Karnataka 2nd PUC Biology Important Questions Chapter 7 Evolution
Question 1.
Define evolution?
Answer:
It is descent with modification.
Question 2.
What does Big bang theory states?
Answer:
It states that single large explosion created the universe.
Question 3.
Who proposed the chemical evolution of life?
Answer:
Oparin of Russia and Haldane of England gave the chemical evolution of life.
Question 4.
Define the theory of A biogenesis?
Answer:
It states that life originated from non living material spontaneously and continuously.
![]()
Question 5.
Name the Biologist who demonstrated experiments and proved that life comes from pre existing life?
Answer:
Louis Pasteur.
Question 6.
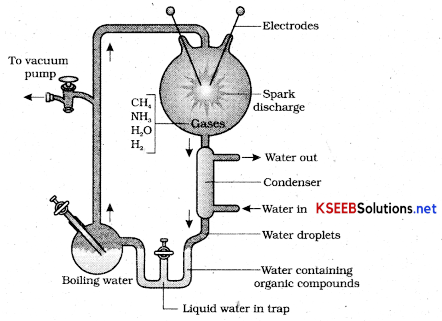
Give the diagrammatic representation of Stanley Millers Experiment
Answer:
Stanley Miller and Urey created electric discharge in a closed flask containing CH4, N2, NH3 and water vapour at 800C. He observed formation of amino acids.
This experiments justifies that organic molecules could be formed from the primitive gases on the pri mordial earth.
Question 7.
What are homologous organs? Give an example each from plants and animals?
Answer:
Homologous organs are organs whose origin or structure is same but they are functionally different. Ex. Forelimbs of whales, bats, cheetah share similarity in pattern of forelimbs bones but perfonn different functions. Ex. Thoms and tendrils of Bougainvillea cucurbita and cucurbit have same origin but different functions – Thoms are defensive in function where as tendrils help the plant in climbing.
Question 8.
What are analogous organs? Give an example from plants and animals?
Answer:
Analogous organs are organs whose origin is different but they perform same function.
Ex. Flippers of penguin and dolphins have different structure but perform the function of flight Ex. Wings of bird and butterfly are not anatomically similar but perform similar function.
Question 9.
What is Adaptive radiation?
Answer:
Process of evolution of different species in a given geographical area starting from a point and literally radiating to other areas of geography (habitats) is called adaptive radiation. Ex. Darwinian finches.
![]()
Question 10.
Industrial melanism in peppered moth is an excellent example of natural selection. Justify the statement.
Answer:
Evidence From Natural Selection:
A supporting evolution for natural selection comes from England. In a collection of moths made in 1850’s i.e., before industrialization sets in, it was observed that those were more white winged moths on trees than dark winged or raelanised moths.
But after industrialization it was found that there were more dark winged moths in the same area so the proportion was reversed.
Predators will spot a moth against a contrasting background. Before industrial revolution the grey colored or white moth were more because lichens are light in color and they got deposited on trees so white winged moth got camouflaged.
After Industrial revolution due to soot deposition population of dark winged or melanised moth increased as white winged moth were traced
Excess use of herbicides, pesticides only resulted in selection of resistant varieties. It is true for microbes against which we employ antibiotics or drugs against eukaryotic organisms/cells.
Question 11.
State Hardy Weinberg principle?
Answer:
It states that the allelic frequencies in a population are stable and constant from one generation to another generation.
Question 12.
Name the five factors which effect Hardy Weinberg equilibrium?
Answer:
The factors which affect the Hardy Weinberg equilibrium are gene flow, gene migration, genetic drift, mutation, genetic recombination, natural selection.
Question 13.
What is saltation
Answer:
Single large step in mutation is saltation.
![]()
Question 14.
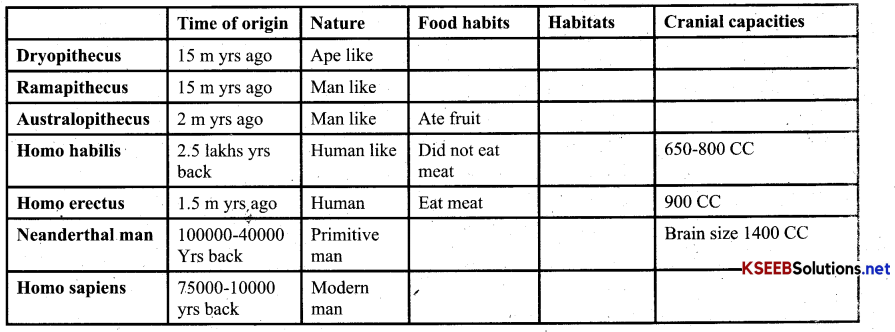
Mention the time of origin, nature, food habits, habitats, cranial capacities of following hominids?
Answer:
- Drvopithclus
- RamapIhecus
- Australopithecus
- Homo hairs
- Homo erectus
- Neanderthal man
- Homo sapiens.
→ Evolution:
Biological evolution is descent with modification.
→ Origin of Universe:
- Universe is very old almost 20 Billion years.
- Huge clusters of galaxies comprise the universe.
- Galaxies contain stars and clouds of gas and dust.
- According to Big bang theory single large explosion created the universe. .
- As the universe expanded and cooled materials condensed under the influence of gravity to form stars and planets.
- Earth is among the 8 planets revolving round the sun
- Earth is formed 4.5 billion years back.
→ Theory of Panspermia:
Some scientists believed that life came from outside. Early Greek thinkers thought units of life called spores were transferred to different planets including Earth. ‘Panspermia’ is a favourite idea of astronomers.
→ Theory of a Biogenesis:
- It states that life originated from non living material continuously and spontaneously.
- This theory states that life came out of decaying and rotting matter like straw, mud etc.
→ Theory of Biogenesis:
It states that life comes from pre existing life. This theoiy was given by a scientist Louis Pasteur. He showed that in pre sterilized flasks, life did not come from killed yeast while in another flask open to air new organisms arose from killed yeast.
![]()
→ Theory of Chemical Evolution of Life:nd. This theory states that life was preceded by chemical evolution i.e., formation of divers organic molecules from inorganic constituents.
→ Evolution of Life Forms – A Theory:
Charles Darwin made a sea voyage in a ship called H.M.S Beagle. Any population has built in variation in characteristics. Those characteristics which enable some to survive better in natural conditions would out breed others that are less endowed to survive under natural conditions.
Fitness as per Darwin is reproductive fitness which means those who are better fit in an environment leave more progeny than others. They will survive more and are selected by nature. This is called as selection.
→ Evidence of Evolution:
Comparative anatomy and Morphology- It includes both homologous and Analogous organs.
Homologous organs have same origin but perform different functions. Whales, bats, cheetah and human (all mammals) share similarities in the pattern of bones of forelimbs but function is different. In whales forelimbs helps in swimming, in bats forelimbs helps in fight. In cheetah and human forelimbs help, in running. Thus homologous organs show divergent evolution.
Analogous organs have different origin but perform same function. Wings of butterfly and birds look alike perform same function but their structure is different. Analogous structures are a result of convergent evolution. Other examples of analogy are eye of octopus and of mammals or the flippers of penguins and dolphins.
→ Fossil Evidence / Evidence From Paleontology:
Fossils are remains of hard parts of life forms found in rocks. Different aged rock sediments contain fossils of different life forms that died during the formation of particular sediment. A study of fossils in different sedimentary layers indicates geological period in which they existed.
→ Evidence From Natural Selection:
A supporting evolution for natural selection comes from England. In a collection of moths made in 1850’s i.e., before industrialization sets in, it was observed that those were more white winged moths on trees than dark-winged or raelanised moths.
But after industrialization it was found that there were more dark winged moths in the same area so the proportion was reversed.
Predators will spot a moth against a contrasting background. Before industrial revolution the grey colored or white moth were more because lichens are light in color and they got deposited on trees so white winged moth got camouflaged.
After Industrial revolution due to soot deposition population of dark winged or melanised moth increased as white-winged moth were traced
Excess use of herbicides, pesticides only resulted in selection of resistant varieties. It is true for microbes against which we employ antibiotics or drugs against eukaryotic organisms/cells.
→ Biological Evolution:
Branching descent and natural selection are the two key concepts of Darwinian theory of evolution.
Lamarck gave the theory of use and disuse of orgHe gave the example of Giraffe. Giraffe used to raise its neck to reach the leaves of trees. Slowly giraffe had a long neck.
![]()
→ Mechanism Of Evolution:
Hugo Devries based on his work on evening primrose. Evolution of Darwin is gradual while Devries believed mutation caused speciation and hence it is saltation (single length step in mutation).
→ Hardy Weinberg Principle:
It states that allelic frequencies in a population are stable and constant from one generation to another. It is represented by binomial equation (p + q)2 = p2 + 2pq + q2. Five factors are known to affect Hardy Weinberg equilibrium. These are gene migration or gene flow, gehetic drift mutation, genetic recombination, natural selection. When migration of a section of population to another place occurs gene frequencies change in the original as well as in the new population. New genes 7 alleles are added to the new population and lost from the old population. Sometimes the change in allelic frequency is so different in the new population that they become a different species. The original drifted population becomes founders and the effect is founder’s effect.
→ Origin And Evolution of Man:
About 15 millidn years ago primates called Dryopithecus and Ramapithecus were existing. They were hairy and walked like gorillas and chimpanzees.
Ramapithecus were more man like while Dryopithecus were ape like. Few fossils of man like bones have been discovered in Ethiopia and Tanzania. These revealed hominid features leading to the belief that about 3-4 mya ago, man like primates walked in Eastern Africa. They were not taller than 4 feet but walked upright.
Two million years ago Australopithecines lived in east African grasslands. Evidence showed they hunted with stone weapons but ate fruit. This creature was called hominid and was called Homo habilis. Brain capacity was between 650 – 800 CC. they did not eat meat.
Fossils discovered in Java in 1891 revealed the next stage i.e. Homo erectus about 1.5 million years ago. Homo erectus had a large brain around 900 CC. they ate meat.
Meanwhile Neanderthal man had a brain size of 1400CC and lived in east and central Asia between 1,00,000 – 40,000 years back. They used hides to protect their body and buried their dead.
Homo sapiens arose in Africa. During ice age between 75,000-10,000 years ago modem Homo sapiens arose. Pre historic cave art developed 15000 years ago. Agriculture and human settlement started.