Karnataka 2nd PUC Biology Important Questions Chapter 3 Human Reproduction
Question 1.
What are viviparous organisms?
Answer:
Organisms in which the young one develops within the body of female are termed as viviparous organisms.
Question 2.
List out the reproductive events in humans. Any four?
Answer:
It includes the following.
- Gametogenesis
- Insemination
- Fertilization
- Implantation
- Gestation or Pregnancy
- Parturition.
Question 3.
Define gametogenesis.
Answer:
Formation of haploid male gametes called sperm and female gamete called ovum is termed as gametogenesis.
Question 4.
What is implantation?
Answer:
Attachment of embryo to the endometrial wall of uterus is termed as implantation
![]()
Question 5.
Define Parturition?
Answer:
Delivery of thr baby is termed as parturition.
Question 6.
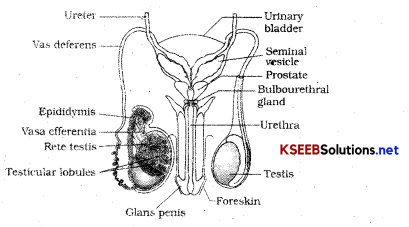
Draw a neat labelled diagram male reproductive system in humans.
Answer:
Question 7.
Describe the male reproductive system?
Answer:
It is located in the pelvic region and consists of
- A pair of testes
- Accessory ducts
- Glands
- External genitalia.
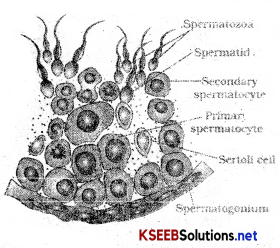
1. The testes are situated outside the abdominal cavity within a pouch termed as scrotum. Scrotum helps in maintaining low temperature of the testes (2-2.5°c lower than normal internal body temperature. The testis is oval in shape, contains 250 compartments called testicular lobules. Each lobule contains 1-3 highly coiled seminiferous tubule in which sperms are produced. Each seminiferous tubule is lined on inside by 2 types of cells male germ cells, spermatogonia, sertoli cells.
Male germ cells undergo meiotic division to form sperms where as sertoli cells provide nourishment to germ cells.
Region outside the seminiferous tubule is termed as interstitial spaces which contains blood vessels, interstitial cells or leydig cells.
Leydig cells synthesise testicular hormones termed as androgens.
2. Male sex accessory ducts include rete testis, vasa efferentia, epididymis and vas deferens. Seminiferous tubules open into rete testis which leads to vasa efferentia. Vasa efferentia opens into epididymis which leads to was deferens which loops over urinary bladder. Vas deferens receives a duct from seminal vesicle and opens into urethra as ejaculatory duct.
The ducts store and transport sperms from testis to outside through urethra opens up into urethral meatus.
3. Male accessory glands include paired seminal vesicles, a prostrate gland and a paired bulbo urethral glands secretions of which comprise seminal plasma which is rich in fructose, calcium and certain enzymes.
4. External genitalia is penis which is made up special tissue which helps in erection of penis to facilitate insemination. Enlarged end of penis is glans penis opened by foreskin.
Question 8.
Which cells of testes secrete androgens?
Answer:
Leydig cells of testes secrete androgens.
![]()
Question 9.
What is the function of sertoli cell?
Answer:
The function of sertoli cells is to provide nourishment to germ cells during spermatogenesis.
Question 10.
Give the function of scrotum?
Answer:
It helps in maintaining low temperature of testes (2-2.5°c lower than normal internal body temperature).
Question 11.
What is the function of bulbourethral glands?
Answer:
The secretions of the bulbourethral glands help in the lubrication of the penis.
Question 12.
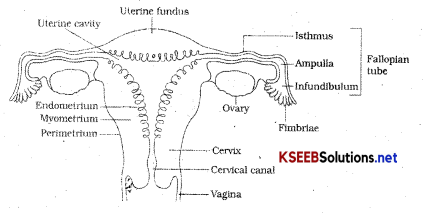
Draw a neat labeled diagram of sectional view of the female reproductive system?
Answer:
Question 13.
Describe female reproductive system in detail?
Answer:
Female reproductive system consists of a pair of ovaries, a pair of oviducts, uterus cervix, vagina, external genitalia in pelvic region.
Ovaries are the primary female sex organ which produces the female gamete or ovum and several steroid hormones. Each ovary is 2 – 4cm in length and connected to the pelvic wall and uterus by ligaments.
Oviducts (fallopian tubes), uterus, vagina constitute the female accessory ducts. Each fallopian tube is 10-12 cm long and it extends from periphery of each ovary to uterus.
The part closer to the ovary is infundibulum which contains finger like projections termed as fimbriae which helps in collection of ovum after ovulation. Infundibulum leads to a wider ampulla which leads to a narrow Isthmus which is the last part of oviducts and it joins the uterus. Uterus is single and also called womb shape is like inverted pear. Uterus opens into vagina through narrow cervix. Cavity of cervix along with vagina forms birth canal. Uterus has 3 layers outer thin perimetrium, middle muscular myometrium and inner glandular layer endometrium.
Female external genitalia include mons, pubis, labia majora, labia minora, hymen, clitoris.
Some important one mark questions from this topic:
Question 14.
Name the finger like projections present in the ovary at the end of infundibulum?
Answer:
Fimbriae.
Question 15.
What is the other name for oviduct?
Answer:
Fallopian tube.
Question 16.
What are the 3 parts of fallopian tube?
Answer:
Infundibulum, Ampulla, Isthmus.
Question 17.
Give the other name for uterus?
Answer:
It is termed as womb.
Question 18.
What forms birth canal?
Answer:
Cervical canal along with vagina forms birth canal.
![]()
Question 19.
Mention any two hormones secreted by ovary.
Answer:
Progesterone, Estrogen.
Question 20.
Draw a sectional view of the mammary gland?
Answer:
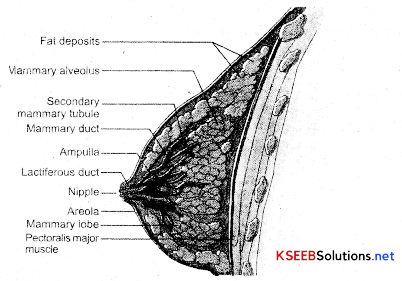
Mammary Gland — Diagrammatic Sectional View
Question 21.
Write a note on mammary gland?
Answer:
- It is characteristic of all female mammals.
- They are paired structures that contain glandular tissue and variable amount of fat.
- Glandular tissue of each breast is divided into 10-20 mammary lobes which contain alveoli which secrete milk
- Mammary lobe join to form mammary duct. Mammary duct is connected to laticiferous duct through mammary ampulla.
- Through laticiferous duct milk is sucked out.
Question 22.
What are the 2 types of gametogenesis?
Answer:
They are:
- Spermatogenesis
- Oogenesis
Question 23.
What is Spermato genesis?
Answer:
The process of production of sperms in the male gonad or testes is spermatogenesis.
Question 24.
Define oogenesis?
Answer:
The process of formation of mature female gamete or ovum in the female gonad or ovary is oogenesis.
![]()
Question 25.
Define spermiogenesis?
Answer:
Spermatids are transformed into spermatozoa (sperms) by the process called spermiogenesis.
Question 26.
What is Spermiation?
Answer:
Sperm heads become embedded in sertoli cells and are released from seminiferous tubules by the process of Spermiation.
Question 27.
What is semen?
Answer:
Seminal plasma along with sperms constitute semen.
Question 28.
Give a detailed account of spermatogenesis?
Answer:
The spermatogonia which is found on inner wall of seminiferans tubule multiply by mitotic division and contain 46 chromosomes. It enlarges to form primary spermatocyte which undergoes Ist Meiosis to form 2 secondary spermatocytes which are equal in size and contains 23 chromosomes.
The secondary spermatocytes undergo the second meiotic division to form four equal haploid spermatids. Spermatids are transformed into sperms by spermiogenesis. Sperms are released from seminiferous tubules by the process called spermiation.
Question 29.
Give an account of hormonal control of spermatogenesis?
Answer:
- Spermatogenesis starts at the age of puberty due to significant increase in the secretion of gonadotropin-releasing hormone.
- The increased level of GnRH acts at the anterior pituitary gland and stimulates secretions of two gonadotrophins – Luteinising hormone and Follicle-stimulating hormone.
- L-H acts at Leydig cells and stimulates synthesis and secretion of androgens. Androgens stimulate spermato genesis.
- F.S.H acts on sertoli cells and stimulates the secretion of some factors which stimulate the process of spermiogenesis.
![]()
Question 30.
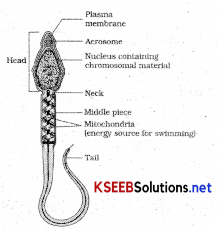
Draw a neat labeled diagram of human sperm.
Answer:
Any four labels:
Question 31.
Describe the structure of human sperm
Answer:
It is a microscopic structure and it is composed of a head, neck a middle piece and tail. Plasma membrane envelops whole body of sperm. Sperm head consists of a haploid nucleus and it is covered by cap like structure termed acrosome. Acrosome is filled with enzymes which help in the fertilisation of ovum. Middle piece possess mitochondria which produce energy for movement of tail. Human male ejaculates about 200 to 300 million sperms during coitus. Secretions of epididymis, vas deferens, seminal vesicle and prostrate are essential for maturation and motility of sperms.
Question 32.
Describe the process of Oogenesis with a schematic representation.
Answer:
The process of formation of mature female gamete is termed as oogenesis, Oogonia are formed within each foetal ovary no more oogonia are formed and added after birth. These cells enter prophase I of meiosis I and get arrested at primary oocyte stage, primary oocyte gets surrounded by layer of granulosa cells and is called primary follicle. The primary follicle gets surrounded by more layer of granulosa cells and forms secondary follicle. Secondary follicle gets converted to tertiary follicle which has a fluid filled cavity called antrum.
Theca layer is organised into outer theca externa, inner theca interna. Primary oocytae within the tertiary follicle grows in size and completes its first meiotic division to form a large haploid secondary oocyte and a tiny first polar body. Secondary oocyte retains bulk of nutrient-rich cytoplasm. Tertiary follicle forms a mature Grafian follicle. Secondary oocyte forms a new membrane zona pellucida Grafian follicle rypturcs to release secondary oocyte from ovary – process is ovulation.
The reproductive cycle in the female primates (Eg. monkeys, apes and human beings is termed as menstrual cycle.
Question 33.
Define menarche?
Answer:
First menstruation begins at puberty and is termed as menarche.
Question 34.
Define ovulation?
Answer:
Release of ovum/secondary oocyte from the Graafian follicle is termed as ovulation.
![]()
Question 35.
What is the function of corpus luteum?
Answer:
It secretes large amount of progesterone which is essential for maintenance of endometrium.
Question 36.
Ovulation takes place on the 14th day of menstrual cycle why?
Answer:
Graafian follicle matures and ruptures usually on the 14th day due to rapid secretion of L H or L.H surge.
Question 37.
Define menopause?
Answer:
In human beings menstrual cycle ceases around 50 years of age and it is termed as menopause.
Question 38.
Name the hormones secreted by Leydig cells and corpus luteum.
Answer:
Progesterone is the hormone secreted by corpus luteum. Androgen hormone is secreted by Leydig cells.
Question 39.
Name the four major events of menstrual cycle
Answer:
The four events of menstrual cycle are:
- Menstrual phase
- Follicular phase
![]()
Question 40.
What is menstrual cycle. Explain each events?
Answer:
The cycle of events starting from one menstruation till the next one is called as the menstrual cycle. Cycle starts with menstrual phase, where menstrual flow occurs and it lasts for 3-5 days. Menstrual flow is due to the breakdown of endometrial lining of uterus and its blood vessels which forms liquid that comes out through vagina. Menstruation occurs only if the released ovum is not fertilised. Lack of menstruation indicates pregnancy but stress, poor health may also lead to it.
The second phase is follicular phase during which the primary follicles in the ovary grow to become fully mature Grafian follicle and the endometrial lining of uterus regenerates. These changes in ovary, uterus are accompanied by changes in pituitary and ovarian hormones. L.H and F.S.H hormone increase in levels during the follicular phase and help in follicular development.
During ovulatory phase which occurs at the mid-cycle there is a surge in L.H. hormone secretion which induces rupture of Graafian follicle and the release of ovum (Ovulation).
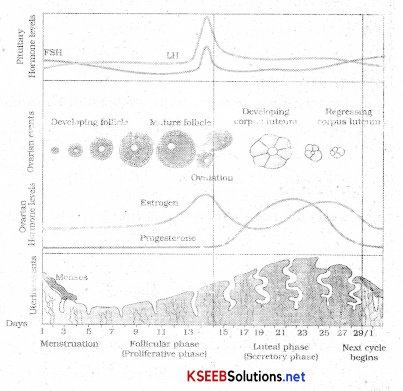
After ovulatory phase is the luteal phase where the remaining parts of Graafian follicle transforms as corpus luteum. Corpus luteum secretes large amount of progesterone which is essential for maintenance of endometrium.
Endometrium is essential for implantation of fertilised ovum and other events of pregnancy.
During pregnancy menstrual cycle stops.
In the absence of fertilisation corpus luteum degenerates, endometrium disintegrates leading to menstruation. Thus there is marking of a new cycle.
During copulation semen is released by penis into vagina of the female. This process is termed as insemination. Motile sperms swim pass through cervix, then enter uterus and finally reach the ampullary isthmus junction of fallopian tube. Ovum released by ovary also reaches the ampullary isthmic junction and this is the place where fertilisation takes place. Process of fusion of sperm with an ovum is called fertilisation. During fertilisation, a sperm comes in contact with the zone Pellucida layer of the ovum. A change in membrane occurs and entry of more sperms is blocked. Thus it ensures only 1 sperm can fertilise an ovum. The acrosome of sperm secretes certain enzymes which helps the sperm to reach the cytoplasm of the ovum. The meiotic division of secondary oocyte is completed and there is formation of a haploid ovum and a second polar body.
Sperm and ovum fuse to form a diploid zygote.
Sex determination of a child:
- The sex of the child is determined at the stage of fertilization.
- Chromosome pattern in human female is XX and in the human male it is XY.
- When the sperm carrying the X chromosome fuses with the egg carrying an X chromosome, the result is a female child with XX chromosome.
- When sperm carrying the Y chromosome fuses with an ovum carrying the X chromosome the result is a male child with XX chromosome.
- Thus human males are heterogametic with XY chromosome and human females are homogametic with XX chromosome.
- The pattern of sex determination is XY-XY type.
Question 41.
What is the process of sex determination in humans termed as?
Answer:
- It is termed as XX-XY type of sex determination.
- When the sperm carrying the X chromosome fuses with an ovum carrying X chromosome the result is a female child with XX chromosome.
- When the sperm carrying the Y chromosome fuses with an ovum carrying the X chromosome the result is a male child with an XY chromosome.
The mitotic division starts as the zygote moves through the isthmus of the oviduct called cleavage towards the uterus and forms 2, 4, 8, 16 daughter cells called blastomeres.
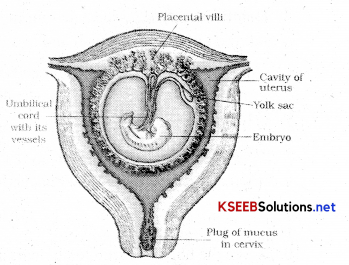
The chorionic villi and uterine tissue become interdigitated with each other and jointly form a structural and functional unit between the developing embryo (foetus) and maternal body called the placenta.
The average duration of human pregnancy is about 9 months which is called the gestation period. Vigorous contraction of the uterus at the end of pregnancy causes expulsion/delivery of the foetus. This process of delivery of the foetus (childbirth) is called parturition.
![]()
Question 42.
Define cleavage.
Answer:
The zygote undergoes repeated mitotic division at the ampullary-isthmus junction of the oviduct and it is termed as cleavage.
Question 43.
Name the two layers of a blastocyst?
Answer:
The two layers of the blastocyst are
- outer trophoblast
- Inner cell mass.
Question 44.
What is implantation?
Answer:
Blastocyst becomes embedded to the endometrium of uterus termed as implantation.
Question 45.
What is morula?
Answer:
Embryo with 8-16 blastomere is called morula.
Question 46.
Define placenta?
Answer:
The placenta is an organic connection between maternal tissue and foetus through which physilogical exchange takes place.
Question 47.
Write four hormones secreted by the placenta?
Answer:
The four hormones secreted by placenta are
- Human chorionic Gonadotrophin (LCG).
- Human placental lactogen (LPL).
- Estrogen.
- Progestogen.
Question 48.
What are the functions of placenta 2?
Answer:
- It facilitates the supply of O2 and nutrients to the embryo and helps in the removal of CO2 and excretory material produced by the embryo.
- The placenta is connected to the embryo through an umbilical cord which helps in the transport of substances to and from the embryo.
- Placenta also acts as an endocrine tissue and produces several hormones like human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), human placental lactogen(hPL), estrogen, progestogen.
Question 49.
Define parturition and Lactation?
Answer:
Vigorous contraction of uterus’ at the end of pregnancy causes expulsion/delivery of the foetus the process of delivery of the foetus is called childbirth.
![]()
Question 50.
Which hormone hastens childbirth 2?
Answer:
Oxytocin.
Question 51.
Define lactation?
Answer:
The mammary glands of females undergo differentiation during pregnancy and start producing milk towards the end of pregnancy termed lactation,
Question 52.
What is colostrum 2?
Answer:
Milk produced during the initial few days of lactation is termed as colostrum which contains several antibodies essential to develop resistance in newborns.
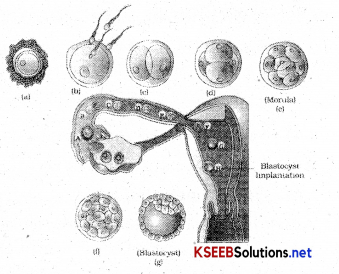
- The zygote undergoes repeated mitotic division at the ampullary isthmic junction of oviduct and it is cleavage.
- Zygote forms 2,4,8,16 daughter cells called blastomeres. Embryo with 8-16 blastomere is-called morula.
Morula continues to divide and forms blastocyst. - The blastocyst has 2 layers outer layer called trophoblast and inner cell mass. Trophoblast gets attached to the endometrium of the uterus.
- Inner cell mass forms embryo.
- Blastocyst beocmes embedded to the endometrium of uterus termed as implantation.
Pregnancy:
- After implantation finger-like projections appear on the trophoblast called chorionic Villi which is surrounded by uterine tissue and maternal blood.
- Chorionic Villi and uterine tissue become linked with one another and jointly form a structural and functional unit between the developing embryo and maternal body called the placenta.
- The placenta is thus an organic connection between maternal tissue and fetus through which physiological exchange takes place.
Question 53.
Name the hormones secreted by Leydig cells and corpus luteum.
Answer:
Progesterone is the hormone secreted by the corpus luteum. Androgen hormone is secreted by Leydig cells.
- It facilitates the supply of oxygen and nutrients to the embryo and helps in the removal of CO2 and excretory material produced by the embryo.
- The placenta is connected to the embryo through an umbilical cord which helps in the transport of substances to and from the embryo.
- Placenta also acts as an endocrine tissue and produces several hormones like human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), human placental lactogen (hPL), estrogen, progestogen.
- Relaxin is a hormone secreted in the later stage of pregnancy and supports fetal growth.
Question 54.
Define Cleavage?
Answer:
The zygote undergoes repeated mitotic division when it is at the isthmus of the oviduct and it is termed as cleavage.
![]()
Question 55.
Define Placenta?
Answer:
The placenta is an organic connection between maternal tissue and fetus through which physiological exchange takes place.
Question 56.
What is Colostrum?
Answer:
Milk produced during the initial few days of lactation is colostrum which contains several antibodies necessary to develop resistance against diseases.
Question 57.
Write four hormones secreted by the placenta?
Answer:
The four hormones secreted by the placenta are:
- Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG)
- Human Placental lactogen (hPL)
- Estrogen
- Progestogen
Question 58.
Define fertilisation.
Answer:
The process of fusion of a sperm with an ovum is called fertilisation.
![]()
Question 59.
Name the hormone secreted by the Corpus luteum and Leydig cells.
Answer:
Progesterone is the hormone secreted by corpus lutcum and Androgen hormone is seended by and Leydigeells
Question 60.
Name the hormones secreted by Leydig cells and corpus luteum
Answer:
Progesterone is the hormone secreted by corpus luteum. Androgen hormone is secreted by Leydig cells.
Question 61.
Refine foetal ejection reflex.
Answer:
The signal of parturition originates from the fully developed fetus and placenta which induce mild uterine contractions called fetal ejection reflex.
Question 62.
What is parturition?
Answer:
Rigorous contraction of the uterus at the end of pregnancy leading to delivery of the fetus is called parturition.
![]()
Question 63.
What are stem cells.
Answer:
Inner cell mass contains cells called stein cells which have the potency to give rise to all tissues and organs.
→ Embryonic Development:
Immediately after implantation the inner cell mass differentiates into outer layer called ectoderm and inner layer called endoderm. Mesoderm appears in between outer ectodeim and inner endoderm and all these three layers gives rise to all tissues in adults.
- Human pregnancy lasts 9 months. After the first month of pregnancy the embryo heart is formed.
- By second month of pregnancy, foetus develops limbs and digits.
- By 12 weeks (the first trimester) limbs and external genital organs are developed
- Head develops during fifth month.
- By second trimester body is covered with fine hair, eyelids separate, eyelashes are formed.
- By end of nine months foetus is fully developed and is ready for delivery.
→ Parturition and Lactation:
- The average duration of human pregnancy is 9 months and it is called gestation period.
- Vigorous contraction of uterus at the end of pregnancy causes expulsion/delivery of foetus. The delivery of foetus is Parturition.
(March 2015) Signal of parturition originate from fully developed foetus and placenta induces mild uterine contractions termed as foetal ejection reflex and triggers the release of oxytocin from maternal pituitary oxytoin causes rapid uterine contractions and is preferred for parturtean.
The mammary glands of the female undergo differentiation during pregnancy and produce milk towards the end of pregnancy termed lactation. Milk produced during initial few days of lactation is termed as colostrum which contains several antibodies essential to develop resistance for new bom babies.