Karnataka 2nd PUC Biology Important Questions Chapter 15 Biodiversity and Conservation
Question 1.
Define biodiversity?
Answer:
The combined diversity at all the levels of biological organization is biodiversity.
Or
The sum total of all kinds of life forms of the biosphere.
Question 2.
Define biodiversity? Write any two types of biodiversity.
Answer:
The combined diversity at all the levels of biological organization.
Two types:
- Genetic diversity
- Species diversity.
Question 3.
Name the scientist who popularized the term biodiversity.
Answer:
Edward Wilson.
Question 4.
Mention three levels of biodiversity.
Answer:
Genetic diversity, Species diversity and Ecological diversity.
![]()
Question 5.
Explain genetic diversity with examples.
Answer:
A single species showing high diversity at the genetic level over its distributional range.
Example:
- Rawolfia vomitoria a medicinal plant growing in different regions of Himalayan ranges shows differences in potency and concentration of an active chemical called reserpine due to genetic diversity. .
- India has more than 50000 genetically different strains of rice 1000 varieties of mango.
Question 6.
What is species diversity? Give an example.
Answer:
The diversity at the species level in a given area. Eg: The western Ghats have greater amphibian species diversity than the eastern diversity.
Question 7.
What is ecological diversity.? Give one examlpaes.
Answer:
Diversity at ecosystem or at habitat level. Eg: India has one of the richest diversity of habitats like deserts; rain forests, mangroves, coral, etc than Norway.
Question 8.
Write a note on the latitudinal gradient pattern of animal and plants distribution.
Answer:
The latitudinal gradient is an index used to show the distribution of fauna and flora from the poles to the tropic. In general species diversity decreases as we move away from the equator towards the poles.
Eg: Tropics harbor more species than temperate or polar areas.
Colombia – 1400 species of birds, India has 1200 species New York has 105 species and green land has 56 species.
The tropical Amazon forest has the greatest biodiversity on earth. It is home to more than 40000 species of plants, 3000 fishes, 1300 birds, 427 mammals, 378 reptiles, and 125000 invertebrates.
Question 9.
Why tropics account for their greater biological diversity.
Answer:
- Tropical latitudes have remained relatively undisturbed for millions of years and thus had a long evolutionary time for species diversification.
- Tropical environments are bees seasonal relatively more constant and predictable, which leads to niche specialization and lead to a greater species diversity.
- There is more solar energy available in the tropics which contributes to higher productivity.
Question 10.
Describe species – Are a relationships to explain fundamental ecological relationships.
Answer:
- Alexander von Humboldt observed that “Speties richness increases with increase explored area but up to a certain limit” As the area of the region increases the number of species.
- The relation between species richness and area for a wide variety of taxa turns out to be a rectangular hyperbola.
- On a logarithmic scale, the relationship is a straight line described by the equation.
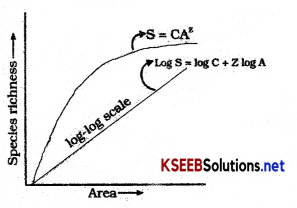
Log S = Log C + Z log A
Where S = Species richness, A = Area
Z = Slope of the line, & C = Y intercept.
Ecologists have discovered that value of Z line in the range 0.01 to 0.02 regardless of taxonomic group or the region.
We will find the slope of the line much steeper in species are relationships among very large areas like the entire continents.
Question 11.
List the characters of a stable community in an ecosystem.
Answer:
Communities with more species tend to be more stable than those with fewer species. Community should not show too much variation in productivity from year to year. And it must be resistant to occasional disturbances and invasion of alien species.
Question 12.
Write a note on David Tilman’s long-term ecosystem experiments?
Answer:
He found that plots with more species showed less year to year variation in total biomass.and he also showed that increased diversity contributed to higher productivity from his experiments.
![]()
Question 13.
Explain the rivet popper hypothesis?
Answer:
- Paul Ehrlich put for ward rivet popper hypothesis to explain the importance of each species.
- He compared each species to rivets in an airplane, and airplane to ecosystem If these rivets are removed by passengers traveling in it, to take home (i.e, species extinct popping) it may not affect the flight safety initially but if more rivets are removed the plane becomes dangerously weak, and if continued it may become critical.
- Hypothesis says that ecosystem is important, and when disturbed, it results in decreasing the ecological balance.
- Loss of rivets on the wings of airplane (key species that drive major ecosystem functions) is obviously a more serious threat to flight safety, than loss of a few rivets on the seats or windows inside the plane.
Question 14.
Mention the number of extinct species as listed under IUCN red list (2004).
Answer:
IUCN documents 784 spegies which includes 338 vertebrates, 359 invertebrates and 87 plants.
Question 15.
Name any four recent extinct organisms as per IUCN Red List.
Answer:
Dodo, Quagga, Thylarine, Steller’s sea cow and three subspecies of tiger namely Bali, Javan and Caspian .
Question 16.
Which group of animal kingdom appears to be more vulnerable to extinction.
Answer:
Amphibians.
[Note: Since the origin and diversification of life on earth there were five episodes of mars extinction of species. Presently the sixth mars extinctions is in progress, where we can see different in rates the current rates are 100 to 1000 times farter than in pre human times. Our activities are responsible for the faster extinction rates, if continues like this, all the species on earth might be wiped out within the next 100 years].
Question 17.
Explain the effects of loss of biodiversity in a region.
Answer:
Decline in plant production. Lowered resistance to environmental conditions like drought.
Increased variability in certain ecosystem processes such as plant productivity, water use, and pest and disease cycles.
![]()
Question 18.
Mention ‘The Evil Quartet’ of biodiversity loss.
Answer:
- Habitat loss and fragmentation.
- Alien species invasions.
- Co-extinctions.
- Overexploitation.
Question 19.
List out any two effects of loss of biodiversity.
Answer:
- Co-extinctions.
- Overexploitation.
Question 20.
Introduction of some alien species cause s biodiversity loss, Justify the statement With an example.
OR
Alien species invasion leads to extinction of indigenous species justify the statement by considering two animals as examples purposes in posing a threat to the indigenous.
Answer:
Alien species are the species which are translocated beyond its home range. This intentional or chance introduction of exotic species into new territories by humans adversely affects the native species.
Examples:
- Introduction of Nile perch into Lake Victoria, led to extinction of more than 200 species of Cichlid fish in the lake.
- African catfish Glarions gariepinces for aquaculture, Catfishes in our rivers.
Question 21.
Explain 3 causes of biodiversity losses with examples.
Answer:
1. Habitat loss and fragmentation: The destruction of ecosystem by human, activities is the most important
cause for driving animals and plants to extinction.
Due to fragmentation of habitats by humans mammals and birds requiring large territories and certain animals with migratory habit are badly affected leading to population declines.
Eg: Tropical rainforests – These once covered more than 14% of earth’s land surface are now not more than 6%. The amazon rain forest millions of species is being cut and cleared for cultivation soya beans or conversion to grasslands for raising beef cattle.
2. Over-exploitation: Humans have always depended on nature for food and shelter, harvesting these sources to the point of extinction or diminishing leads to overexploitation.
Ex: Steller’s sea Low and passenger pigeon were extinct due to overexploitation by humans. Overfishing of much marine fish populations around the world endangering their existence.
3. Co-extinctions: The simultaneous extinction of two or more species. When one species become extinct, the plant and animal species with it also becomes extinct.
Eg: 1. If host fish becomes extinct, parasites that depend on it also become extinct.
2. Mutualism of plant – pollinators, where extinction of one leads to the extinction of the other.
Question 22.
How does fragmentation of large habitats due to human activities lead to population decline?
Answer:
Increased risk of genetic consequences, climatic changes and less adaptability leads to population decline.
Question 23.
Explain benefits commonly listed for the biodiversity conservation.
Answer:
There are many reason for conservation. They can be grouped into three sections.
1. Narrowly utilitarian: It focuses the essential services rendered by biodiversity with respect to economic benefits from nature which includes food, firewood, fibre construction material, industrial products and products of medicinal importance.
2. Broadly utilitarian: This arguments says that biodiversity plays a major role in many ecosystem services that nature provides.
- Amazon forest is estimated to produce 20% of total oxygen in the earth’s atmosphere.
- Pollination is another service ecosystems provide through pollinators.
- Aesthetic values.
3. Ethical: Ethical aspect puts forth certain moral principles or rules to conserve biodiversity. We need to realize that every species has an intrinsic value even if it is not of economic value
Question 24.
Define Bioprospecting.
Answer:
Bioprospecting is a process used for exploring molecular, genetic and species-level diversity for products of economic importance in the medicinal field.
Question 25.
Mention the two types of biodiversity conservation?
Answer:
In-situ conservation & Ex-situ conservation.
![]()
Question 26.
What is Ex-Situ conservation? Mention two examples.
Answer:
In this approach the conservation of species outside their natural habitats.
Eg: Botanical gardens, Zoo gene bank, seed bank, cryopreservation, tissue culture.
Question 27.
What is In-Situ conservation? Mention two examples?
Answer:
In this approach the conservation of species in their natural habitats or on site conservation.
Ex: Biosphere, reserves, National park, Sanctuaries.
Question 28.
What are biodiversity hot spots.
Answer:
These are the regions with very high levels of species richness high degree of endemism and with accelerated habitat loss.
Question 29.
Name the hot spots of India.
Answer:
The Western Ghats, and Sri Lanka, Indo-Burma and Himalaya and North Eastern Himalayas.
Question 30.
How many hot spots are there in the world?
Answer:
34 Hot spots.
Question 31.
What are sacred groves? Mention any two examples.
Answer:
Sacred grooves are the traditionally conserved patches of forest where dedicated to local deities considering the landscape as sacred. Eg: Aravalli Hills in Rajasthan, the Western Ghats in Karnataka and Maharashtra, Khasi hills of Meghalaya. Sarguja, Chanda, and Bastar areas of Madhya Pradesh.
Question 32.
What is endemism?
Answer:
Species are confined to a particular geographical region and not found anywhere.
Question 33.
Mention the number of Biosphere reserves, National parks, and Wild Life Sanctuaries in India.
Answer:
Biosphere reserves – 14, National Parks – 90 Wild Life Sanctuaries – 448.
Question 34.
Write a note on international efforts for conserving Biodiversity.
Answer:
Biodiversity conservation is a important global issue. The historic convention on biological diversity was ‘The Earth Summit’ held in Rio de Janeiro (1992) which called all nations to conserve biodiversity:
The World summit on sustainable development held in 2002 in Johannesburg, South Africa, where 190 countries pledged their commitment to achieve by 2010 a significant reduce in Biodiversity loss.
→ Biodiversity:
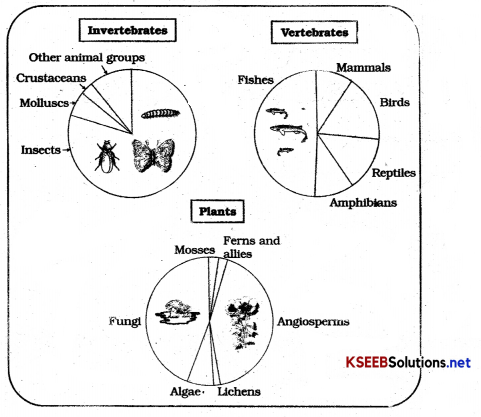
The rich variety of living organisms with which they share this planet are always astonishing and fascinating to humans. It is hard to believe that there are more than 20000 species of ants, 300000 species of beetles, 28000 species of fishes and nearly 20000 species of orchids
![]()
→ How Many Species are There On Earth and How Many in India
The total number of plant and animal species is more than 1.5 million as listed by IUCN (2004).
According to Robert may global species diversity is 7 million.
Animal species 70% and plants 22% of the total.
Among animals insects share 70% of the total with most species richness.
India having only 2.4% of worlds land area shares 8.1 percent of the global species diversity and considered One of the 12 mega diversity countries of the world.
→ Why Should We Conserve Bio-Diversity
We need to conserve biodiversity in order to maintain our own life, which demands planned management programmer.