Karnataka 2nd PUC Biology Important Questions Chapter 14 Ecosystem
Question 1.
Define Ecosystem?
Answer:
Ecosystem: It is a functional unit of nature. “It is an interaction between living organisms, among themselves and also with the surrounding physical environment”.
Question 2.
Give any two examples of Terrestrial and Aquatic man made ecosystem?
Answer:
- Terrestrial ecosystem: Ex: Forest, grassland and desert.
- Aquatic ecosystem: Ex: Pond, lake, wetland, river and estuary.
- Man made ecosystem Ex: Crop field, Aquarium.
Question 3.
Mention the structural component of ecosystem?
Answer:
Interaction of abiotic and biotic component result in a physical structure and that is characteristic for each type of ecosystem.
Question 4.
What is species composition of an ecosystem?
Answer:
Species Composition is an “Identification and description of plant and animal species of an ecosystem”.
Question 5.
Define stratification? Give an example.
Answer:
Stratification is a “Vertical description of different species occupying different levels in an ecosystem.
Ex: Tree occupy top layer of forest, shrubs secpnd and herbs and grasses bottom layers.
Question 6.
Give an example of an ecosystem to understand distribution and role of components?
Answer:
To understand distribution and role of components in a ecosystem, Pond is considered as ain example.
![]()
Question 7.
Describe pond ecosystem along with basic events?
Answer:
Abiotic Components:
- Water with all the dissolved inorganic and organic substances.
- Rich soil deposits at the bottom of the pond.
- Solar input, temperature, day length and climatic conditions.
Biotic Components:
Autotrophes: Phytoplankton’s, Algae, Floating, (producers) submerged and marginal plants at the edge of pond. Consumers: Zooplankton, swimming and bottom dwelling animals.
Decomposers: Fungi, bacteria and flagellates at the bottom of the pond.
Above systems performs all the functions of an Ecosystem.
- Producers convert inorganic into organic materials with the help of radiant energy of the sun.
- These autotrophs are consumers by heterotrophs (consumers).
- Decomposers decompose and release them back which is reused by autotrophs.
Thus there is a cyclic exchange of materials between living and abiotic environment in pond ecosystem.
Question 8.
Name functional compositions of ecosystem?
Answer:
The components of the ecosystem are seen to function as a unit.
- Productivity
- Decomposition
- Nutrient recycling.
Question 9.
Define productivity?
Answer:
‘Productivity is the rate of synthesis of biomass produce at any trophic level during a given period of tune” It is measured as weight (g/m2) or energy (k/cal/m2).
![]()
Question 10.
Differentiate between primary and secondary productivity?
Answer:
| Primary productivity | Secondary productivity |
| It is the rate of production of biomass or organic matter per unit area by producers | It is the rate of productivity of biomass or organic matter per unit area by consumers. |
Primary productivity is further classified into 2 types.
Question 11.
Differentiate between GPP and NPP?
Answer:
|
(GPP) Gross primary productivity |
(NPP) Net primary productivity |
| It is the total amount of food/organic matter or biomass produced by the producers during photosynthesis. | It is the small amount of GPP by plants in Respiration (R) NPP = GPP – R |
[Note:
- The annual NPP of the biosphere is 170 billion tons of organic matter.
- Ocean contribute only 55 billion tons and the remaining 115tons is by land.]
Question 12.
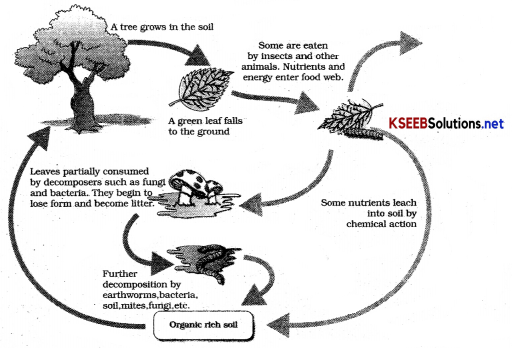
Define decomposition and represent decomposition cycle in terrestrial ecosystem?
Answer:
“The process of breaking down of complex organic matter into inorganic substances like Carbon dioxide, Water and Nutrients in nature”is known as decomposition.
Question 13.
Define detritus? or Detritivores.
Answer:
Dead plant remains such as leaves, bark, flowers, fruits, and dead remains of animals including faecal matter constitute detritus or detritus feeding invertebrates are known as detritivores.
Question 14.
Why Earth worms are known as farmer’s friend?
Answer:
They break down the complex organic matter and help in loosening the soil for aeration and helps in growth of plants. They are known as detrivores.
Question 15.
Explain the steps involved in Decomposition?
Answer:
Important steps in the process of Decomposition:
- Fragmentation: Breaking down detritus into smaller particles by detrivores.
- Leaching: Water-soluble inorganic nutrients produced during decomposition, go down into deeper layers of soil and get precipitated as unavailable salts
- Catabolism: Bacterial and Fungal enzymes degrade detritus into simpler inorganic substances.
- Humification: The simplified detritus gets converted into dark coloured amorphous substances called humus in the soil. This process is Humification. It serves as reservoir of nutrients.
- Mineralisation: The humus further is degraded by microbes and inorganic nutrients are released into the soil. It is the formation of minerals.
![]()
Question 16.
Mention the factors which regulate decomposition?
Answer:
Factors which regulate Decomposition:
- Oxygen is required.
- Chemical composition of detritus and climatic factors
- Slow in detritus containing lignin and chitin.
- Faster in detritus with Nitrogen and water soluble sugars. . .
- Warm and moist environment favour decomposition.
Question 17.
Write a note on energy flow or Given an account of energy flow in an Ecosystem?
Answer:
- Sun is the only source of energy for all Ecosystems on earth.
- Less than 50% of incident solar radiation is Photosynthetically Active Radiation (PAR). Photosynthetically active radiation. It is unidirectional, which flows from producers to herbivores to carnivores.
- Producers capture only 2-10% of solar radiation, some is lost as heat, where some energy is used in respiration of producers and also providing food for herbivores and then to decomposers. So only 10% of herbivore productivity is used to support carnivore productivity and much least energy will reach the top carnivore.
Question 18.
Define PAR?
Answer:
PAR is the amount of light (400-700nm) available for photosynthesis. (Light wave length range).
Question 19.
What is ten percent law?
Answer:
Plants capture only 2-10 percent of the photosynthetically active radiation, there is unidirectional flow of energy through food chain.
Question 20.
What are producers? Give examples.
Answer:
Producers: “Green plants”. These are the photosynthetic organisms which are capable of synthesizing their own food using sunlight. Primary consumers depend on these producers. Ex: phytoplanktons, Algae and higher plants.
Question 21.
What are consumers?
Answer:
Consumers: Organisms which depends on other plants or organisms for their food needs. Also known as heterotrophes.
![]()
Question 22.
Mention the consumer types with an example?
Answer:
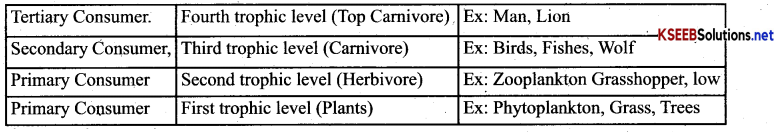
- Primary consumers (Herbivores) feed on producers
- Secondary Consumers (Primary carnivores) feeds on herbivores
- Tertiary consumers (Secondary carnivores) feed on secondary consumers.

Question 23.
Define food chain?
Answer:
Food chain describes the structure and function of the various trophic levels and function of the various trophic levels and their interrelationship in an Ecosystem. [A series of organisms each dependent on the next as a source of food].
Question 24.
Differentiate between Grazing Food Chain (GFC) and Detritus Food Chain (DFC)?
Answer:

Question 25.
Which is the major channel for energy flow in aquatic ecosystem?
Answer:
Grazing Food Chain – is major channel for energy flow in aquatic Ecosystem.
Question 26.
Which is the major channel for energy flow in terrestrial ecosystem?
Answer:
Detritus Food Chain – is major channel for energy flow in terrestrial ecosystem.
Question 27.
Define food web?
Answer:
“It is a network of food chains, which becomes interconnected at various trophic levels in an Ecosystem.
![]()
Question 28.
Define trophic level?
Answer:
Organism occupy a specific place in the food chain based on the source of their food is known as trophic level.
The amount of energy decreases from first trophic level to the last, trophic level. Representation of trophic levels in an Ecosystem.
Question 29.
Represent different trophic levels of Ecosystem with examples?
Answer:
Question 30.
Define standing crop?
Answer:
Standing crop: Each trophic level has a certain mass of living material at a particular time. It measures as biomass or the number in a unit area. [Note: Measurement of biomass in terms of dry weight is more accurate].
Question 31.
Define Ecological Pyramids and mention its types?
Answer:
It is a graphical representation of various trophic level of a food chain. Pyramid of number, Pyramid of Energy,
Pyramid of Biomas.
[Notes:
- It is expressed in terms of number, biomass and Energy.
- The base of each pyramid represents producers and the top represent the tertiary consumer.]
Question 32.
Describe the types of Ecological pyramids?
Answer:
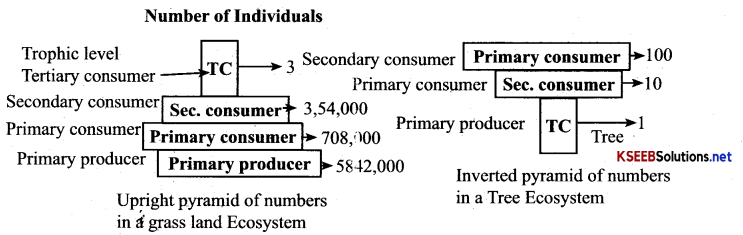
Pyramid of numbers: It is a graphic representation of the numbers of individuals in the various trophic level of food chain.
- Pyramid of number in most Ecosystems is upright.
- In tree ecosystem it is inverted.
OR
Diagrammatically represent the pyramid of number in an Ecosystem?
OR
Represent pyramid of number in grassland ecosystem.
Answer:
OR
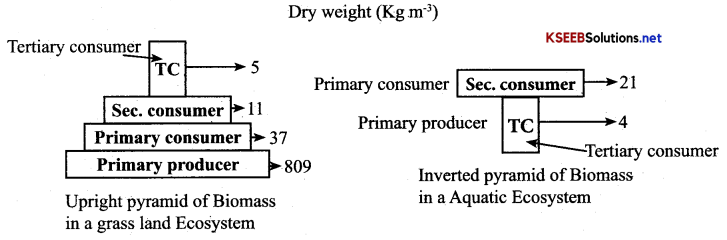
Define pyramid of biomass?
Answer:
“It is a graphic representation of Biomass present per unit area at different trophic levels of food chain.
OR
Give diagrammatic representation of Pyramid of Biomass?
Answer:
OR
Define pyramid of energy?
or
Define Ecological pyramid? Describe pyramid of Energy flow with example?
or
Draw an ideal pyramid of energy and mention the units?
Answer:
“It is the graphic representation of amount of energy trapped per unit time and area in different trophic levels of a food chain”.
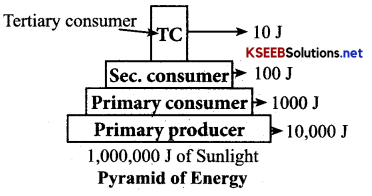
Question 33.
Why pyramid of energy is always upright?
Answer:
Pyramid of energy is always upright, because when energy flows from a particular trophic level to the next, some energy is always lost as heat at each step. Limitations of Ecological Pyramids.
![]()
Question 34.
List the limitations of ecological pyramids?
Answer:
- A species may occupy more than one trophic level in the same ecosystem at the same time.
- It assumes a simple food chain.
- It does not accommodate a food web
- Saprophytes are not taken into account in ecological pyramids.
[Note: If producers are more in number and biomass than the consumers – Upright pyramid. Ex: Grassland (Biomass and Energy)].
If the number of producers is less than the consumers – Inverted pyramid. Ex: Aquatic Ecosystem (Bio¬mass), Tree Ecosystem (Number)].
Question 35.
What is ecological succession?
Answer:
Ecological succession: “The gradual and fairly predictable change in the species composition of a given area”.
Question 36.
With reference to ecological succession define the following:
(a) Climax community
(b) Sere
(c) Pioneer species
Answer:
Climax community: The composition and structural changes lead finally to a community that is near equilibrium with the environment, or Final community that established and maintain equilibrium with physical environment.
Sere: The entire sequence of communities that successively change in a given area.
Pioneer Species: The species which invade bare area in a Ecological succession.
[The individual transitional communities are several stages further successive stages there will be a change in the diversity, increase in number of species and total biomass].
Types of ecological succession.
Question 37.
Distinguish primary’ succession with secondary succession?
OR
Write types of plant succession.
Answer:
| Primary succession | Secondary succession |
| 1. Starts where no living organism never existed organism existed. | 1. Occurs in an area which have lost all living. |
| 2. The establishment of a new biotic Community is generally slow. | 2. Generally faster |
| 3. It occurs on bare rock, cooled lava, newly created pond. | 3. It occurs on abandoned form lands, burned/ cut forest, flooded lands. |
[Note: As succession proceeds, the number and types of animals and decomposers also change.]
Question 38.
Why secondary succession faster than primary pressure?
Answer:
Secondary secession begins in an area where fertile soil and substratum are already present.
![]()
Question 39.
Distinguish between Hydrarch and Xerarch?
Answer:
- Hydrarch succession: It takes place in water or wetter/ habitats and results in series of changes from hydric to mesic condition.
- Xerarch succession: If plant succession takes place in dry area and results in changes from xeric to mesic condition.
Question 40.
Define Pioneer species? Give an example.
Answer:
The species which invade bare area in ecological succession are called pioneer species.
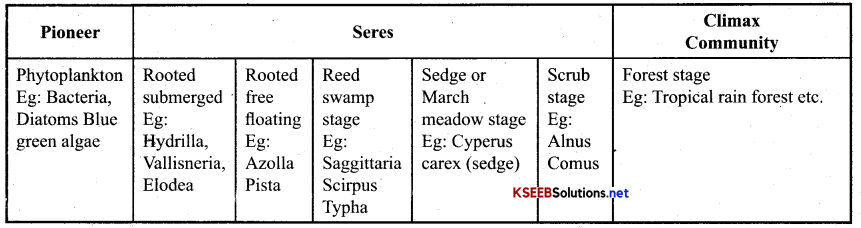
Ex: Lichens in Xerarch succession and phytoplanktons in Hydric succession.
Question 41.
Name the pioneer species in succession of hydric and Xeric?
Answer:
- Phytoplanktons in water.
- Crustose lichens on rocks.
Question 42.
Explain xerarch successionor?
Answer:
- Lichens the pioneer species invade (grown on) a bare rock since they are resistant to desiccation and high temperature
- Lichens secretes acids to dissolves rock, helping in weathering of rock and soil formation.
- The accumulation of soil and humus leads to growth of bryophytes and are capable of accumulating soil.
- The thick layer of soil with humus results in growth of herbs (place for seed for germination) and Trees.
- Ultimately a stable climax community is formed which ends up with Forest.
Question 43.
Explain hydrarch succession?
Answer:
- Phytoplanktons are pioneer species consisting of unicellular colonial forms of green algae, followed by zooplanktons like amoeba, paramoecium, etc.
- Death & decomposition of these planktons provide organic matter, which favours the growth of next plant stages.
- Phytoplanktons are replaced by free floating angiosperms & then by rooted hydrophytes, sedges, grasses, & finally the trees.
- The climax community remains in equillibrium stage, as long as environment remains unchanged.
- The climax is a forest. It may be tropical deciduous or monsoon forests etc.
Question 44.
Mention the components of a succession in a Hydrosere?
Answer:
Question 45.
Define Nutrient cycling and Standing state?
Answer:
- Nutrient cycling – The movement of nutrient elements through the various components of an ecosystem. It is known as biogeochemical cycles.
- Standing state – The number of nutrients such as Carbon, Nitrogen, Potassium, Calcium etc. present in the soil at any given time.
Question 46.
Name 2 types of nutrient cycles along with examples?
Answer:
- Gaseous – Eg: Nitrogen & Carbon cycle in atmosphere.
- Sedimentary – Eg: Sulphur & Phosphorus cycle in Earth’s crust.
[Note: Environment factors like soil, moisture, pH, temperature regulate the release of nutrient into the atmosphere.
The reservoir helps to maintain imbalance in the rate of nutrient influx and efflux.]
![]()
Question 47.
What are biogeochemical cycles? Mention two types, with example.
Answer:
The movement of nutrient elements through the various components of an Ecosystem.
Two types:
- Gaseous. Ex: Nitrogen/Carbon cycle.
- Sedimentary Ex: Sulphur/Phosphorus cycle.
Question 48.
Give an example for gaseous cycle?
Answer:
Nitrogen cycle/Carbon cycle.
Question 49.
Give the schematic representation of carbon cycle?
Answer:
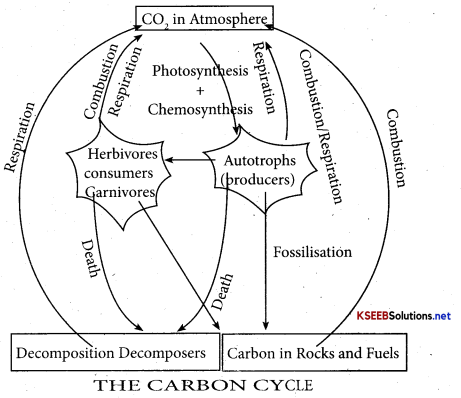
Question 50.
Explain carbon cycle (or) outline salient features of carbon cycling in an ecosystem.
Answer:
Explanation:
- In Total quantity of global carbon, 71 % C is found dissolved in oceans and ocean regulates the amount of CO. in the Atmosphere.
- Carbon cycling, involves atmosphere, ocean and through living and dead organisms.
- 41013kg of carbon is fixed by photosynthesis annually.
- Respiration activities of producers and consumers return carbon to the atmosphere as CO2
- Decomposers return back CO2 during decor position of organic wastes and dead organic matter of land and oceans.
- Another source of CO2 is burning of fire wood, fossil fuels, combustion of organic matter, Volcanic eruptions, hot springs etc.
- Some amount of fixed carbon is lost to Sediments and removed from circulation.
Question 51.
Why carbon cycle is known as perfect cycle?
Answer:
The carbon cycle is a perfect cycle, because the carbon is returned to atmosphere as soon as it is removed and circulated uniformly. [Rapid deforestation, burning of fossil fuel increase CO2 cone, in atmosphere],
![]()
Question 52.
Explain Phosphorus Cycle?
Answer:
- It is a sedimentary cycle and sediments of rocks are the reservoirs which contain phosphorus as phosphates.
- Phosphorus is present in biological membranes, nucleic acids and cellular energy transfer system.
- Animals shell, bones and teeth are made up of phosphorus.
- During weathering of phosphate rocks, inorganic phosphorus is added to the soil and is absorbed by the roots of the plants.
- Herbivores and other animals obtain this element from plants.
- The waste products and the dead organisms are decomposed by phosphating Bacteria and add phosphorus to the soil.
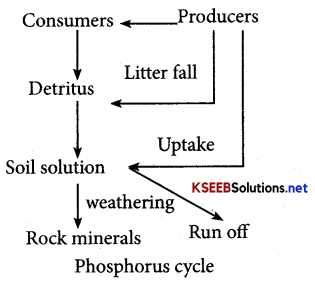
Question 53.
Why phosphorus cycle is known as imperfect cycle?
Answer:
Phosphorus cycle is imperfect cycle because the biological processes account for considerable loss of phosphorus form the cycle.
Question 54.
Differentiate between Carbon and Phosphorus cycle?
Answer:
| Carbon Cycle | Phosphorus cycle |
| 1.Atmosphere is the reservoir of carbon. | 1. Earth’s crust is the reservoir of Phosphorus. |
| 2. It is perfect cycle. | 2. It is imperfect cycle. |
| 3. Gaseous exchange between organism and environment is more. | 3. Gaseous exchange between organism environment is less. |
| 4. Respirator release of Carbon to atmosphere. | 4. No respiration release of Phosphorus. |
Question 55.
Define Ecosystem services?
Answer:
“The products formed in ecosystems are named as Ecosystem Services.”
![]()
Question 56.
List few ecosystem services?
Answer:
- Healthy forest ecosystems purify air and water, mitigate droughts floods, cycle nutrients, maitain fertile soils, provide wild life habitat.
- Maintain biodiversity, pollinate crops. Storage site for Carbon.
- Ecosystem provides aesthetic, cultural and spiritual values.
Note: Robert Constanza has put an average price tag of US 33 trillion a year on their ecosystem services which is nearly twice the valve of global gross national product Gross National Productivity (GNP). (18 trillion).
→ Succession in Plants:
Based on the nature of habitat it is classified as Hydrosere and Xerosere or Hydrarch and Xerarch.