Karnataka 2nd PUC Economics Important Questions Chapter 1 Introduction to Macro Economics
Question 1.
Who traced macroeconomics first?
Answer:
‘J.M.Keynes’ traced macroeconomics first.
Question 2.
What do you mean by laissez faire policy?
Answer:
Laissez faire means ‘Leave us alone’ i.e., the government should not intervene or interfere in the market.
Question 3.
Which policy was proved wrong by the Great depression?
Answer:
“Laissey faire policy’ was proved wrong by the Great depression.
![]()
Question 4.
Name the book which was published by J.M.Keynes?
Answer:
The book which was published by J.M. Keynes was “The General theory of employment, Interest and Money” in 1936.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What do you mean by JMacro- economics?
Answer:
Macro economics refers to the study of aggregates covering the entire economy, such as general employment, general price level and wage level etc.
Question 2.
Define Macro Economics?
Answer:
According to K.E.Boulding, Macro Economics is the study of the nature, relationships and behaviour of aggregates of economic quantities.
Question 3.
What do you mean by nature of macro-economics?
Answer:
The nature of macro-economics explains you the central theme of economy. It studies the economic activities as a whole and it helps us to understand how the economy functions in different situations.
Question 4.
Name any two areas of study under macro-economics?
Answer:
The important areas of study under macro-economics are:
- National income
- Aggregate employment
- General price level
- Consumption etc.
![]()
Question 5.
Who are the pioneers in micro and macro-economics?
Answer:
(a) Alfred Marshall is considered as pioneer of micro-economics
(b) John Maynard Keynes is considered as pioneer of macro-economics. (J.M.Keynes)
Question 6.
How does macro economics depend on micro-economics?
Answer:
Macro-economics variables depend upon the level and behaviour of micro-economic variables in the economy.
Ex: Aggregate demand in the economy is simply the sum of demand at the micro level. *
![]()
Question 7.
Name two limitations of macro economics?
Answer:
The two limitations of macro economics are:
- Excessive generalization
- No clear picture
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain the cirucumstances for the emergence of macro economic study?
Answer:
Macroeconomics can be traced in the •works of Mercantilists. But the foundation of macro-economics was laid by J.M.Keynes in his most celebrated book. ‘The General theory of Employment Interest, and Money’ published in 1936.
Economic thought and policies, prior to 1930, was dominated by classical economists. They believed in laissez faire policy. The laissez faire advocated to leave the economic activity to the market.
The role government should be minimal as the invisible hands will ensure equilibrium and full employment.
The Great depression of 1930 proved the classical economic policy wrong, the inadequances of automatic functioning was clearly visible. This necessitated new ‘ interpretation and analysis of macro economics. Keynes filled the macro economics with his fresh and revolutionary approach through his “General theory”. It dominated the economic policy till the mid 1970s Later, various schools of thought namely monetarism, neoclassical macro-economics, supply side economics and neo-keynesian economics have strengthened macroeconomics.
Presently, macro-economies lias become inevitable for various policy formulations:
- National income
- Employment
- Poverty
- Fluctuations in economic cycles
- Inflation
- Foreign trade etc
Question 2.
Write four elements about the scope of Macroeconomics?
Answer:
The four elements about the scope of Macroeconomics are:
- It studies about major sectors of economy.
- It studies about the generation of National in the country
- It studies factors like aggregate demand aggregate supply, aggregate consumption, aggregate savings and aggregate investement etc.
- It helps studies about the International trade.
Question 3.
‘Although macroeconomics has gained maximum popularity, yet it not free from limitations’ Justify this Statement.
Answer:
Limitations of macro-economics are:
Neglects micro study:
Macroeconomics completely neglects micro study. It will not consider individuals, production units, sectors and components of the economy.
No clear picture:
Macroeconomics, as it studies aggregates and averages, will not give a clear picture of the functioning of the economy.
Wrong conclusions:
The macroeconomic study may some time lead to wrong conclusions. Because, what is true’of an economy may not be true of an individual. Thus macro economics may be misleading.
Excessive generalization:
The greatest defect Macroeconomics is its excessive generalization. Its approach, most of the times, is misleading. It may therefore lead to wrong conclusions.
The Problem of aggregation:
Macro economics deals with such aggregates as aggregate of consumption, savings and investment. All these factors consist ofheterogenous elements. Money is a measuring rod of value. But its value keeps on changing. Consequently economic aggregates become immeasurable and incomparable in real terms.
![]()
Question 4.
Discuss the nature and scope of macro-economics?
Answer:
The Nature and scope of Macro-Economics:
The natue of macro-economics explains you the central theme of economy. It studies the economic activites as a whole and it helps us to understand how the economy functions in different situations.
The situations which are studied and solved bymacr-economics are:
- How to generate and spend the income though production of goods and services.
- How to allocate the human resources and non-human resources in different economic sector.
- How and what policies regarding production, income, expenditure be formulated for the growth and development of an economy
- What policies should be formulated regarding foreign trade to serve the interest of people at large
- How the different variables like output level, price level and employment bear close relationsip.
Scope of Macroeconomics:
It refers to the areas of study under macro economics. The scope of macro-economics can be explained as follows:
Major sectors:
The economy in a democratic set up has any major interdependent sectors like house hold sector, producer sector, government sector and external sector. While studying the economy, macro economists should consider each sector for the complete study of Macro economics.
National income:
Here we study the various concepts National income such as NDP, GDP, GNP,
Exercises
Question 1.
What is the difference between microeconomics and macroeconomics?
Answer:
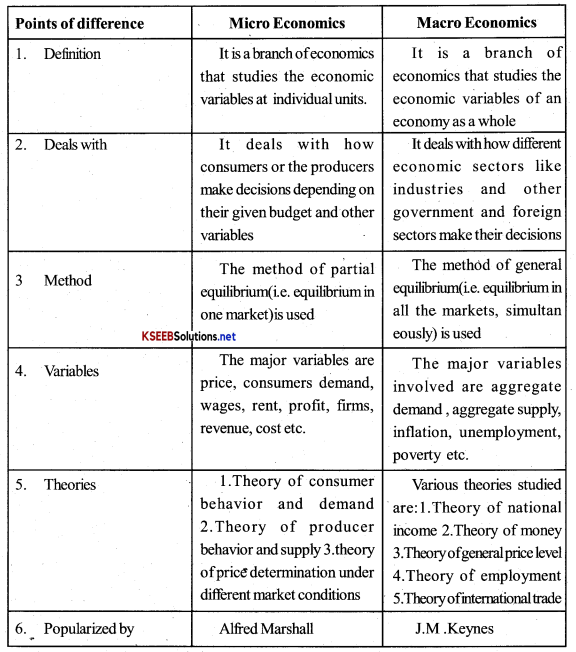
Question 2.
What are the important features of a capitalist economy?
Answer:
Capitalist economy is an economic system where the means of production are privately owned. These means of production are driven by the motive of profit-making. This economic structure is also known as free market economy or laissez faire.
Following are the features of a capitalist economy:
1. Role of the government: The government provides the basic framework for the smooth functioning of an economy. It provides the basic framework and is responsible for the maintenance of law and order, justice, growth and stability, defence, etc.
2. Profit motive: The economic agents are driven by the prime motive of profit maximization.
3. Central problems: The central problems of an economy are solved by the market forces of demand and supply, i.e., the law of demand and supply qperates here. The producers will supply only those goods and services that are demanded by the economy.
4. Role of private sector: The role of private individuals is more dominant. The main role of undertaking production and organizing factors of production are played by the private individuals and capitalists.
5. Laissez-faire: This economy is also called ‘laissez faire’. It has minimum interference or restriction from the government.
![]()
Question 3.
Describe the four major sectors in an economy according to the macroeconomic point of view?
Answer:
The four major sectors of an economy according to the macroeconomic point of view are:
- Households
- Firms
- Government
- External sector
These can be represented in the following flow chart:
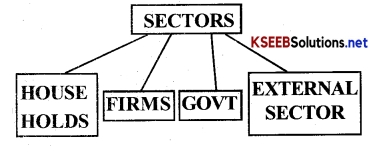
1. Households: Households buy goods and services for consumption and also supply factors of production like land, labour, capital, and entrepreneur. Households provide the market for the output of the firms.
2. Firms: Firms are economic units that carry out production. They employ and organize the resources and supply goods and services to households.
3. Government: A state/government provides law and order, maintains growth and stability and provides administrative services. The main motive of a government is to undertake developmental projects such as dams, roads, heavy industries that usually have long gestation periods. The government invests in education, health sector and provides these services at a nominal price. The motive of a government is to serve and not to make profits, iv. External sector: This sector is engaged in export and import (external trade) of goods and services. If domestically produced goods and services are sold to the rest of the world, then it is called export. If the goods and services are purchased from the rest of the world, then it is called import.
Question 4.
Describe the Great Depression of 1929.
Answer:
The Great Depression was a severe economic crisis that started in the year 1929. It originated in the United States of America with the crash ofthe stock market and gradually spread to other countries of the world. The main cause behind this crisis was the fall in aggregate demand due to underconsumption and over investment. Due to underconsumption and over investment the stock of finished goods started piling up, which resulted in low price level and consequently the low-profit leveL The money in the economy was converted into unsold stock of finished goods that lead to an acute M in employment and hence income level fell drastically. The demand for goods in the economy was so low that the production was lowered leading to unemployment. In the USA, the rate of unemployment increased from 3% to 25%.
The Great Depression has its own implications and importance in economics, as it leads to the failure of the classical approach of economics. Those who believed in the market forces of demand and supply, paved the way for the emergence of the Keynesian approach. It was this incident that provided the economists with sufficient evidence to recognize macroeconomics as a separate branch of economics.
The cause and effect relationship of the Great Depression can be summed up in this flow chart
Low demand → overinvestment low level of employment, low level of output, low income and low demand.