Karnataka 2nd PUC Business Studies Important Questions Chapter 7 Directing
Question 1.
It is a concerned with instructing, guiding, and inspiring people in the organization to achieve its objectives. Name it.
Answer:
Directing
Question 2.
Every manager from top executive to supervisor performs the functions of directing. Which characteristics of directing are referred here.
Answer:
Directing takes place at every level of management
Question 3.
It take place throughout the life of the organization irrespective of people occupying managerial positions.
Mention the characteristic of directing highlighted here and also explains two more characteristics.
Answer:
Directing is a continuous process
Question 4.
“Directing is the least important functions of management”. Do you agree with this statement? Give any two reasons in support of your Answer.
Or
“Directing is not at all reinsured in an organization” do you agree? Give any two reasons in support of your Answer.
Answer:
No, I do not agree with this statement and explain any two point of importance of directing.
Question 5.
“A supervisor is not at all reinsured in an organization” do you agree? Give any three reasons in support of your Answer.
Or
“The post of supervisor should be abolished in the hierarchy of managers”. Do you agree? Give any three reasons in support of your Answer.
Answer:
No, I do not agree because a supervisor performs number of important functions.
![]()
Question 6.
It means overseeing the subordinates at work. Which element of directing is referred to?
Answer:
Supervision
Question 7.
Supervisor acts as a link between workers and management. How?
Answer:
Supervisor conveys management ideas to the workers on hand and workers problems to the management on the other
Question 8.
Which element of directing helps in inspiring subordinates to give their best to the organization. Explain any three points of importance of this element.
Answer:
Explain importance of motivation
Question 9.
Under these incentives schemes employees are offered company shares at a set price which is lower than market. Which incentive scheme is mentioned here? Also explain three more financial incentives.
Answer:
Explain co-partnership/ stock option scheme.
Other financial incentives are:
- profit sharing
- bonus
- commission etc.
Question 10.
To satisfy the social and psychological needs which type of incentives are needed? Explain four types of such incentives.
Answer:
Non-monitory incentives are needed to satisfy the social and psychological needs. Type of non-monitory incentives are:
- status
- career development opportunity
- organizational climate
- job security
- assignment of challenging job etc.
Question 11.
It is defined as the process of influencing other people to work willingly for group objectives. Mention this element of directing.
Answer:
Leadership
Question 12.
Name the type of formal communication in which the persons of the departments one at a higher position other at lower, communication with each other. Also state the problem which may arise in this type of communications.
Answer:
This type of communication is diagonal communication and state it’s any two limitations
![]()
Question 13.
Name the type of written communicatIon ¡n which two departmental heads communicate with each other. Why is this type of communication reinsured?
Answer:
In horizontal communication two departmental needs communicate with each other. Such communication generally relates to the officially accepted and recognized activities of the organization
Question 14.
Ramesh and suresh are working in the same organization but in different departments. One day at lunch time suresh informed ramesh that due to computerization many people are going to be retrcnched soon from the
organization.name, which type of communication of this. State any two limitations of this type of communication.
Answer:
It is an example of informal communication and also explain any two limitations Of informal communication
Question 15.
There are some barriers in communications, which are concerned with encoding and decoding of message. State any three such barriers.
Answer:
It refers to semantic barriers to communication:-
- Symbols with different meanings
- Badly expressed message
- Unclarified assumptions
Question 16.
There are some barriers to 4a communications which are c&iaces with organizational structure regulations. State any three barriers.
Answer:
Organizational barriers:
- Organizational policy
- Status
- rules and regulations
Question 17.
There are some barriers in communication which are concerned with the state of mind of both the sender and the receiver. State any three such barriers.
Answer:
It refers to psychological barriers:
- Premature evaluation
- Loss by transmission and poor attention
- Lake of attention
Question 18.
Name the process of exchanging ideas, facts and information?
Answer:
Communication.
![]()
Question 19.
Name the element of directing under which sub-ordinates share his views with his superior.
Answer:
Communication.
Question 20.
Which type of communication takes place between superior sub-ordinates in the office?
Answer:
Formal Communication.
Question 21.
Name and explain the last steps of communication process.
Answer:
Feedback ‘it is the response given to sender for the message sent.
Question 22.
Name the grapevine network in which an individual communicate with only those people whom he trusts?
Answer:
Cluster grapevine network.
Question 23.
The employees of Infosys Ltd. have formed a dramatic group for their recreation. Name the type of an organization. Explain any three limitations of it.
Answer:
Informal organizations and explain any three limitations.
I. One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What is Directing?
Answer:
It is concerned with managing members of an organisation.
Question 2.
Mention any one importance of Directing.
Answer:
It helps in better co-ordination.
Question 3.
Mention any one of the elements of Directing?
Answer:
Delegation of work.
Question 4.
What is Supervision?
Answer:
It is concerned with observing the work of sub-ordinates.
![]()
Question 5.
What is leadership?
Answer:
The process of influencing sub-ordinates to work and achieve organisation goals.
Question 6.
Mention any one of the importance of Supervision?
Answer:
It acts as a link between workers and management.
Question 7.
From which language the word motivation is derived from.
Answer:
It is derived from Latin word ‘movere’ which means to move.
Question 8.
Mention any one Maslow’s hierarchy of needs.
Answer:
Physiological needs.
Question 9.
What is communication?
Answer:
It is exchange of information by two or more persons.
Question 10.
Mention any one importance of Communication.
Answer:
It increases productivity.
![]()
Question 11.
Mention any one type of Communication.
Answer:
Formal Communication.
Question 12.
Mention any one of the barriers to effective communication.
Answer:
Physical barriers.
Question 13.
Mention any one of two solutions to overcome barriers of Communication.
Answer:
Communication should be done in a language understood by both sender and receiver.
Question 14.
Which type of communication is called Grapevine Communication.
Answer:
Informal Communication.
Question 15.
State any one element of direction.
Answer:
Delegation.
Question 16.
Name any one need of human beings as stated by Maslow.
Answer:
Physiological Needs.
Question 17.
State any one style of leadership.
Answer:
Autocratic leadership.
![]()
Question 18.
Write any one quality of a successful leader.
Answer:
Confidence.
Question 19.
Name any one barrier of communication.
Answer:
Physical Barriers like distance.
Question 20.
State any one way to overcome the barriers to effective communication.
Answer:
Clarity of ideas.
II. Two Marks Question and Answers
Question 1.
Define Direction.
Answer:
According to Koontz and O’Donnell ‘Direction is the interpersonal aspect of managing by which sub-ordinates are led to understand and contribute effectively and efficiently to the attainment of enterprise objectives’.
Question 2.
State any two elements of Direction.
Answer:
(a) Delegation – Which involves issuing direction to sub-ordinates.
(b) Supervision – It is concerned which observing the work of sub-ordinates.
Question 3.
What is Supervision?
Answer:
It is an act of overseeing, management by overseeing keeps an eye on sub-ordinates to make sure they are performing as required or not.
Question 4.
Define Motivation.
Answer:
According to Koontz and O’Donnell. ‘Motivation is a general term applying to entire class of drives, needs, wishes and similar forces’.
![]()
Question 5.
Name any two styles of Leadership.
Answer:
(a) Autocratic leadership
(b) Democratic leadership
Question 6.
Define Communication.
Answer:
According to George Terry, ‘Communication is a exchange of facts, ideas, opinions or emotions by two or more persons.
Question 7.
What is Formal Communication.
Answer:
A type of verbal presentation or document intended to share information using formal channels of the organisation.
Question 8.
What is grapevine communication?
Answer:
Informal communication or grapevine is an informal channel of business communication. It is called so, because it stretches throughout the organisation in all directions irrespective of authority levels.
Question 9.
Give the meaning of sematic barreirs of communication?
Answer:
Sematic barriers: The use of difficult and multiple uses of languages, words, figures, and symbols create sematic barriers.
Question 10.
What is Directing?
Answer:
It is one of the most important functions of management which is concerned with managing members of an organisation.
![]()
Question 11.
Mention any two importance of Directing.
Answer:
(a) It ensure efficient use of resources.
(b) It helps to maintain discipline in the organisation.
Question 12.
Mention any two importances of Supervision.
Answer:
(a) It helps in planning and organising work.
(b) It acts as a vital link between workers and management.
Question 13.
What is Motivation?
Answer:
It is that element of directing which helps in converting the ability to work in workers to willingness to work.
Question 14.
Mention any two stages of Maslow’s Hierarchy of needs.
Answer:
(a) Physiological needs
(b) Safety needs.
Question 15.
What is Leadership?
Answer:
It is a quality of a character and personality giving apersonthe ability to gain the confidence of others and lead them.
Question 16.
Define Leadership?
Answer:
According to Koontz and O’Donnell, ‘Leadership is the ability of a manager to induce sub-ordinates to work with confidence and goal.’
Question 17.
Mention any two qualities of a successful leader.
Answer:
(a) Positive attitude
(b) Emotional stability.
Question 18.
What is Communication?
Answer:
It is an act of conveying information, ideas, opinions from one person to another person.
Question 19.
Mention any two importance of Communication.
Answer:
(a) It ensures smooth and uninterrupted working of an organisation.
(b) It helps in effective decision making.
![]()
Question 20.
Mention any two types of Formal Communication.
Answer:
(a) Downward Communication.
(b) Upward Communication.
Question 21.
What is Informal Communication?
Answer:
A casual form of information sharing typically used in personal conversations with friends and family members.
Question 22.
Mention any two barriers of Effective Communication.
Answer:
(a) Physical Barriers.
(b) Organisational Barriers.
III. Five Marks Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Explain the importance of motivation.
Answer:
Importance of Motivation:
(a) Productive use of resources: Modem organisations work through physical, financial and human resources. The utilisation of these resources depends on the willingness of people to work. Motivation enables people to convert physical and financial resources into useful products. It helps management to get the best out of human and non – human resources.
(b) Increased efficiency and output: Motivation enables to people to work enthusiastically. Performance is the product of not only the ability to do a task but the willingness to do it with zeal and enthusiasm. Motivation bridges the gap between the overall efficiency and output and helps in reducing the cost of operation.
(c) Achievement of goals: Motivation causes goal directed behaviour. It helps people to move in a desired direction and earn rewards. If people are not properly motivated no useful purpose can be served by planning, organising and staffing functions.
(d) Stability in work force: Attractive motivational schemes satisfy the needs of employees. As a result their commitment to the organisational work increases. This helps to reduce employee turnover and absenteesim from work.
(e) Development of friendly relations: Motivating employees through attractive rewards, promotional opportunities etc. encourages then to consider the well being of the firm as their own. This helps in developing cordial relations between the management and workers.
Question 2.
Explain briefly the importance of Supervision.
Answer:
(a) A supervisor guides the workers in doing a job.
(b) He helps in planning and organising the work.
(c) He acts as a vital link between workers and management.
(d) He motivates workers and procures maximum efficiency from them.
(e) He compares the actual performance of workers with the standards and help them identify their weakness.
(f) It helps in identifying the capabilities of workers and assign work accordingly.
![]()
Question 3.
Explain the types of Leaderships.
Answer:
(a) Autocratic Style: This type of leadership includes a leader who decides policies for a group all by himself without consulting anybody.
(b) Democratic Style: It is exactly the opposite style of autocratic style, here a leader takes decision for a group after consulting all and selecting the best alternative available.
(c) Bureaucratic Style: Here the leader is not concerned with people but he is concerned with following the policies of the organisation before taking a decision.
(d) Free Run Style: Here the leader entrusts the decision making authority to his sub-ordinates, leader hardly makes any contribution in this style.
(e) Executive Style: Here the leader develops a strategy after concerning the situation and also people who are involved.
Question 4.
Write the meaning and importance of communication
Answer:
Communication is an act of conveying information, ideas, opinions from one person to another.
Importance of Communication:
(a) Co-ordination: It is important to achieve a common goal in a organisation and communication helps in achieving it.
(b) Smooth Working: It ensures smooth and uninterrupted working in an organisation.
(c) Effective Decision Making: It helps in making sound and effective decisionmaking.
(d) Managerial Efficiency: all the functions of management cannot be discharged properly without communication.
(e) Co-operation: among workers is possible only when there is a formal or informal communication between them.
(f) Effective Leadership: one who has mastered communication skill becomes a successful leader,
(g) Increases Productivity: A good system of communication helps in achieving maximum productivity.
(h) Morale Building: It builds the morale of workers and motivates better participation.
Question 5.
Explain the advantages of good communication.
Answer:
The advantages of good communication are:
(a) Co ordination: Communication helps in coordinating the activities of the employees of an organisation in achieving organisational objectives.
(b) Effective decision making: A good communication system enables correct and complete information to be passed on the the top management. This assists the management in their decision making process and ensures that the right decision taken.
(c) Managerial Efficiency: Management is able to carry out its functions of planning, organising, control, etc. only if the communication system is strong. So good communication is essential to increase mangement efficiency.
(d) Increases Productivity: A good system of communication helps the management to achieve maximum productivity with minimum cost, elimination of waste, reduction o f cost etc..
(e) Co operation: Co – operation among workers is possible only when there is an exchange of information between individuals and groups and between management and employees. This promotes industrial peace and maximises production.
(f) Moral Binding: An effective system of communication builds good moral and improves human
relations.
![]()
Question 6.
Explain the importances of Directing.
Answer:
(a) It involves delegation of work and assiging responsibilities.
(b) It ensures optimum utilization of resources.
(c) It is an essential element for effective supervision, motivation, leadership and communication.
(d) It provides clarity of work and ensures efficiency.
(e) It maintains discipline in organisation and ensures smooth functioning of work.
Question 7.
Mention the elements of Direction.
Answer:
(a) Delegation – means giving instructions to sub-ordinates.
(b) Supervision – It is concerned with observing the work of sub-ordinates.
(c) Leadership – It is concerned with influencing sub-ordinates to work and achieve organisational goals.
(d) Motivation – It helps in converting the ability to work of employees to willingness to work.
(e) Communication – It is a exchange of infoirnation by two or more persons.
(f) Co-ordination – It implies proper integration of activities of various organisations members.
IV. Ten Marks Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Explain the importance of direction as a function of management.
Answer:
Importance of Directing
(a) Action Oriented: Directing is action oriented. It involves delegation of authority and assigning of responsibilities.
(b) Integration of efforts: It integrates efforts of employees at various levels by proper delegation of authority and responsibility which in turn helps in achieving organisationsl objectives.
(c) Efficient use of resources: Directing involves the bringing in proper methods of doing work. It helps in the efficient use of resources of the organisation.
(d) Essential element: Directing is essential for effective supervision, motivation, leadership and communication
(e) Efficiency: Proper direction will help the employees to achieve their best as it provides clarity or work. It ensures efficiency.
(f) Flexibility: Directing helps to bring flexibility in the organisation. It convinces the subordinates to accept the changes which the management intends to bring in future.
(g) Clarity: Directing gives clarity in authority and responsibility, this helps to minimise the ambiguity in the work.
(h) Discipline: It helps to maintain the discipline in the organisation, which results in smooth functioning of the work.
(i) Co – ordination: It co ordinates different activities of the management.
(j) Creation of Leaders: Good direction create good leaders.
Question 2.
Explain how supervision plays an important role as an element of direction.
Answer:
Supervision is concerned with initiating actions, putting the plans and decisions by stimulation of the human resources of the enterprises. Thus, it is clear that supervision , consists of the process and technique involved in issuing instructions and conforming the operations are carried out as planned. Importance of Supervision
Importance of Supervision can be explained as below:
(a) Issue of orders and instructions: A supervisor guides the workers in doing a job and helps them in clearing their doubts.
(b) Planning and organising the work: Supervision helps in planning and organising the work. It guides the subordinates. It lays down production targets and determines the procedures for doing the work.
(c) Vital link between workers and management: Supervision represents both workers and the management. It acts as a link between them. It communicates the policies of the management to workers and also provides the feedback of the workers to the management.
(d) Motivating subordinates: It inspires teamwork and secures maximum co – operation from the workers.
(e) Feedback to workers: It compares the actual performance of the workers with the standards and helps in identifying the weaknesses of the workers. As a result workers can improve their performance in future.
(f) Proper assignment of work: Supervision helps to identify the capabilities of workers and assigns the work accordingly.
(g) Maintain discipline: Supervision is directly responsible for enforcing the rules and regulations of the organisation, which helps to maintain discipline.
![]()
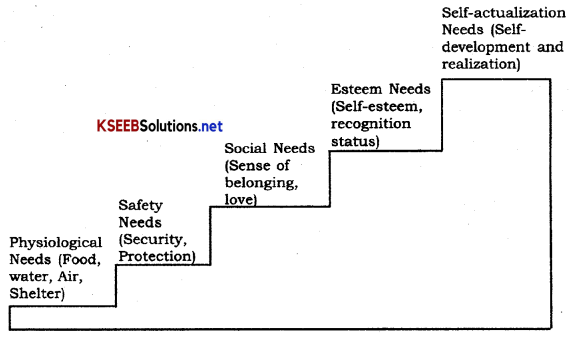
Question 3.
Explain Maslow’s Hierarchy of needs.
Answer:
(a) Physiological needs: It includes basic needs such as food, shelter, clothing etc., which are the most powerful motivators.
(b) Safety needs: After satisfaction of physiological needs, needs like job security insurance etc to cover risks arises.
(c) Social needs: It includes belongingness, association, acceptance, friendship and love.
(d) Esteem needs: Self respect is a key to such need and respect comes from being a accepted, recognition within the group and community.
(e) Self actualization needs: It includes the need to realise one’s capabilities and potentials by achieving specific goals.
Question 4.
Explain the qualities of a successful Leader?
Answer:
(a) Honesty: A successful leader should be honest.
(b) Enthusiastic: Asuccessful leader should have enthusiasm to face challenges.
(c) Good Personality: A good leader should have tidy and good appearance.
(d) Ability of Delegation: The success of leadership depends on the ability of a leader to assign work to his sub-ordinates.
(e) Communication: He should be very good at communication to sub-ordinates.
(f) Confidence: A self confident person can only create confidence in sub-ordinates.
(g) Initiative: A quality of initiativeness describes the quality of willingness to take risks.
(h) Positive Attitude: A good leader should have a positive set of mind for achieving goals even in difficult situations.
(i) Passion: He should be passionate towards the work he does.
(j) Creativity: Good leader should search for different methods of doing work effectively in order to avoid foredom.
(k) Emotional Stability: He should have control over his emotions and sentiments.
(l) Generosity: He should be able to build a rappo with his sub-ordinates and should be generous enough to praise good work of sub-ordinates.
Question 5.
What are the barriers to Effective Communication? Explain.
Answer:
1. Physical Barriers: It includes barriers which is caused by materialistic things like machines, plant layout and equipments.
(a) Distance – Communication obstructed by long distance.
(b) Noise – Communication obstructed by noise of machineries.
(c) Physical Management: Communication obstructed by physical arrangement of sources like men, money, material and machine.
2. Semantic Barriers:
It includes barriers which are caused by inability to understand a language or signs,
(a) Language – one of the most important barriers found all over the world, there will be a problem in communication if the sendei and receiver donot understand same language.
(b) Jargons: People often find it difficult to understand technical and unfamiliar terms drawn from literature.
3. Organisational Barriers: There arises from the organisational goals, regulations, structure and culture.
(a) Poor Planning: It refers to inability to design a proper plan.
(b) Organisational Distance: Distance between sender and receiver. .
(c) Timing: often good communication can be obstructed if not done on time.
4. Psychological Barriers: These arises only due to lack of interest in people for whom communication is meant.
(a) Perception: It depends on how the receiver understands it.
(b) Filtering: In downward and upward movement of communication there is a possibility of information getting filtered.
(c) Emotions: It creates a major barrier to communication.
(d) Viewpoint: Where the information is not clearly understood the receiver interprets it the way he wants.
Question 6.
Explain the way of overcome the barriers of Communication?
Answer:
(a) The person sending the communication should be very clear in what he wants to say.
(b) There should be proper structure for sending communication.
(c) It should not be sent by keeping the ability of own to understand but also understand the ability of the receiver.
(d) Suggestions should be welcomed from all comers before preparing communication planning.
(e) Should be aware of language, tone and content of message before sending.
(f) The need and interest of receiver should be kept in mind and it should be effective.
(g) Proper feedback should be collected to understand whether the receiver has received the message properly or not.
(h) It should be in accordance with the objectives, policies and programmes of the organisation.
(i) A follow up communication should be established in order ensure that the communication has been established as desired.
(j) Basic essence of communication is that both sender and receiver should be good listeners.
Question 1.
Draw the chart of Maslow’s Theory of Hierarchy of Needs.
Answer:
Question 2.
State any 10 qualities of a Successful Leader.
Answer:
(a) Honesty
(b) Initiatives
(c) Enthusiastic
(d) Positive Attitude
(e) Good Personality
(f) Emotional Stability
(g) Good Communication
(h) Generosity
(i) Confidence
(j) Creativity
Exercises
Short Answer Type Questions
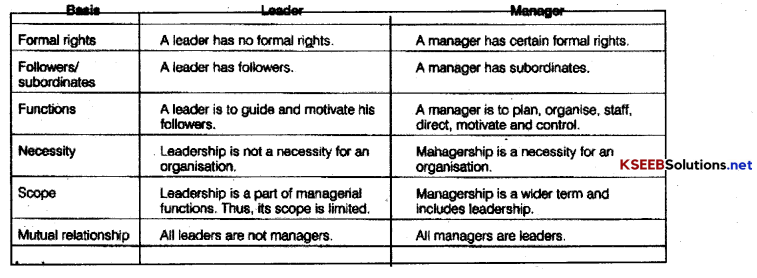
Question 1.
Distinguish between leaders and managers.
Answer:
Difference between Managers and Leaders
Question 2.
Define Motivation.
Answer:
Motivation is defined as inducing. inspiring and stimulating a person to perform with their best ability, to accomplish the goal. It depends upon satisfying the needs of people. In the words of Farland, “motivation is the way in which urges, desires, aspirations or needs, direct control and explain the behavior ofhuman beings”.
![]()
Question 3.
What is informal communication?
Answer:
The social interactions, gossips, friendly talks and non-official matters which are discussed among different members of organisation who are not officially recognised is known as informal communication or we can say the communication that takes place without following the formal guidelines of communication Is said to be informal communication. This type of communication establishes the personal relationship among employees. It is flexible, dynamic and no records of information communication are maintained under this Informal communication system is generally referred to as “Grapevine”.
Question 4.
What are semantic barriers of communication?
Answer:
While communicating a message, misrepresentation of communication causes misunderstanding on account of use of wrong words lack of vocabulary skills, faulty translations, different interpretations is known as semantic barriers. It is concerned with the problems which arises in the process of encoding and decoding of message into words or impressions.
Main causes of semantic barriers are listed below
- Badly expressed message
- Symbols with different meanings
- Faulty translations
- Unclarified assumptions
- Technical jargon
- Body language and gesture decoding
Question 5.
Who is a supervisor?
Answer:
Supervision means instructing, guiding, monitoring motivating and observing the activities of employees from over and above. The person who is performing the work of supervision is known as supervisor. Supervisor is the link between management and subordinates. He is the person who translates the policies and plan of management to the subordinates and revert back the complaint, suggestions and feedback of subordinates to management.
Question 6.
What are the elements of directing?
Answer:
Directing comprises of four elements
- Supervision: It can be understood as the process of guiding and instructing the efforts of employees.
- Motivation: The process of encouraging the employees in order to help them in achieving the desired goals is known as motivation
- leadership: It is the process of influencing the behaviour of people by making them strive voluntarily towards achievement of organisational goals.
- Communication: It is the process of exchange of ideas, Views, facts, feelings etc between or among people to create common understanding.
Question 7.
Explain the process of motivation.
Answer:
Motivation process is based on how unsatisfied human need gets satisfied and results in reduction of tension.
The steps of the motivation process are as follows
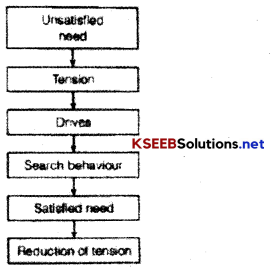
- Unsatisfied Need: The need of an individual which is not satisfied.
- Tension Unsatisfied: need creates tension
- Drive: This tension creates drive and an Individual starts looking for alternatives to satisfy the need.
- Search Behaviour: Then he starts behaving as per chosen option.
- Satisfied Need: after opting the chosen behaviour his need got satisfied.
- Reduction of Tension: The fulfilment of need results in relieving of tension.
![]()
Question 8.
Explain different networks of grapevine communications.
Answer:
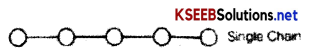
Grapevine communications may follow different types of network they are
1. Single Strand Network Each person communicates to the other in sequence.
![]()
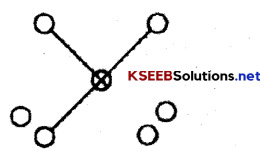
2. Gossip Network Each person communicates with all on non-selective basis.
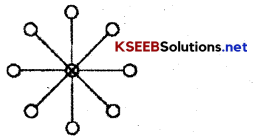
3. Probability Network the Individual communicates randomly with other Individual
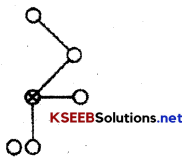
4. Cluster Network The individual communicates with only those people whom he trusts
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain the principles of Directing.
Answer:
Principles of Directing:
1. Maximum Individual Contribution: This principle emphasises that directing techniques must help every employee to contribute to his maximum potential in order to achieve the organisational goals. It should help In bringing out unused or dormant potential of an employee to improve the efficiency of the organisation, e.g., suitable and appropriate Incentives should be given to encourage employees to improve their performance.
2. Harmony of Objectives: Most of the lime It happens that the organisational objectives and Individual objectives move in opposite directions, The person In charge of a team of workers should guide and Instruct his team In such a manner that they realise the Importance Of both the objectives.
3. Unity of Command: This principle insists that a person in the organisation should receive Instructions from one superior only. If Instructions are received from more than one, it creates confusion, conflict and disorder In the organisation Adherence to this principle ensures effective direction.
4. Appropriateness of Direction Technique According to this principle: Appropriate motivational and leadership technique should be used while directing the people based on subordinate needs capabilities. Attitudes etc., e.g.. Combination ofboth monetary and non-monetary Incentives should be used to elicit the right response from the employees.
5. Managerial Communication: Directing should convey clear Instructions to create total understanding to subordinates through proper feedback the manager should ensure that subordinate understands his instructions clearly.
6. Use of Informal Organisation: Informal groups or organisations exist within every formal organisation and every manager should spot and make use of such organisations for effective directing
7. Leadership: While directing the subordinates managers should exercise good leadership as it can influence the subordinates positively without causing dissatisfaction among them
8. Follow Through: Mere giving of an order is not sufficient Managers should follow It up by reviewing continuously whether orders are being implemented accordingly or any problems are being faced by the subordinates.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain the qualities of a good leader. Do the qualities alone ensure leadership success?
Answer:
Some of the qualities required by all leaders are
1. Physical Features: It is believed that good physical features attract people. Height, weight, health, appearance determine the physical personality of an individual.
2. Knowledge: A good leader should have required knowledge and competence Only such person can Instruct subordinates correctly and Influence them
3. Integrity: He should be a role model to other regarding the ethics and values A leader should possess high level of integrity and honesty.
4. Initiative: A good leader never waits for opportunities to come to his way rather he grabs the opportunity and use it to the advantage of organisation.
5. Communication and Motivation Skills: A leader should be a good communicator. He should have the capacity to explain his Ideas and make the people to understand his Ideas. He should also understand the needs of people and motivate them through satisfying their needs.
6. Self Confidence: A high level of self-confidence is very important for any leader He should not lose his confidence even in most difficult times A person who is not himself confident will never be successful in providing confidence to his followers
7. Decisiveness Leader: Should be able to take decisions while managing the work. Once he is convinced about a fact, he should be firm and should not change opinions frequently.
8. Social Skills: A leader should be sociable and friendly with his colleagues and followers. He should understand people and maintain good human relations with them. Many times, the success of an organisation is attributed to the leader, but due credit is not given to the followers. Many followers related factors like their skills, knowledge, commitment, willingness to co-operate team spirit etc. make a person an effective leader It is said that followers make a person, a good leader by acceptance of leadership. Therefore both followers and leaders are playing an vital role in leadership process.
Question 3.
Discuss Maslow’s Need Hierarchy theory of motivation.
Answer:
Maslow’s need Hierarchy; Theory of Motivation is a psychological term and the needs of an employee plays an important role In motivation. In order to study motivation various researchers developed theories on them. Among them Abraham Maslow’s need Hierarchy theory is considered of worth.
As per him, there exists a Hierarchy of five needs these are
1. Basic Physiological Needs; These needs are most basic in the hierarchy and corresponds to primary needs. Food, clothing shelter are a few examples of this type of need Basic salary helps to fulfil these needs
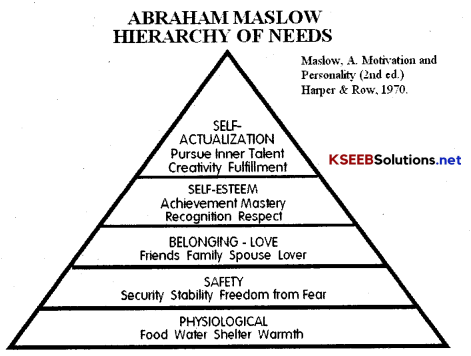
2. Safety/Security Needs When the basic needs satisfied, people start thinking of future. These needs provide security and protection from
3. Affiliation/Belonging Need These needs refer to human feeling ofbelongingness. We all as human beings look forward to being accepted In the society e.g.. friendship.
4. Esteem Needs These include factors such as self-respect, autonomous status, attention An individual wants a respect and recognition from others in this need
5. Self-actualisation Needs It is the highest level of need in the hierarchy It refers to the drive to become what one is capable of becoming The needs include growth self-fulfilment and achievement of goals etc.
![]()
Question 4.
What are the common barriers to effective communication suggest measures to overcome them?
Answer:
Common Barriers to Effective Communication Managers in all organisations lace problems due to communication barriers these barriers may prevent a communication or filter part of it or carry Incorrect meaning due to which misunderstanding may be created. Therefore all managers should take some steps to overcome these barriers.
There are broadly four groups of barriers
1. Semantic Barriers Semantic barriers are concerned with problems and obstructions In the process of encoding and decoding of message into words or -expressions Normally such barriers result on account of use of wrong words, faulty translations, different interpretations etc.
These are discussed below
(a) Badly Expressed Message: Sometimes the message is not communicated correctly by the manager because of inadequate vocabulary, usage of wrong words. Omission of needed words etc.
(b) Symbols with Different Meaning: A word may have several meanings Receiver has to perceive one such meaning for the word used by communicator.
(c) Faulty Translations sometimes while translating If incorrect translation is done due to poor command over both the languages then meaning of the message changes This leads to cause different meanings to the communications.
(d) Unclarified Assumptions: Sometimes communication may have certain assumptions which are subject to different interpretations the one should always clear the meaning of what he is instructing the worker to do, so that the worker has no doubts in his mind.
(e) Technical Jargon: Sometimes specialists may use technical words in their communication by which the receiver IS not aware Therefore, they may not understand the complete conversation.
(f) Body Language and Gesture Decoding: The body movement and body gestures plays an important role in conveying the message. If there is no match between what is said and what is expressed In body movements, communications may be wrongly perceived.
2. Psychological Barriers: Emotional or psychological factors acts as barrier to communications e.g., a person who is warned cannot understand what is being told.
Some of the psychological barriers are
(a) Premature Evaluation: Sometimes people evaluate the meaning of message before the sender completes his message. Such premature evaluation may be due to preconceived notions.
(b) Lack of Attention If the mind is pre-occupied then the result is non-listening of message by receiver act as a major psychological barrier.
(c) Loss by Transmission and Poor (Retention): When message passes through various levels. Successive transmission of message results in loss of information. It happens mostly with oral communication. Also people cannot retain the information for a long time if they are inattentive or not interested.
(d) Distrust: If the communicator and communicate do not believe on each other. They cannot understand each other’s message in its original sense as they are not giving importance to the information exchanged.
3. Organisational Barriers: The factors related to organisation structure, authority relationships, rules and regulations may sometimes act as barriers to effective communication some of these barriers are
(a) Organisational Policy: If the organisational policy is not supportive to free flow of communication, it may hamper effectiveness of communications.
(b) Rules and Regulations: Rigid rules and cumbersome procedures maybe a hurdle to communication similarly, communi cation through prescribed channel may result in delays.
(c) Status: Status of superior may create psychological distance between him and his subordinates the people working at higher level may not allow his subordinates to express their feelings freely.
(d) Complex Organisational: Structure In an organisation where there are number of managerial levels, communications gets delayed and distorted as number of filtering points are more
(e) Organisational Facilities: For smooth clear and timely communication proper facilities are required like frequent meetings suggestion box. Internet connection, Intercom facility. Lack or ineffectiveness of these facilities may create communication problems
4. Personal Barriers: The personal factors of both sender and receiver may exert influence on effective communication.
Some of the personal barriers are
(a) Fear of Challenge to Authority: If a superior feels that a particular communication may affect his authority negatively then he/she may not speak it out clearly and openly.
(b) Lack of Confidence of Superior: on his Subordinate If superiors do not have confidence on their subordinates, they may not seek their advice or opinions.
(c) Unwillingness to Communicate: Sometime subordinate or may not be prepared to communicate with their superiors if they think that it may adversely affect their interests.
(d) Lack of Proper Incentives: If there is no reward for communication then employees may not be motivated to communication e.q., if there is no reward or appreciation for a good suggestion, the subordinate may not be willing to offer useful suggestions again Some measures which can be adopted by organisations to improve communications are
- Clarify the Ideas Before Communi cation: The entire message to be communicated should be studied in depth analysed and stated in such a manner that It is clearly conveyed to subordinates. The message should be encoded In simple language which is understandable.
- Communication According to the Needs of Receives: All managers should be aware of the understanding level
5. Co-Partnership/Stock Option: Under these Incentives schemes, employees are offered company shares at a set price which is lower than market price The allotment of shares creates a peeling of ownership to the employees and makes them to contribute more for the growth of the organisation.
6. Retirement Benefits: Several retirement benefits such as provident fund, pension and gratuity provide financial security to employees after their retirement. This act as an Incentive when they are In serves in the organisation.
7. Perquisites: In many companies’ perquisites and fringe benefits are offered such as car allowance, housing, medical aid, and education etc. over and above the salary.
These measures help to provide motivation to the employees/managers
Non-financial Incentives: Incentives that help in fulfilling our psychological emotional and social needs are known as non-financial incentives some of the non-financial Incentives are
1. Status: Status means ranking or high positions In the organisation. Whatever power position prestige an employee enjoys in the organisation are indicated by his status Psychological, social and esteem needs of an Individual are satisfied by status given to their job.
2. Organisational Climate: This indicates the characteristics which describe an organisation and distinguish one from the other. Individual autonomy, reward orientation, consideration to employees, etc. are some of the positive features of an organisation. If managers try and include more of these In an organisation helps to develop better organisational climate
3. Career Advancement Opportunity: Managers should provide opportunity to employees to improve their skills and be promoted to the higher level Jobs appropriate skill development programmes and sound promotion policy Will help employees 10 achieve promotions. Promotions have always worked as tonic and encourages employees to exhibit improved performance
4. Job Enrichment: Job enrichment is concerned with designing jobs that include greater variety of work contentment require higher ofknowledge and Skill, give workers more autonomy level and responsibility and provide opportunity for personal growth and a meaningful work experience
5. Employee Recognition Programmes: Recognition means acknowledgement With a show of appreciation. When such appreciation is given to the work performed by employees, they feel motivated to perform/work at higher level, eg-,
(a) Congratulate the employee
(b) Displaying names of star performers
(c) Installing awards
(d) Distributing mementos
6. Job Security: Employees want their job to be secure. They want certain stab lily about future income and work so that they ‘ do not feet warned on these aspects and work with greater zeal There is only one problem with this Incentive i.e., when people feel that they are not likely to lose their jobs. They may become relaxed.
7. Employee Participation: It means Involving employees In decision making of the Issues related to them. In many companies, these programmes are In practice In the form of joint management committees. Work committees canteen committees etc.
8. Employee Empowerment: Empowerment means giving more autonomy and powers to subordinates. Empowerment makes people feel that their Jobs are important. This feeling contributes positively to the use of skills and talents in the Job performance,
Question 5.
The workers always try7 to show their inability when any new7 work is given to them. They are always unwilling to take up any kind of work. Due to sudden rise in demand a firm wants to meet excess orders. The supervisor is finding it difficult to cope up with the situation. Suggest ways for the supervisor to handle the problem.
Answer:
The supervisor can take help of monetary incentives to motivate the workers Their wages can be linked to productivity they can earn more incentives besides wages by producing goods. Supervisor should also play the role of a good leader and encourage them to accept any kind of work as it would lead to Increase exposure to the industry and better job prospects.
![]()
Question 6.
Workers of a factory often come to the production manager with the grievances. .The production manager finds himself overburd ened w ith so many tasks advise a way to relieve the production managers.
Answer:
To overcome the problem the production manager should take the folio wing measures:
- Arrange necessary training programmes
- Prepare a work schedule
- Recommend the cases of the workers for promotion, rewards. Transfer, punishmentetc.
- Proper availability of materials. Machines and tools for the workers
- Delegate sum of authorities.
Question 7.
In an organisation employees always . feel they are under stress. They take last initiative and fear to express their problems before the manager. What do you think is wrong with the manager?
Answer:
The manager should adopt more friendly approach towards the workers. The manager should encourage a system of two-way communication; provide an outlet to workers to share their feelings, suggestions and problems.
Question 8.
In an organisation all the employees take things easy and are free to approach anyone for minor queries and problems. This has resulted in everyone taking to each other and thus resulting in inefficiency in the office. It has also resulted in- loss of secrecy and confidential information being leaked out. What system do you think the manager should adopt to improve communication?
Answer:
Excess of everything is bad. More use of Informal communication is resulting in this problem. A proper chain of command should be established. Only the necessary information should be passed through chain of command the employees will not be allowed to communicate at all levels. This Will save time and more discipline.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Which one of the following is not an element of direction?
(a) Motivation
(b) Communication
(c) Delegation
(d) Supervision
Answer:
(c) Delegation is not en element of direction.
![]()
Question 2.
The motivation theory which classifies needs in hierarchical order is
(a) Fred Luthans
(b) Scott
(c) Abraham Maslow
(d) Peter F Drucker
Answer:
(c) Abraham Maslow gave the hierarchy offive human needs.
Question 3.
Which of the following ¡Is a financial incentive?
(a) Promotion
(b) Stock incentive
(e) Job security
(d) Employee participation
Answer:
(b) Stock incentive is a financial incentive which is a employee stock option with a tax benefiL
Question 4.
Which of the following is not an element of communication process?
(a) Decoding
(b) Communication
(c) Channel
(d) Receiver
Answer:
(b) communication is not the element of communication process, it is understood as a process of exchange.
![]()
Question 5.
Grapevine is
(a) Formal communication
(b) Barrier to communication
(c) Lateral communication
(d) Informal communication
Answer:
(d) Informal system of communi cation is referred as “Grapevine ”.
Question 6.
Status comes under the following type of barriers .
(a) Semantic barrier
(b) Organisational barrier
(c) Non semantic barrier
(d) Psychological barrier
Answer:
(b) Status related to organisation, Thus, it is a organisational barrier.
Question 7.
The software company promoted by Narayan Murthy is
(a) Wipro
(b) Infosys
(c) Satyam
(d) HCL
Answer:
(b) Narayana Murthy promoted Infosys.
Question 8.
The highest level need in need Hierarchy of Abraham Maslow
(a) Safety need
(b) Belongingness need
(c) Self actualisation need
(d) Prestige need
Answer:
(c) Self actualisation need is the highest level of need as it refers to the drive to become what one is capable of becoming.
Question 9.
The process of converting the message into communication symbols is known as
(a) Media
(b) Encoding
(c) Feedback
(d) Decoding
Answer:
(b) The process of converting message into symbol is known as Encoding.
![]()
Question 10.
The communication network in which all subordinates under a supervisor communicate through supervisor only is
(a) single chain
(b) inverted
(c) wheel
(d) free flow
Answer:
(c) In the wheel network, the communication takes place in such a manner that subordinates under a supervisor communicate through supervisor only.
Case Problems:
Y limited is a bank functioning in India. It is planning to diversify into increase business. Lately, the Government of India has allowed the private sector to gain entry in the mcrease business. Previously, it was the prerogative of LIC and GIC to do insurance business. But now with liberalisation of the economy and to make the field competitive other companies have been given licenses to start insurance business under the regulation of Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority’. Y limited plans to recruit high quality employees and agents and exercise effective direction to capture a substantial part of life and non-life insurance business.
Question 1.
Identify how the company can supervise its employees and agents effectively. What benefits will the company derive from effective supervision?
Answer:
The company can supervise is employees and agents by taking the following steps:
- Training programmes should be organised
- Make them understand the various policies so that they can convince their clients.
- Establishing targets for them and also monetary incentives.
- Regularised system for submission of periodical reports of their performance.
The benefits of the above steps will be
- Trained personnel will give better performance. They can Improve upon their skills
- Knowledge of the products of the Insurance company will ensure better satisfaction for the clients.
- They will compete to give better performance and earn higher incentives.
- It will help in identifying the areas where workers and agents need specialised training programmes.
Question 2.
What financial and non-financial incentives can the company use for employees and agents separately to motivate them? What benefits company will get from them?
Answer:
Incentives for Employees
1. Financial
(a) Productivity linked wage incentive
(b) Bonus
(c) Co-partnership
(d) Employee stock option
2. Non-financial
(a) Job-security
(b) Status
(c) Employee empowerment
(d) Employee recognition program
Incentives for Agents
(i) Financial
(a) Commission
(b) Bonus like paid vacation
3. Non-financial Incentive
(a) Cordial relationship
(b) Career advancement opportunity
(c) Job enrichment
(d) Recognition programmes like certificate of merit etc.
(e) Company achieves the motivation among the employees and they will contribute more in achieving targets.
![]()
Question 3.
How can the company ensure that higher order needs i.e., the esteem and self-actualisation needs are met?
Answer:
The higher order needs can be satisfied through
(i) Career advancement opportunity
(ii) Assignment of challenging job
(iii) Perquisites
(iv) Participation in management decisions
Question 4.
Identify the qualities of leadership in this line of business that the company manager must possess to motivate employees and agents.
Answer:
The qualities ofleaders which the manager of the Insurance company must possess are
- Intelligence
- Good communication skills
- Self-confidence, integrity and honesty
- Good listener
- Pleasing personality
Question 5.
Give a model of formal communication system that the company can follow.
Identify the barriers in this model, how can they be removed?
Answer:
The most suitable model for formal communication
Barriers to Effective Communication
1. Barriers Due to Organisational Structure: An organisational structure is complex with numerous levels in between which creates distance between the top management and the workers. With long lines of communication, there is possibility of message losing its significance.
2. Psychological Barriers: Everyone perceives information in the light of their own experiences, prejudices and thinking.
3. Inability to communicate: The lack of ability to communicate leads to misunderstanding and confusion. Different people have different meaning for same words.
4. Status and Position: Sometimes, effective flow of communication is hampered by status and position of the sender and receiver.
Measures to Overcome the Barriers
- Clarity in the thoughts of the sender is must for effective communication.
- The sender should try to make the message meaningful and understandable
- Message should be precise and to the point.
- The sender should always take the feedback from the receiver.
Question 6.
How can informal communication help to supplement the formal communication model given by you in answer to the question?
Answer:
Informal communication takes place outside the official channels of communication It fills the gaps that might exist in formal communication.
Merits of Informal communication are
- It helps the members to discuss the matters which cannot be discussed at the official leveL
- It is a way of knowing the reactions and opinions of the people about a change.
- It helps in building team spirit,
- The information flows at a faster