Karnataka 2nd PUC Biology Important Questions Chapter 4 Reproductive Health
Question 1.
Overpopulation India is the first country which initiates plans and programs at national level some of them are-
Answer:
(a) Family planning program – 1951.
(b) Reproduction and child health care program -1997(RCH).
Question 2.
Define Reproductive health according to WHO?
Answer:
According to W.H.O reproductive health means total well-being in all aspects of reproduction physical,
emotional, behavioural and social.
Question 3.
When was family planning programmes initiated at the national level in India?
Answer:
Family planning programmes were initiated in India in the year 1951.
Question 4.
Expand R.C.H?
Answer:
Reproductive and child health care programme.
![]()
Question 5.
What is R.C.H? Mention its goals?
Answer:
R.C.H is reproductive and child health care programme and its goals are-
- 1 To create awareness among people about various reproductive related aspects.
- To provides facilities and support for building a reproductively healthy society.
Question 6.
Name male and female sterilization techniques in humans?
Answer:
Male sterilization technique is vasectomy and female sterilization technique is tubectomy.
Question 7.
Name anyone intrauterine device?
Answer:
CuT (Copper T)
Question 8.
Expands M.M.R?
Answer:
Maternal mortality rate.
Question 9.
Give the full form of I.M.R?
Answer:
Infant Mortality Rate.
Question 10.
What is intrauterine devices?
Answer:
These devices are inserted by doctors or expert nurses in the uterus through vagina.
Question 11.
Name any three natural methods of contraception?
Answer:
The three natural methods of contraception are-
- Periodic abstinence.
- Coitus interruptus or withdrawal method.
- Lactational amenorrhea
![]()
Question 12.
What is oral contraception? Name oral contraception.
Answer:
Oral administration of small doses of progestagens- estrogen combination is a contraceptive method used by females. They are used in the form of tablets called pills Saheli is an oral contraceptive.
Medical Termination of pregnancy MTP.
Intentional or voluntary termination of pregnancy before full term is called medical termination of pregnancy (MTP) or induced abortion.
- Nearly 45-50 million MTPs are performed in a year all over world.
- MTP can decrease the population to some extent.
- In many countries, the debate was whether to accept/legalize MTP or not.
Question 13.
Why MTP?
Answer:
- To get rid of unwanted pregnancies either due to casual unprotected intercourse or failure of the contraceptive used during coitus or rapes.
- Useful in continued pregnancies which could be harmful or even fatal to mother or foetus or both.
Question 14.
When are MTPs safe?
Answer:
They are safe during the first trimester upto 12 weeks of pregnancy, second trimester abortions are much riskier.
![]()
Question 15.
Write any two preventive measures to control STDs.
Answer:
- Avoid sex with unknown persons/multiple partners.
- Always use condoms during intercourse.
- Avoid sex with unknown persons/multiple partners.
- Always use condoms during intercourse.
- In case of doubt one must consult a qualified doctor without delay.
Question 16.
Define MTP?
Answer:
Intentional or voluntary termination of pregnancy before full term is called medical termination of pregnancy (MTP) or induced abortion.
Question 17.
What is the safe period of MTP?
Answer:
It is considered safe during the first trimester (Up to 12 weeks of pregnancy)
Question 18.
List any four symptoms of sexual transmitted diseases?
Answer:
Itching, fluid discharge, slight pain, swelling in the genital region.
![]()
Question 19.
What are sexually transmitted diseases?
Answer:
Disease or infections which are transmitted through sexual intercourse with an infected person are called STDs or venereal disease. Ex. Gonorrhoea, Syphilis, Genital herpes, AIDS.
Infertility – A large number of couples over the world including India are infertile i e they are unable to produce children in spite of unprotected sexual cohabitation.
The reasons could be physical, congenital diseases, drugs, immunological or psychological. Hence couple. , could be assisted to have their own child through special techniques termed as Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART)
1. In – vitro Fertilization and Embryo Transfer (I.V.F-E.T) or test tube baby. In vitro fertilization takes place outside the body followed by embryo transfer. This method popularly termed as a Test tube baby programme involved a procedure in which ova from the wife and sperms from husband are collected and induced to form a zygote under simulated conditions in the laboratory.
2. ZIFT – Zygote intrafallopian transfer Zygote or early embryos (with upto 8 blastomeres) is then transferred into fallopian tube and embryos with more than 8 blastomeres into the uterus (Intrauterine transfer) or IUT.
3. (GIFT- Transfer of an ovum collected from a donor into the fallopian tube of another female who cannot produce one but can provide suitable environment for fertilisation is GIFT.
4. ICSI – Intracytoplasmic sperm injection is another procedure to form an embryo in the laboratory m which a sperm is directly injected into as ovum), (March 2016)
5. AI (Artificial insemination) is a technique in which the semen is collected either from husband Or a healthy donor and is artificially introduced either into the vagina or uterus of the female. All these techniques require extremely high precision handling by special professional
Question 20.
What is infertility?
Answer:
Inability to produce a child or inability to conceive (pregnancy) is called infertility.
Question 21.
Expand the following terms?
Answer:
- GIFT-Gamete Intrafallopian transfer
- ZIFT- Zygote Intrafallopian transfer
- IVF-ET-Invitro fertilization-embryo transfer technique
- ICSI- Intra Cytoplasmic sperm injection
![]()
Question 22.
What is population explosion? Mention the causes, effects, and control of overpopulation?
Answer:
Population explosion is the sudden increase in population.
Causes:
- The decline in death rate.
- The decline in Maternal Mortality Rate (MMR) and Infant Mortality Rate (IMR).
- Increase in the number of people in reproducible age.
Effects:
- Absolute scarcity can occur of the basic requirements i.e., food, shelter and clothing.
- 2 It might also lead to poor conditions of living.
Control of Population:
- The motivation of smaller families by using several contraceptive methods.
- To have two children. Every couple must follow the slogan Hum Do Hamare Do.
- The marriageable age should be raised and in female it should be 18years and in case of males it should be 21 years.
- Incentives should be given to couple with small families.
→ Definition:
W.H.O (World Health Organisation) defines reproductive health as a means of total well-being in all aspects o Reproduction i.e. physical, emotional, social and behavioral
Reproductive Health – Problems and strategies various problem and strategies of reproductive health are
- Overpopulation
- Sex education
- Knowledge about birth control methods and care of mother and child
- Awareness about social evils.
→ Sex Education:
- The introduction of sex education in schools and colleges is a step to disseminate right information to adolescents about reproductive organs, secondary sexual characters.
- Adolescence and related changes safe and hygienic sexual practices, sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) etc.
- This knowledge will save the young people from myths and misconceptions about sex related aspects and help them to lead a reproductively healthy life later.
- Awareness About Social Evils: Creating awareness about consequences of uncontrolled population growth and social evils like sex abuse and sex related crimes is another important aspects of RCH programme.
→ Implementation of Reproductive Health:
- Successful implementation of various action plans for maintaining reproductive health requires strong infrastructural facilities, professional expertise and material support.
- Medical assistance and care should be provided to people in reproductive age.
- Related problems, pregnancy, delivery, STDs, abortions, Contraception, menstrual problems, infertility etc.
- Statutory ban should be there on amniocentesis for sex determination to legally check increasing female foeticide.
- Research on various reproduction-related areas are encouraged and supported by Governmental and non- Governmental agencies to find new methods.
- Better awareness about sex-related matters increased no. of medically assisted deliveries, better post natal care lead to decreased maternal and infant mortality rate. Increased no. of couples with small families’ better detection and care of STDs and overall increase medical facilities for all sex-related problems.
→ Population Explosion And Birth Control:
- Population increased significantly due to increased health condition. World population which was around 2 billion in 1900 increased to 6 Billon by 2000.
- A rapid decline in death rate maternal mortality rate (MMR) and infant mortality rate (IMR) and an increase in number of people in reproducible age are reasons for this.
- Most important step to overcome this problem is to motivate smaller families by using contraceptive methods.
- Advertisements in the media, as well as posters, show a happy couple with a slogan Hum do Hamaare do.
- Rise of marriageable age of female to 18years and males to 21 years and incentives given to couples with small families are two of other measures taken to solve this problem.
![]()
→ Family Planning:
Planning for a small family by adopting scientific method of birth control is called family planning Contraceptive methods can be broadly divided into
- Temporary method
- Permanent method
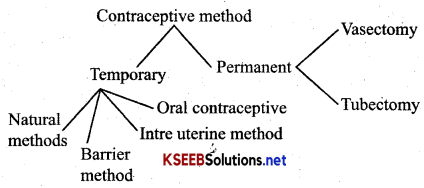
Natural methods are of 3 types
- Periodic abstinence.
- Withdrawal or coitus interruptus.
- Lactational amenorrhoea.
1. Periodic abstinence is a method in which couples avoid or abstain from coitus from 10-17* of the menstrual cycle when ovulation is expected.
2. Withdrawal or coitus interruptus is another method in which the partner withdraws his penis from vagina just before ejaculation to avoid insemination.
3. Lactational Amenorrhea :
1. It is an absence of menstruation and the fact that menstrual cycle does not occur during the period of intense lactation following parturition. As long as mother breastfeeds the child the chances of conception are almost nil.
2. In barrier methods ovum and sperms are prevented from physically meeting with the help of barrier methods available for both males and females. Condoms are the barriers made of thin latex sheath and used to cover the penis in male, vagina and cervix in females just before coitus so that the ejaculated semen would not enter into reproductive tract.
3. Condoms are also used to protect the user from contracting STD’s and AIDS. Diaphragms cervical caps and vaults are also barriers made of rubber capsand insertedinto female reproductive tract to cover the cervix during coitus. They block entry of sperms through cervix.
4. I.U.D are intra uterine devices inserted in the uterus through the vagina. I.U.D’s are available as non-medicated IUDs (Lippe’s loop) Cu releasing IUDs (Cu T, Cu 7, Multiload 375), hormone-releasing IUDs (Progestasert, LNG-20). IUDs increase phagocytosis of sperms within the uterus and Cu ions suppress sperm motility. Hormone releasing IUD’s make the uterus unsuitable for implantation and cervix hostile to the sperms.).
5. Oral Contraception – It includes administration of small doses of progestogens or progestogen/estrogen combinations and it is a contraceptive method used by females. They are used in the form of tablets called pills. Pills have to be taken for a period of 21 days starting from within first five days of menstrual cycle. After 7days during which menstruation occurs the pattern has to be repeated till female’s desires to prevent conception. Sahctius is a famous oral pill.
6. Progesterone alone or in combination with estrogen can be used by females as injection or implants under the skin.
![]()
→ Permanent Methods/Surgical Methods:
(Surgical methods also called sterilisation are terminal methods to prevent pregnancies. Sterilisation procedure in male is termed as vasectomy and in females it is tubectomy. In vasectomy a small part of the vas deferens is removed or tied up through a small incision on the scrotum. In tubectomy a small part of the fallopian tube is removed or tied up through a small incision in the abdomen or through the vagina.)
→ Sexually Transmitted Disease (Stds):
Diseases or infections which are transmitted through sexual intercourse with an infected person are collectively called STDs or venereal disease or reproductive tract Infections (RTI).
Some of the STDs are
(a) Gonorrhoea
(b) Syphilis
(c) Genital herpes
(d) Chlamydiosis
(e) Genital warts
(f) Trichomoniasis
(g) Hepatitis
(h) AIDS.
→ Mode Of Transmissions:
- Sexual contact with infected persons.
- Sharing of infected needles, surgical instruments with infected persons.
- Transfusion of contaminated blood.
- STDs can be transmitted from an infected mother to the foetus.
→ Common Symptoms of Stds:
- Itching, fluid discharge, slight pain, swelling etc, in the genital region
- Infected females may be asymptomatic for a long time.
- Social stigma attached to STDs deters the infected persons from going for proper treatment.
- Complications that can occur later includes pelvic inflammatory disease, abortion, ectopic pregnancy, infertility, cancer of reproductive tract.