Karnataka 2nd PUC Business Studies Important Questions Chapter 5 Organising
Question 1.
Name the function of management which coordinates the Physical, Financial, and Human resources and establishes productive relations among them for the achievement of specific goals.
Answer:
Organizing
Question 2.
Name and explain the two steps in the process of organizing which come after identification and division of work and departmentation.
Answer:
Assignment of duties and establishing reporting relationships.
Question 3.
Axar Ltd. is manufacturing Toys and has Production Sales, Purchase and Finance Department, which type of organizational structure would you suggest to them? State any three advantages of this organizational structure.
Answer:
I would suggest a functional structure from Axar Ltd.
Question 4.
Kohli Ltd. is manufacturing computers, soaps, and textiles. Which type of organizational structure would suit the requirement of such an organization? State any three advantages of this organizational structure?
Answer:
Divisional Structure would suit the requirement of KohliLtd.
Question 5.
It is a system of consciously coordinated activities of two or more people towards common objectives. Mention this system of organization and explain its two features.
Answer:
Formal organization
![]()
Question 6.
It is a network of personal and social relations not established or required by the formal organization but arising spontaneously as people associate with one another. Name this organization and give its three advantages.
Answer:
Informal organization
Question 7.
The directors of Natesh Ltd. An organization manufacturing computers has asked its marketing manager to achieve a target rate of 100 computers per day. The marketing manager has delegated the task to his deputy sales manager working under him. The deputy sales managers could not achieve the target. Is the marketing manager responsible for the failure of his deputy sales manager? Explain in brief, the relevant principle in support of your answer.?
Answer:
Yes, the marketing manager is responsible for the non-achievement of the target sales.
Question 8.
The Director of Kumar Ltd, an organization manufacturing computer wants to double the sales and given this responsibility to their sales manager. The Sales Manager has no authority either to increase, sales expense or appoint a new salesman. Hence, he could not achieve this target. Is the sales manager responsible for not achieving the target? Explain in brief, the relevant principle in support of your answer.
Answer:
No, the sales manager is not responsible for not achieving the target. The principle involved is the purity of authority and responsibility.
Question 9.
It refers to the systematic delegation of authority from top management to the lower-level managers. Mention the name of it.
Answer:
Decentralization.
Question 10.
“If we delegate the authority, we multiply it by two if we decentralize it, we multiply it by many,“ How?
Answer:
The scope of delegation of authority is limited as it is confined to a manager and his immediate subordinate in the work unit. Scope of decentralization. It involves systematic delegation of authority at all levels and in all functions of the organization. It is an extension of delegation to the lowest levels in the organization
![]()
Question 11.
The employee of VIRAJ Ltd., take part in volleyball matches on Sunday. Name the types of organizations formed.
Answer:
Informal organization
Question 12.
“The first Step in the process of organizing is identification and division of work” Why is his work divided into manageable activities?
Answer:
The work is divided into manageable activities so that duplication of efforts and resources can be avoided and the burden of work can be shared among the employees.
Question 13.
While allocating work to various employees how the work must be assigned?
Answer:
The work must be assigned to those who are best fitted to perform it well.
Question 14.
Which Function of management is concerned with building a stable framework or structure of various parts of an enterprise?
Answer:
Organizing.
Question 15.
How can a department or division be created?
Answer:
It can be created on the basis of-
(a) territory and
(b) products
Question 16.
How does an informal organization emerge?
Answer:
Informal organization emerges from within the formal organization when people interact beyond their officially defined roles.
Question 17.
Name the organization which has the benefit of Easy to fix responsibility?
Answer:
Formal organization
![]()
Question 18.
Name the type of organization that does not have predetermined objectives?
Answer:
Informal organization.
Question 19.
A Fashion design house has the following main job: (1) Manufacturing (2) Finance (3)Marketing (4) Personal (5) Research and Development Which organizational structure will you prefer for this type of company and why?
Answer:
A functional organizational structure will be suitable.
Question 20.
VINEETHA runs a shoe manufacturing factory. She wants to expand her business. For expansion, she contemplated entering into the manufacturing of leather bags and western formal wear apart from the running business of shoes. By doing this her company will be able to provide many products to working women under one roof. Which organization structure will you suggest to her and why?
Answer:
In this situation, a Divisional Structure will be suitable as it provides equal importance to all products. Also, describe the advantages of divisional organization structure.
Question 21.
Name the activity which increases the importance of the role of subordinates?
Answer:
Decentralization.
I. One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Which is the 2nd function of Management?
Answer:
Organizing.
Question 2.
Name any one of the Resources.
Answer:
Money.
Question 3.
Name any one importance of Organising.
Answer:
Optimum utilization of resources.
![]()
Question 4.
For which kind of Organisations does the functional structure suit?
Answer:
Large Organisations.
Question 5.
An Organisation involved in the production of different lines of products should adopt which type of organization structure.
Answer:
Divisional Structure.
Question 6.
Write a feature of formal Organisation.
Answer:
It is created to achieve predetermined objectives.
Question 7.
Write a feature of informal Organisation.
Answer:
It is unplanned and has no predetermined objectives.
Question 8.
What is Delegation?
Answer:
It is a process of transferring authority from superiors to subordinates.
Question 9.
Write the meaning of Authority.
Answer:
It is the right to give orders.
![]()
Question 10.
Write the meaning of Responsibility.
Answer:
It is the duty to perform according to the given orders.
Question 11.
Write the meaning of Accountability.
Answer:
It is a state of being answerable to the job performed.
Question 12.
Write anyone importance of Delegation.
Answer:
Effective Management.
Question 13.
What is Centralisation?
Answer:
It means the decision-making power is in the hands of a single or few people.
Question 14.
What is Decentralisation?
Answer:
It means the decision-making power is in the hands of more persons.
Question 15.
State any one importance of Decentralisation.
Answer:
The democratic system of decision-making.
Question 16.
Give the meaning Organising?
Answer:
A function that brings together all the necessary resources.
Question 17.
Name anyone step involved in the Organising process.
Answer:
Departmentalisation.
Question 18.
Name a type of Organisation Structure.
Answer:
Functional Structure.
Question 19.
Give the meaning of formal Organisation?
Answer:
A formal organization is one that is governed by proper rules and regulations.
Question 20.
Give the meaning informal Organisation?
Answer:
It refers to an organization where the relationship between people working in the organization is not established by formal authority.
Question 21.
Write any one element of delegation.
Answer:
Authority.
![]()
Question 22.
Give the meaning of centralization.
Answer:
The concentration of authority at the top level for decision-making with one or few managers is known as the centralization of authority.
II. Two Marks Question and Answers
Question 1.
Define Organising.
Answer:
According to Henry Fayol ‘To organize a business is to provide it with everything useful to its functioning – raw materials, machine tools, capital, and personnel.
Question 2.
What is the organizing process?
Answer:
The organizing process refers to the identification and division of activities among all the employees. It specifies and divides the duties among departments and employees and lays down the scope of authority and responsibility of each job. It helps to maintain coordination between the activities of various individuals and departments.
Question 3.
What is the functional structure of an organization?
Answer:
Functional Structure:
Grouping jobs of similar nature and organizing these major functions as separate departments create a functional structure. All departments report to a coordination head.
Question 4.
What is the divisional structure of an organization?
Answer:
Grouping of activities on the basis of product is known as a divisional structure of the organization. Under this structure the top-level delegates extensive authority to the divisional heads.
![]()
Question 5.
What is Delegation?
Answer:
Delegation of authority merely means the granting of authority to subordinates to operate within prescribed limits.
Question 6.
What is Decentralisation?
Answer:
Decentralization means that the concentration of the decision-making power lies in the hands of more persons.
Question 7.
What is Organising?
Answer:
It is a process of identifying and grouping the work to be performed. It aims at bringing together all the necessary resources for the accomplishment of organizational goals.
Question 8.
Mention any two importances of Organising.
Answer:
(a) Optimum utilization of resources,
(b) Effective administration.
Question 9.
Mention any two steps involved in the Organising process.
Answer:
(a) Identification and division of work
(b) Departmentalisation.
Question 10.
Mention any two types of Organisational Structures.
Answer:
(a) FunctionalStructure.
(b) Divisional Structure.
Question 11.
What is Functional Structure?
Answer:
It is an organizational structure that groups together similar kinds of jobs by creating separate departments and all the departments will have a Co-ordinating Head.
Question 12.
Mention any two situations where the functional structure is suitable in Organisation.
Answer:
(a) When the size of the organization is large.
(b) When the authority is decentralized.
Question 13.
What is Divisional Structure?
Answer:
It is an organizational structure where a grouping of activities are done on the basis of product and the divisional head is responsible for the smooth functioning of the division.
Question 14.
Mention any two situations where the functional structure is suitable in an Organisation.
Answer:
(a) If an organization is involved in the production of different lines of products.
(b) If the organization needs product specialization.
Question 15.
What is a Formal Organisation?
Answer:
Formal Organisation refers to a structure of well-defined jobs each bearing a definite measure of authority, responsibility, and accountability.
![]()
Question 16.
What is an Informal Organisation?
Answer:
It refers to the relationship between the people in the organization based on the personal attitudes, prejudices, likes and dislikes, etc.,
Question 17.
Mention the elements of delegation.
Answer:
(a) Authority
(b) Responsibility
(c) Accountability
Question 18.
What is Authority?
Answer:
Authority is a rightful or legal power to command or to act, a power which gives the right to give orders to make decisions.
Question 19.
What is Responsibility?
Answer:
It is a state of being responsible or accountable or answerable as for a trust, obligation, or debt.
Question 20.
What is Accountability?
Answer:
It means being answerable, it is an obligation to carry out responsibility and give reports to superiors.
Question 21.
Mention any two importance of delegation.
Answer:
(a) Effective Management
(b) Employee Development.
Question 22.
What is Centralisation?
Answer:
Centralization means that the concentration of the decision-making power lies in the hands of one or few people.
Question 23.
Write any two importances of Decentralisation.
Answer:
(a) Democratic system of decision making.
(b) It facilitates growth.
III. Five Marks Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Explain the Organising process.
Answer:
(a) Identification of Work: The process of Organising starts with the identification of work.
(b) Division of Work: After the first step, the whole work has to be divided into manageable activities.
(c) Departmentalisation: It refers to a grouping of activities of similar nature.
- on the basis of function
- on the basis of the type of product manufactured.
(d) Assignment of Duties: In order to ensure effective performance it is necessary to assign the work to a different set of people who have the ability to do it.
(e) Establishment of reporting relationships: After allocation, it is very essential to establish such clear relationships.
Question 2.
Explain the elements of delegation.
Answer:
The elements of the delegation are as follows:
1. Authority: Authority is the power to command employees and instruct them to perform a job. Authority determines the superior-subordinate relationship. lt flows from top to bottom, i.e., the superior has authority over the subordinate, wherein the superior communicates his decision to the subordinate expecting to perform it. The subordinate executes the decision as per the guidelines of the superior.
2. Responsibility: Responsibility is the obligation of a subordinate to perform the assigned duty. It arises from a superior-subordinate relationship because the subordinate is bound to perform the duty assigned to him. Thus, responsibility flows upwards i.e., the subordinate is always responsible to his superior.
3. Accountability: Accountability means being answerable for the final results. It is an obligation to carry out responsibility and to give reports about one’s performance to the superior. Authority can be delegated by a superior to his subordinate but accountability can never be delegated.
![]()
Question 3.
Explain the importance of Delegation.
Answer:
(a) Delegation enables effective management and increases working capacity.
(b) It is very much necessary for the smooth functioning of a business.
(c) It gives more opportunities to utilize the talents of employees and motivate them to grow.
(d) It facilitates growth and expansion by providing properly trained and experienced personnel.
(e) It helps in better coordination among various departments and functions of management.
(f) It creates a chain for superiors and subordinates on the basis of the hierarchy of management.
Question 4.
Explain the importance of Decentralisation.
Answer:
(a) Quick decision-making: Managers are free to make their own decisions.
(b) Democratic system: It avoids centralization of power and promotes a democratic approach.
(c) Incentive to workers: It provides job satisfaction and boosts the morale of employees.
(d) Facilitates growth: It enables managers of the lower levels to perform well and promote a sense of competitiveness.
(e) Development of Executives: Even the sub-ordinates get a chance to take a decision and get a promotion.
(f) Reduces workload: Decentralisation distributes the work and reduces the burden.
IV. Ten Marks Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Define Organising and Explain the importance of Organising.
Answer:
According to Henry Fayol ‘To organize a business is to provide it with everything useful to its functioning – raw materials, machine tools, capital, and personnel.
Importance of Organising:
(a) Organising leads to optimum utilization of resources without any wastage.
(b) Organising helps the organization to flexible and adjust to any kind of changes in the environment.
(c) Organising provides a clear description of all the work that has to be done and it minimizes confusion and duplication.
(d) Organising helps in systematic allocation and avoids repetitions and increases efficiency.
(e) Organising helps in defining different work relationships and clearly defines the lines of communication.
(f) It helps the organization to take up new challenges and promote growth and diversification
Question 2.
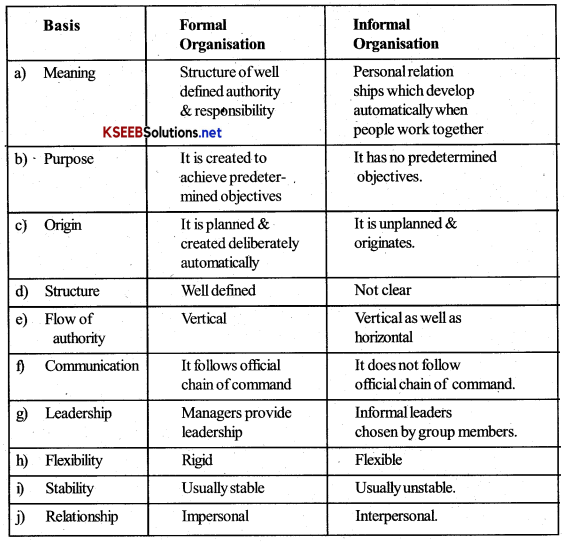
Distinguish between formal and informal Organisation.
Answer:
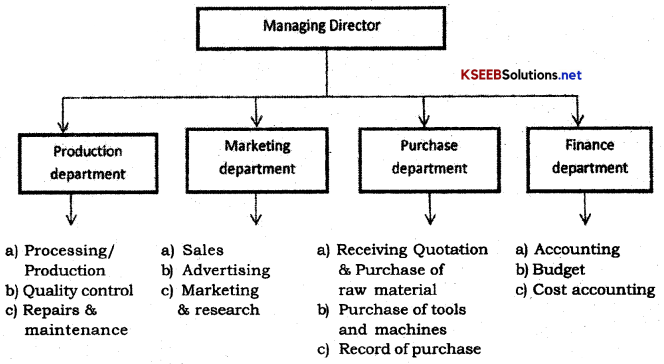
1. Draw a Functional Chart of an Organisation.
Answer:
Exercises
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Define‘Organising’?
Answer:
Organizing is defined as a process that initiates the implementation of plans by clarifying jobs, working relationships and effectively deploying resources for the attainment of identified and desired results.
![]()
Question 2.
What are the steps in the process of organizing?
Answer:
Organizing involves the following steps that need to be taken in series:
- Identification and Division of Work: The organizing process begins with identifying and division of total work into small units.
- Departmentalization: After dividing the work, related and similar jobs are grouped together and put under one department.
- Assignment of Duties: After departmentalization, the work is assigned according to the ability of individuals.
- Establishing Reporting Relationship: Assigning duties is not enough. Each individual should also know, who he has to take orders and to whom he is accountable. Thus, reporting relationship helps in co-ordination among various departments.
Question 3.
Discuss the elements of delegation.
Answer:
The elements of the delegation are as follows:
1. Authority:
It refers to the right of an individual to command his subordinates and to take action within the scope of his position. The concept of authority arises from the established scalar chain, which links the various job positions and levels of an organization. It must be noted that authority is restricted by laws and the rules and regulations of the organizations. Authority flows downward.
2. Responsibility:
Responsibility is the obligation of a subordinate to properly perform the assigned duty. It arises from a superior-subordinate relationship because the subordinate is bound to perform the duty assigned to him by his superior. Responsibility flows upward.
3. Accountability:
Accountability implies being answerable for the final outcome. Once authority has been delegated and responsibility accepted, one cannot deny accountability. It cannot be delegated and flows upwards i.e., a subordinate will be accountable to a superior for satisfactory performance of work.
Question 4.
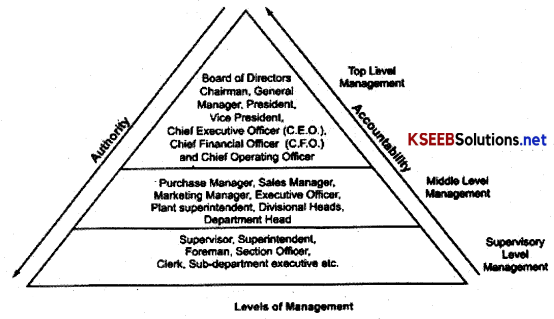
What does the term ‘Span of management’ refer to?
Answer:
Is the number of subordinates under a superior or we can say, it means how many employees can be effectively managed by a superior. The span of management, to a large extent gives shape to the organizational structure, e.q., if the number of subordinates under a superior keeps increasing when we move downward then the shape of the organizational structure will be as follows.
Question 5.
Under what circumstances would functional structure prove to be an appropriate choice?
Answer:
The functional structure would prove to be most suitable when the size of the organization is large, has diversified activities, and operations require a high degree of specialization. It promotes control and coordination within a department, increased managerial and operational efficiency, results in increased profits.
![]()
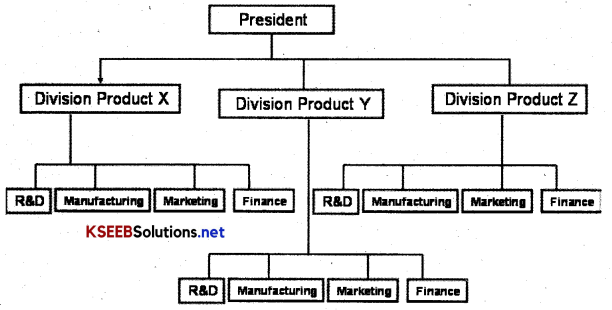
Question 6.
Draw a diagram depicting a divisional structure.
Answer:
Diagram of Divisional Structure
Question 7.
Can a large-sized organization be totally centralized or decentralized? Give your opinion.
Answer:
No large organization cannot be totally centralized or decentralized. Complete centralization would imply conceptualization of all decision-making functions at the apex of the management hierarchy. Such a scenario would obviate the need for a management hierarchy. On the other hand, complete decentralization would imply the delegation of all decision-making functions to the lower level of the hierarchy and this would finish off the need for higher, managerial positions. Both the situations are unrealistic.
As an organization grows in size and complexity, there is a tendency to move towards decentralized decision-making. This is because, in large organizations those employees, who are directly and closely involved with certain operations tend to have more knowledge about them than the top management, which may only be indirectly associated with individual operations. Hence, there is a need for balance between these co-existing forces.
Question 8.
Decentralization is extending delegation to the lowest level. Comment.
Answer:
Decentralization is extending delegation to the lowest level: Decentralisation explains the manner in which decision-making responsibilities are divided among hierarchical levels. Decentralization refers to the delegation of authority throughout all the levels of the organization. Decision-making authority is shared with lower levels and is consequently placed nearest to the point of action. In other words, decision-making authority is pushed down the chain of command.
Delegation is the process and decentralization is the end result, e.g., If the director gives the responsibility to the production head to complete the target of20,000 units and authorize him to hire the workers, the production head further shares his responsibility with the manager to select the worker. The manager shares his responsibility with supervisors, who are dealing with workers, authorizes him to select workers. Here, the responsibility is distributed at every level. That’s why we say systematic delegation leads to decentralization.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Why is delegation considered essential for effective organizing? Effective delegation leads to the following benefits
Answer:
1. Effective Management: By empowering the employees, the managers are able to function more efficiently as they get more time to concentrate on important matters. This makes the working of all the levels effective and efficient.
2. Employee Development: As a result of delegation, employees get more opportunities to utilize their talent and this may give rise to talent abilities in them. It makes them better leaders and decision-makers. Delegation empowers the employees by providing them with the chance to use their skills, gain experience and develop themselves for higher positions.
3. Motivation of Employees: Delegation helps in developing the talents of the employees. It also has psychological benefits. Responsibility for work builds the self-esteem of an employee and improves his confidence. He feels encouraged and tries to improve his performance further.
4. Facilitation of Growth: Delegation helps in the expansion of an organization by providing a ready workforce to take up leading positions in new ventures. Trained and experienced employees are able to play significant roles in the launch of new projects.
5. Basis of Management Hierarchy Delegation of authority establishes superior-subordinate, which management. The extent of delegated is the basis of the hierarchy of authority also decides the power that each job position enjoys in the organization
6. Better Co-ordination: Due to delegation work, duties, power all becomes very clear. This helps to avoid overlapping duties and duplication of effort as it gives a clear picture of the work being done at various levels. Such clarity in reporting relationships helps in developing and maintaining effective coordination amongst the departments, levels, and functions of management.
![]()
Question 2.
What is a divisional structure? Discuss its advantages and limitations.
Answer:
A divisional structure comprises separate business units or divisions. Each unit has a divisional manager responsible for the performance and who has authority over the unit. Generally, manpower is grouped on the basis of different products manufactured.
Merits:
1. Skill Development: Product specialization helps in the development of varied skills in a divisional head and this prepares him for higher positions as he gains experience in all functions.
2. Accountability Divisional heads are accountable for profits, as revenues and costs are related to different departments. Can be easily identified and assigned to them. This provides a proper basis for performance measurement.
3. Quick Decision Making: It promotes flexibility and initiative because each division functions as an autonomous unit which leads to faster decision making.
4. Facilitates Expansion: It facilitates growth as new divisions can be added without interrupting the existing operations, by merely adding another divisional head and staff for the new product line.
Demerits
The divisional structure has certain disadvantages
- Conflicts: May arise among different divisions with reference to allocation of funds.
- Higher: Cost providing each division with a separate set of similar functions increases expenditure.
- Ignoring Organisational Goals: It provides managers with the authority to supervise all activities related to a particular division. In course of time, such a manager may gain power and in a bid to assert his independence may Ignore organizational interests.
Question 3.
Decentralization is an optional policy. Explain why an organization would choose to be decentralized.
Answer:
Decentralization is much more than the mere transfer of authority to the lower levels of the management hierarchy.
Its importance can be understood from the following Points
1. Develops Initiative among Subordinates: When lower managerial levels are given the freedom to make their own decisions they learn to depend on their judgment. A decentralized policy helps to identify those executives, who have the necessary potential to become dynamic leaders.
2. Develops Managerial Talent for the Future: Formal training plays an important part in equipping subordinates with skills that help them rise in the organization, but equally important is the experience gained by handling assignments independently. It gives them a chance to prove their abilities and creates a reservoir of qualified manpower.
3. Quick Decision Making: In a decentralized organization, however, since decisions are taken at levels, which are nearest to the points of action and there is no requirement for approval from many levels the process is much faster.
4. Relief to Top Management: Decentralisation leaves the top management with more time, which they can devote to important policy decisions rather than occupying their time with both policies as well as operational decisions.
5. Facilitates Growth: Decentralisation awards greater autonomy to the lower levels of management as well as divisional or departmental heads. This allows them to function in a manner best suited to their department and develops a sense of competition amongst the departments. Consequently, the productivity levels increase and the organization is able to generate more returns, which can be used for expansion purposes.
6. Better Control: Decentralisation makes it possible to evaluate performance at each level and the departments can be individually held accountable for their results. The extent of achievement of organizational objectives as well as the contribution of each department in the meeting, the overall objectives can be ascertained.
Question 4.
How does the informal organization support the formal organization?
Answer:
The informal organization offers many benefits Important among them are given as follows
1. Quick Feedback: Prescribed lines of communication are not followed. Thus, the informal organization leads to faster spread of Information as well as quick feedback
2. Social Needs: It helps to fulfill the social needs of the members and allows them to find like-minded people. This enhances their job satisfaction since it gives them a sense of belongingness in the organization
3. Organisational Objectives: It contributes towards the fulfillment of organizational objectives by compensating for inadequacies in the formal organization e.g., feedbacks on new policies, etc can be tested through an Informal network.
Question 5.
Distinguish between centralization and decentralization.
Answer:
Difference between centralization and decentralization
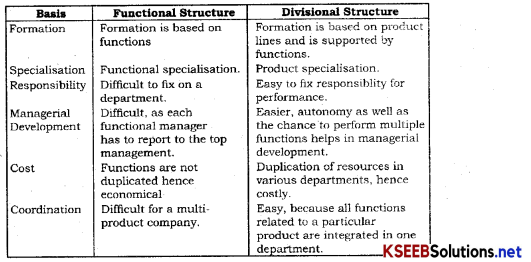
Question 6.
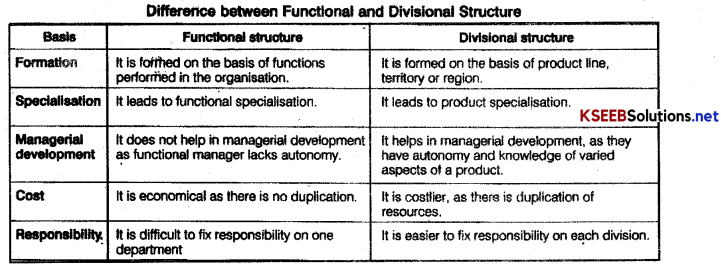
How is a functional structure different from a divisional structure?
Answer:
Difference between functional and divisional structure
Question 7.
Neha runs a factory wherein she manufactures shoes. The business has been doing well and she intends to expand by diversifying into leather bags as well as Western formal wear, thereby making her company a complete provider of corporate me. This will enable her to market the business unit as the one-stop for working women. Which type of structure would you recommend for her expanded organization and why?
Answer:
Neha should decide on the divisional structure because:
- She will diversify her unit now into varied product lines.
- Such a structure would enable her to know the profit margins from each product line and accordingly, she can plan and select the specific product for future diversification.
- It will facilitate further expansion without disturbing the existing units.
Question 8.
The production manager asked the foreman to achieve a target production of 200 units per day, but he doesn’t give him the authority to requisition tools and materials from, the store’s department. Can the production manager blame the foreman if he is not able to achieve the desired target? Give Reasons.
Answer:
No, the production manager cannot hold the foreman responsible for the incomplete work as the foreman was not given authority by the manager. The principle of authority responsibility says that there should be a balance between authority and responsibility. If the authority given is more, then it leads to misuse of authority and if responsibility is more, then the work will not be completed.
Question 9.
A manager enhances the production target from 500 units to 700 units per month, but the authority to draw raw material was not given by him. The production manager could not achieve the revised production target. Who is responsible and which principle was violated?
Answer:
The manager is responsible for work not being completed. The principle of authority responsibility is violated.
![]()
Question 10.
A company has its registered office in Delhi, manufacturing unit at Gurgaon, and marketing and sales department at Faridabad. The company manufactures consumer products. Which type of organizational structure should it adopt to achieve its target?
Answer:
- As a company is performing separate functions in separate areas, then it should adopt a functional structure
- The services of experts are common to all products. It will be economical as no duplication will take place.
- The span of management can be increased as workers will be doing some type of work.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Which of the following is not an element of delegation?
(a) Accountability
(b) Authority
(c) Responsibility
(d) Informal organisation
Answer:
(d) Informal organization is not an element of delegation.
Question 2.
A network of social relationships that arise spontaneously due to interaction at work is called
(a) formal organization
(b) informal organization
(c) decentralization
(d) delegation
Answer:
(b) Informal organization implies social interaction amongst people.
Question 3.
Which of the following does not follow the scalar chain?
(a) Functional structure
(b) Divisional structure
(c) Formal organisation
(d) Informal organisation
Answer:
(d) Informal organization does not follow the scalar chain.
Question 4.
A tall structure has a
(a) narrow span of management
(b) a wide span of management
(c) no span of management
(d) fewer levels of management
Answer:
(a) A tall structure has a narrow span of management.
Question 5.
Centralization refers to
(a) retention of decision-making authority
(b) dispersal of decision-making authority
(c) creating divisions as profit centers
(d) opening new centers or branches
Answer:
(a) Centralisation implies a concentration of all decision-making functions at the apex of the management.
Question 6.
For delegation to be effective, it is essential that responsibility be accompanied by necessary
(a) authority
(b) manpower
(c) incentives
(d) promotions
Answer:
(a) Authority refers to the right of an individual to command his subordinates Thus, It is essential that responsibility be accompanied by the necessary authority.
![]()
Question 7.
The span of management refers to
(a) number of managers
(b) length of term for which a manager is appointed
(c) number of subordinates under a superior
(d) number of members in top management
Answer:
(c) Span of management is the number of subordinates under a superior.
Question 8.
The form of organization known for giving rise to rumors is called
(a) centralised organization
(b) decentralised organization
(c) informal organization
(d) formal organization
Answer:
(c) As is informal organization excess of interactions among people giving rise to rumors.
Question 9.
Grouping of activities on the basis of product lines is a part of
(a) delegated organization
(b) divisional organization
(c) functional organization
(d) autonomous organization
Answer:
(b) Divisional organization implies grouping of activities on the basis of product lines.
Question 10.
Grouping of activities on the basis of functions is a part of
(a) decentralized organisation
(b) divisional organization
(c) functional organization
(d) centralised organization
Answer:
(c) Functional organization implies grouping of activities on the basis of functions
Case Problems:
Question 1.
A company, which manufactures a popular brand of toys, has been enjoying good market reputation. It has a functional organizational structure with separate departments for production, marketing, finance, human resources, and research and development. Lately to use its brand name and also to cash on to new business opportunities it is thinking to diversify into the manufacture of a new range of electronic toys for which a new market is emerging.
Question
Prepare a report regarding organization structure giving concrete reasons with regard to benefits the company will derive from the steps it should take.
Answer:
In the given situation, the organization should shift from functional structure to divisional structure as the company wants to diversity, by adding a new product line. The reasons and benefits are
- The performance of each unit can be easily assessed,
- New product lines can be easily added without disturbing the existing units.
- Decision-making is faster.
- The divisional structure maintains a short line of communication with customers and provides better services to them.
Question 2.
A company manufacturing sewing machines set up in 1945 by the British promoters follows formal organization culture in totality. It is facing a lot of problems in delays in decision making. As the result, it is not able to adapt to changing business environment. The workforce is also not motivated since they cannot vent their grievances except through formal channels, which involve red tape. Employee turnover is high. Its market share is also declining due to changed circumstances and the business environment.
Question
You are to advise the company with regard to change it should bring about its organizational structure to overcome the problems faced by it. Give reasons in terms of benefits it will derive from the changes suggested by you. In which sectors can the company diversify, keeping in mind the declining market for the product the company is manufacturing?
Answer:
The suggestions are
- To overcome the limitations of formal organization, the management should encourage workers to interact and socialize with each other through get-together outings. In this way, everyone will interact and like-minded people will come closer. The net result will be a more satisfied workforce.
- The management should try to decentralize the organizational structure.
- The suggested area where the business can be diversified is textile machinery like embroidery units, sequencing units, buttoning units.
![]()
Question 3.
A company X limited manufacturing cosmetics, which has enjoyed a pre-eminent position in business, has grown in size. Its business was very good till 1991. But after that, a new liberalized environment has seen the entry of many MNC’s in the sector. As the result, the market share of X limited has declined. The company had followed a very centralized business model with directors and divisional heads making even minor decisions. Before 1991, this business model had served the company very well as consumers have no choice. But now the company is under pressure to reform.
Question
What organization structure changes should the company bring about in order to retain its market share? How will the changes suggested by you help the firm?
Keep in mind that the sector in which the company is FMCG.
Answer:
The company X Ltd is working in a centralized way, which is not giving enough time to the higher officials to think of better policies, strategies to handle the changes in the changing environment. The company should thus get decentralized so that the routine type of work, Involving minor decisions can be looked after by the lower levels.
This Will give/save more time for the directors and divisional heads to plan strategies to fight competition