Karnataka 2nd PUC Economics Important Questions Chapter 1 Introduction to Micro Economics
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is economics about?
Answer:
Economics is the study of the problem of choice arising out of scarcity of resources that have alternative uses.
Question 2.
Define scarcity?
Answer:
Scarcity means a shortage of resources in relation to their demand.
Question 3.
What is an economy?
An economy is a system by which people get their living
Question 4.
Define central problem?
Answer:
The central problem is concerned with the problems of choice or the problem of resource allocation
Question 5.
What do you mean by positive economic analysis?
Answer:
It deals with what is or how an economic problem facing an economy is solved. It analyses the cause of effect relationship
![]()
Question 6.
What do you understand by normative economic analysis?
Answer:
Normative economics analysis deals with What ought to be or How an economic problem should be solved.
Question 7.
Give one reason which gives rise to the economic problems?
Answer:
Scarcity of resources that have alternative uses
Question 8.
Name the three central problems of an economy?
Answer:
The three central problems of an economy are:
- What to produce
- How to produce
- For whom to produce
Question 9.
What does the opportunity cost?
Answer:
It is the cost of the next best alternative forgone.
Question 10.
Why there is a need for economizing resources?
Answer:
Resources are scarce in comparison to their demand therefore it is necessary to use resources in the best possible manner without wasting them.
Question 11.
Why PPC is concave to the origin?
Answer:
PPC is concave to the origin because of increased marginal opportunity cost.
![]()
Question 12.
Define marginal rate of transformation?
Answer:
MRT is the ratio of a unit of one good sacrificed to produce one more unit of other goods
MRT = Δy / Δx
Question 13.
What does a point inside the PPC indicate?
Answer:
Any point inside the production possibility curve indicates the underutilization of resources.
Question 14.
Give two examples each of Microeconomics & macro-economics?
Answer:
- Micro-economics- Individual demand, individual supply
- Macro-economics- Aggregate demand, aggregate supply
Question 15.
What does a rightward shift of PPC indicates?
Answer:
It indicates
- Growth of resources
- Improvement in technology
Question 16.
What is meant by economising resources?
Answer:
It means wisely use of resources.
Question 17.
What do you mean by unlimited wants?
Answer:
It means that there is no limit to human wants (needs) They are unlimited (infinite)
Question 18.
Name any two branches of economics?
Answer:
The two branches of economics are:
- Microeconomic
- Macroeconomics
Question 19.
Give the name of different definitions of economics given by different economists?
Answer:
The definitions of economics are:
- Wealth definition- Adam Smith
- Welfare definition – Pro. Alfred marshall
- Scarcity definition- Lionel Robbins
- Growth definition- Paul A. Samuelson
![]()
Question 20.
What are the basic economic activities of the economy?
Answer:
The basic activity of the economy is
- Production
- Consumption
- Exchange of goods
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain the problem of “ What to produce” with the help of an example? What to produce:
Answer:
The first central problem of an economy in which goods and services should be produced to satisfy the human wants of the people, this problem arises due to the fact that means are scarce in relation to the wants.
We can produce a number of combinations such as producer goods and capital goods. We have to decide whether consumer goods are to be produced or capital goods. After deciding what goods should be produced, we will decide the quantity of each good le. how much of consumer goods and how much of producer goods are to be produced
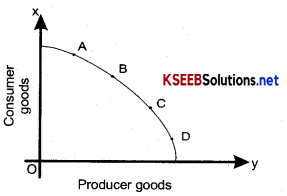
If a society produces more consumer goods, it will have fewer resources to produce producer goods, on the production possibility curve, the problem ‘What to produce’ is the problem of choosing the points on the curve (A, B,C and D)
Question 2.
What is the production possibility frontier?
Answer:
It is a boundary line that shows a maximum of two goods that can be produced with the help of given resources and technology at a given period of time.
Ex: An economy can produce two goods say rice or oil by using all its resources The different combinations of office and oil are as follows:
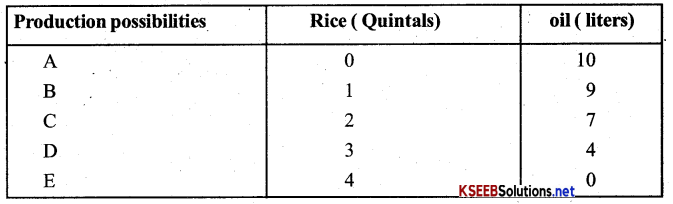
Question 3.
Why does an economic problem arise? Explain the problem of ‘How to produce’?
Answer:
An economic problem arises due to unlimited wants & limited resources which have alternative uses.
How to produce:
It is a problem of choice of technique There are two types of techniques of production
- The capital-intensive technique (using more capital and less labour) and
- Labour intensive technique (using more labour in relation to capital).
An economy has to decide as to what technique is to be used in a given industry to have the least possible cost to produce each unit of commodity or service, It is called the most efficient technical method of production.
Question 4.
Explain the three basic economic activities that take place in an economy?
Answer:
The three economic activities that take place in an economy are:
- Production
- Consumption
- Capital formation
1. Production: It is an activity that creates or adds utility to goods and services. utility of goods can be created or added by changing the shape, place etc.
2. Consumption: Using up of goods and services for satisfying the human needs, with the consumption the utility of goods and services decreases or destroyed.
3. Capital formation (Investment): It is the addition to the capital stock of the economy in a given period, The surplus of production over consumption in an accounting year is also defined as capital formation.
![]()
Question 5.
Give the properties of the production possibility curve?
Answer:
1. It slopes downward to the right: The downwards slope or negative slope of the production po ssibility curve shows that if more of one good is to be produced then loss of other goods will be produced
2. It is concave to the point of origin: Production possibility curve has a concave slope towards point of origin, The concave slope shows that more and more unit of one commodity shall have to be sacrificd to produce .additional units of another commodity
Question 6.
An economy produces two goods:
Answer:
Chocolates and Biscuits. The following tables summarise its production possibilities. Calculate the marginal Opportunity cost of chocolates at various combination
| Chocolates (in thousands) | Biscuits (in lakhs) |
| 0 | 90,000 |
| 1 | 80,000 |
| 2 | 68,000 |
| 3 | 52,000 |
| 4 | 34,000 |
| 5 | 10,000 |
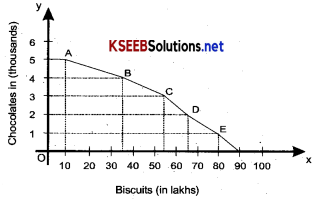
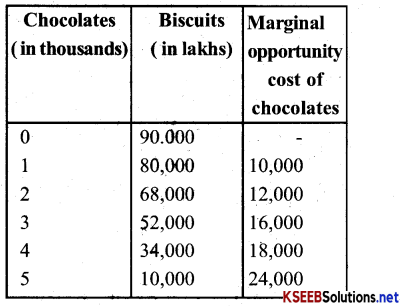
Question 7.
Explain any two features of a centrally planned economy?
Answer:
Two features of a centrally planned economy are as follows:
- Ownership of means of production: In a centrally planned economy, all factor factors of production like land, man-made resources and natural resources are owned by state.
- Motive: In a centrally planned economy social welfare in the primary motive of all activities
Question 8.
Identify which of the following are the subject matter of microeconomics or macroeconomics?
(i) General price level
(ii) Price determination of a commodity
(iii) National income
(iv) Supply by a firm
(v) Iron- steel industry
(vi) Government budget
Answer:
(a) Subject matter of microeconomics:
- Price determination of a commodity
- Supply by a firm
- The iron-steel industry, because they are individual units.
(b) Subject matter of macro-economics
- General price level
- National Income &
- Government budget, because they are aggregate units
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
How are central problems solved in different economics?
Answer:
There are three different economies
- Market economy
- Centrally Planned economy
- Mixed economy
Central problems are solved differently in different economies as it is clear from the following details:
1. Market economy:
In a market economy, those goods are pro¬duced which offer high prices and high profits to the producer.
The producer will use that technique of production which keep the cost of production as low as possible
The producer will produce the goods for
the rich who can afford high prices, a poor section of the society are generally ignored.
In short all decisions are related to the maximisation of profits.
2. Centrally Planned economy:
In a centrally planned economy decisions regarding ‘What to produce’,” How to pro¬duce” and Whom to produce are taken by a government or a central authority appointed by the government of the country. All decision are taken with a view to maximising social welfare.
3. Mixed economy:
In mixed economy, decision regarding ‘What, how and for whom to produce are taken on the basis of market forces as well as on the basis of social consideration.
Exercises
Question 1.
Discuss the central problems of an economy
OR
How does an economic problem arise?
Answer:
We know that available resources are -limited in relation to their requirement. Therefore, it is important to economise on their use.
The problem of resource allocation in the economy assumes the following there forms in an economy.
The major central problems are as follows:
- What to produce? (Problems of choice)
- How to produce? (Problems of choice of technique)
- For whom to produce (Problems of distribution)
1. What to produce:
The first central problem of an economy is to decide what to produce, the problem of what to produce is the problem of choice between commodities and this problem arises due to scarcity of resources.
2. How to produce:
The next problem of an economy is to decide as to how to produce goods and services ‘ How to produce’ is the problem of choice of technique” since resources are limited, it becomes necessary to choose a technology
3. For whom to produce:
The third basic problem of an economy is to decide for whom the goods shall be produced. The problem “ For whom to produce” is a problem of distribution of goods and services among the members of societies.
![]()
Question 2.
What do you mean by the production possibilities of an economy?
Answer:
Production possibilities mean that an economy can produce various combinations of the two goods with its limited resources and technology.
Question 3.
What is a production possibility frontier?
Answer:
The production possibility curve is called the production possibility frontiers and gives the combination of two goods that can be produced when the resources of the economy are fully utilised
OR
The curve gives the maximum amount of one commodity (ex: com) that can be produced in the economy for any given amount of other commodity (ex: cotton) and vice versa, this curve is called the production possibility frontier.
Question 4.
Discuss the subject matter of economics?
Answer:
Subject matter of economics is the study of different activities which are directed towards the maximisation of satisfaction of an indivdual and maximisation of social welfare at the level of the country as a whole.
Question 5.
Distinguish between a centrally planned economy and market economy?
Answer:
1. Centrally planned economy:
In a centrally planned economy or socialist economy, here all the economic activities are controlled and managed by the central government rather than the private business.
In such economies the government takes decision about allocation of resources and the government decides What to produce, How to produce and What prices are to fixed
The countries like North Korea, Cuba, China & Vietnam etc., follow a centrally planned economic system.
2. Market economy:
Market economy or capitalistic economy is an economy where the private sector plays important role in taking economic decision and allocation of resources
In market economics, private individuals own the factors of production Here profit is the ‘Sole motive’ and there will be no interference by the government in the economic activities of the economy.
The countries like America, Japan, Australia etc., follow a market economy.
![]()
Question 6.
What do you understand by positive economic analysis?
Answer:
It deals with what is (or) how an economic problem facing an economy is solved. It analyses the “ cause & effect relationship”
Question 7.
What do you understand by normative economics analysis?
Answer:
The normative economic analysis deals with what ought to be (or) how an economic problem should be solved
Question 8.
Distinguish between micro-economic & macroeconomic?
Answer:
| Micro-economic | Macro-economics |
| 1. It studies individual economic unit | 1. It studies aggregate economic unit |
| 2. It deals with the economic activities of a firm or an industry | 2. It deals with the aggregates like aggregate demand, supply, aggregate employment, national income, expenditure etc. |
| 3. Its central problem are price determination & allocation of resources | 3. Its central problem is the determination of level of income and employment in the economy |
| 4. Demand and supply are the tools of micro-economic analysis | 4. Aggregate demand and aggregate supply are the main tools of analysis. |