Karnataka 2nd PUC Biology Important Questions Chapter 16 Environmental Issues
Question 1.
Define pollution?
Answer:
Pollution is defined as an undesirable change in physical, chemical or biological characteristics of air, water, land, soil.
Question 2.
Name the main source of air pollution?
Answer:
Pollutants emitted by automobiles are the main sources of air pollution.
Question 3.
Name any two metals found in catalytic converter?
Answer:
Platinum and palladium.
Question 4.
In which year was Air prevention and control of pollution act amended to include noise as air pollution?
Answer:
1987.
![]()
Question 5.
Name the city in which entire public road transport runs on CNG?
Answer:
Delhi.
Question 6.
How do automobiles fitted with catalytic converters reduce air pollution? Suggest thehydro best fuel for such vehicles?
Answer:
Catalytic converters have expensive metals like platinum-palladium and rhodium as catalysts. As exhaust emission passes through catalytic converter, unbumt hydrocarbons are converted into CO2 and H2O, CO and NO are changed to CO2 and N2 gas. Unleaded petrol is the best fuel.
Question 7.
Why is CNG considered better than diesel? Explain.
Answer:
- CNG bums more efficiently unlike diesel or petrol.
- Very little of it is left unburnt.
- It cannot be adulterated.
- It is cheaper than petrol or diesel.
Question 8.
Explain any three measures which will control vehicular air pollution in Indian cities?
Answer:
Three measures used to control vehicular air pollution in Indian cities are:
- Use of CNG as fuel in automobiles because it bums more efficiently and little of it is left unbumt. It is also cheaper.
- Use of unleaded petrol.
- Use of catalytic converter in the vehicles as it reduces emission of poisonous gases.
Question 9.
What is noise pollution?
Answer:
It is an undesirable high level of sound.
![]()
Question 10.
A noise of which decibel damages ear drums thus causing permanent hearing ability?
Answer:
A noise above 150 d B damages ear drums and causes permanent hearing ability.
Question 11.
Define water pollution?
Answer:
Water pollution is any undesirable change in the physical, chemical, biological properties of water.
Question 12.
Define Bio-magnification?
Answer:
An increased concentration of toxins at successive trophic levels is termed as Bio-magnification.
Question 13.
What is Eutrophication?
Answer:
It is natural aging of a iake by biological enrichment of its water.
Question 14.
Define B O D (Biochemical oxygen demand)?
Answer:
The amount of oxygen required for microbial breakdown of biodegradable organic matter is called biochemical oxygen demand.
Question 15.
What are algal blooms?
Answer:
Domestic sewage contains nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorous which favour the excessive growth of planktonic algae termed as algal blooms.
![]()
Question 16.
What are the various constituents of domestic sewage? Discuss the effects of sewage discharge on a river?
Answer:
Various constituents of domestic sewage are:
- Suspended solids – Grit made of sand, silt and clay.
- Colloidal material – Includes faecal matter, bacteria, paper fibers.
- Dissolved solids – They are inorganic nutrients and organic compounds
- Pathogens – A number of pathogens cause various diseases like typhoid, cholera, dysentery etc
Effects of sewage discharge on a river:
Domestic sewage mainly contains biodegradable organic wastes which are decomposed by decomposers like bacteria and other microorganisms. Decomposers require O2 for their activity and hence BOD increases. Many aquatic organisms die due to a lack of dissolved O2. Domestic sewage contains N2 and P which favours excess growth of algae called algal bloom. Excessive growth of water hyacinth imbalances the water ecosystem and thus the aquatic animals die.
Question 17.
What is the raw material for poly blend?
Answer:
Plastic wastes.
Question 18.
Expand F O A M?
Answer:
Friend of Areata Marsh.
Question 19.
Where were Ecosan toilets first developed?
Answer:
Kerala, Sri-Lanka.
![]()
Question 20.
How solid wastes are categorized and disposed?
Answer:
Solid Wastes:
Discarded solid materials produced due to various human activities. They are of following types
- Municipal solid wastes- wastes from homes, offices, schools, hospitals that are collected and disposed of by the municipality which generally consists of paper, leather, textile, rubber, glass, etc
- Industrial wastes – it includes scraps, fly ash etc
- Hospital wastes include hazardous waste containing disinfectants and other harmful chemicals generated by hospitals.
- E wastes(electronic wastes)- Damaged electronic goods and irreparable computers.
Methods of Solid Waste Disposal:
- Open burning.
- Sanitary landfills
- Ragpickers
- Natural breakdown
- Recycling
- Incineration
Remedy for plastic waste: A fine powder of recycling modified plastic is called poly blend. It is miked with bitumen to lay roads in Bangalore.
Question 21.
Mention how e wastes is produced and disposed off. Write the solution for its treatmen?
Answer:
Irreparable computers and other electronic goods are termed as e wastes. They are buried in landfills or incinerated. Recycling is the only treatment for e wastes.
Question 22.
What is polyblend?
Answer:
A fine powder of recycling modified plastic is called polyblend.
![]()
Question 23.
What is the cause of Radioactive pollution?
Answer:
- Leakage of radioactive materials from power plants
- Unsafe disposal of radioactive wastes.
Greenhouse effect and Global Warming:
The progressive warming of the earth’s surface due to an increase of greenhouse gases is called greenhouse effect.
Green house gases – CO2, CH4(methane), N2O(Nitrous oxide) CFC, and water vapour.
Significance of greenhouse effects:
- It is essential to make the earth warmer for organisms to live otherwise the earth will have frozen temperature around -18C.
- Global warming: It is the heating up of earth due to green house effect or increase in mean temperature of earth due to greenhouse gases is called global warming.
- The term green house has been derived from a phenomenon that occurs in green house.
Question 24.
Discuss the consequences of (a) Global warming (b) Ozone depletion.
Answer:
Global warning: It is the heating up of earth due to greenhouse effect or increase in mean temperature of earth due to greenhouse gases is called global warming. –
Effects:
- The temperature of the earth has increased by 0.6° C in the last three decades and it leads to changes in precipitation patterns
- The rise in temperature leads to deleterious changes in the environment resulting in odd climatic changes called the EL Nino effect.
- The rise in temperature will lead to increased melting of polar ice caps which will cause the rise in sea level.
Causes of Ozone depletion:
(a) O3 degradation has increased due to chloroform carbons (CFCs)
(b) CFCs are refrigerants that react with UV in stratosphere to release chloride atoms.
(c) Chloride atoms act as catalysts to degrade ozone and release molecular oxygen.
(d) CFCs have permanent and continued effect as chlorine atoms are not consumed.
(e) Over the Antarctic region there has been thinning of large area of ozone layer which has resulted in the formation of ozone holes.
Question 25.
Name any three gases contributing to greenhouse effect?
Answer:
CO2, Nitrous oxide, CH4
Question 26.
Name two greenhouse gases produced by anaerobic microbes?
Answer:
CO2, and CH.
![]()
Question 27.
What type of UV radiation can be lethal to organisms?
Answer:
UV-B radiation.
Question 28.
Write the unit used for measuring ozone thickness?
Answer:
Dobson Units
Question 29.
How is snow blindness caused in humans?
Answer:
In human eye, cornea absorbs UV-B radiation and a high dose of UV-B causes inflammation of the cornea causing snow blindness.
Question 30.
Which of the following is not a green house gas? CO2, CH4, O2, CFCs?
Answer:
O2
Question 31.
What is global warming? List four strategies for reducing global warming?
Answer:
Increase in the level of green house gases in the atmosphere causes the rise in global mean temperature called global warming.
Four strategies for reducing global wartning are:
- Reducing deforestation
- Planting trees
- Slowing down the growth of human population
- Reduction in emission of greenhouse gases.
Question 32.
Chlorofluorocarbons CFCs are widely used as refrigerants. Then why it is suggested to reduce its emission as far as possible? Explain.
Answer:
CFCs are widely used as refrigerants. CFCs discharged in the lower part of atmosphere move upward and reach the stratosphere. In stratosphere UV rays act on them releasing chloride atoms. Chloride atoms degrade O3 releasing molecular O2. Whatever CFCs are added to the stratosphere have permanent and continuing effects on O3.
![]()
Question 33.
Write short notes on:
Answer:
(a) Greenhouse gases
(b) O3 depletion.
(a) Greenhouse gases – CO2, CH4(methane), N2O(Nitrous oxide) CFC and water vapour.
Significance of greenhouse effects:
It is essential to make the earth warmer for organisms to live otherwise earth will have frozen temperatures around -18C.
(b) Causes of Ozone depletion:
(a) O3 degradation has increased due to chloroflouro carbons (CFCs)
(b) CFCs are refrigerants which react with UV in stratosphere to release chloride atoms.
(c) Chloride atoms act as catalysts to degrade ozone and release molecular oxygen.
(d) CFCs have permanent and continued effect as chloride atoms are not consumed.
(e) Over the Antarctic region there has been thinning of large area of ozone layer which has resulted in the formation of ozone holes.
- Deforestation is defined as conversion of forested area to non-forested area.
- Removal of forest areas to fulfill the need of growing human population is called deforestation.
- Almost 40% forests have been lost in the tropics and 1% in the temperate region.
Causes of deforestation:
(a) Human settlements.
(b) Forest fires
(c) Hydroelectric projects
(d) Overgrazing by livestock.
(e) Demand for wood.
(f) Jhum cultivation or slash and bum agriculture – The farmers cut the forest trees and bum the plant remains. The land is then used for farming and cattle grazing. After cultivation, the land is left barren for years.
Effects of deforestation:
- Increase in CO2 concentration in the atmosphere.
- Loss of biodiversity due to habitat destruction.
- Disturbance in hydrologic cycle.
- Soil erosion that may lead to desertification.
Reforestation:
It is a process of restoring a forest that once existed but was removed at some point of time in the past. It may occur naturally in a deforested area.
People’s Participation in Conservation of Forests:
- In 1731, a Bishnoi woman Amrita Devi, showed exemplary courage by hugging a tree in order to prevent its cutting. Her three daughters and hundreds of other Bishnoi’s followed her and were killed by soldiers of king of Jodhpur.
- The Government of India has instituted Amrita Devi Bishnoi Wild life protection award for individuals or communities from rural areas that shows extraordinary courage and dedication in protecting wildlife.
- Chipko movement was started in Garhwal Himalayas in 1974 by Sri Sundarlal Bahuguna to prevent cutting down of trees. Local women hugged trees to prevent their cutting.
- In 1980, the Government of India has introduced the concept of Joint Forest Management to work closely with the local communities for protecting and managing forests on mutual benefits.
![]()
→ Pollution is defined as an undesirable change in physical, chemical or biological characteristics of air, water, land or soil.
Pollutants are the agents which bring about an undesirable change in the properties of air, water and soil.
Govt, of India has passed the Environment Protection Act 19861 protect and improve the quality of environment.
→ Air Pollution:
Any undesirable change in the physical, chemical or biological characteristics of air that exerts adverse effects on human beings is defined as air pollution.
→ Causes:
(a) Smoke from forest fires, volcanic eruptions etc
(b) Decomposition of garbage resulting in release of unwanted gases into the atmosphere.
(c) Burning of fossil fuels in automobiles and industries release particulate and air pollutants
(d) Use of leaded petrol.
(e) Gaseous wastes or particulate byproducts of various industries.
(ii) Air pollutants can be classified into two groups.
(a) Particulate pollutants eg metallic particles, dust particles, soot and smoke.
(b) Gaseous pollutants eg. CO, NO2, nitrogen hydrogen sulphide H2S, Sulphur dioxide SO2 etc.
→ Harmful Effects:
(a) Carbon Monoxide causes giddiness, headache, decreased vision, cardiovascular malfunction, asphyxia.
(b) H2S causes nauses, eye and throat irritation.
(c) Sulphur dioxide causes respiratory tract diseases like asthma, bronchitis, cancer, emphysema etc.
(d) Fine particulates cause breathing, respiratory symptoms, irritation, inflammations and damage of the lungs.
→ Control Methods Of Air Pollution
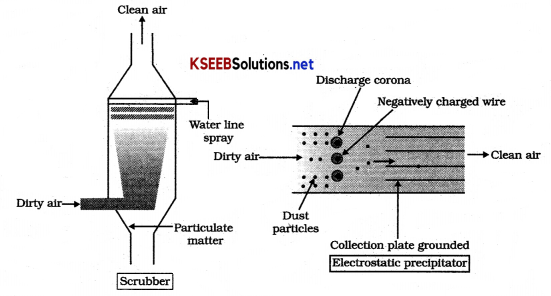
(a) Electrostatic precipitator(ESP).
- It is an electrical device to remove particulate matter present in the exhaust of thermal power plant.
- More than 99% of particulate matter can be removed by this method.
- ESP has electrode wires’and a stage of collecting plates.
- Electrode wires are provided with electric current of several thousand volts which produces a corona that releases electrons.
- These electrons attach to dust particles and give them a negative charge with in a small fraction of second.
- Collecting pates are earthed so that they can attract dust particles.
(b) Scrubber
- It is used to remove gases like sulphur dioxide from industrial exhaust.
- The exhaust is passed through a spray of water or lime.
- Water dissolves gases and lime reacts with S02 to form a precipitate of calcium sulphate and sulphide. Clean air
(c) Catalytic converters
- They are fitted into automobiles for reducing the emission of poisonous gases like NO2 and CO.
- They have expensive metals like platinum-palladium and rhodium as catalysts.
- Motor vehicles fitted with catalytic converter should use unleaded petrol as leaded petrol inactivates the catalyst.
![]()
→ Control Of Air Pollution In Delhi:
- All buses of Delhi were converted to run on CNG by end of 2002.
- Advantages of CNG over diesel/petrol.
(a) CNG bums more efficiently without leaving any unbumt remnant behind.
(b) CNG is cheaper than petrol or diesel.
(c) CNG cannot be siphoned by thieves and adulterated like petrol or diesel.
→ Noise Pollution:
Noise is defined as undesired high level of sound.
Causes
- Loudspeakers and music systems used for entertainment.
- Jet planes and rockets.
- Industrial noises.
→ Harmful Effects:
- Sleeplessness
- Stress
- Increased rate of heartbeats
- Breathing problems.
- Damage of eardrums impairing hearing ability permanently.
![]()
→ Control Methods:
- Industrial noises can be reduced by using sound absorbent materials or by muffling noise.
- Delimitation of the home-free zone around hospitals and schools.
- Stringent laws should be laid for permissible sound levels of crackers and loudspeakers.
- Setting timing after which loudspeakers cannot be played.
→ Water Pollution:
Water pollution is an undesirable change in the physical, chemical, biological properties of water that may affect human beings and domestic species.
Water pollution is caused due to:
1. Domestic Sewage
- Domestic sewage contains
- Suspended solids. Ex. Sand, Silt, Clay
- Colloidal materials ex. Faecal matter, bacteria, paper, cloth etc
- dissolved materials ex. Nitrates, sodium, calcium salt.
- Domestic sewage has biodegradable organic wastes which can be decomposed by decomposers.
2. Industrial Wastes
- Industries like petroleum, paper manufacturer release waste water containing heavy metals like mercury and many organic compounds
- Mercury, DDT are well known for Biomagnification.
- Bio-magnification is increased concentration of toxins at successive trophic levels. Toxic substances cannot be metabolized or excreted and therefore get accumulated in an organism and are passed onto higher trophic levels.
3. Eutrophication – It is natural aging of a lake by biological enrichment of its water. Water in a young lake is
cold and clear and with time it gets enriched with nutrients which encourages growth of aquatic plant life and animal life.
4. BOD (biochemical Oxygen Demand) – The amount of 02 required for microbial breakdown of biodegradable organic matter is called BOD. It is higher in polluted water and less in drinking water. (March 2014 and 2015)
5. Algal bloom – (March 2014) Domestic sewage contains nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus which favour the excessive growth of planktonic (free-floating) algae called an algal bloom. Algal bloom causes fish mortality and deterioration of water quality.
6. Heated thermal waste waters flowing out of electricity generating unit. Ex: Thermal power plants constitute another important category of pollutants. Thermal wastewater eliminates or reduces the number of organisms sensitive to high temperature and may enhance the growth of plants and fish only after causing damage to flora and fauna.
→ Integrated Waste Water Treatment:
Wastewater including sewage can be treated by using a mix of artificial and natural processes.
Cleaning includes:
- Conventional sedimentation, filtering, chlorine treatment.
- Biologists developed six connected marshes over 60 hectares of marshland which included algae, fungi, bacteria. FOAM (Friends of Areata Marsh)are safeguarding this project.
Ecosan toilets has been developed in Kerala, Sri-Lanka for ecological sanitation.
![]()
→ Solid Wastes:
Discarded solid materials produced due to various human activities. They are of following types
- Municipal solid wastes- wastes from homes, offices, schools, hospitals that are collected and disposed by municipality which generally consists of paper, leather, textile, rubber, glass etc
- Industrial wastes – it includes scraps, fly ash etc
- Hospital wastes include hazardous waste containing disinfectant and other harmful chemical generated by hospitals.
- E wastes(electronic wastes)- Damaged electronic goods and irreparable computers.
→ Methods of Solid Waste Disposal:
- Open burning.
- Sanitary landfills
- Ragpickers
- Natural breakdown
- Recycling
- Incineration
Remedy for plastic waste: A fine powder of recycling modified plastic is called poly blend. It is mixed with bitumen to lay roads in Bangalore.
→ Soil Pollution:
Undesirable changes in soil profile affecting its productivity are called soil pollution.
Causes:
- Chemical seepage from industries.
- Inorganic fertilizers and pesticides.
→ Harmful Effects:
- Non-target organisms in the soil are killed.
- Soil becomes infertile.
- Pesticides can results in bio-magnification.
→ Control Methods:
- Safe disposal of industrial wastes.
- Organic farming- it is a zero-waste procedure where waste products from one process are cycled in as nutrients for other processes allowing maximum utilization of resource and increasing the efficiency of production.
![]()
→ Case Study of Organic Farming:
- Ramesh Chandra Dagar includes beekeeping, dairy management, water harvesting, composting and agriculture in a chain of processes.
- Chemical fertilizers are not required as cattle excreta is used as manure.
- Crop wastes is used for making compost which is used as a natural fertilizer. Compost generates natural gas which is used for energy needs on farm.
→ Radio – Active Pollution:
Nuclear energy was assumed to be a natural non-polluting way of electricity generations till the incidents at three mile Island and Chernobyl. It is now considered as the most potent pollutant.
Causes:
- Leakage of radioactive materials from power plants.
- Unsafe disposal of radioactive wastes.
→ Harmful Effects:
- Radiations from nuclear waste causes mutation at a very high rate.
- At high doses, nuclear radiations are lethal.
- At low doses, radiation causes disorders and cancer.
→ Effects
- The temperature of the earth has increased by 0.6″ C in the last three decades and it leads to changes in precipitation patterns
- Rise in temperature leads to deleterious changes in environment resulting in odd climatic changes called the EL Nino effect.
- Rise in temperature will leads to it increased melting of polar ice caps which will cause the rise in sea level.
![]()
→ Control of Global Warming:
Global warming can be controlled by:
(a) Reducing deforestation
(b) Planting trees (afforestation).
(c) Slowing down the growth of human population.
(d) Reduction of emission of green house gases into the atmosphere.
(e) Cutting down use of fossil fuels
(f) Improving efficiency of energy usage.
→ Ozone Depletion:
Ozone is of two types-
- Bad ozone formed in troposphere and is harmful to plants and animals.
- Good ozone formed in the stratosphere and absorbs harmful UV radiations from the sun. Thickness of ozone is measured in Dobson units (D U).
→ Formation of Ozone:
Nascent oxygen combines with molecular (O2) to form ozone by the action of UV rays (Equation)
Ozone is degraded into molecular oxygen in the stratosphere by the UV action to maintain a balance between production and degradation.
![]()
→ Causes of Ozone Depletion
(a) O3 degradation has increased due to chloroflouro carbons (CFCs).
(b) CFCs are refrigerants which react with UV in stratosphere to release chloride atoms.
(c) Chloride atoms act as catalysts to degrade ozone and release molecular oxygen.
(d) CFCs have permanent and continued effect as chloride atoms are not consumed.
(e) Over the Antarctic region there has been thinning of large areas of ozone layer which has resulted in the formation of ozone holes.
![]()
→ Harmful Effects:
(a) UV -B damages DNA and proteins of living organisms causing mutation.
(b) It causes skin aging, skin cell damage and skin cancers.
(c) UV-B is absorbed by human eye and at high dose it causes inflammation of cornea. This is called as snow blindness cataract.
→ Control of Ozone Depletion:
(a) An international treaty, Montreal Protocol, was signed at Montreal Canada in 1987 to curb the emission of ozone-depleting substances.
(b) More protocol has been laid down in controlling emission of CFCs.