Karnataka 2nd PUC Business Studies Important Questions Chapter 2 Principles of Management
Question 1.
How are principles of management formed?
Answer:
They are formed by practice and experimentation.
Question 2.
Why is it said that the principles of ‘ management are universal?
Answer:
Because they can be applied to all types of organization business as well as non-business, small as well as large, public sector as well as private sectors.
Question 3.
Why is it said that principles of management are flexible?
Answer:
Because they can be modified by the managers when the situation so demands.
Question 4.
Which principles of management promote team spirit.
Answer:
Esprit De Corps.
Question 5.
Who was the first to identify functions of management?
Answer:
Henri PayPal.
Question 6.
Which principle of management suggests that a subordinate should receive orders from and be accountable to one superior?
Answer:
Principle of unity of command.
![]()
Question 7.
Who gave the concept of scientific management? What was his profession?
Answer:
F.W. Taylor gave the concept of scientific management and he was an American mechanical engineer.
Question 8.
Which principle of scientific management suggests the introduction of scientific investigation and analysis of management practice?
Answer:
Science, not the Rule of Thumb.
Question 9.
What is the basis of the formation of scientific management?
Answer:
Observation & Experimentation.
Question 10.
Which principle of management is violated if an employee is asked to receive orders from two superiors?
Answer:
Principle of Unity of Command.
Question 11.
“Workers should be encouraged to develop and carry out their plans for improvements”. Identify the principle of management formulated by Fayol.
Answer:
Principle of the initiative.
Question 12.
It has been observed that the prevailing situation in an organization is due to the violations of the principle of ‘order’. What might have been your observation?
Answer:
People and materials are not in suitable places at the appropriate times.
Question 13.
Which principle of management is violated when a manager grants one month of medical leave to a superior with pay and only one week of medical leave to an accountant?
Answer:
Principle of equity.
![]()
Question 14.
Manu, a manager expects his colleagues to get work out of subordinates without giving them any powers. Which principle of management is being overlooked and why?
Answer:
Principle of parity of Authority and Responsibility.
Question 15.
Which principle of management aims at securing the loyalty and devotion of the employees by giving them fair and just treatment?
Answer:
Principle of Equity.
Question 16.
Which principle of management envisages that each group of activities having the same objective must have one head and one plan? Explain the principle with a suitable example.
Answer:
Unity of Direction
Question 17.
If an organization does not provide the right place for physical and human recourses in the organization, which principle is violated? What are its consequences?
Answer:
Principle of Order
Question 18.
The production manager of an automobile company asked the foreman to achieve a target production of200 units (Scooters) per day. But he did not give him the authority to requisition tools and materials from the store department. Can the production managers blame the foreman if he is not able to achieve the desired target? Explain briefly the principle relating to the situation.
Answer:
No, the production manager cannot blame the foreman because he did not give material from the store’s department. Since he had no authority, he could not fulfill his responsibility. Also, explain the principle of Parity of Authority.
Question 19.
Name and explain the principle of Fayol which suggests that communication from top to bottom should follow the official lines of command?
Answer:
Principle of Scalar Chain.
![]()
Question 20.
Identify the technique of scientific management which are described by the statement given below:
(i) When specialists supervise each worker.
Answer:
Functional Foremanship.
(ii) Change in the attitude of workers and management towards one another. From competition to Cooperation.
Answer:
Mental Revolution
(iii) When uniformity is introduced in materials. Machine, tools, method of works, and working conditions after, due research.
Answer:
Standardization of works.
Question 21.
Girish & Harish are typists in a company having the same educational qualification. Girish is getting Rs.3000 per month and Harish Rs. 4000 per month as salary for the same working hour. Which principle of management is violated in this case? Name and explain the principle?
Answer:
Principle of fair remuneration.
I. One Mark Questions and Answer
Question 1.
What acts as a guide for Managers?
Answer:
Management Principles.
Question 2.
What is a Principle?
Answer:
A Principle is a fundamental statement of truth that provides guidelines for action.
Question 3.
Write any one feature of principles of Management.
Answer:
Universal applicability.
Question 4.
Name the book published by Henry Fayol.
Answer:
General and Industrial Management.
Question 5.
How many principles were propounded by Henry Fayol?
Answer:
14.
![]()
Question 6.
What is Discipline?
Answer:
It means obedience to organizational rules.
Question 7.
Which is the route by which employees of the same level can communicate with each other.
Answer:
Gang Plank.
Question 8.
What is Gang Plank?
Answer:
It is a route by which employees of the same level can communicate with each other.
Question 9.
When can the unity of command principle violate?
Answer:
When the employee gets a command from two or more superiors.
Question 10.
What leads to escapism?
Answer:
Dual subordination.
Question 11.
What is Dual sub-ordination?
Answer:
When an employee takes orders from more than one superior it is called dual subordination.
Question 12.
What leads to the wastage of resources?
Answer:
If the principle of direction is violated.
Question 13.
What does equity ensure?
Answer:
Workers, loyalty, and devotion.
Question 14.
What should be minimized to maintain organizational efficiency?
Answer:
Employees turnover.
![]()
Question 15.
What is Initiative?
Answer:
It is a step taken by employees for his self-motivation.
Question 16.
What is‘Esprit de corps’?
Answer:
Spirit of Co-operation.
Question 17.
What leads to an increase in production?
Answer:
Spirit of Co-operation.
Question 18.
Who published the Article‘Principles of Management’s 1911?
Answer:
Fredrick Winslow Taylor.
Question 19.
Name the book written by Fredrick Winslow Taylor.
Answer:
‘Sleep Floor Work’.
Question 20.
Who proposed Scientific Management?
Answer:
Fredrick Winslow Taylor.
![]()
Question 21.
Who opposed the Rule of Thumb?
Answer:
Fredrick Winslow Taylor.
Question 22.
What reduces the practice of the Rule of Thumb?
Answer:
Application of Scientific Management Principles.
Question 23.
Who is the father of General Management?
Answer:
Henry Fayol.
Question 24.
Who is the father of Scientific Management?
Answer:
Fredrick Winslow Taylor.
Question 25.
Give the meaning of responsibility?
Answer:
A state of being answerable or accountable for an obligation.
Question 26.
State any one feature of principles of management.
Answer:
Universal applicability.
Question 27.
Mention any one Fayol’s Principle of Management.
Answer:
Division of Work.
Question 28.
Give the meaning of authority?
Answer:
A legal power to command or to act
Question 29.
What is meant by the Centralisation of Authority?
Answer:
It means the decision-making power is in a single or few hands.
![]()
Question 30.
What is meant by decentralization of authority?
Answer:
It means the decision-making power is with more persons.
Question 31.
When is Gang Plank used?
Answer:
In case of emergency.
II. Two Marks Question and Answers
Question 1.
Give the meaning of Principles of Management?
Answer:
Principles of Management acts as a guide for managers to deal with human beings whose behavior is very much unpredictable.
Question 2.
What do you mean by universal applicability of principles of Management?
Answer:
Principles of Management are applicable to all types of organizations but it differs on the basis of nature of the organization, the scale of operation and size of the organization.
Question 3.
Give the meaning of Authority and Responsibility?
Answer:
Authority:
Authority is a rightful or legal power to command or to act, a power that gives the right to give orders or make decisions.
Responsibility:
It is a state of being responsible or accountable or answerable as for a trust, obligation, or debt.
Question 4.
What do you mean by Unity of Command?
Answer:
It means to avoid dual sub-ordination i.e, every individual should get orders from one person and not from two or more superiors.
Question 5.
What are centralization and decentralization of authority?
Answer:
The concentration of decision-making power in the hands of one or few is called the centralization of authority or power. Dispersal of decision-making power among more persons is called decentralization.
Question 6.
What is the Scalar Chain principle of management?
Answer:
The formal lines of authority from the highest to the lowest ranks are known as the scalar chains.
According to Fayol, “Organisation should have a chain of authority and communication from top to bottom and should be followed by managers and subordinates”.
Question 7.
What is meant by Esprit de Corps?
Answer:
It means spirit of co-operation, promoting team spirit among employees is one of the necessary steps that a manager should take. It helps in the minimization of the wastage of resources.
Question 8.
What is Scientific Management? According to Fredrick Winslow Taylor
Answer:
‘Scientific management means knowing exactly what you want men to do and seeing that they do it in the best of cheapest way.
Question 9.
Why Fredrick Winslow Taylor is considered the father of Scientific Management?
Answer:
At the time of the rule of Thumb in most of the organizations around the world, Fredrick Winslow Taylor was the person who proposed scientific management and opposed the rule of thumb; hence he is considered as the father of Scientific Management.
Question 10.
What is meant by division of work according to Fayol?
Answer:
F.W.Taylor thought that by scientific analysis of work, it would be possible to find “one best way to do it. “He proposed scientific, management as against solving industrial problems by personal judgment of owners or managers. That is why he is called the father of Scientific Management.
![]()
Question 11.
Why Henry Fayol is considered as ‘Father of General Management?’
Answer:
Henry Fayol is considered the father of General Management as he has contributed a lot to the world of management with his concepts and theories of management which are universally applied in all fields.
Question 12.
Differentiate between authority and responsibility.
Answer:
Authority is the right to give orders and obtain obedience whereas responsibility refers to accountability which is the result of authority. There cannot be one without the other. Excess authority may lead to misuse of power and responsibility without authority may lead to slavery.
Question 13.
Distinguish between Centralisation and Decentralisation of authority.
Answer:
The concentration of decision-making power in the hands of one or few is called centralization of authority or power whereas the dispersal of decision-making power among more persons is called decentralization. A proper adjustment between the two is necessary to achieve the maximum objectives of the business.
Question 14.
What is Gang Plank?
Answer:
It is a route by which the employees of the same level communicate with each other directly. It is one of the shorter routes of Scalar Chains.
Question 15.
Explain the flexible nature of principles of Management.
Answer:
The principles of Management are very much flexible i.e, they are not of rigid nature hence they can be well modified according to the situation.
Question 16.
What is the Centralisation of power?
Answer:
It means that the concentration of the decision-making power lies in the hands of one or few people.
Question 17.
What is Decentralisation of Power?
Answer:
It means that the concentration of the decision-making power lies among more persons.
Question 18.
What do you mean by Division of Work?
Answer:
It is a procedure where the work will be divided, sub-divided, and allotted to various people according to their skills, knowledge, and experience in a particular area.
Question 19.
What is Scalar Chain?
Answer:
A scalar Chain is a formal line of authority from the highest executive to the lowest for the purpose of communication.
Question 20.
What do you mean by Equity?
Answer:
It is a behavior where justice and kindness will be equal for all employees which ensures loyalty and devotion of the employee towards the organization.
![]()
Question 21.
What is Initiative?
Answer:
It refers to steps taken by employees towards self-motivation. Employees of all levels should be given the freedom to take initiatives but it should not go against the policies of the organisation
Question 22.
What do you mean by Rule of Thumb?
Answer:
Rule of Thumb is a method of solving problems in an organization on the basis of the personal judgment of owners.
Question 23.
What is Optimum Production?
Answer:
It is one of the principles of scientific management which favored large-scale production and opposes any kind of control by managers and workers in stoppage of continuous increase in production.
Question 24.
What is Discipline?
Answer:
It is training to act in accordance with the established rules of a organisation. It is necessary to have good superiors at all levels which can improve the quality and quantity of work.
III. Five Marks Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Explain any five features of Principles of Management
Answer:
The following are the features of Principles of Management.
(a) Universal Applicability: It means it is applicable to all types of big, small, profit, non-profit, private, and public sectors.
(b) General Guidelines: Principles always provide general guidelines but they do not provide readymade solutions to all kinds of management problems.
(c) It is purposeful: It exists for the achievement of specific objectives, all the activities are goal-oriented.
(d) It is formed by practice and experimentation: Principles are formed by experience as well as experimentation.
(e) Flexibility: The principles of management are very much flexible i.e, they are not of rigid nature; hence they can be well modified according to the situation.
Question 2.
Explain any five of Fayol’s Principles of Management.
Answer:
Henry Fayol has suggested 14 principles of management and they are as follows:
(a) Division of Work: It is a procedure where the work is divided among various people on the basis of skills and knowledge they possess.
(b) Authority and Responsibility: Authority is the rightful power to command responsibility is a state of being answerable for an obligation.
(c) Discipline: It is training to act in accordance with established rules of an organization
(d) Unity of Command: An employee should get orders from only one superior.
(e) Unity of Direction: One leader to lead and ensure unity of action and coordination.
![]()
Question 3.
Explain the principles of Scientific Management of Fredrick Winslow Taylor.
Answer:
The following are the principles of Scientific Management proposed by Fredrick Winslow Taylor.
(a) Science does not thumb rule: Scientific management is an attempt to increase production to reduce the efforts of employees with the introduction of Time and Motion studies to fix performance standards.
(b) Harmony, not discord: There should be a harmony between the relationship between management and workers both should transfer their thoughts.
(c) Co-operation, not individualism: There should be almost co-operation between all levels of management and employees instead of individualism to achieve the management objectives.
(d) Development of each and every person to his greatest efficiency and prosperity: According to Taylor, efficiency can be achieved right from the beginning i.e., selection of personnel and there should be proper training at all levels.
(e) Optimum Production: It favors large-scale production opposes any kind of control in stoppage of continuous increase in production.
IV. Ten Marks Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Explain the features of Principles of Management
Answer:
The following are the features of Principles of Management.
(a) Universal Applicability: It means it is applicable to all types of big, small, profit, non-profit, private, and public sectors.
(b) General Guidelines: Principles always provide general guidelines but they do not provide readymade solutions to all kinds of management problems.
(c) It is purposeful: It exists for the achievement of specific objectives, all the activities are goal-oriented.
(d) It is formed by practice and experimentation: Principles are formed by experience as well as experimentation.
(e) Flexibility: The principles of management are very much flexible i. e, they are not of rigid nature; hence they can be well modified according to the situation.
(f) It involves social process: It is used by people and for people; it is concerned with interpersonal relationships.
(g) It aims at influencing human behavior: It helps to understand the relationship between humans and other resources
(h) Cause and effect relationships: It tells us the result after a particular principle is applied in a given situation.
(i) It is intangible: The principles and their applicability cannot be seen, but its presence can be felt.
(j) Contingent: The application of management principles contingent. i.e, it depends on the situation.
Question 2.
Explain Fayol’s Principles of Management.
Answer:
Henry Fayol has suggested 14 principles of management and they are as follows:
(a) Division of Work: It is .a procedure where the work is divided among various people on the basis of skills and knowledge they possess.
(b) Authority and Responsibility: Authority is the rightful power to command responsibility is a state of being answerable for an obligation.
(c) Discipline: It is training to act in accordance with established rules of an organization
(d) Unity of Command: An employee should get orders from only one superior.
(e) Unity of Direction: One leader to lead and ensure unity of action and coordination.
(f) Sub-ordination of individual interest to general interest: Every worker should show interest towards the achievement of organizational goals. The organization is more important than individuals or groups of employees.
(g) Remuneration of Employees: Remuneration paid to the employees should be fair and satisfactory.
(h) Centralisation and Decentralisation: Centralisation and Decentralisation are essential in every organization to achieve maximum organizational objectives.
(i) Scalar Principles: It refers to a formal chain of authority from the highest executive to the lowest for communication purposes.
(j) Order According to Fayol: ‘There is a place for everything and everything must be in its place.
(k) Equity: Fayol emphasizes kindliness and justice towards all sections of workers.
(l) Stability of Tenure of Personnel: The turnover of employees should be minimized to maintain organizational efficiency.
(m) Initiative: It refers to steps taken by employees towards self-motivation.
(n) Esprit de Corps: It is a step that every manager should take to promote the spirit of co-operation among the employees.
Question 3.
Explain the principles of Scientific Management of Fredrick Winslow Taylor.
Answer:
The following are the principles of Scientific Management proposed by Fredrick Winslow Taylor,
(a) Science does not thumb rule: Scientific management is an attempt to increase production to reduce the efforts of employees with the introduction of Time and Motion studies to fix performance standards.
(b) Harmony, not discord: There should be a harmony between the relationship between management and workers both should transfer their thoughts.
(c) Co-operation, not individualism: There should be almost co-operation between all levels of management and employees instead of individualism to achieve the management objectives.
(d) Development of each and every person to his greatest efficiency and prosperity: According to Taylor, efficiency can be achieved right from the beginning i. e., selection of personnel and there should be proper training at all levels.
(e) Optimum Production: It favors large-scale production opposes any kind of control in stoppage of continuous increase in production.
![]()
Question 4.
State any 10 Fayol’s Principles of Management.
Answer:
(a) Division of Work
(b) Discipline
(c) Unity of Command
(d) Unity of Direction
(e) Centralisation
(f) Remuneration
(g) Scalar Chain
(h) Order
(i) Equity
(j) Esprit de Corps
Exercises
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
How is the Principle of ‘Unity of Command’ useful to management? Explain briefly.
Answer:
The principle of unity of Command implies that each and every subordinate should have one and only one boss’s orders and instructions should come from only one head This helps the working of any organization in the following manner.
- Authority responsibility relationship Is clearly defined.
- Subordinates are known for whom they are accountable.
- Discipline and order are maintained.
Question 2.
Define scientific management. State any three of its principles.
Answer:
Scientific management can be defined as knowing exactly what you want men to do and seeing that they do it In the best and cheapest way.
Scientific management aims at choosing the best. Method to get the maximum output from the workers the principles of scientific management are mainly applicable to the shop-floor level
Three principles of scientific management are as follows
1. Science, Not Rule of Thumb When different managers use their own different methods to get the work done it is rule of thumb. Taylor believed that there was only one best method to maximize efficiency. Taylor advised that every organization should compare the results of different methods, test them again and again and finally select one best method of getting the work done.
2. Harmony, Not Discord Managers are an extension of the management and serve as a link between workers and the owners. Workers have to take instructions from the managers and managers have to get the work done through the workers. Oftentimes the relation between them is spoilt which is very harmful to everyone-workers, managers, and owners. This class conflict should be replaced by harmony between the two. Both should change their thinking towards each other. Both should give importance to each other. This is known as the mental revolution.
3. Co-operation, Not Individualism There should be complete co-operation between the labor and the management instead of individualism. This principle is an extension of the principle of ‘Harmony not discord. ’ The management and the workers should not compete with each other rather co-operate with each other. Management should consider all good suggestions made by the employees which can help in cost reduction. At the same time, workers should never think of going or strikes in order to get their unreasonable demands fulfilled.
![]()
Question 3.
If an organization does not provide the right place for physical and human resources in an organization, * which principle is violated? What are the consequences of it?
Answer:
The principle of order is violated if an organization does not provide the right place for physical and human resources.
If this principle is violated then
- Lots of time will be wasted in locating the different resources.
- This will lead to delayed decisions.
- Wastage of energy will lead to inefficiency and delay in production.
- Causes hindrance in the activities of the business.
Question 4.
Explain any four points regarding the significance of Principles of management:
Answer:
Significance of principles of management
1. Providing Managers with useful Insights into Reality When managers follow principles it adds to their knowledge, ability, and understanding of managerial situations and circumstances. This improves managerial efficiency e.g. when managers use the principle of delegation then they get more time to concentrate on critical areas of working.
2. Scientific Decision making management principles: help in thoughtful decision making, They emphasize logic rather than blind faith. Here, decisions are based on the objective assessment of the situation.
3. Optimum Utilisation of Resources and Effective Administration Principles: help the managers to conceptualize the net effect of their decision rather than going for trial and error method resulting in saved time, efforts and energy thereby increased productivity.
4. Management Training, Education, and Research Principles of management are the basis for management theory. As such they are used as a basis for management training, education and research. These principles provide the basic groundwork for the development of management as a subject. Professional courses like BBA, MBA also teaches these principles as part of their curriculum
Question 5.
Explain the principle of ‘Scalar Chain’ and gangplank.
Answer:
Principle of Scalar Chain and Gangplank: The formal lines of authority from highest to lowest ranks are known as the scalar chains.
According to Fayol, “Organisation should have a chain of authority and communication that runs from top to bottom and should be followed by managers and subordinates.
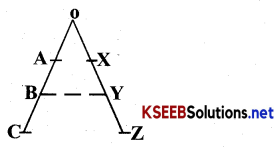
In the diagram, 0 is heading 2 teams where A and X are at the same level, B and Yare at the same level and C and Z are at the same level. The line of communication is clearly defined A to B to C and X to Y to Z. Authority responsibility relationship is also very clear. But C and Z cannot directly contact each other. This sometimes may take a lot of time during an emergency to communicate as per the prescribed flow to avoid this problem a system known as ”Gang Plank’ was introduced wherein Cor Z could contact each other and same way Band Y could contact each other.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain the principles of scientific management given by Taylor.
Answer:
Principles of scientific management are given by FW Taylor:
1. Science, Not Rule of Thumb when different managers use their own different methods to get the work done it is rule of thumb. Taylor believed that there was only one best method to maximize efficiency. Taylor advised that every organization should compare the results of different methods, test them again and again and finally select one best method of getting the work done.
2. Harmony, Not Discord Managers are an extension of the management and serve as a link between workers and the owners. Workers have to take the instructions from the managers and managers have to get the work done through the workers. Sometimes the relation between them is spoilt, which is very harmful to everyone-workers, managers, and owners. This class conflict should be replaced by harmony between the two. Both should change their thinking towards each other. This is known as the mental revolution.
3. Co-operation, Not Individualism There should be complete co-operation between the labor and the management instead of individualism: This principle is an extension of the principle of harmony, not discord. The management and the workers should not compete with each other rather co-operate with each other. Management should consider all good suggestions made by the employees which can help in cost reduction. At the same time, workers should never think of going on strikes in order to get their unreasonable demands fulfilled.
4. Development of Each and Every person to His or her Greatest Efficiency and Prosperity Scientific management also stood for worker development. Taylor believed that workers should be aware of the ‘best method’. On the other hand, all organizations should select employees carefully in order to get maximum efficiency.
When the duties are allotted, the perfect match should be made between the requirements of the job and the capabilities of the worker. Training should be provided to improve the skills further. In this way, efficiency will go higher resulting in prosperity for both workers and the company.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain the following principles of management by Fayol with examples.
(a) Unity of direction
(b) Equity
(c) Esprit de Corps
(d) Order
(e) Centralisation and decentralisation (1) Initiative
Fayol introduced general principles of management Some of them have been explained below
(a) Unity of Direction: All the units of an organization should be moving towards the same objective Each group of activities having the same objective must have one head and one plan. Each group should have its own in charge and on no account the working of two divisions neither be overlapped.
(b) Equity: This principle emphasize kindliness and justice in the behavior of managers towards workers. This will ensure loyalty and devotion. Lazy personnel should be dealt with sternly and strictly There should be no discrimination against anyone on account of gender, religion, caste language or nationality, etc. All decisions should be merit-based
(c) Esprit de Corps This principle emphasizes building harmony and team spirit among employees. In a large organization, large workforce teamwork is very important. Teamwork due to leads to better coordination while working. The head of each team should give credit for good results to the whole team rather than confining it to his own self.
(d) Order: A place for everything and everyone in his/her place. Basically, it means orderliness. If there is a fixed place for different things in a factory and they remain
In their places then no time is wasted. In locating them the same way if every personnel is allocated an area to operate from then his co-workers head or subordinates, anyone can contact him easily.
(e) Centralisation and Decentralisation: Concentration of authority in a few hands is centralization and its dispersal among more number of people is decentralization Fayol believed that an organization should not work with any one of them in isolation A combination of both is important simple, easy and work of routine type should be decentralized and critical important type of work should be centralized.
(f) Initiative: Initiative means taking the first step with self-motivation workers should be encouraged to develop and carry out their plans for improvements according to Fayol. Initiatives should be encouraged. A good company should invite suggestions from employees which can result in substantial cost/time reduction. Rewards can be given to fruitful suggestions.
Question 3.
Explain the technique of ‘Functional Foremanship’ and the concept of ‘Mental Revolution’ as enunciated by Taylor.
Answer:
Functional Foremanship: Taylor advocated the separation of planning and execution functions. This concept was extended to the lowest level of the shop floor. It was known as functional foremanship.
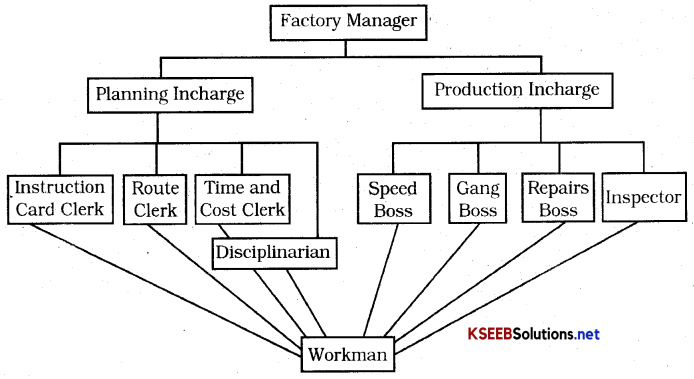
Under the factory manager, there is planning in charge and production in charge. Under the planning in charge, the work goes as follows
- 1. Instruction Card Clerk Drafts instructions for the workers,
- 2. Route Clerk specifies the route of production.
- Time and Cost Clerk Prepare time and cost sheet.
- Disciplinarian ensures discipline,
Under the production in charge, the work goes as follows
- Speed Boss: Timely and accurate completion of work,
- Gang Boss: Keeping tools and machines ready for operation by workers.
- Repairs Boss: Ensure proper working conditions of machines.
- Inspector: Checks the quality of work. Mental Revolution
In a factory, the managers serve as a link between the owners and the workers The managers have to get the work done from the workers which creates sometimes problems between the two. Taylor emphasized that there should be harmony between the management and workers. Both should realize that each one is important. For this both had to change their thoughts for each other, This is known as ‘Mental Revolution. Management should share the gains of the company with the workers and at the same time workers should work hard and be ready to accept any change made for the betterment of the organization.
Question 4.
Discuss the following techniques of scientific work-study
(a) Time study
(b) Motion study
(c) Fatigue study
(d) Method study
(e) Simplification and standardization of work
Answer:
Some of the techniques of scientific work-study are
(a) Time Study:
It determines the standard time taken to perform a well-defined job. The standard time is fixed for the whole of the task by taking several readings. The method Qftitne study will depend upon volume and frequency of the task, the cycle time of the operation, and time measurement costs there are three objectives achieved through time study
- Determine the number of workers
- Frame suitable incentive schemes
- Determines labor costs.
e.g.. If the standard time is taken to do a piece of work is 20 minutes then one work can be done 3 times In an hour and a total of 21 times (3×7 hours per day) the work can be done on a single day.
(b) Motion Study:
Motion study refers to the study of movements like lifting putting objects sitting and changing pros and cons On close examination of body motions e.g., It is possible to find out three types of motions
- Motions that are productive.
- Motions that are incidental.
- Motions that are unproductive.
Out of the above three workers were motivated to eliminate the third type completely and reduce the second one to the minimum this help in increasing productivity
(c) Fatigue Study:
The fatigue study seeks to determine the amount and frequency of rest intervals in completing a task. A person is bound to feel tired physically and mentally if he does not take a rest while working. The next intervals will help one to regain stamina and work again with the same efficiency for e.g., in an organization working hours are 9 to 5. There is a lunch break of an hour for the workers to take a rest similarly In a school there is a break for the students and teachers after 4 periods of continuous learning.
(d) Method Study:
The objective of the method study is to find out one best way of doing the job. Different managers would use their own different methods of getting the work done. But there is always one best method. Right from procurement of raw materials till the final product is delivered to the customer every activity is the part of method study.
The objective of the whole exercise is to minimize the cost of production and maximize the satisfaction of the customer.
(e) Simplification and Standardisation of Work:
Standardization refers to the process of setting standards for every business activity e.g., process, raw material, time, product, machinery, methods, or working conditions. The objective of standardization are
- To reduce products to fixed types, sizes, features, etc.
- To establish interchangeability of various parts.
- To establish standards of excellence and quality in materials.
- To establish standards of performance of men and machines.
Simplification aims at eliminating unnecessary diversity of products. It results in savings of the cost of labor, machines, and tools. It implies reduced inventories, fuller utilization of equipment, and increasing turnover.
Question 5.
Discuss the differences between the contributions of Taylor and Fayol.
Answer:
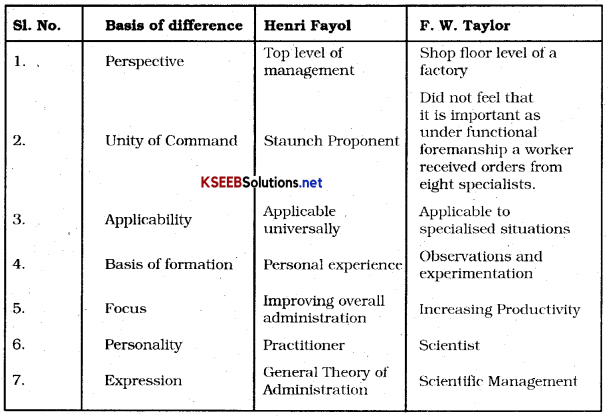
![]()
Question 6.
Discuss the relevance of Taylor and Fayol’s contribution in the contemporary business environment.
Answer:
Relevance of Taylor and Favours contribution in the contemporary business environment. Both Fayol and Taylor have given principles of management to improve efficiency In an organization. Taylor gave us scientific principles of management which are being adopted by all organizations to improve productivity at the shop floor level, the principles help in giving effective results. In the same manner, Henry Fayol gave in general principles of management which when implemented at any of the levels-top, middle or lower and helps in achieving better coordination, remove ambiguity, and encourage the employees to improve their work performance.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Principles of management are not
(a) universal
(b) flexible
(c) absolute
(d) behavioral
Answer:
(c) Principles of management are not absolute as they are flexible behavioral and universal in nature
Question 2.
How are principles of management formed?
(a) In a laboratory
(b) By experiences of managers
(c) By experiences of customers
(d) By propagation of social scientists
Answer:
(b) Principles of management are formed by the experiences of manager as it provides useful insights into reality.
Question 3.
The principles of management are significant because of
(a) increase in efficiency
(b) initiative
(c) optimum utilization of resources
(d) adaptation to changing technology
Answer:
(c) Principles of management are Significant because it helps in increasing overall efficiency.
Question 4.
Henry Fayol was a
(a) social scientist
(b) mining engineer
(c) accountant
(d) production engineer
Answer:
(b) Henry Fayol was a mining engineer and management theorist.
![]()
Question 5.
Which of the following statement best describes the principle of ‘Division of Work’?
(a) Work should be divided into small tasks
(b) Labour should be divided
(c) Resources should be divided among jobs
(d) It leads to specialization
Answer:
(a) Division of work implies division of work into small tasks.
Question 6.
‘She/He keeps machines, materials, tools, etc ready for operations by concerned workers*. Whose work is described by this sentence under functional foremanship?
(a) Instruction card clerk
(b) Repair boss
(c) Gang boss
(d) Route clerk
Answer:
(c) Gang boss, keeping machines and tools.
Question 7.
Which of the following is not a Principle of management given by Taylor?
(a) Science, not the rule of the thumb
(b) Functional foremanship
(c) Maximum, not restricted output
(d) Harmony, not discord
Answer:
(b) Taylor advocated the separation of planning and execution functions. This concept is known as functional foremanship.
Question 8.
Management should find ‘One best way’ to perform a task. Which technique of scientific management is defined in this sentence?
(a) Time study
(b) Motion study
(c) Fatigue study
(d) Method study
Answer:
(d) The objective of the method study is to find out one best way of doing the job.
Question 9.
Which of the following statements best describes ‘Mental Revolution?
(a) It implies a change of attitude
(b) The management and workers should not play the game of one-upmanship
(c) Both management and workers require each other.
(d) Workers should be pain more wages
Answer:
(a) Mental revolution implies a change in the attitude of workers and management towards one another.
![]()
Question 10.
Which of the following statements is false about Taylor and Fayol?
(a) Fayol was a mining engineer whereas Taylor was a mechanical engineer
(b) Fayol’s principles are applicable in specialized situations whereas Taylor’s principles have universal application
(c) Fayol’s principles were formed through personal experience whereas Taylor’s principles were formed through experimentation
(d) Fayol’s principles are applicable at the top level of management whereas Taylor’s principles are applicable at the shop floor
Answer:
(b) Fayol’s principles are uni vers ally applicable whereas Taylor’s principles applied in special
Case Problem:
Question 1.
‘F’ limited was engaged in the business
of food processing and selling its products under a popular brand. Lately, the business was expanding due to good quality and reasonable prices. Also with more people working the market for processed food was increasing. New players were also coming to cash in on the new trend. In order to keep its market share in the short run, the company directed its existing workforce to work overtime.
But this resulted in many problems. Due to the increased pressure of work, the efficiency of the workers declined. Sometimes the subordinates had to work for more than one superior resulting in declining efficiency. The divisions that were previously working on one product were also made to work on two or more products. This resulted in a lot of overlapping and wastage. The workers were becoming undisciplined. The spirit of teamwork, which had characterized the company, previously was beginning to wane.
Workers were feeling cheated and the initiative was declining. The quality of the products was beginning to decline and market share was on the verge of a decrease.
Actually, the company had implemented changes without creating the required infrastructure.
Identify the principle of management (out of 14 given by Henry Fayol) that were being violated by the company.
Answer:
The company violated the following principles
- 1. Division of work
- 2. Of command
- 3. Unity of direction
- Discipline
- Subordination of individual interest to general interest
- Order
- Initiative
- Remuneration
Question 2.
Do you think that introduction of scientific management as recommended by M consultants will result in the intended outcome?
Answer:
Though scientific management IS the best solution but still it Will not be able to give very effective results as It has its own limitations
1. As competition has increased market research now will not help much.
2. Appointing professionals increases the cost.
3. Principle of the initiative will not help if functional foremanship will also be adopted.
4. In a differential piece wage system only efficient workers may gain, the others will be in pain as they might lose their wages if the target is not met. This will lead to instability which is harmful.
5. Lot of stress will be generated from top to lower levels.
![]()
Question 3.
What precautions should the company undertake to implement the changes?
Answer:
Give your enunciated answer with regard to each technique in points 1 through 6 in the case problem.
A large number of changes will not be accepted by anyone. So the company should play safely while making any changes.
- Trained staff can be appointed for a few areas and workers can be trained to improve efficiency levels.
- Production planning to be done with care.
- Functional foremanship can be introduced but it does not lead to the clear killing of the initiative. Workers should be consulted for suggestions.
- Optimum use of the method, time, motion, and fatigue study should be done.,
- Standardization can be implemented for the material, machinery, and features of the product.
- Financial incentives should be provided to workers to get more work father than adopting a differential piece wage system.