Karnataka 2nd PUC Biology Important Questions Chapter 8 Human Health and Disease
Question 1.
What is disease? Mention two types with examples.
Answer:
Disease: Impaired physiological functioning of the body due to impairment, characterised by various signs and symptoms.
- Infectious diseases: Transmitted easily from one person to another. Ex: viral, Bacterial, Fungal etc.
- Non-infectious diseases: Diseases which do not transmit. Ex: Allergies, Genetic disorders, Cancer etc.
Question 2.
Define pathogen
Answer:
Pathogen → Disease causing organisms. They make entry into host, withstand hosts defence mechanism multiply and survive.
Question 3.
Name the causative orgapism of Typhoid?
Answer:
Pathogen – Salmonella typhii, Host – Children, Man’s intestine
Question 4.
Mention the symptoms of typhoid?
Answer:
Symptoms: High fever (39-40° C) head ache, weakness, liver and spleen enlargement. Intestinal perforation leads to death.
Question 5.
Name the confirmatory test for typhoid?
Answer:
Confirmed by test – Widal test.
Question 6.
Write the mode of transmission of typhoid.
Answer:
- Transmission: Through contaminated water and food, insects, house fly etc.,
- Classic Case: Mary Mallon – She was a typhoid carrier, who continued to spread typhoid through food she served.
- Prevention: By good sanitation, cleanliness.
Question 7.
Name the pathogen of pneumonia? Mode of infection.
Answer:
Pathogen: Streptococcus pneumoniae. Haemophilus influenza. Host: Human, (in alveoli of lungs)
Question 8.
Write the symptoms of pneumonia?
Answer:
- Symptoms: Persistent dry cough, high fever, chest pain, head ache, alveoli get filled with fluid. Breath
- Shortness. In severe cases, lips and finger nails turn grey to bluish in colour, which is known as Cyanosis.
- Transmission: Spreads by sputum of the patient, A healthy person acquires the infection by inhaling air born pathogens released by infected person.
![]()
Question 9.
How Pneumonia is prevented?
Answer:
Prevention: Vaccination (Pneumococcal), hygienic habits.
Question 10.
Name the disease caused by Rhinovirus and write its symptoms?
Answer:
- Disease: Common Cold.
- Host: Man (Nose and respiratory passage)
- Symptoms: Sore throat, hoarseness, cough nasal congestion,
- Transmission: Inhalation of droplets from cough and sneezes of an infected person, Contact with mucous contaminated objects like pen, book, keyboard, mouse etc,
- Prevention: Hygienic habits.
Question 11.
Name the causative organisms of Malaria?
Answer:
- Pathogen: Plasmodium vivax.
- P. falciparum causes malignant malaria which is fatal
Question 12.
Name the two hosts of Plasmodium?
Answer:
Host: Man and Mosquito
Question 13.
Write the symptoms of Malaria?
Answer:
Symptoms: Fever every 48/72 hrs, Cold, hot and sweating stages. On .chronic cases patients become anaemic and because of RBC destruction enlargement of liver and spleen may occur.
Question 14.
Name the insect vector which transmit malaria?
Answer:
Transmission: Female Anopheles mosquito acts as Vector which spreads disease from unhealthy to healthy person.
Question 15.
Give schematic representation of life cycle of Plasmodium?
Answer:
The life cycle of plasmodium (Malarial Parasite):
- Plasmodium enters the human body when mosquito (infected) of Anopheles) bites, as sporozoites (infection form).
- Parasites (Merozoites) multiply increase their no in liver cells and attack RBCs and results in rupturing of RBC, with the release of toxic substance Haemazoin which leads to the chills and fevers every 3 to 4 hours.
- These parasites enter the mosquito’s body when female Anopheles bites an infected person.
- Fertilisation and development of parasites takes place in mosquito gut and
- Matured sporozoites from gut migrate to salivary glands.
- When these mosquitoes bite human, sporozoites are injected to the body.
Question 16.
Name two hosts of plasmodium?
Answer:
Man Mosquitos.
Question 17.
Name the infectious stage of plasmodium?
Answer:
sporozoites.
Question 18.
Name the site of sexual reproduction of plasmodium?
Answer:
Female Anopheles mosquito.
Question 19.
Name the disease caused by Entamoeba histolytica?
Answer:
Disease: AMGEBIASIS (Amoebic dysentery).
![]()
Question 20.
Name the pathogen which causes Amoebic dysentry?
Answer:
- Pathogen: Entamoeba histolytica
- Host: Large intestine of man.
Question 21.
Write the symptoms of Amoebiasis?
Answer:
Symptoms: Constipation, abdominal pain, Cramps, stools with excess mueous and blood clots.
Question 22.
Write the mode of infection of Amoebiasis?
Answer:
Transmission: Through house flies, which carry parasite by faeces of infected person to food products and water.
Question 23.
How do you prevent Amoebiasis?
Answer:
Prevention: Hygienic habits.
Question 24.
Name the causative organism of Ascariasis?
Answer:
Ascaris lumbricoides.
Question 25.
Name the disease caused by Ascaris lumbricoides?
Answer:
Pathogen: Ascariasis Host: Man’s intestine.
Question 26.
Mention symptoms of Ascariasis?
Answer:
- Symptoms: Internal bleeding, muscular pain, fever, blockage of intestinal passage, anaemia.
- Transmission: Through faeces of infected persons which contaminate soil, water, plants etc. A healthy person acquires this infection through unwashed vegetables, fruits etc.
![]()
Question 27.
Name the pathogen, vector and a symptom of filariasis
Answer:
- Pathogen: Wuchereria bancrofti
- Host: Man.
- Disease: Elephantiasis/Filariasis
- Symptoms: Chronic inflammation of the organs in which they live. The lymphatic vessels of the lower limbs, genital organs are affected resulting in gross deformities.
Question 28.
Name the pathogen which causes elephantiasis?
Answer:
- Pathogen: Wuchereria bancrofti
- Host: Man.
Question 29.
Name the disease caused by Wuchereria Bancroft?
Answer:
Disease: Elephantiasis/Filariasis
Question 30.
Mention a few symptoms of Filariasis?
Answer:
Symptoms: Chronic inflammation of the organs in which they live. The lymphatic vessels of the lower limbs, genital organs are affected resulting in gross deformities.
Question 31.
Write the mode of infection of Filariasis?
Answer:
Transmission: Through female culex mosquito vectors.
Question 32.
Name the disease caused by Trichophyton?
Answer:
Disease: Ringworm (infectious disease).
Question 33.
Name the pathogen which causes Ring worm disease?
Answer:
Pathogen: Microsporum, Trichophyton, Epidermophyton are pathogens.
Host: Man
Question 34.
Mention symptoms of ring worm disease?
Answer:
Symptoms: Dry scaly lesions on skin, nails and scalp. Itchy reddish rashes, in shape of ring, Heat and moisture help these fungi to grow.
In Face and neck – Barbar’s itch. Foot-Athlet’s foot.
Transmission: Heat and moisture help these fungi to grow between toes, skin folds, groin. Ringworms are acquired by soil or using towels clothes, combs of infected individuals.
![]()
Question 35.
Write a note on public health measures?
Answer:
1. Maintenance of public hygiene and personal hygiene
| Public Hygiene | Personal Hygiene |
| Proper disposal of waste and excreta. Periodic cleaning of water reservoirs, pools, tanks. | Keeping the body clean, consumption of clean drinking water, food, vegetables, fruits etc. Close contact with infected persons are avoided. |
2. Awareness: Quare of infectious diseases – transmission, infection and preventive measures.
3. For air born diseases: like pneumonia and cold contact with infected persons should be avoided.
4. For vector-mediated diseases like Malaria and Filariasis
- Control and eliminate breeding places (stagnant water) in and around residential areas.
- Mosquito nets, spraying insecticides
- Introducing fishes like Gambusia which feeds on mosquito larvae.
- Doors and windows should be provided with mesh.
5. Vaccination: Vaccines and immunisation – to eradicate diseases complete eradication done – smallpox.
Polio, pneumonia, tetanus is controlled.
Biotechnology newer and safer vaccines.
Question 36.
Mention the preventive measures for vector-borne diseases?
Answer:
“The ability of the host to fight against the disease-causing organisms due to immune system in the body”,
i. e, resistance to disease.
Question 37.
Define Immunity and mention its types?
Answer:
Immunity- 2 types
- Innate Immunity.
- Acquired Immunity.
Question 38.
What is Innate immunity? Explain the 4 types?
Answer:
It is the non-specific type of defence, present by birth. It provides different types of barriers to the entry of foreign agents to our body. They are of 4 types of Barriers.
- Physical Barriers
- Physiological Barriers
- Cellular Barriers
- Cytakine Barriers
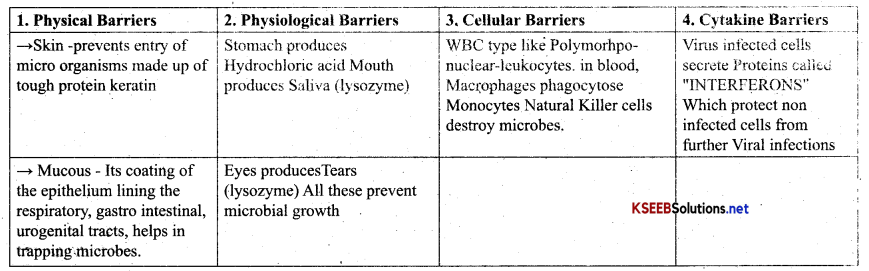
Question 39.
What is Acquired immunity?
Answer:
Acquired immunity: “It is pathogen-specific immunity developed by our body in response to diseases by microbes. It is characterised by memory”.
The body will be having a memory of the first encounter called primary response with low intensity, subsequent attacks by the same pathogen will encounter with the secondary response with high intensity, because of memory or first encounter.
Question 40.
Difference between innate immunity and acquired immunity?
Answer:
| Innate Immunity | Acquired Immunity |
| 1. It is called inborn immunity | 1. It is called Adaptive immunity. |
| 2. It is present since birth. | 2. It is developed during life time. |
| 3. Remains throughout life. | 3. Short lived or life long |
Question 41.
Differentiate between B lymphocytes and T lymphocytes?
Answer:
| B-lymphocytes | T-lymphocytes |
| 1. Originate in the bone marrow and differentiate there itself and gets matured into B-lymphocytes | 1. Originate in the bone marrow and migrate to thymus gland and mature into T- lymphocytes. |
| 2. Produce antibodies in the blood in response to pathogens. (Antibody-mediated immune system -AMIS) | 2. do not produce antibodies but help B-lymphocytes to produce anti Bodies. (Cell-mediated immune system-CMlS). |
| 3. Operate through humoral immune response (i.e., thro1 blood) | 3. Operate through cells. |
Question 42.
Which type of immune system is responsible for graft rejection?
Answer:
Cell-mediated immune system.
Question 43.
Draw the well-labelled diagram of an antibody molecule?
Answer:
Structure of Antibody Molecule:
Each antibody molecule has four peptide chins – 2 small Light Chains. -2 Longer heavy chains, so represented as H2 L2 these 4 chains are lead together by disulphide bonds. This antibody is a ‘ Y’ shaped protein molecule whose surface ‘shape’ reacts with antigen.
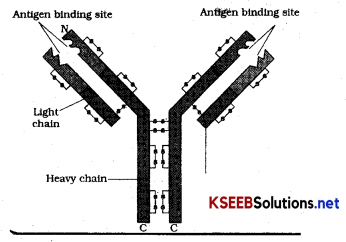
![]()
Question 44.
Differentiate between Active and Passive immunity?
Answer:
| Active immunity | Passive immunity |
| 1. Developed when host is exposed to antigens, and antibodies are produced naturally. | 1. Developed when ready made antibodies are given to protect the body against pathogens. |
| 2. Slow and takes time to give its full response and lasts longer. | 2. Fast gives short lived immunity. |
| 3. Antibody produced harmless | 3. Harmful |
| 4. Effective on large no of infections | 4. Effective only on limited infections. |
Question 45.
What is colostrum? Mention its importance.
Answer:
Ex: In Mother initial days of lactation, contain Colostrum, which has (IgA) antibodies to protect the infant.
Question 46.
Name the antibody passed from mother to foetus through placenta? (1M)
Answer:
Foetus receives antibodies (IgG) from mother through placenta.
Question 47.
Differentiate between Vaccination and Immunisation?
Answer:
| Vaccination |
Immunisation |
| 1. The process of introduction of inactivated/ weakened pathogen into a healthy person to produce immunity. | 1. The process by which body produces antibodies against the vaccine (Primary response) and develop the ability to neutralise pathogens during actual infection (Secondary response) |
| 2. Vaccines generate memory B and T cells and produce quick immune response and increase antibody production |
Question 48.
Passive immunization is required for snake venom. Why?
Answer:
If quick response is required like tetanus antibodies and antitoxins are directly injected. Snake bites-injection contain preformed antibodies against snake venom. —> passive immunisation.
Question 49.
Name vaccine produced in micobes thro Rec DNA technology.
Answer:
Recent Rec. DNA teck, allowed production of antigens of pathogen in bacteria or yeast.
Ex: hepatitis B vaccine produced from yeast.
Question 50.
Define Allergy?
Answer:
Allergy: The exaggerated response of the immune system to certain antigen (foreign substance) percent in the environment.
![]()
Question 51.
What are allergens?
Answer:
Allergens: The substances in response to immune system.
Question 52.
Name the antibody produced during Allergy?
Answer:
- Antibodies produce for allergy are of IgE type, for example dust pollens, animal dander etc. .
- Allergy is due to the production of chemicals like Histamine and serotonin from the mast calls.
- Determining cause of allergy, patient is exposed to allergens in tiny, increasing doses and reactions are studied.
Question 53.
Name the drugs for Allergy?
Answer:
Drugs: Antihistamine, Adrenalin and Steroids.
Question 54.
Why children in metro city are sensitive to allergies?
Answer:
More children in metro-cities sensitivity to allergens due to protected environment provided early in life.
Question 55.
Define Auto immunity. Give an example?
Answer:
Our own immune system attacks healthy cells in our body by mistake, (attack self cells), due to genetic or unknown reasons, which results in damage to the body.
Ex: Rheumatoid Arthritis.
![]()
Question 56.
What are lymphoid organs?
Answer:
Lymphoid organs: Organs where origin, maturation and proliferation of lymphocytes occur.
Primary lymphoid organs- Bone marrow and Thymus, these are the organs where immature lymphocytes undergo differentiation and maturation. After maturation they migrate to secondary lymphoid organs (spleen, lymphnodes, tonsils., Peyer’s patches of small intestine and appendix) and become effector cells. (Secondary’ . lymphoid organs).
Question 57.
Name the main lymphoid organ where lymphocytes are produced?
Answer:
Bone marrow → Main lymphoid organ – Lymphocytes and blood cells produced.
Question 58.
Define Thymus gland?
Answer:
Thymus → lobed organ located near the heart, beneath breast bone.
(Larger in size (birth time) grow (puberty) later degenerates.)
Question 59.
Name the graveyard of blood?
Answer:
Spleen: Graveyard of blood – filter blood from microbes. It acts by phagocytosis.
Question 60.
What are lymphnodes? Mention its function.
Answer:
Lymphnodes: Small nodes, solid structures located at different points along lymphatic system. Filters micro- organisms and antigens which activate lymphocytes.
Lymphoid tissue present in lining of major respiratory, digestive and urogenital tracts called as
Question 61.
Expand MALT and GALT?
Answer:
Mucus Associated LymphatimTissue (MALT); GALT → Gut Associated Lymphoid Tissue.
Question 62.
Expand AIDS?
Answer:
Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome. First reported in 1981.
Question 63.
Name the pathogen which causes AIDS?
Answer:
Pathogen → Human Immuno Deficiency Virus (HIV).
Question 64.
Name the virus group to which the AIDS belongs to?
Answer:
Belongs to Retroviruses (RNA is genetic material).
![]()
Question 65.
Write the mode of transmission of AIDS?
Answer:
Transmission: Sexual contact with infected person, multiple see partners Blood transfusion, injected needles (drug addicts) Injected mother to her child through placenta, spread through body fluids.
Question 66.
Mention the symptoms of AIDS?
Answer:
Symptoms: 5-10 years after infection. Fever, diarrhoea, weight loss couldn’t overcome infections like viruses ” fungi mycobacterium and parasite like Toxoplasma. Immuno defecient.
Question 67.
Draw a neat labelled diagram of RNA replication in humans?
Answer:
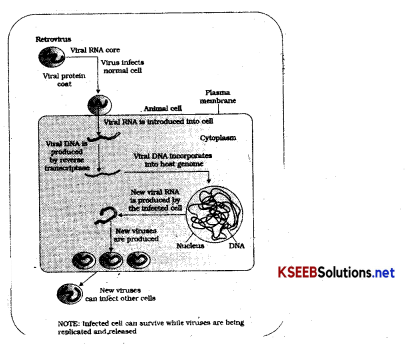
Question 68.
Explain mode of replication of HIV in humans?
Answer:
- When virus enters the body it enters into macrophages, where viral RNA is converted into DNA by reverse transcriptase.
- Viral DNA gets incorporated into host cell’s DNA and directs host DNA to produce viral RNA copies are released as viral particles.
- The infected cells break open and released virus infect new cells (Tlym)
- This process is repeated and leads to deerese in no of helper flymphin infected person.
Question 69.
Name the diagnostic test for AIDS?
Answer:
ELISA – (Enzyme Linked Immuno Sorbant Assay) Test Anti retro viral drugs ate partially effective, which can prolong life, but cannot prevent death.
Question 70.
Write the preventive measures of AIDS?
Answer:
No cure, prevention is the best option national AIDS control organisation (NGO) people world hea’ organisation (WHO) – programmes. Prevention by using disposable syringes, needles, free distribution e condoms, controlling drug abuse, regular check-ups etc.
Question 71.
Define Cancer?
Answer:
“Condition in which there is uncontrolled cell division resulting in the abnormal growth of excess tissue”
Question 72.
List any three types of cancer cells?
Answer:
Characters of Cancer cells:
- Absence of contact inhibition.
- Uncontrolled cell division.
- Give rise to tumours.
- It may show metastasis.
Question 73.
Differentiate between Benign and Malignant tumours?
Answer:
|
Benign |
Malignant |
| 1. Confined to original location do not spread to other parts | 1. Proliferating neoplastic/tumour cells spread rapidly and damage surrounding tissues (normal) |
| 2. Non-Fatal | 2. Fatal |
Question 74.
Define Metastasis? (1M) Why it is fatal.
Answer:
Metastasis- Character of malignant tumours. The process of carrying malignant tumour cells, times to other parts along with blood and where ever they are lodged they produce a new tumour.
Question 75.
What are Carcinogens?
Answer:
Cancer-causing agents – Carcinogens
![]()
Question 76.
Classify carcinogens for example?
Answer:

Oncogenic viruses have genes called viral oncogenes.
Question 77.
Describe the methods of detection of Cancer?
Answer:
- Biopsy-where piece of suspected tissue cut into thin section, stained and examined.
- Histopathological studies-tissues, blood, bone marrow
- Techniques- Xrays, CT, MRT for detection in Internal organs. CT uses 3D image MRI uses strong
magnetic fields and non-ionising radiations to accurately detection. - Antibodies against Cancer-specific antigens
- Molecular biology-to detect genes.
Question 78.
Write a note on the treatment of Cancer?
Answer:
Treatment of Cancer
- Surgery (Benign tumours)
- Radiation therapy-tumour cells are irradiated lethally.
Chemotherapy – kill cancerous cells.
The majority of drugs have side effects – hair loss, anaemia, etc. Since tumour cells avoid the immune system. Helps in activating the immune system and destroy tumours
Question 79.
Name the biological response Immuno therapy modifier in treatment of Cancer?
Answer:
Patients are given biological response modifiers-a interferon.
Question 80.
Define drug and drug abuse?
Answer:
Drug: Any chemical compound that alters the biochemical or physiological process of tissue or organisms. When these drugs taken neither approved nor supervised by medical professionals – it is known as Drug abuse.
Commonly abused drugs.
Question 81.
Name the source of Opioids?
Answer:
Opioids: Extracted from the latex of poppy plant-Papaver Somniferum. These are Drugs that bind to receptors in our CNS and gastrointestinal tract.
Question 82.
What is Morphine?
Answer:
Morphine is a main alkaloid or Opium, by (Morphine is used as painkiller and sedative)acetylation of this.
Question 83.
What is SMACK? Give its ill-effects of drug abuse.
Answer:
Heroin (SMACK or brown sugar) diacetylmorphine, is produced which is a bitter, crystalline compound. It acts as a depressant and slows down body function. Taken by snorting and injection.
![]()
Question 84.
What are cannabinoids and name the products?
Answer:
2 Cannabinoids: → Group of chemicals, interact with cannabinoid receptors in the brain.
Extracted from the inflorescence of Cannabis sativa. Marijuana, Hashish, (Charas) and Ganja.
Effect on the cardiovascular system of the body.
Taken by inhalation and orally.
Question 85.
Name the source of cocaine?
Answer:
3 COCAINE → Extracted from Erythroxylum coca.
Question 86.
Write a note on action of cocaine on human body?
Answer:
Interferes with the transport of neurotransmitter Dopamine.
Stimulate CNS Known as Coke or Crack.
Taken by snorting Excess dosage-Hallucination
Question 87.
Name the plants which have hallucinogenic properties?
Answer:
Atropa belladonna and Datura – Hallucinogenic properties.
| Drugs like Barbiturates amphetamines (LSD) Lysergicacid Diethylamides | Medicines are given for mental illnesses like depression and insomnia. |
Question 88.
Name the source of Nicotine?
Answer:
NICOTINE → from Tobacco plant-Nicotiana tabaecum
Question 89.
Write the effect of nicotine on human body?
Answer:
- Stimulates adrenal gland to release adrenaline and noradrenaline into blood which increace heart rate, and BP.
- Smoking → Cancers of lung, throat, urinary bladder causing → oral cancer. Smoking increases carbon monoxide in blood and causes deficiency of O2 in the body.
Question 90.
Write the source and effect on the human body of the following drugs? Morphine, Cocaine, Marijuana?
Answer:
Adolescence and Drug/Alcohol Abuse
Child → Maturity process and period – leads to adolescence. Vulnerable phase of mental and psychological development, with curiosity, adventure, excitement and experimentation push towards abuses. Less supportive family → leads to abuse. If under pressure and stress in studies – it leads persuade to try alcohol and drugs.
Media promote this perception.
Addiction and Dependence
Because of known benefits – drugs are frequently used
![]()
Question 91.
Define addiction?
Answer:
Addiction: A sense of craving for anything which interferes with a person’s ability to function normally.
It is a psychological attachment to certain effects. When their effects (Temporary well being or euphoria) and their use become self-destructive.
Even once the use of these drugs leads to greater addiction, one becomes dependent on their use.
Question 92.
What is withdrawal syndrome?
Answer:
Dependence-Tendency of the body to experience unpleasant symptoms when dose of drugs/alcohol (regular) is abruptly discontinued is with drawl syndrome.
But relieved when use is resumed again. This withdrawal syndrome is characterised by-Anxiety shakiness, Nausea, sweating etc. and the person may need medical supervision.
Patient suffers from severe withdrawal syndrome, which makes him/her to ignore all social norms in order to get needs.
Question 93.
Mention the harmful effects of drugs/Alcohol?
Answer:
- Drug: Violence, Damage heart, liver, brain, Overdose leads to death. Intravenous injection-AIDS and Hep B.
- Alcohol: Liver’ disease-Cirrhoses (stores fat instead of glycogen) BP, Heart attack, Nervous system and circulatory system is affected.
Question 94.
Write a note of misuse of drugs?
Answer:
Misuse of Drugs
Sportspersons to enhance their performance.
Steroids in females-depression, menstrual cycle impaired, masculine characters.
Males: It makes acne, causes aggressiveness, decreased sperm production, Baldness and enlargement of prostate gland stunted growth in males and females.
Question 95.
Write a note on preventive and control measures of drug and alcohol abuse? (March 2014)
Answer:
Prevention and Control:
- Avoid undue peer pressure: No child should be pressurised to perform beyond his/her limits in studies/sports/ activities
- Education and Counselling!’ Channelise child’s energy into healthy pursuits like sports, reading, music and Yoga.
- Seeking help from parents and peers: Guidance, advice, keeping away from friends who indulges them for abuse.
- Looking for danger signs: Parents and teachers should watch, friends should bring notice to parents.
- Seeking professional and medical help: help available from Qualified psychologists, psychiatrists and rehabilitation programmes. Detoxification programmes should be made available. With such help, the affected person get rid of problems completely to lead a normal and healthy life.
→ Health: State of complete physical, mental and social well being and not merely an absence of disease or infirmity
- People – Healthy – Efficient work → productivity increases → Economic prosperity.
- Health is affected by Impairment due to genetic disorders, infections lifestyles.
→ Immune System in The Body:
The immune system has the capacity to recognise the entry of antigens through all possible routes into the body and mobilise its cells to destroy them.