Karnataka 2nd PUC Business Studies Important Questions Chapter 11 Marketing Management
I. One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Define Market.
Answer:
According to Philip Kotler ‘A market is an area for potential exchanges’.
Question 2.
Name any one element of Marketing Mix.
Answer:
Price Mix.
Question 3.
Mention one function of Marketing.
Answer:
Pricing.
Question 4.
State a factor affecting pricing decision.
Answer:
Business Objectives.
Question 5.
Name a middleman in the channel of distribution.
Answer:
Wholesaler.
Question 6.
Name any one feature of advertisement
Answer:
It is a paid form of communication. The advertiser needs to pay to the communicator or the media for providing the space or time for exhibiting the message.
![]()
Question 7.
Mention any one essentials of an Advertisement Copy.
Answer:
Attention value.
Question 8.
State a feature of personal selling.
Answer:
Personoal selling is informative in nature. The seller or his representatives provide information about the product, its use and benefits to the prospective consumers.
Question 9.
What is a Brand?
Answer:
A brand is any name, letter or symbol which helps the customer to identify the product.
Question 10.
What is Price?
Answer:
Price represents the value of the product in terms of money.
Question 11.
State any one method of Sales Promotion.
Answer:
Discount, Free Samples.
Question 12.
State any one channel of distribution.
Answer:
Producer – Agent-Wholesaler-Retailer- Consumer channel.
Question 13.
Mention any one objective of advertising.
Answer:
To influence the behaviour of prospective buyers favourably towards the product or service of the firm.
![]()
Question 14.
Give an example for quantity gift.
Answer:
Offering one shirt free on the purchase of two shirts [Buy 2 get one free]
Question 15.
Mention any one of the elements of Product Mix.
Answer:
Branding.
Question 16.
Mention any one of the factors affecting Pricing Decisions.
Answer:
Cost of Production.
Question 17.
Mention any one channel of Distribution.
Answer:
Producer – Wholesaler – Retailer – Consumer.
Question 18.
Mention any one element of Promotion.
Answer:
Advertising.
Question 19.
Mention any one advantage of Advertising.
Answer:
To support personal selling.
![]()
Question 20.
Mention any one feature of Salesmanship.
Answer:
Personal selling is informative in nature.s
Question 21.
Mention any one quality of successful ‘ salesman.
Answer:
Good health and appearance.
Question 22.
Mention any one of the objects of Sales Promotion.
Answer:
To attract potential customers.
Question 23.
What is a Label?
Answer:
It is a piece of paper affixed on product which gives the information of the product.
Question 24.
What is Labelling?
Answer:
It refers to designing and affixing appropriate label to a product or its container.
![]()
Question 25.
Mention any one advantage of Advertising.
Answer:
Education to consumers about products.
II. Two Marks Question and Answers
Question 1.
What is Market?
Answer:
Market is an arrangement which provides opportunity of exchanging goods and services for money or money’s worth.
Question 2.
Name any two elements of Marketing Mix.
Answer:
(a) Product Mix
(b) Price Mix
Question 3.
What is Branding?
Answer:
A Brand is a name, term, symbol, mark or design or a combination of them which is intended to identify and differentiate products from other competitors in market.
Question 4.
State the meaning of Grading?
Answer:
It is a process of dividing the commodities into lots that have similar characteristics as to type, size, shape, weight, quality, performance etc.
Question 5.
What is Packing?
Answer:
It includes wrapping, filling or compressing of goods to protect them from spoilage, pilferage, breakage, leakage etc.,
![]()
Question 6.
What do you mean by Packaging?
Answer:
It involves designing and producing such appropriate packages for each unit of the product as well as for the bulk units of product.
Question 7.
What is Warranty?
Answer:
It is a written undertaking given by the producer to the customer, promising to repairs, exchange or replace the product if any manufacturing defects are found in the product within mentioned time period from the date of purchase.
Question 8.
What is Guarantee?
Answer:
It is a promise or assurance given by the manufactures about the quality and durability of a product and if there is any defect, the product will be repaired or replaced at free of charge.
Question 9.
What do you mean by Labelling?
Answer:
A label is a pieces, of information affixed on a product, labelling refers to designing and affixing appropriate label to a product or its container.
Question 10.
Give the meaning of Product?
Answer:
A product is a bundle of utilities consisting of various features and accompanying services.
Question 11.
What is Pricing?
Answer:
Pricing is a method adopted by a firm to set its selling price. It usually depends on firms strategies for pricing.
Question 12.
Give the meaning of Publicity?
Answer:
It is a movement of information with the effect of increasing public awareness about a product.
Question 13.
What is Advertising?
Answer:
Advertising is any paid form of non¬personal presentation and promotion ofgoods, services or ideas by an identified sponsor.
![]()
Question 14.
What do you mean by Sales Promotion?
Answer:
Sales Promotion are the set of marketing activities undertaken to boost sales of a product.
Question 15.
What do you mean by Personal Selling?
Answer:
It is an act of negotiating, emphasizing inducing and making a prospective buyer to take a decision in favour of products being offered to him.
Question 16.
What do you mean by Advertisement Copy?
Answer:
It represents the text or body of advertisemegbnt, it includes the title, heading, illustrations, pictures, themes etc., intended to pass the message to the prospective buyer.
Question 17.
Write any two differences between Advertisiñg and Personal Selling.
Answer:

Question 18.
Mention any two channels of distribution.:
Answer:
- One Level Channel (Producer-Retailer-Consumer Channel)
- Two Level Channel (Producer-Retailer-Consumer Channel)
Question 19.
What is Sweepstakes?
Answer:
It is a promotional tool ¡n which winners are selected through lucky draw among the visitors of the shop and they will be given different types of prizes.
Question 20.
Define Market.
Answer:
According to American Marketing Association ‘A Market is an aggregate demand of the potential buyers for a product / service.
Question 21.
What is Marketing?
Answer:
It is comprised of all those activities which helps the flow of goods fromthe producer to the ultimate user.
Question 22.
Define Marketing?
Answer:
According to Clark and Clark ‘Marketing consists of those efforts which effect transfer in ownership of goods and care of their physical distribution.
Question 23.
What is Marketing Management?
Answer:
Marketing Management refers to planning, organising, directing and control of the activities involved in exchange of goods and services between producers and consumers.
Question 24.
Mention any two functions of Marketing.
Answer:
(a) Buying and Selling.
(b) Storage and Warehousing.
![]()
Question 25.
What is Marketing Mix?
Answer:
It is a combination of four inputs that revolves around the consumer satisfaction as the local point.
Question 26.
What are the important variables of Product Mix?
Answer:
Brand, Style, Color, Design, Package.
Question 27.
What is Promotion?
Answer:
It deals with personal and impersonal persuasive communication about the product.
Question 28.
What does Promotion Mix includes?
Answer:
Personal Selling, Advertising, Sales Promotion, Trade Fairs and Exhibition.
Question 29.
What do you mean by Physical Distribution?
Answer:
It is concerned with making available of goods and services at right time, right place.
Question 30.
What is After-Sale Service?
Answer:
It is a function which includes assessing consumers satisfaction upon usage of the product or upon realising the service provided by the seller.
![]()
Question 31.
What is Home Delivery?
Answer:
It is a optional service provided by the sellers to their customers to deliver the bought articles to their door-steps.
III. Five Marks Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Briefly Explain any five elements of Product Mix.
Answer:
(a) Brand: A Brand is a name, term, symbol, mark or design or a combination of them which is intended to identify and differentiate products from other competitiors in market.
(b) Grading: It is a process of dividing the commodities . into lots that have similar characteristics as to type, size, shape, weight, quality, performance etc.
(c) Packing: It includes wrapping, filling or compressing of goods to protect them from spoilage, pilferage, breakage, leakage etc.,
(d) Packaging: It involves designing and producing such appropriate packages for each unit of the product as well as for the bulk units of product.
(e) Labelling: A label is a piece of information affixed on a product, labelling refers to designing and affixing appropriate label to a product or its container.
(f) Guarantee: It is a promise or assurance given by the manufactures about the quality and durability of a product and if there is any defect the product will be repaired or replaced at free of charge.
(g) Warranty: It is a written undertaking given by the producer to the customer, promising to repairs, exchange or replace the product if any manufacturing defects are found in the product with in mentioned time period from the date of purchase.
(h) After Sale Service: It is a function which includes assessing consumers satisfaction upon usage of the product or upon realising the service provided by the seller.
(i) Home Delivery: It is a optional service provided by the sellers to their customers to deliver the bought articles to their door-steps.
Question 2.
Write any five factors affecting Pricing Decision,
Answer:
(a) Objectives of the Business.
(b) Cost involves in the production of product.
(c) Quality of materials used in production.
(d) All the other elements of marketing mix.
(e) Demand for the product in the market.
(f) Availability of substitutes of the product.
(g) Pricing policy of the competitors.
(h) Channels of distribution.
(i) Government policies regarding certain products.
Question 3.
Explain briefly the channels of distribution.
Answer:
It refers to the route path in which the product flows fromproducer to consumer.
Important Channels of Distributions:
(a) Direct Channel / Zero Level Channel (Sales without middlemen)
(b) One Level Channel (Producer – Retailer – Consumer Channel)
(c) Two Level Channel (Producer – Whole Saler – Retailer – Consumer Channel)
(d) Three Level Channel (Producer – Agent – Whole Saler – Consumer Channel)
Question 4.
State the objectives of Advertising.
Answer:
(a) To create demand for a product
(b) To retain the demand for existing product
(c) To extend the market for an existing product
(d) To assist the salesman in the effort of sales promotion.
(e) To create brand preference and loyalty
(f) To improve the market share for the product.
![]()
Question 5.
What are the merits of advertising?
Answer:
Merits of Advertising: Advertising has been helpful to different groups of the society such as to the producers and sellers, to the customers, to the society etc.
Some of the general benefits of advertising are given below:
(a) Steady demand: Advertising helps to maintain steady and regular demand for the product or service of a concern. This even helps for regular production.
(b) Increase in sales: Constant advertising helps to increase the sales volume for both producers and traders.
(c) Economies of production: Advertising leads to creation of more demand. This in turn leads to large scale production. Large scale production leads to reduction in cost per unit of the product or service.
(d) Convenience: Advertising helps the consumers in making their purchases more convenient and comfortable, as their time and efforts are reduced in shopping.
(e) Education of consumers: Advertising educates the consumers by giving them details about the new products that can satisfy their needs.
(f) Better standard of living: Advertising helps the people to improve their living standards by persuading them to purchase newer and better quality products.
(g) Employment: Advertising create more employment opportunities directly in the advertising industry as well as indirectly in other industries.
(h) Survival of media: Advertisement brings good revenue to all mass media such as newspapers, magazines, T. V., Radio etc., and thereby contributes for their survival.
Question 6.
Give the limitations of advertising. Some of the limitations of advertising are as under:
Answer:
(a) Less effective: It is less effective medium of promotion as there is no face to face interaction between the seller and customer.
(b) Lack of feedback: It is difficult to ascertain the effectiveness of advertising, as there is no immediate feedback from the customers to the producer or seller.
(c) Rigid: Advertisement capy once prepared cannot be changed easily to suit each individual. It gives only a general appeal. It is not as flexible as that of personal selling.
(d) Confusion among customers: Too many advertisements on a similar type of products, making similar claims may result in confusion among customers in choosing the right product.
(e) Additional Cost: Advertising expenses are included in the total cost of the product which increases the cost of the product that is recovered from the customers.
(f) Misleading: Customers are cheated by misleading advertisements. Claims made in advertisements seem to be untrue when product is purchased and put to use practically.
Question 7.
What are the arguments raised against advertising?
Answer:
Advertisement is often criticised as an economic waste or a social waste. The following arguments/objections are raised in this respect.
(a) Increases the needs and wants: Advertisement multiplies the needs and wants of the people by inducing them to buy things which they do not require or cannot afford to buy.
(b) Adds to cost: The expenses spent on advertisement are ultimately absorbed into cost per unit of a product/service. The effect is increase in price to the consumers.
(c) Creates confusion: Many advertisements by different producers of similar product creat confusion among the cusotmers. Hence, customers will not be able make right choice.
(d) Creation of monopoly: Big companies which can spend more money for advertisement create brand monopoly, this hampers the growth and survival of small companies.
(e) Undermines social values: Some advertisements influence the consumers by their design and style rather than their actual performance. Further, few advertisements are indecent and unethical. Such advertisements undermine the social ethics and values.
(f) No – additional demand: Advertising does not always increase the demand and sale of the product. It merely shifts the demand from one product to another. As a result money spent on advertising is a waste from the point of view of the economy
(g) Fails to attract attention: Many advertisements either escape the attention of the people or maybe ignored by them. As a result the amount spent on advertisement becomes wasteful.
Conclusion: Inspite of the above criticisms, advertising is always a favourable tool for marketing in the present economic setup.
Question 8.
What are the essentials of a good Advertisement Copy?
Answer:
(a) Attention Value: The advertisement copy should draw attention of the people by using attractive colors, pictures, music etc.,
(b) Suggestive Value: The advertisement copy should suggest the customer how to use the product and what are its benefits,
(c) Convincing Value: An advertisement copy should convince the consumers the benefits of the product and create a desire in them to buy the product.
(d) Remembrance Value: People must remember the message of the advertisement for a long time. An advertisement copy should have remembrance value.
(e) Sentimental Value: Sentiments influence human behavior hence an advertisement copy should have sentimental value.
(f) Simplicity: Advertisement copy should be as simple as possible and easily understood by others.
Question 9.
What are the features of Personal Selling.
Answer:
(a) It helps in the creation of demand
(b) Salesmanship generates income and provides employment
(c) Direct contact with the customers helps an organisation to understand their needs, tastes and preferences easily.
(d) It avoids the accumulation and stocks.
(e) It enlightens the consumers about a new product.
(f) It increases the standard of living of the people.
![]()
Question 10.
Write any five differences between Advertising and Salesmanship.
Answer:
Advertising
(a) It is impersonal in nature
(b) It consumes less time
(c) Advertisements are not flexible
(d) Advertising the beginning salesmanship follows it .
(e) Public response cannot be known immediately
Salesmanship
(a) It is personal in nature
(b) It involves a lot of time and efforts
(c) A salesman can adjust and adopt different strategies to convince different customers
(d) Advertisements
(e) Salesman can understand the reaction of public immediately.
Question 11.
What are the objects of Sales Promotion.
Answer:
(a) An information about a new brand can be passed onto consumers.
(b) Market share of the product can be improved.
(c) To retain the existing customers and to build a strong base for loyal customers.
(d) To create a good image for the product with public.
(e) To attract new and potential buyers as much as possible.
(f) To encourage repurchase among the customers.
(g) To obtain more dealer orders.
Question 12.
Briefly explain any 5 Sales Promotion methods.
Answer:
(a) Discount: A product will be offered at a special rate for a limited period of time and rate would be relatively less compared to the rate ofthe same in other periods.
(b) Refunds: Buyers have to fill a refund offer card and the producers may offer to refund a part of price paid by customers just to push more sales.
(c) Product Compliment: Giving a product absolutely free of cost with the purchase of a particular products. ,
(d) Quality Gift: A method used to give consumers extra quantity of the same product upon purchase.
(e) Instant Draw and Assured gifts: Consumers are induced to buy products because of assured gifts given immediately after purchase.
IV. Ten Marks Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Briefly explain the marketing functions.
Answer:
(a) Collection of Market Information: In this function a marketer collects all the information relating to market conditions and potential for growth.
(b) Market Planning: It involves formulating a series ofplan to achieve marketing objectives.
(c) Product designing and development: After gathering information, a producer has to design a product and develop the product according to the customer needs.
(d) Standardisation and Grading Standardisation refers to prescribing the limits of grades on the basis of which products may be sorted and to which producer of goods must conform. Grading refers to sorting of products as per specified standards.
(e) Packing and Labelling: Packing means providing the product a suitable container, covers or box for protection. Labelling is a process of affixing a label which consists of information regarding the product. ,
(f) Branding: It is an activity of creating a brand to the product which helps the consumers in distinguishing the product from other similar products available in the market.
(g) Pricing: It is one of the most important functions of marketing which is involved in determining the price or value of the product.
(h) Promotion: It deals with personal and impersonal persuasive communication about the product.
(i) Channeling Distribution: This function includes the finalising the channel through which the products can be distributed.
(j) Transportation: Its main objective is to transfer the physical possession of products from seller to buyers.
(k) Warehousing: It involves storing and protection of goods till there is a demand for the product.
(l) Customer Support Services: It includes handling consumer grievances and providing proper feedback for then- enquiries.
Question 2.
What do you mean by Marketing Mix? Explain briefly the elements of Marketing Mix.
Answer:
Marketing Mix is made up of four elements namely product, price, promotion and place, it revolves around the satisfaction of customer needs.
Elements of Marketing Mix
(a) Product Mix: A product is anything which satisfy the needs of customers, the product mix has following important variables, brand, style, color, design, package, warranty etc.,
(b) Price Mix: Price represents the value of the products expressed in terms of money. Price Mix involves, pricing strategy, pricing policy, credit terms, discount, allowances.
(c) Promotion Mix: Promotion deals with informing the potential buyers regarding a product. It includes, personal selling, publicity, advertising, sales promotion.
(d) Place Mix: Place or physical distribution mix is concerned with making the products available at the right time at right place, it includes distribution channels, transport warehousing, inventory.
Question 3.
Explain the factors affecting pricing decisions.
Answer:
(a) Objectives of the Business.
(b) Costinvolvesintheproductionofproduct.
(c) Quality of materials used in production.
(d) All the other elements of marketing mix.
(e) Demand for the product in the market.
(f) Availability of substitutes of the product.
(g) Pricing policy of the competitors.
(h) Channels of distribution.
(i) Government policies regarding certain products.
Question 4.
What are the qualities of a Successful Salesman?
Answer:
1. Physical Qualities
These are some of the most important categories of qualities that improve the personality of a salesman to do his job successfully.
Various physical qualities are as follows:
(a) Good health
(b) Good appearance
(c) Good dress
(d) Good posture
(e) Good speech
(f) Pleasant voice
2. Psychological Qualities:
It improves the personality of a salesman and help him to do his job better.
Various psychological qualities are.
(a) Intelligence
(b) Resourcefulness
(c) Cool temper
(d) Alertness
(e) Sharp memory
(f) Keen observation.
3. Social Qualities:
It contributes to the personality of a salesman and improves sales. Various social qualities are as follows.
(a) Courtesy
(b) Good manners
(c) Enthusiasm
(d) Cheerfulness
(e) Patience
(f) Self-confidence
4. Character Qualities:
It contributes a lot to the personality of a salesman. Various character qualities are as follows.
(a) Honesty
(b) Loyalty
(c) Determination
(d) Courage
(e) Maturity
(f) Reliability
![]()
Question 5.
Bring out the Merits and Demerits of advertising.
Answer:
Merits:
(a) It helps in maintaining demand.
(b) It increases the sales of a product.
(c) It creates more demand for the product and leads to large scale production.
(d) It helps consumer in making their purchase decisions.
(e) It educates the consumers by giving them details of the products.
(f) It creates employment opportunities.
(g) It improves the standard of living.
Demerits:
(a) It is difficult to ascertain the effectiveness of advertising.
(b) There is no proper feedback
(c) Advertisements one created cannot be charged easily.
(d) Too many advertisements creates contusion among consumers.
(e) Advertisements are too expensive and a big burden to companie’s if they foil to generate consumers.
(f) Most of the time advertisements are misleading and untrue.
Question 6.
Briefly explain the methods of sales promotion.
Answer:
(a) Discount: A product will be offered at a special rate for a limited period of time and rate would be relatively less compared to the rate of the same in other periods.
(b) Refunds: Buyers have to fill a refund offer card and the producers may offer to refund a part of price paid by customers just to push more sales.
(c) Product Compliment: Giving a product absolutely free of cost with the purchase of a particular products.
(d) Quality Gift: A method used to give consumers extra quantity of the same product upon purchase.
(e) Instant Draw and Assured gifts: Consumers are induced to buy products because of assured gifts given immediately after purchase.
(f) Lucky Draw: A few customers will get costly gifts for their regular purchase and the winner is decided through lucky draw.
(g) Usable Benefit: Customer cards are issued and after each purchase customer gets loyalty points and he can redeem there points to get some benefit or gifts.
(h) Full Finance at Low Rates: It is a method used by producers to provide finance facilities for consumers who do not have money but have a desire to buy, the loans are provided at low rates and consumers can repay in the form of EMI’s
(i) Free Samples Providing samples for free to attract customers, it is mostly done when the product is new in the market,
(j) Sweepstakes: In this winners are selected through lucky draw among the visitors of the shop and they will be given different types of prizes.
Question 7.
As an advertiser, what essentials do you expect in a good advertisement copy?
Answer:
(a) Attention Value: The advertisement copy should draw attention of the people by using attractive colors, pictures, music etc.,
(b) Suggestive Value: The advertisement copy should suggest the customer how to use the product and what are its benefits.
(c) Convincing Value: An advertisement copy should convince the consumers the benefits of the product and create a desire in them to buy the product.
(d) Remembrance Value: People must remember the message of the advertisement for a long time. An advertisement copy should have remembrance value.
(e) Sentimental Value: Sentiments influence human behavior hence an advertisement copy should have sentimental value.
(f) Simplicity: Advertisement copy should be as simple as possible and easily understood by others.
Question 8.
Name one of the first companies in the world to actively study the influence of consumer products on the
environment.
Answer:
Procter and Gamble.
![]()
Question 9.
Give two examples of convenience product
Answer:
- Bread
- Ice cream.
Question 10.
Name two shopping products.
Answer:
- Car
- Furniture
- Garments.
Question 11.
Name two techniques of sales promotion.
Answer:
- Discount
- Premiums.
Question 12.
What factor changes want into demand?
Answer:
Money or purchasing power and willingness to spend the money.
Question 13.
Which goods last long and contribute directly to the making or developing of finished goods?
Answer:
Capital Goods.
Question 14.
Name the elements which are popularly known as 3 p’s of marketing.
Answer:
Physical Evidence, People, Process.
Question 15.
Which goods are of unique character and buyer identifies with them?
Answer:
Speciality goods.
Question 16.
Give some innovative ideas of getting information about the trends/demand pattern in market.
Answer:
Market Survey, Market Research, Online Research, Feedback.
Question 17.
Sony Ltd. introduced a television set with new features in the market at a . high price but when the same features used by other electronic companies in their television sets then the prices of Sony Ltd’s television sets was reduced by the company. Mention the name of strategy the company is following. Also explain the strategy in short.
Answer:
The name of strategy is Price Skimming. Under this strategy a high price is charged for an innovative product and later on the price is reduced when more marketers enter the market with same type of product.
Question 18.
Distinguish between Selling and Marketing on the basis of following points: (i) Focus (ii) Objective (iii) Supremacy.
Answer:
- Focus- Selling focuses on the need of seller whereas marketing focuses on the need of consumer.
- Objective- The main objective of selling is to maximize the profit and sale whereas the main objective of marketing is earning optimum profit with customer satisfaction.
- Supremacy- In selling, producer is considered the kingpin of market whereas in marketing, consumer is considered the kingpin of the market.
Question 19.
Explain any three functions of ‘packaging’.
Answer:
- Product Identification,
- Product Protection,
- Product Promotion.
![]()
Question 20.
‘Expenditure on advertising is a social waste.’ Do you agree? Discuss.
Answer:
This statement is only partially correct. The opponents of advertising say that the expenditure on advertising is a social waste as it adds to the cost, multiplies the needs of people and undermines the social values.
Question 21.
Name and explain the concept which concentrates on the need of the customers.
Answer:
Marketing concept.
Question 22.
‘Blindly following the goal of customer satisfaction had led to many social and environmental ills.’ Do you agree? What should be done?
Answer:
Despite of superiority of marketing concept, it faced criticism from the people who are concerned about society and environment. They argue that companies should not blindly follow the goal of customer satisfaction. This may lead to many social and environmental ills. For example a customer may want to have drugs so just to satisfy customer the firms should not supply him drugs. Some products bring harmful effects on environment so these should not be supplied.
Question 23.
‘Product is a bundle of utilities.’ Do you agree? Comment.
Answer:
Yes, product is a bundle of utilities. A product is purchased because of its capability to provide satisfaction of certain needs. A buyer buys a product or service for what it does for her or the benefit it provides to her.
There can be three types of benefits a customer may seek to satisfy from the purchase of a product, viz.,
- Functional Benefits,
- Psychological Benefits and
- Social Benefits.
Question 24.
How does branding help in creating product differentiation? Discuss.
Answer:
The process of giving a name or a sign or symbol, etc. to a product is called branding. It helps a firm in distinguishing its product from that of its competitors. This enables a firm to secure and control the market for its products. Thus, branding enables marking product differentiatioal
Question 25.
List the promotional messages given on the package of any three consumer products of your choice and comment how can these promotional messages help in the sale of these products.
Answer:
Promotional messages given on the package helps in promotion of the product. These messages give reason to purchase the product.
Some promotional messages are:
- Amla Hair Oil states, ‘baalon mein dum, life mein fun’.
- Detergent powder says, ‘Keep cloth, look good and your machine in top condition’
- Tomato Ketchup mentions, ‘20% Extra Free’.
Exercises
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is marketing? What functions does it play with process of exchange of goods and services? Explain.
Answer:
Marketing is a total system of business activities designed to plan. Price, promote and distribute want satisfying goods and services to present and potential customers.
Marketing is concerned with exchange of goods and services from producer to consumers which involves many activities.
1. Gathering and Analysing Market Information: This is done to identify the needs of the customers and take various decisions for the successful marketing of the products and services.
2. Marketing Planning: Another important activity or area of work of a marketer is to develop appropriate marketing plans, so that the marketing objective of the organisation can be achieved.
3. Product Designing and Development: The design ofthe product contributes to make the product attractive to the target customers. A good design can improve performance of a product andalso give it a competitive advantage in the market.
4. Standardisation and Grading: Standardisation refers to producing goods of predetermined specification which helps in achieving uniformity and consistency in the output which reduces the need for Inspection, Testing and evaluation of the products. Grading is the process of classification of products into different groups, on the basis of its features such as quality, size etc. It ensures that goods belong to a particular quality helps in releasing higher prices for high quality output.
5. Packaging and Labelling: Packaging refers to designing the package for the products. Labelling refers to designing the label to be put on the package. Packaging provides protection to the product and also helps in its promotion. Labelling helps in self-service.
6. Branding Brand: names help in creating product differentiations i.e., how the product can be distinguished from its competitors.
7. Customer Support Service: Marketing management relates to developing customer support service such as after-sales services, handling customer complaints. All these aims at providing customer satisfaction which is a key to marketing success.
8. Pricing of Product: Price is an important factor affecting the success or failure of a product in the market. The marketers have to analyse properly the factors determining the price of a product.
9. Promotion of products and services involves informing the customers about the firm’s product, its features etc. and persuading them to purchase these products. It includes four method advertising, sales promotion, personal selling and publicity.
10. Physical Distribution the important decisions areas under physical distribution include managing inventory, storage, warehousing and transportation of goods from one place to the other.
11. Transportation involves physical movement of goods from one place to another. Amarketer has to perform this function very efficiently keeping in mind the nature of product. Cost, location of target market etc.
12. Storage or Warehousing In order to maintain smooth flow of products in the market, there is a need for proper storage of the products. Further, there is a need for storage of adequate stock of goods to protect against unavoidable delays in delivery or to meet out contingencies in the demand. Wholesalers and retailers are playing an important role.
![]()
Question 2.
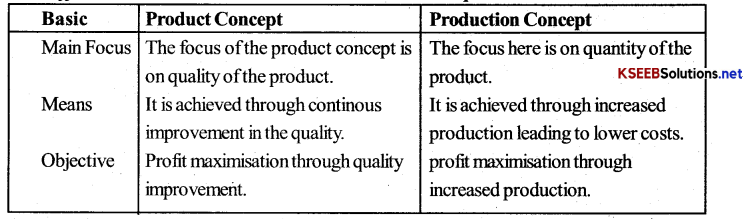
Distinguish between the product concept and the production concept of marketing.
Answer:
Difference between Product and Production Concept
Question 3.
Product is a bundle of utilities. Do you agree? Comment.
Answer:
Yes, product is a bundle ofutilities, which is purchased because of its capability to provide satisfaction of certain need. A buyer buys a product or service for what it does or service for what it does for her or the benefits it provides.
There can be three types of benefits, it provides to a customer, they are
- functional benefits
- psychological benefits
- social benefits.
e. g., the purchase of a motorcycle provides functional utility of transportation, but at the same time satisfies the need for prestige and esteem and provides social benefit by the way of acceptance from a group by riding it.
Question 4.
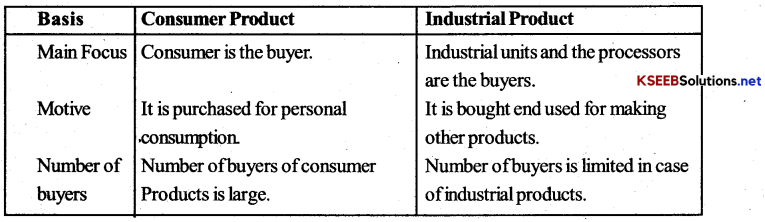
What are industrial products? How are they different from consumer products? Explain.
Answer:
Industrial products are those products. Which are used as inputs in providing other products e.g., raw material, engines, tools, lubricants etc. The difference between consumer products and industrial products is based on their ultimate use and nature of purchases.
Question 5.
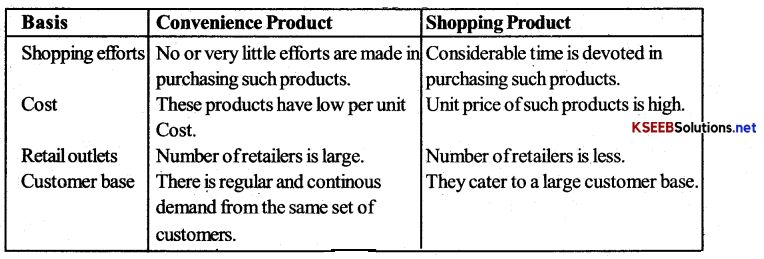
Distinguish between convenience product and shopping product.
Answer:
Difference between Convenience and Shopping Product
Question 6.
Products is a mixture of tangible and intangible attributes. Discuss.
Answer:
In marketing, product is a mixture of tangible and intangible-attributes which are capable ofbeing exchanged for a value, with ability to satisfy customer needs. Beside physical objects, include services, ideas, persons and places in the concept of product. Thus, product maybe defined as anything that can be offered in a market to satisfy a want or need. It is offered for attention, acquisition, use or consumption.
![]()
Question 7.
Describe the functions of labelling in the marketing of products.
Answer:
Label on a product provides detailed information about the product, its contents, methods of use etc.
The various functions performed by a label are as follows
1. Describe the Product and Specify its Contents: One of the most important functions of labels is that it describes the product, its usage, cautions in use etc. and specify its contents.
2. Identification of the Product or Brand: A label helps in identifying the product or brand e.g., we can easily pick our favourite soap from a number of packages only because of its label.
3. Grading of Products: Labels help grading the products into different categories. Sometimes, marketers assign different grades to indicate features or quality of the product e.g., different type of tea is sold by some brands under Yellow, Red and Green label categories.
4. Help in Promotion of Products: An important function of label is to aid in promotion of the products. A carefully designed label can attract the customer to purchase. So, many labels provide promotional messages, some show discount or other schemes etc.
5. Providing Information Required by Law: Another important function of labelling is to provide information required by law. e.g., the statutory warning on the package of cigarette or pah masala – ‘Smoking is injurious to health’ or ‘Chewing tobacco causes cancer.
Question 8.
Discuss the role of intermediaries in the distribution of consumer nondurable products.
Answer:
The term channels of distribution refers the facility to the movement of goods and services and their title between the point of production and point of consumption, by performing a variety of marketing activities.
Following are the functions performed by the channels of distribution
1. Accumulation: It aims at holding the stock to match between the consumer demand and supply condition, warehousing helps in maintaining continuous flow of goods and services.
2. Promotion: The marketing channels also help in promoting the demand for the product by displaying demonstrating and participating in various promotional activities organised by the producers.
3. Negotiating: The marketing channels are the intermediaries between the producers and the consumers. They attempt to reach final agreement on price and other terms of the offer, so that transfer of ownership is properly affected.
4. Risk Taking: Risk taking is the basic responsibility of the intermediaries. It may arise out of physical deteriorations, changes in price levels, natural calamities, change in fashion etc. These are unavoidable as they hold sufficiently large and variety of inventories till the sale of stock.
5. Grading/Sorting: Grading is the process whereby they sort the products on the basis of different sizes, qualities, moisture contents and so on. It helps us realising the time value for the product and at the same time ultimate consumer feels satisfied with the uniform quality of the product.
6. Packaging: The products are packed in the small tradable lots for the convenience of the consumer.
7. Assembling/Assortment: Marketing channels aim at satisfying the needs of the customers. The products desired by the consumer may not be available in the market. They procure such goods from different sources, assemble or assort them as per the requirements of the consumers.
Question 9.
Explain the factors determining choice of channels of distribution.
Answer:
The choice of channels depend on various factors, which are discussed as follows:
1. Product Related Factors: The important product-related consideration is deciding the channels. It includes whether the’ product is an industrial product or a consumer product. Industrial product require shorter channel and consumer products require longer channel.
2. Company Characteristics: The important company characteristics affecting the choice of channels of distribution include the financial strength of the company and the degree of control it wants to hold on other channel members. Direct selling involves lot of foods to be invested in fixed assets say starting own retail outlets or engaging large number at salesforce. Similarly if the management want to have greater control on the channel number, short channels are used but ifthe management do not want more control over the middlemen, it can go in for longer channel or large number of intermediaries.
3. Competitive Factors: The choice of channel is also affected by what the competitor has selected as its channel. Sometimes, firm may decide to go for the same channel and sometimes absolutely opposite.
4. Market Factors: Important market factors affecting the choice of channel of distribution include size of market, geographical concentration of potential buyers and quantity purchased.
5. Environmental Factors Sometimes environmental factors also help in deciding the channel of distribution, e.q., in a depressed economy, marketers use shorter channels to distribute their goods In an economical way.
Question 10.
Explain briefly the components of physical distribution.
Answer:
The main components of physical distribution are as follows
1. Order Processing: If a firm takes more time to process the order, and then the consumer remains dissatisfied. Therefore, order processing has to be made faster by using information technology.
2. Inventory Control: Inventories ensure the availability of the product as and when consumer demand arises. There are various factors that influence a firm decision regarding the level of inventory e.g., degree of accuracy of sales forecast, cost of blocking of the working capital etc.
3. Warehousing: It refers to the storage of goods from the time of production to the time of consumption, Warehousing is important as it creates time utility.
4. Transportation: It creates place utility, It refers to the carrying of raw materials or finished goods from one place to another, The most important thing to be kept in mind is that the value addition by transportation should be greater than the cost of transportation,
![]()
Question 11.
Define advertising, what are its main features? Explain.
Answer:
Advertising is defined as the impersonal form of communication which is paid form by the marketer to promote some goods or services, it is commonly used as the promotional tool of the company, the important features of advertising are as follows
- Paid Form Advertising is a ‘paid form’ of communication which means the sponsor has to bear the cost of communication with the prospects,
- Impersonality There is no direct lace to face contact between the prospect and advertiser, It is, therefore, referred as the impersonal method of promotion,
- Identified Sponsor advertising is % undertaken by some identified individual or company, who makes the advertising efforts and also bears the cost of it.
Question 12.
Discuss the role of ‘Sales Promotion’ as an element of the promotion mix.
Answer:
Sales promotion includes those marketing activities other than personal selling, advertising, and publicity that stimulate consumer purchasing and dealer effectiveness, such as display, shows and exhibitions, demonstrations and various non-current selling efforts not in the ordinary routine,
The main objectives of sales promotion activities are
- Creation of demand for the product.
- Educating the consumers about new products or new uses of the old product.
- Building the brand loyalty for the product among the consumers,
Long Answer Type Questions
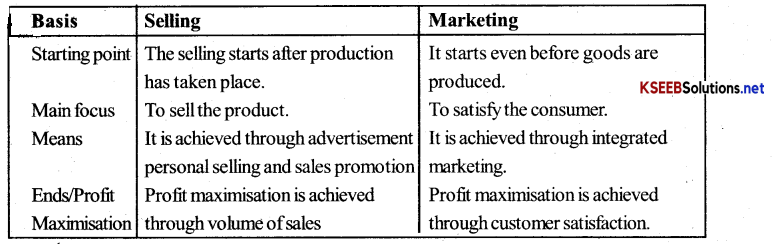
Question 1.
Define Marketing, How is it different from selling? Discuss.
Answer:
Marketing is a total system of business activities designed to plan, price, promote and distribute want, satisfying goods and services to present and potential customers.
Question 2.
What is the marketing concept? Ho tv does it help in the effective marketing of goods and services?
Answer:
Orientation of marketing implies that focus on the satisfaction of customers need, is the key to the success of any organisation in the market. All the decisions in the firm are taken from the point of view of the customers, e.g., What product will be produced, with what features and at what price shall it be sold or where shall it be made available for sale will depend on what do the customer wants.
Marketing concept helps in effective marketing of goods and services by using the following
- Identification of market or customer who are chosen e.s the target of marketing effort.
- Understanding needs and wants of customers in the target market.
- Development of products or services for satisfying needs of the target market.
- Satisfying needs of target market better than the competitors.
- Doing all this at a profit.
Question 3.
What is marketing mix? What are its main elements? Explain.
Answer:
Marketing mix refers to the combination of four basic elements known as four P’s – Product, Price, Promotion and Place.
The various components of marketing mix are
1. Product Mix: Product mix basically concerns with the features related to a product e.g., range, quality, size, labelling, packaging, branding etc. All products must satisfy consumer needs and expectations. It aims at providing good quality products at fair prices.
2. Price Mix: It includes decisions relating to price determination, discounts and allowances credit terms. It covers pricing objectives and pricing policies. Price should cover not only cost of production and selling expenses but also a reasonable profit margin. The price policy adopted by the enterprise should not only be cost-based but also demand-based and competition-based.
3. Place Mix: Place mix links the seller and buyer. The choice of channels of distribution and transport are the two major issues here. There are various factors which help in deciding the channel e.g., the time and the place, where the goods have to reach or transportation. It is the nature of goods, place of destination, cost and availability etc.
4. Promotion Mix: It refers to all marketing activities to increase the volume of sales of the product of an enterprise. It consists of means of marketing communication with a view to informing and persuading prospective buyers to buy a certain product. It includes advertising, personal selling, publicity and sales promotion.
Question 4.
How does branding help in creating product differentiation? Does it help in marketing of goods and services? Explain.
Answer:
Branding helps a firm in distinguishing its products from that of its competitors. This helps the firm to secure and control the market for its products. If products were sold by generic names, it would be very difficult for the marketers to distinguish their products from its competitors. Thus, most marketers give a name to their product, which helps in identifying and distinguishing their products from their competitors product. This process of giving a name or a sign or a symbol etc to a product is called Branding.
![]()
Question 5.
What are the factors affecting determination of the price of a product or service? Explain.
Answer:
There are number of factors which affect the fixation ofthe price of a product.
Some of the important factors in this regard are discussed as below
1. Product Cost: The cost sets the minimum level or the floor price at which the product maybe sold. There are broadly three types of cost-fixed costs, variable costs and semi-variable cost. Total cost IS the sum of all these three. Generally, all firms try to cover all their costs, at least in the long Sun. In addition, they aim at earning a margin of profit over and above the costs.
2. The Utility and Demand: The utility provided by the product and the Intensity of demand of the buyer sets the upper limit of price. Which a buyer would be prepared to pay. In feet the price must reflect the interest of both the parties to the transaction – the buyer and the seller. The buyer may be ready to pay up to the point, where the utility from the product is at least equal to the sacrifice made in terms of the price paid. The seller would, however, try to cover the costs. According to the law of demand, consumers generally purchase more units at a low price than at a high price.
3. The Extent of Competition in the Market: The price is also affected by the nature and degree of competition. The price will tend to reach the upper limit in case there is less degree of competition while under free competition, the price will tend to be set at the lowest level.
4. Government and Legal Regulations: In order to profit the interest of public against unfair practices in the field of price fixing, Government can intervene and regulate the price of commodities. Government can declare a product as essential product and regulate its price.
5. Pricing Objectives: Pricing objectives are another important factor affecting the fixation of the price of a product or a service. Apart from price maximisation, the pricing objectives of a firm may include.
(a) Obtaining Market Share Leadership: If a firm objective is to obtain larger share of the market, it will keep the price of its products at lower level, so that greater number of people are attracted to purchase the products.
(b) Surviving in a Competitive Market: If a firm is facing difficulties surviving in the market because of intense competition or introduction of a more efficient substitute by a competitor.
(c) Attaining Product Quality: Leadership higher prices are charged to cover high In this case, normally quality and high cost of R&D (Research and Development).
6. Marketing Methods used Price Fixation: Price is also affected by other elements of marketing such as distribution system, quality of salesmen employed, quality and amount of advertising, sales promotion efforts. The type of packaging, product differentiation, credit facility and customer service provided.
Question 6.
What do you mean by ‘Channels of distribution’? What functions do they play in the distribution of goods and services? Explain.
Answer:
People, institutions, merchants, and functionaries, who take part in the distribution of goods and services are called ‘Channels of Distribution’. Channels of distribution are a set of firms and individuals that take title or assist in transferring title, to particular goods or services as it moves from the producers to the consumers. Channels of distribution smoothen the flow of goods by creating possession, place and time utilities. They facilitate movement of goods by overcoming various barriers
The important function performed by middlemen are:
1. Sorting: Middlemen procure supplies of goods from a variety of sources, which is often not of the same quality, nature, and size. These goods are sorted into homogeneous groups on the basis of the size or quality.
2. Accumulation: This function involves accumulation of goods into larger homogeneous stock, which help in maintaining continuous flow of supply.
3. Allocation: Involves breaking homogeneous stock Into smaller, marketable lots to sell them to different types ofbuyers.
4. Assorting: Middlemen build an assortment of products for resale. There is usually a difference between the product lines made by manufacturers and the assortment or combinations desired by the users. Middlemen produce variety of goods from different sources and delivers them in combinations, desired by customers.
5. Product Promotion: Middlemen also participate in some sales promotion activities, such as demonstration, special display, contests etc. to increase the sale of products.
6. Negotiation: Channels operate with manufacturers on the one hand and customer on the other. They negotiate the price, quality, guarantee and other related matters with customers, so that transfer of ownership is properly affected.
7. Risk Taking: In the process of distribution of goods, the merchant middlemen take title of the goods and thereby assume risks on account of price and demand fluctuations, spoilage, destinations etc.
Question 7.
Explain the major activities involved in the physical distribution at products.
Answer:
Physical distribution covers all the activities required to physically move goods from manufacturer to the customers. Important activities involved in the physical distribution include transportation, warehousing, material handling and inventory control.
1. Order Processing: In a typical buyer-seller relationship order placement is the first step. Products flow from the manufacturers to customers via channel members while orders flow from customers to manufacturers. Therefore, a good speedy and accurate system of order processing becomes a necessity.
2. Transportation: It is the means of carrying goods and raw materials from the point of production to the point of sale. It is one of the major elements in the physical distribution of goods. It is important because unless the good are physically made available. The sale cannot be completed.
3. Warehousing: Refers to the act of storing and assorting products in order to create time utility in them.
The basic purpose of warehousing activities is to arrange placement of goods and provide facilities to store them. The need for warehousing arises because there may be difference between the times, a product is produced and the time it is required for consumption. Generally, the efficiency of a firm in serving its customers will depend on, where these warehouses are located and where are these to be delivered.
4. Inventory Control: A very important decision in respect of inventory is deciding about the level of inventory. Higher the level of inventory, higher will be the level of service to customers but the cost of carrying the inventory will also be high because lot of capital would be tied up in the stock. The decision regarding level of inventory involves prediction about the demand for the product. A correct estimate of the demand helps to hold inventory and cost level down to a minimum.
The major factors determining inventory levels include.
(a) Firm’s policy regarding the level of customer service. Higher the level of service, greater will be the need to keep more inventories.
(b) Degree of accuracy of the sales forecast. In case more accurate estimates are available, the need for keeping very high level of Inventory can be minimised.
(c) Responsiveness of the distribution system i. e., ability of the system to transmit inventory needs back to the factory and get products to the market.
(d) Cost of inventory, which includes holding cost, such as cost of warehousing, tied up capital etc and the manufacturing cost
![]()
Question 8.
‘Expenditure on advertising is a social waste’. Do yon agree? Discuss.
Answer:
The opponents of advertising say that the expenditure on advertising is a social waste as it adds to the cost, multiplies the needs of the people and undermines social values. The proponents, however argue that advertising is very useful as it increases the reach, brings the per unit cost of production down and adds to the growth of the economy.
Following are the points of criticism
1. Adds to Cost: The opponents of advertising argue that advertising unnecessarily adds to the cost of product, which is ultimately passed on to the buyers in the form of high prices. It is in line that advertisement of a product cost lots of money but it helps to increase the demand for the product as large number ofpotential buyers come to know about the availability of the products, its features etc. and are persuaded to buy it. This increases the demand and therefore the production. As a result, the per unit cost of production comes down as the total co st is divided by larger number of units.
2. Undermines Social Values Advertising: Undermines social values and promotes materialism. It breeds discontentment among people as they come to know about new products and feel dissatisfied with their present state of affairs. This criticism is not entirely true. Advertisement in feet helps buyer by informing them about the new products which maybe improvement over the existing products.
3. Confuses the Buyers another criticism against advertisements is that so many products are being advertised which makes similar claims that the buyer gets confused as to which one is true and which are to be relied upon, e.g., there are so many brands of soaps, shampoos, cars. TVs. cell phones etc. which are advertised. The supporters of advertisement’, however argued that we are all rational human beings who make our decisions for purchase of products on factors, such as price, style, size, etc. Thus the buyers can clear their confusion by analysing the information provided on the advertisements and other sources before taking a decision to purchase a product.
4. Encourages Sale of Inferior Product Advertising does not distinguish between superior and inferior products and persuade people to purchase even the inferiors products. The desired level of quality will depend on the economic status and preferences of the target customers. Advertisements sell products of a given quality and the buyers will buy, if it suits their requirements.
5. Some Advertisements are in Bad Taste Another criticism against advertising is that some advertisements are in bad taste. They show something which is not approved by some people. Some advertisements spoil the relationship between employer and employee, husband and wife etc. From the above discussion, we have learnt that though advertisements are criticised but still they have their own advantages. It is not a social waste, rather it adds value to the social cause by giving a boost to production and generating employment.
Question 9.
Distinguish between advertising and personal selling.
Answer:
Difference between Advertising and Personal Selling
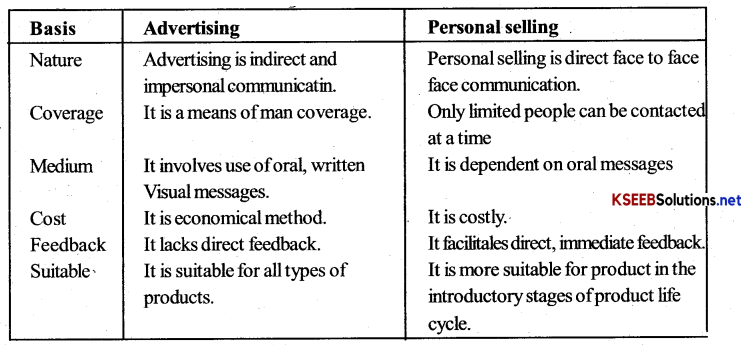
Question 10.
As a marketing manager of a big hotel located at an important tourist destination, what societal concerns would be faced by you and what steps would you plan to take care of these concerns? Discuss.
Answer:
The societal marketing concept holds that the task of any organisation is to identify the needs and wants of the target market and deliver the desired satisfaction in an effective and efficient manner, so that the long term well-being of the consumers and the society is taken care of. In case any business activity encourages pollution, deforestation, storage of resources population explosion, then its benefits cannot be justified. As marketing manager of a big hotel located at an important tourist destination certain care need to be taken regarding environment, they are,
- (i) Proper drainage facility
- (if) In-built plant for re-cycling the waste
- Solar geysers to be used
- Rainwater harvesting
- Proper maintenance of greenery-lawns, parks, gardens
- CNG-based vehicles to be used to provide transport facility to the guests.
Question 11.
Suppose you are the marketing Vice President of an insurance company, planning to design a new medi – claim policy for senior citizens. What information would you like to collect to perform this task and how will, you collect such information? Discuss.
Answer:
The following information about the senior citizens should be collected:
- Age of the senior citizen
- Their source of income
- Medical background
- Present working status
There are various sources of collecting the above information – personal visits, questionnaires, medical reports from nursing homes, doctor clinics, etc.
![]()
Question 12.
What shopping products have been purchased by you/your family in the last six months? Make a list and specify what factors influenced the purchase of each of these products.
Answer:
The following shopping goods were purchased by my family
- Clothes Price, fashion, occasion for which they were bought.
- Refrigerator Brand, price, features, . books, durability.
- Shoes Size, price, brand, material used.
- Furniture (study table) Design, quality, finishing, comfort level, cost.
Question 13.
What information is generally placed on the package of a food product? Design a label for one of the food products of your choice.
Answer:
The following information is normally placed on the package of good product
- Name of the product
- Brand name
- Veg/Non-veg sign (green/red dot)
- Price
- Manufacturing date and date of expiry
- Ingredients
- Net weight
- Directions for use
- FPO mark
- Preservatives used
Question 14.
For buyers of consumer durable products, what ‘customer care services’ would you plan as a manager of a firm marketing new brand of motorcycle. Discuss.
Answer:
For marketing motorcycles, the following customer care services can be planned
- Specified period warranties
- Easy monthly instalments
- Exchange offer
- 0% finance scheme
- Free servicing
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Marketing Management is the______of choosing target markets and getting, keeping and growing customers through creating, delivering, and communicating superior customer value.
(a) Art
(b) Science
(c) Art and science
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(c) Art and science
Question 2.
Marketers operate in which marketplaces:
(a) Consumer and business
(b) Global and non-profit
(c) a & b both
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) a & b both
![]()
Question 3.
“Marketing is an organizational function and a set of processes for creating, communicating and delivering value to customers and for managing customer relationships in ways that benefits the organization and its stakeholders” definition is given by
(a) Philip Kotler
(b) The American Marketing Association
(c) The Association ofNational Advertisers
(d) Peter Drucker
Answer:
(b) The American Marketing Association
Question 4.
Marketing people market following entities:
(a) Goods
(b) Services
(c) Experiences
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 5.
At a fast-food restaurant, what is marketed?
(a) Goods
(b) Service
(c) a & b
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) a & b
Case Problems:
Nokia takes four-lane road to consumers. NEW DELHI after having grabbed a king size 79% share of the 15,000 crore mobile handset market in India, Nokia India has found a new way of connecting people.
The mobile handset manufacturer has i embarked upon a brand new retail strategy that is based on a classification of its consumers into four major groups that separates people in terms of usage, income level and lifestyle.
The classification is based on an extensive survey- the Nokia Segmentation Study -that was carried over two years involving 42,000 consumers from 16 countries. It studied the impact lifestyle choices and attitudes have oh the mobile devices consumers buy and how they use them
The strategy, which was announced globally in June last year, is being unfolded in India now. While the nitty-gritty of the new strategy is still being worked out, it is likely that the company would follow separate marketing strategies for the four different segments. The advertising campaigns could be different for the segments.
Nokia’s entire product portfolio has now been re-aligned towards these four groups to address the specific needs of each. The first of these segments Live, aimed at first time users whose basic need is to stay in touch with voice as the main driver, would have basic handsets low on features and price.
‘These may be functional phones but the target group for these phones range from SEC C (low socio-economic class) to SFCAi i (very high socio-economic class) markets”, says Nokia India marketing head Devinder Kishore. The second segment Connect looks at more evolved users who look for more functionality and features and connectivity. Accordingly, phones in this segment would have GPRS, camera and music capabilities.
The next two categories, Achieve and Explore, are aimed at high-end users and have Nokia’s top-end handsets, e.g., Achieve segment looks at enterprise users who need to have business functionalities in their phones. Nokia’s new E-series has been put under this segment with handsets having QWERTY keyboards and full Internet capabilities.
Aimed at high-end lifestyle users, Explore would be the most prominent segment for the company in the coming years. Says Nokia India multimedia business director Vineet Taneja, “This segment would see the most vibrant growth in the coming year. It will look at five different areas-applications, imaging, mobile, TV, music and gaming. We are fast developing the ecosystem to support these areas.”
Nokia acquired music solution and content provider ‘Loud Eye’ and GPS solution provider ‘Gate5’. It is all slated to launch its most high- profile handset, which boasts ofhaving a 5 mega pixel camera and GPS capabilities apart from iPod quality music, in February.
Says Taneja, “There is increasing demand for convergence and multiple functionalities in high-end handsets. The N-series will try to address that”. Nokia feels that the new platform strategy wherein different handsets are launched under a platform, like the N Series, will become a status and style statement and drive numbers.
Question 1.
Identify the four market segments that Nokia plans to address as per the news report above.
Answer:
Live, Connect, Achieve and Explore.
Question 2.
What is the basis of classification of the market used by the company?
Answer:
SEC: Socio-Economic Class, usage and lifestyle
![]()
Question 3.
What do you mean by realignment of product portfolio? Illustrate this from the case above.
Answer:
It means that whatever product Nokia is planning to develop now, it will be according to the needs of the consumers. The four different handsets are Live, Connect, Achieve and Explore, being planned keeping the needs of four different types of users.
Question 4.
Identify the points that can be highlighted in marketing campaigns for each segment.
Answer:
The points that can be highlighted in marketing campaigns for each segment can be
- Latest-model
- Reasonable price
- Better performance
- Advanced technology
- Consumer-friendly
Question 5.
What are the different considerations in the mind of consumers of each segment while purchasing mobile phones as given in the above case?
Answer:
Different considerations in the mind of each segment while purchasing mobile phones are
- The first of these segments Live, aimed at first time users whose basic need is to stay in touch with voice as the main driver. So, here price of the phone is the main consideration.
- The second segment Connect looks at more evolved users who look for more functionality and features and connectivity. So, here the features of the phone as well as an economic price tag are considered,
- The next two categories, Achieve and Explore, are aimed at high-end users. So here the uniqueness of the handset and its business functionalities are the main points considered by the consumer.