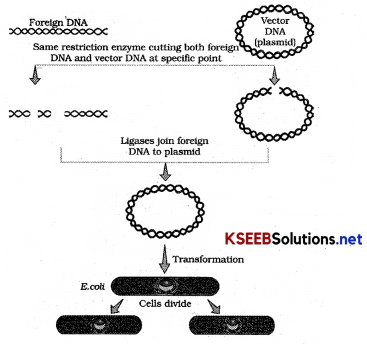
Question 33.
Explain the steps involved in rDNA technology.
Answer:
It is essential to isolate DNA in pure form, so the cell is broken open to release DNA along with other molecules, so treated with enzymes like.
- Lysozyme for Bacteria
- Protease – for Proteins
- Cellulase for Plants
- Ribonuclease – for RNA
- Chitinase for Fungus
Finally, the purified DNA molecules are precipitated after the addition of chilled Ethanol can be seen as a collection of fine threads in the suspension.
Cutting of DNA:
By REN. DNA molecules are incubated with REN where the progress of this process is checked by Agarose gel Electrophoresis. Gene of interest and cut vector are mixed and ligase is added to produce rec. DNA.
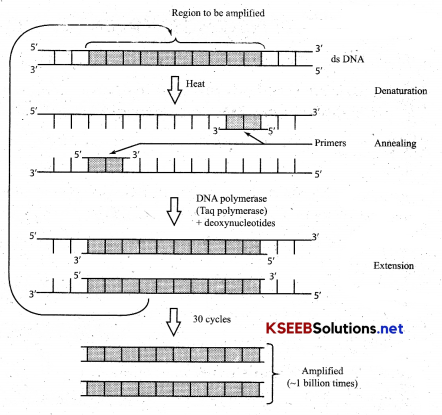
Amplification of Gene:
The process of making many copies of a gene by polymerase chain reaction is known as DNA amplification
(a) Denaturation: Reaction mixture when led to a temp 90-98°C results in separation of two strands of DNA, which acts as template strands for DNA
(b) Annealing: Reaction mixture is cooled at a low temp (40-60°C). two oligonucleotides primers anneal (join) one at each 3’ end of DNA strand.
(c) Primer Extension: Taq DNA polymerase [Enzyme DNA polymerase from Thermus aquaticus bacteria [which is thermostable] extend primers, using nucleotides and DNA templates. The amplified fragment if desired can now be used to ligate with vector for gurther cloning.
Obtaining the foreign gene product:
Recombinant plasmids under proper conditions expressed and synthesise desired proteins and these proteins are separated and purified by following technique i,.e ‘protein encoding gene is expressed in a heterologous host’ which forms Recombinant protein.
Question 34.
How is DNA isolated from cell. Give any 2 examples of enzymes.
Answer:
It is essential to isolate DNA in pure form, so the cell is break open to release DNA along with other molecules, so treated with enzymes like,
- Lysozyme for Bacteria
- Protease – for Proteins
- Cellulase for Plants
- Ribonuclease – for RNA
- Chitinase for Fungus
Finally the purified DNA molecules are precipitated after addition of chilled Ethanol, can be seen as collection of fine threads in the suspension.
Cutting of DNA:
By REN. DNA molecules incubated with REN where the progress of this process is checked by Agarose gel Electrophoresis. Gene of interest and cut vector are mixed and ligase is added to produce rec. DNA.
![]()
Question 35.
Define polymerase chain reaction.
Answer:
It is a process in which gene is amplified into several copies using DNA polymerase.
Question 36.
What is DNA amplification. Mention the steps in PCR technique.
Answer:
The process of making many copies of gene by polymerase chain Reaction is known as DNA amplification
(a) Denaturation: Reaction mixture when led to a temp 90-980C results in separation of two strands of DNA, which acts as template strands for DNA synthesis.
(b) Annealing: Reaction mixture is cooled at a low temp (40-60°C). two oligonucleotides primers anneal (join) one at each 31 end of DNA strand.
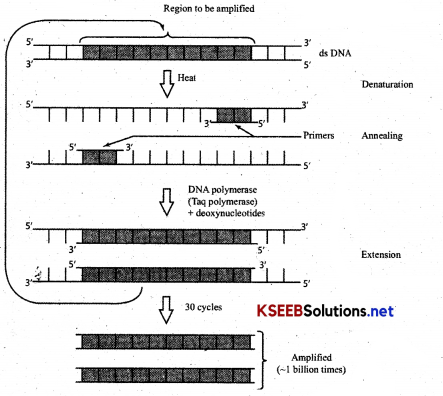
(c) Primer Extension: Taq DNA polymerase [Enzyme DNA polymerase from Thermus aquaticus bacteria [which is thermostable] extend primers, using nucleotides and DNA templates. The amplified fragment if desired can now be used to ligate with vector for further cloning.
Question 37.
Name the source of Taq polymerase.
Answer:
Thermus aquaticus bacteria.
Question 38.
What is Annealing.
Answer:
During PCR technique, the reaction mixture is cooled to 40~450°C and 2 Oligonucleotide primers join at each ends of separated DNA.
Question 39.
What is primer extension.
Answer:
During PCR Taq DNA polymerase extends primers using nucleotides and DNA templates.
![]()
Question 40.
Draw a neat diagram of stirred tank bioreactor or Sparged tank Bioreactor? or Simple stirred tank Bioreactor?
Answer:
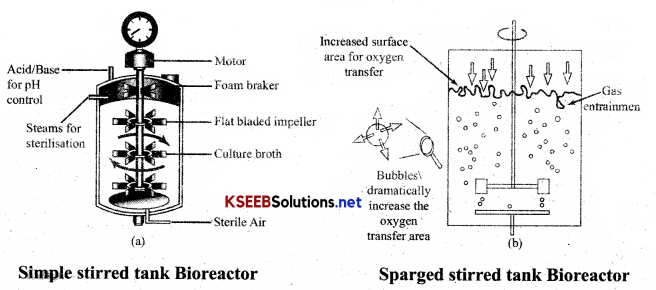
Bioreactor: Container in which substances are treated to stimulate biochemical transformation by microorganisms or enzymes. “Large vessel in which raw materials are biologically converted into specific products using plants/ animal/human cells. The large scale production is carried out in Bioreactor.
A stirred-tank bioreactor is usually cylindrical or with a curved base to facilitate the mixing of the reactor contents. Stirrer facilitates even mixing and O2 availability throughout, and alternatively, air can be bubbled. Aeration and agitation generate foam, which prevents flow of contents, antifoam controls foam. Temperature control system and pH control system and sampling ports are present, so that small volumes of the culture can be withdrawn periodically.
Question 42.
Mention the different steps of process of recombinant DNA technology?
Answer:
(a) Isolation of genetic material DNA.
(b) cutting of DNA at specific locations,
(c) Gel electrophoresis.
(d) Amplification of gene using PCR.
(e) Insertion of recombinant DNA into the host.
(f) Obtaining the foreign gene product,
(g) Down stream processing.
Question 43.
What is polymerase chain reaction?
Answer:
It is a technique in which a gene of choice is amplified into many .copies using primers and DNA polymerase enzyme.
![]()
Question 44.
Define Downstream processing or Write a note on downstream processing.
Answer:
It is the purification of useful products after biosynthetic stages from natural sources i.e., separation and purification of Biosynthetic products.
Downstream processing is the purification of useful products after biosynthetic stages from natural sources,
i. e., separation and purification of Biosynthetic products. “Various processes used for the recovery of useful products after biosynthetic stage”. This includes separation and purification and the product has to be formulated with preservatives. Such formulation has to undergo through clinical trials (drugs) and Quality control testing for each product is required. The downstream processing and quality control testing vary from product to product.
→ Insertion of Recombinant DNA, after making them competent. Once it is received, it becomes genetically . modified cell.
Ex: Transformed E.coli with Rec-DNA resistant to Ampicillin, will grow on ampicillin containing media, where non transformed will not grow.
→ Obtaining The Foreign Gene Product:
Recombinant plasmids under proper conditions gels expressed and synthesise desired proteins and these proteins are separated and purified by following technique i.e., ‘protein encoding gene is expressed in a heterologous host’ which forms Recombinant protein.
→ Downstream Processing: Various processes used for the recovery of useful products after biosynthetic stage”. This includes separation and pu-rification and the product has to be formulated with preservatives. Such formulation has to undergo thorough clinical trials (drugs) and Quality control testing for each product is required. The downstream processing and quality control testing vary from product to product.