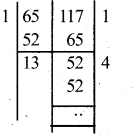
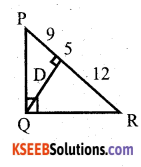
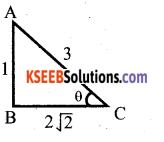
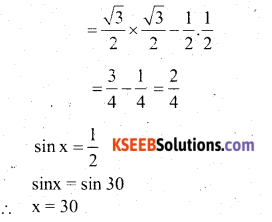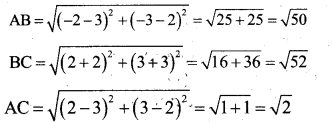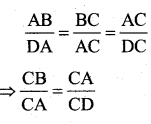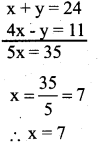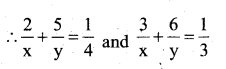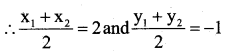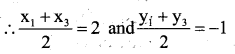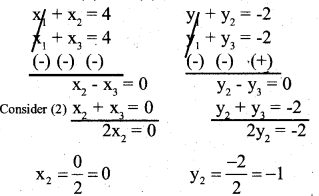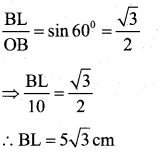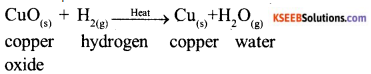Students can Download Karnataka SSLC Maths Model Question Paper 5 with Answers, Karnataka SSLC Maths Model Question Papers with Answers helps you to revise the complete Karnataka State Board Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Karnataka State Syllabus SSLC Maths Model Question Paper 5 with Answers
Time: 3 Hours
Max Marks: 80
I. In the following questions, four choices are given for each question, choose and write the correct answer along with its alphabet: ( 1 × 8 = 8 )
Question 1.
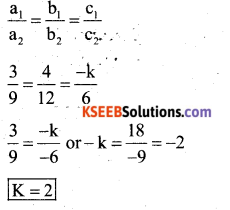
The pair of linear equations 3a + 4b = k, 9a + 12b = 6 have infinitely many solutions when,.
a) K = -2
b) K = 3
c) K = 2
d) K = -3
Answer:
c) K = 2
Solution:
Question 2.
n2 – 1 is divisible by 8, if n is
a) Prime numbers
b) Odd integer
c) Even integer
d) Natural number
Answer:
b) Odd integer
Solution:
n2 – 1
If n is an odd. integer, 1,3,5,
Ex: 12-1 = 1- 1= 0 divisible by 8.
32 – 1=9-1=8 divisible by 8.
52 – 1 = 25 – 1 = 24 divisible by 8.
![]()
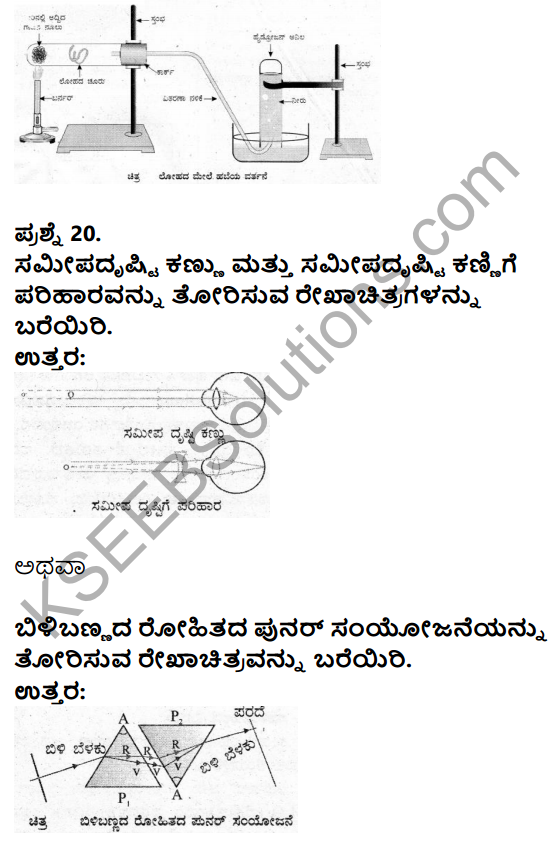
Question 3.
\(\sqrt{1+\tan ^{2} \theta}\) = , where 0<θ< 90°
a) secθ
b) cosec θ
c) cos θ
d) sin θ
Answer:
a) secθ
Solution:
\(\sqrt{1+\tan ^{2} \theta}=\sqrt{\sec ^{2} \theta}=\sec \theta\)
Question 4.
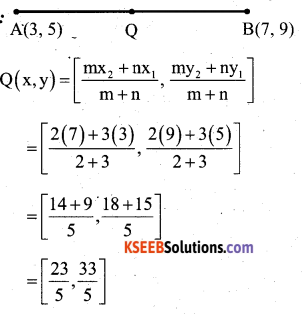
If Q divides the line A(3, 5) and B (7,9) internally in the ratio 2:3, then the co ordinates of Q are.
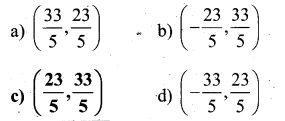
Answer:
c) \(\left(\frac{23}{5}, \frac{33}{5}\right)\)
Solution:
Question 5.
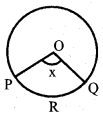
If Area of the sector OPRQ = \(\frac{5}{18}[ /latex] of Area of circle. Then the value of x
a) 25°
b) 50°
c) 75°
d) 100°
Answer:
d) 100°
Solution:
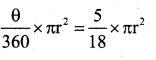
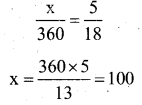
Question 6.
If 1 + 2 + 3 + n terms = 28, then n is equal to
a) 28
b) 7
c) 8
d) 56
Answer:
b) 7
Solution:
[latex]\frac{\mathrm{n}(\mathrm{n}+1)}{2}\)
n(n + 1) = 28 x 2 = 56
n(n + 1) = 7 x 8
∴ n = 7
Question 7.
If E1E2 E3…….E10 are the possible elementary events of a random experiment, then P(E1) + P(E2) + P(E3) + ………P(E10) is equal to
a) 0
b) 1
c) 2
d) 3
Answer:
b) 1
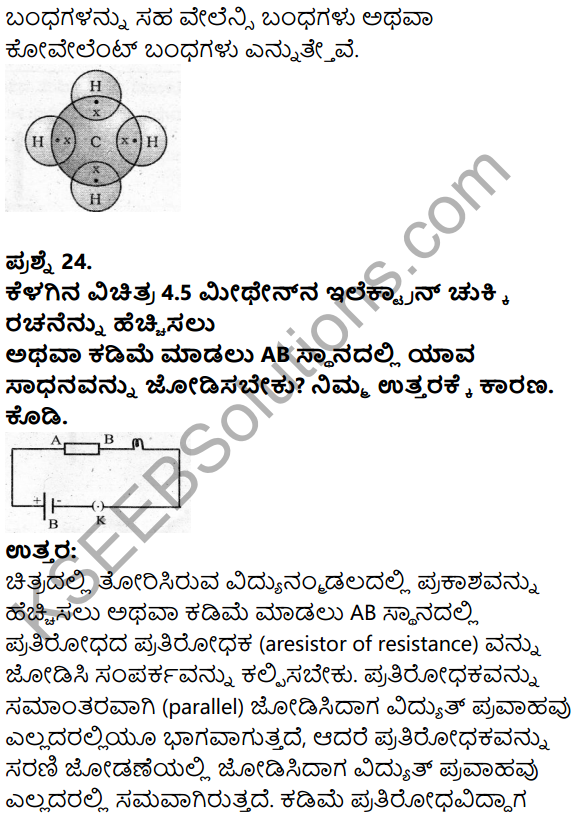
Question 8.
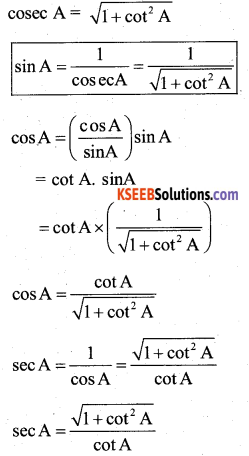
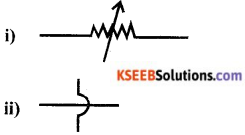
If we express sec A in terms of sin A, then sec A is equal to
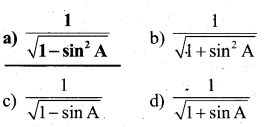
Answer:
\(\frac{1}{\sqrt{1-\sin ^{2} A}}\)
Solution:
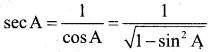
![]()
II. Answer the following Questions : ( 1 x 8 = 8 )
Question 9.
What is the \(\frac{p}{q}\) form of 43.123456789 ?
Answer:
\(\frac{43123456789}{999999999}\)
Question 10.
Write the quadratic equation formed by the roots √3 + √5 and √3 – √5
Answer:
x2 -(α + β)x + αβ = 0
X2 – [3 + √5 + 3 – √5]x + (3 + √5)(3 – √5) = 0
x2 – [6] x + (9 – 5) = 0
x2 – 6 + 4 = 0
Question 11.
Find the value of \(\frac{\sin 26}{\sec 64}+\frac{\cos 26}{\csc 64}\)
Answer:
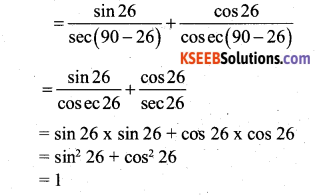
Question 12.
What is the distance between the points p(cos0, sin0) and Q(sin0, -COS0)?
Answer:
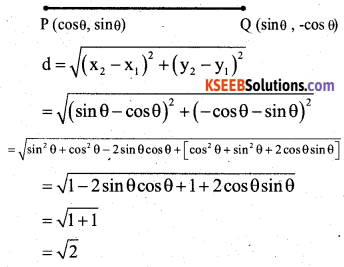
Question 13.
If a number “x” choosen at random from the numbers -2, -1, 0, 1, 2. What is the probability that x2 < 3 ?
Answer:
Clearly “x” can take any of the five given values.
∴ n(x) = 5.
If x2 < 3, then x can take the values -1, 0, 1.
∴ This even A = ,{-1, 0, 1}
n(A) = 3.
P(A) = \(\frac{n(A)}{n(S)}=\frac{3}{5}\)
Question 14.
What is the Area of a circle whose perimeter is 44 cms.
Answer:
2πr = 44
2 x \(\frac{22}{7}\) x r = 44
r = \(\frac{44 \times 7}{22 \times 2}\)
r = 7
A = πr² = \(\frac{22}{7}\) x 7 x 7 = 154cm2
Question 15.
A toy was made by scooping out a hemisphere from each end of a solid cylinder. If the height of the cylinder is h cm and base radius is r cms, find the total surface area of the toy.
Answer:
Total surface Area of the toy = C.S.A of cylinder + 2 [Surface Area of Hemisphere]
= 2πrh + 2πr²
= 2 πr (h + r)

Question 16.
The circumference of a circle exceeds the diameter by 15cm. Find the raidus of the circle.
Answer:
Circumference = 2r + 15
2πr = 2r + 15
2πr – 2r = 15
2 x \(\frac{22}{7}\)r – 2r = 15
Multiply by 7
2 x 22r – 14r = 105 .
30r = 105
r = 3.5
III. Answer the following : (2 x 8 = 16 )
Question 17.
Prove that √5 + √3 is an irrational number.
Answer:

∴ √3 is rational, is a contradiction
∴ √5 + √3 is irrational.
![]()
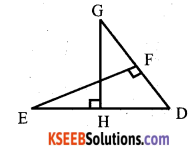
Question 18.
AX and BY are perpendiculars to segment XY. If AO = 5cm, BO = 7cm and Area of ∆ AOX = 150 cm2, find the area of ∆ BOY.
Answer:
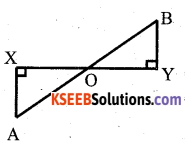
In ∆ OYB and ∆ OXA,
We have ∠X = ∠Y
So, by AA – criterion of similarity, we have
∆ YOB ≅ ∆ XOA
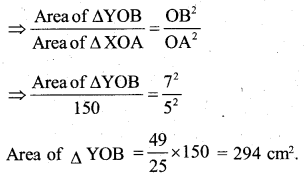
OR
In the given figure, BD ⊥ AC. Prove that AB2 + CD2 = AD2 + BC2
Answer:
Soln: In ∆ BDC,
∠ BDC = 90°
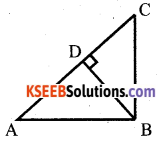
BC2 = BD2 + DC2 (By Pythagoras)
In ∆ BDA, ∠ APB = 90°
AB2 = AD2 + BD2 (By Pythagoras)
AB2 – BC2 = AD2 + BD2 – BD2 – DC2
AB2 + CD2 = AD2 + BC2
Hence proved.
Question 19.
If zeroes of the polynomial p(y) = y3 – 3y2+ y + 1 are a – b, a, a+ b. Find a and b.
Answer:
Sum of the zeroes of p(y) = y3 – 3y2+ y + 1
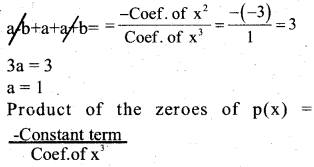
(a-b)(a)(a + b)= \(\frac{-1}{1}\) = -1
(a2 – b2) a = -1
(1 – b2) (1) = -1
– b2 = -1
-b2 = – 1 – 1
-b2 = -2
b2 = 2
b = ±√2
Question 20.
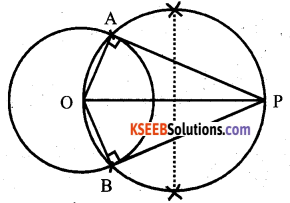
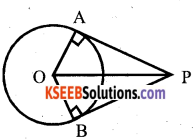
Construct a tangent to a circle of radius 4 cm from a point on the concentric circle of radius 6 cm and measure its length.
Answer:
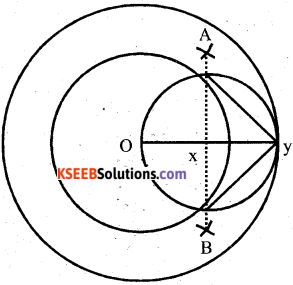
Question 21.
Find the zeroes of the polynomial p(y) = y3 – 5y2 – 16y + 80. If zeroes are α, -α and β.
Answer:
Sum of the zeroes
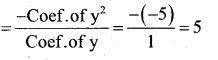
α + (-α) + β = 5
α – α + β = 5
β = 5
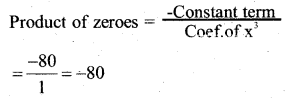
(α )(-α )(β) =-80
-α2β = -80
α2β = 80
α2(5) = 80
α = 80/5 = 16
α = √16
= ±4
Question 22.
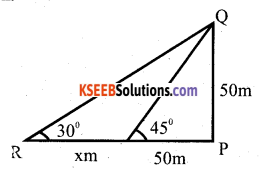
Two pillars of equal height and on either side of a road, which is 100m wide. The angles of elevation of the top of the pillars are 60 and 30 at a point on the road between the pillars. Find the position of the point between the pillars and height of each pillars.
Answer:
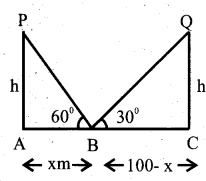
In ∆ PAB,
tab 60 = \(\frac{\mathrm{AP}}{\mathrm{AB}}\)
√3 = h/x
h = √3x
In ∆ BCQ,
tan 30 = \(\frac{\mathrm{CQ}}{\mathrm{BC}}\)
\(\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}=\frac{h}{100-x}\)
h√3 -= 100 – x
(√3x)(√3x) = 100-x
4x = 100
x = 25
∴ h= √3 X 25 = 25√3
= 25 x 1.73 = 43.3
OR
The three metallic spheres of radii are in the ratio of 3 : 4 : 5 are melted to form a single solid sphere of radius 12cm. Find the radius of the three small metallic spheres.
Answer:
Volume of the solid sphere = Sum of the volumes of each sphere
\(\frac{4}{3} \pi r^{3}=\frac{4}{3} \pi\left(r_{1}^{3}+r_{2}^{3}+r_{3}^{3}\right)\)
4 x 123 = 4[(3x)3 + (4x)3 + (5x)3]
1728 = 27x3 + 64x3 + 125x3 1728 = 216 x3
x = \(\frac{1728}{216}\)
x3 = 8 x = 3√8 = 2
∴ R1 = 6, R2 8, R3 = 10
![]()
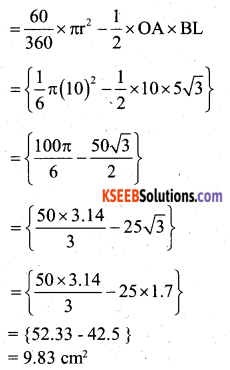
Question 23.
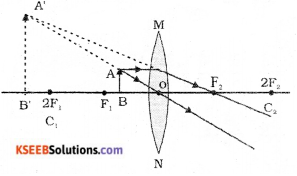
In the given fig. OACB is a quadrant of a circle with centre O and radius 3.5cm. If OD = 2cm, find the area of the shaded region
Answer:
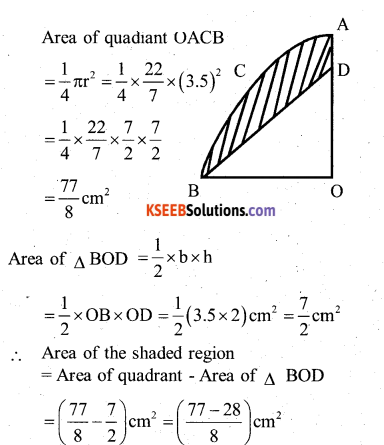
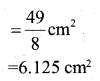
Question 24.
Find the volume of the largest right circular cone that can be cut of a cube of edge 7cm.
Answer:
Given radius of the base of cone = \(\frac{7}{2}\) cm
h = height of cone = 7cm
Volume of the cone = \(\frac{1}{3}\)πr²h
Volume = \(\frac{1}{3} \times \frac{22}{7} \times \frac{7}{2} \times \frac{7}{2} \times 7\)
= \(\frac{22 \times 7 \times 7}{12}\)
= 89.83cm3
IV. Answer the following : ( 3 x 9 = 27 )
Question 25.
The sum of a two digit number and the number obtained by reversing the order of its digits is 165. If the digits differ by 3, find the number.
Answer:
Let the digits at units and tens place of the given number be y and x respectively, then
Given number = 10x + y
Number obtained by reversing the order of the digits = 10y + x
(10x + y) + (10y + x) = 165
10x + y+ 10y + x = 165
(11x+11y=165) = 11 ’
x + y = 15 ……(1)
Digits differ by 3, if x > y
x – y = 3 ……..(2)
Solve (1) and (2)
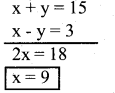
Consider x + y =15
9 + y = 15
y = 15 – 9
y = 6
∴ The number is 96, if y >x, number is 69.
OR
Ten years ago Sudhir was twelve times as old as his son Raghav and ten years, hence, he will be twice as old as his son will be. Find their present ages.
Answer:
Let the present ages of Sudhir and Raghav be x years and y years respectively. Ten years ago, Father ’s age = (x -10) years Son’s age = (y – 10) years,
x- 10= 12(y – 10)
=> x – 10 = 12y – 120
x – 12y = 120+ 10
x – i2y = – 110
x – 12y + 110 = 0. …….(1)
Ten years later, Father’s age = (x + 10) years
Son’s age = (y + 10)
x + 10 = 2(y + 10)
⇒ x+ 10 = 2y + 20
x – 2y = 20 – 10
x – 2y = 10
x – 2y – 10 = 0 ……(2)
Solve (1) and (2)
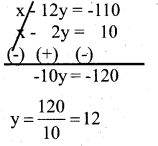
y = 12
x – 12y = 110
x – 12(12) = -110
x – 144 = -110
x = -110 + 144 = 34
∴ Present age of Sudhir = 34 years and present age of Raghav = 12 years.
Question 26.
The altitude of a right triangle is 7cm less than its base. If the hypotenuse is 13cm, find the other two sides.
Answer:
Let the base BC be = x cm
Then its height AB = (x – 7) cm
Hypotenuse AC = 13 cm
In ∆ABC, AC2 = AB2 + BC2
132 = (x – If + (x)2
169 = x2 + 49 – 14x + x2
169 = 2x2 – 14x + 49
2x2 – 14x + 49 – 169 = 0
2x2 – 14x-120 = 0
x2 – 7x – 60 = 0
x2– 12x + 5x-60 = 0
x(x- 12) + 5(x – 12) = 0
(x-12) (x + 5) = 0
(x – 12) = 0 or x + 5 = 0
x = 12 or x = -5
The base of the triangle = 12 cm Length of the altitude = (12 – 7)cm = 5 cm.
![]()
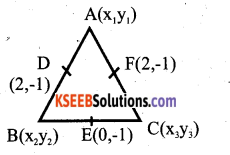
Question 27.
X(2, 5), Y (-1, 2) and Z(5, 8) are the co – ordinates of the vertices of A XYZ. The point A and B lie on XY and XZ respectively such that XA : AY = XB: BZ =1:2. Calculate the co – ordinates of X and Y.
Answer:
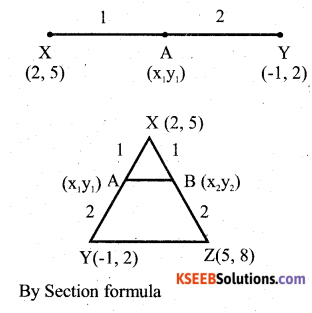
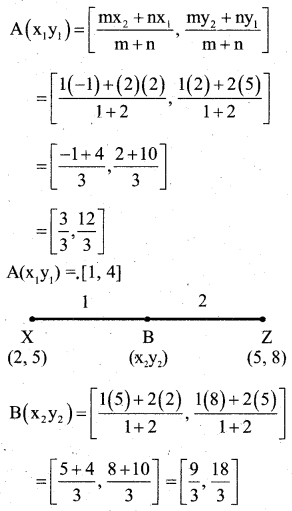
B(X2 y2)= [3, 6]
∴ Co – ordinates of A = (1,4)
Co – ordinates of B = (3, 6)
OR
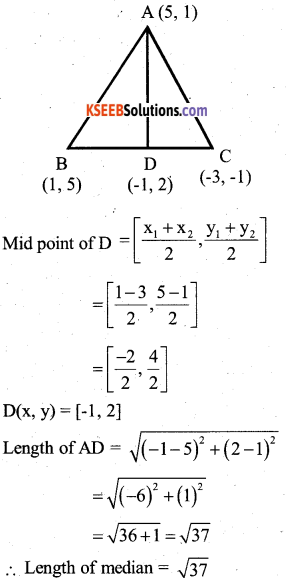
Find the Area of the triangle formed by joining the mid points of the sides of the triangle whose vertices are (0, -1) (2, 1) and
Answer:
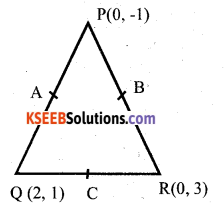
Co – ordinates of A
\(\frac{0+2}{2}, \frac{-1+1}{2}\)
= [1,0]
Co – ordinates of B
\(\frac{0+0}{2}, \frac{-1+3}{2}\)
= [0,1]
Co – ordinates of B
\(\frac{2+0}{2}, \frac{1+3}{2}\)
= [1,2]
∴ Area of A ABC = \(\frac{1}{2}\) Σ x1 (y2 – y3)
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) [1(1-2) + 0(2 – 0) + 1(0-1)]
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) [-1 + 0 + 1]
∴ Area of ∆ ABC = 1 sq. unit
Question 28.
Prove that the tangent at any point of a circle is perpendicular to the radius through the point of contacts.
Answer:
Data : AB is the tangent drawn to a circle centered at O
‘C’ is the point of contact.
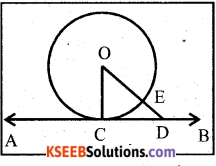
To prove that :
OC ⊥AB
Construction : Mark D .on AB. Join OD.
Let it cut the circle at E
Proof: OE < OD
OE is the radius of the circle.
OE = OC (radii of the same circle)
⇒ OC < OD
⇒ OC is the shortest distance between centre of the circle and tangent AB
∴ OC ⊥ AB
Hence proved.
Question 29.
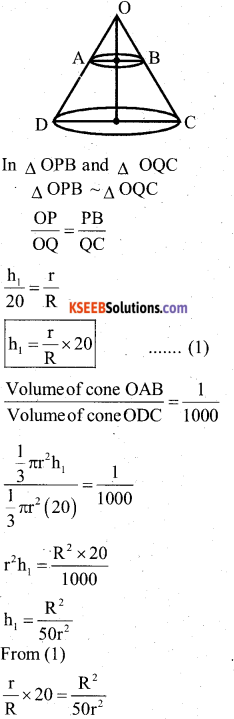
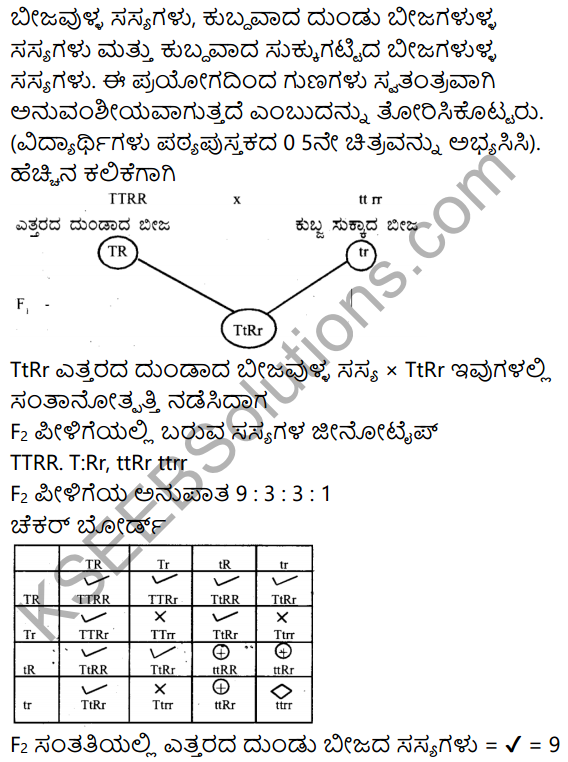
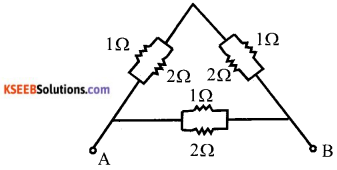
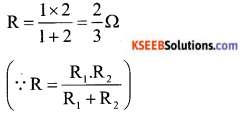
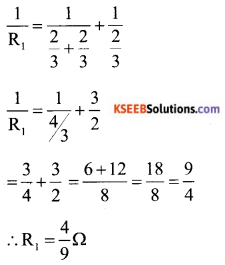
A hollow sphere of internal and external radii are 6cm and Scm respectively is melted and recast into small cones of base radius 2cm and height 8cm. Find the number of cones.
Answer:
Inner radius of a hollow sphere (r) = 6cm
and outer radius (R) = 8cms.

Radius of one small cone (r,) 2cm and
heigh (h) = 8 cm.

OR
A medicine capsule is in the shape of a cylinder with two hemispheres stuch to each of its ends. The length of the entire capsule is 14mm and the diameter of the capsule is 5 mm. Find its surface area.
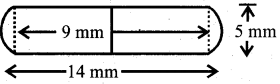
Answer:
Let r mm be the radius and h mm be the height of the cylinder.
r = \(\frac{5}{2}\) mm = 2.5mm
h = (14 – 2 x \(\frac{5}{2}\) mm
= (14-5) mm
= 9 mm
The radius of hemisphere = r = \(\frac{5}{2}\) mm
Now, the surface area of the capsule. = Curved surface Area of the cylinder surface Area of two hemispheres.
= 2πrh + 2 x 2 πr²
= 2πr² (h + 2r)
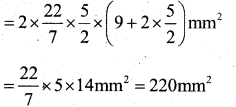
![]()
Question 30.
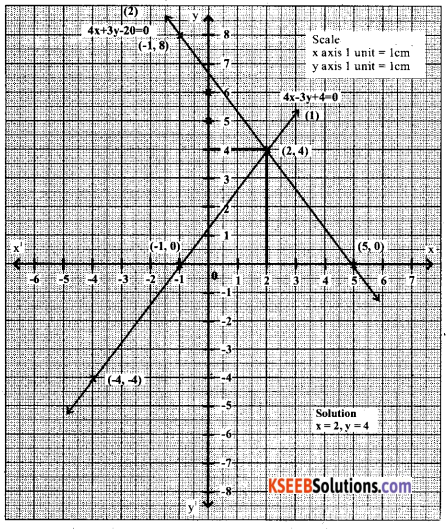
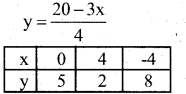
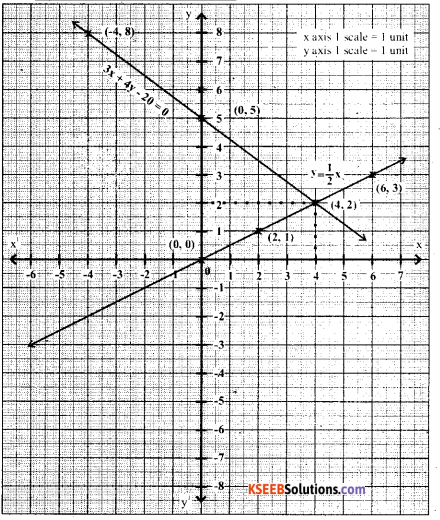
Solve graphically
y = \(\frac{1}{2}\) x and 3x + 4y – 20 = 0
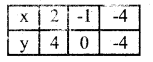
y = \(\frac{1}{2}\) x
3x + 4y – 20 = 0
3x + 4y = 20
4y = 20 – 3x
Question 31.
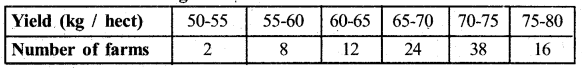
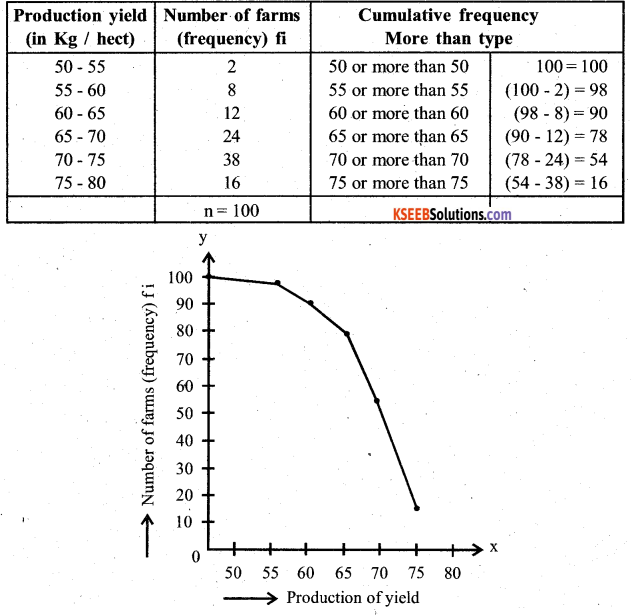
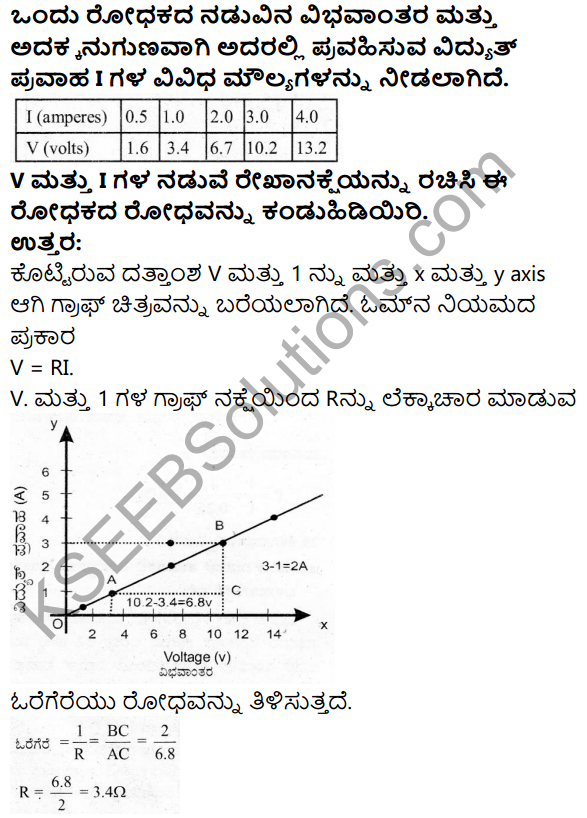
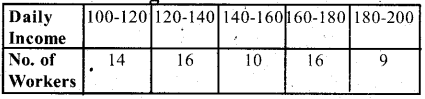
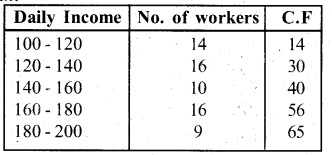
The following distribution gives the daily income of 65 workers of a factory. Convert this into less than type cumulative frequency distribution and draw its ogive.
Answer:
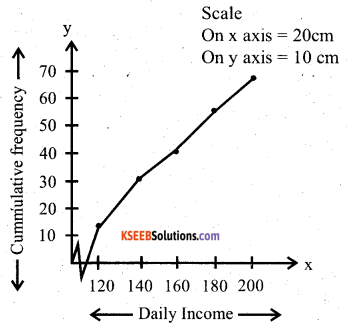
Question 32.
The fourth term of an AP is 11, and 8th term exceeds twice the fourth term by 5. Find AP and find the sum of first 100 terms.
Answer:
Given : T4 = -11 and T8 = 2T4 + 5
T8 = 2(11) + 5
a + 7d = 22 + 5 = 27
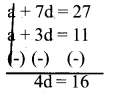
d = 4
a + 7d = 27
a + 7(4) = 27
a+ 28 = 27
a = 27-28 = -1
a = -1
A.P = -1,3, 7, …..
Sn = \(\frac{n}{2}\) [2a + (n-1)d] = \(\frac{100}{2}\) [2(-1) + (99)4]
= 50 [-2 + 396]
= 50 [394]
= 19700
Question 33.
A person on tour has ₹ 360 for his expenses. If he extends his tour for 4 days, he has to cut down his daily expenses by ₹ 3. Find the original duration of tour.
Answer:
Let the original duration of the tour be x days.
Total expenditure on four = 360 ₹
Expenditure per day = \(\frac{360}{x}\)
Duration of the extended tour = (x +4) days
∴ Expenditure per day according to new schedule = \(\frac{360}{x+4}\)
It is given that daily expenses are cut down by 3₹
\(\frac{360}{x}-\frac{360}{x+4}\) = 3
360 (x + 4) – 360x = 3(x) (x + 4)
360x + 1440 – 360x = 3x (x + 4)
1440 = 3x2+ 12x
3x2 + 12x – 1440 = 0
x2 + 4x – 480 = 0
x2 + 24x – 20x – 480 = 0
x(x + 24) – 20(x + 24) = 0
(x + 24) (x – 20) = 0
x + 24 = 0 and x – 20 = 0
x = -24 and x = 20
∴ Duration of tour = 20 days.
OR
Two pipes running together can fill a cistern in 3\(\frac{1}{13}\) minutes. If one pipe
takes 3 minutes more than the other to fill it, find the time in which each pipe would fill the cistern.
Answer:
Let the faster pipe takes x minutes.
Let the smaller pipe take (x + 3) minutes to fill.
Portion of the cistern filled by the faster 1
pipe in one minute = \(\frac{1}{x}\)
⇒ Portion of the cisterin filled by the faster pipe in \(\frac{40}{13}\) minutes
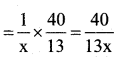
|||ly portion of the cistern filled by the slower pipe in \(\frac{40}{13}\) minutes.
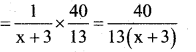
It is given that the cistern is filled in \(\frac{40}{13}\) min.
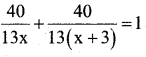
[40(x + 3) + 40x] = [(x) (x +3)] 13
40x + 120 + 40x = (x2 + 3x) 13
80x + 120= 13x2 + 39x
13x2 + 39x – 80x – 120 = 0
13x2 – 41x-120 = 0
13x2 – 65x + 24x – 120 = 0
13x (x – 5) + 24(x – 5) = 0
x – 5 = 0, 13x + 24 = 0
x = 5, 13x = -24, x = \(\frac{-24}{13}\)
Faster pipe fills the cistern in 5 minutes and the slower pipe takes 8 min to fill the cistern.
V. Answer the following : ( 4 x 4 = 16 )
Question 34.
In an AP whose first term is 2, the sum of first five terms is one fourth the sum of the next five terms. Show that T20 = -112. Find S20.
Answer:
a = 2, T1 + T2 + T3 + T4+ T5
= \(\frac{1}{4}\) (T6 + T7 + T8 + T9 + T10)
a + a + d + a + 2d + a + 3d + a + 4d
= \(\frac{1}{4}\)(a + 5d + a + 6d + a + 7d + a + 8d + a + 9d)
5a+ 10d = \(\frac{1}{4}\) (5a + 35d)
5(a + 2d) = \(\frac{1}{4}\) x 5( a + 7d)
a + 2d = \(\frac{1}{4}\) (a + 7d)
4(a+2d) = a+7d
4a + 8d – a – 7d = 0
3a + d = 0
3(2) + d = 0
d = -6
T20 = a + 19d
= 2 +19(-6)
= 2 – 114
T20 = -112
Sn = \(\frac{n}{2}\) [2a + (n-1)d]
Sn = \(\frac{20}{2}\) [2(2) + (20-1)(-6)]
= 10 [4- 114]
= (10) (-110)
S20 = -1100.
OR
A man repays a loan of ₹ 3250 by paying 7 20 in the first month and then increases the payment by ₹ 15 every month. How long will it take to clear his loan?
Answer:
Here, a = 20, c.d = 15, n = ?
Sn = \(\frac{n}{2}\)[2a + (n-1)d]
3250 = \(\frac{n}{2}\) [2 x 20 + (n-1)15]
3250 x 2 = n(40 + 15n- 15)
6500 = n (25 +15n)
6500 = 25n + 15n2
(15n2 + 25n – 6500 = 0)÷ 5
3n2 + 5n – 1300 = 0
3n2-60n + 65n- 1300 = 0
3n(n – 20) + 65 (n – 20) = 0
(n – 20) (3n + 65) = 0
(n – 20) = 0, 3n + 65 = 0
n = 20, 3n = -65
n = \(\frac{-65}{3}\)
∴ Total amount will be paid in 20 months.
![]()
Question 35.
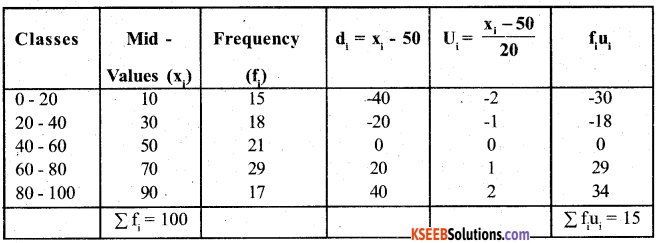
Find the mean, median and mode for * the following frequency distribution.
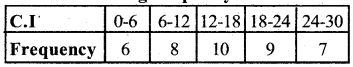
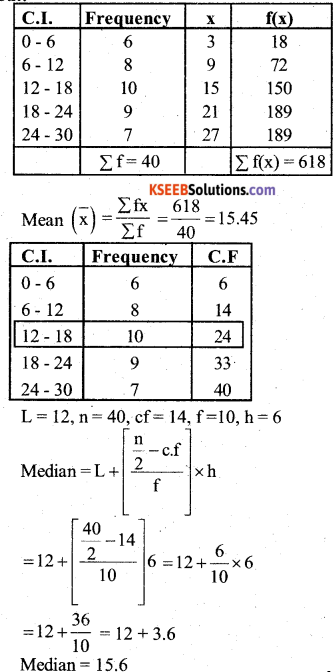
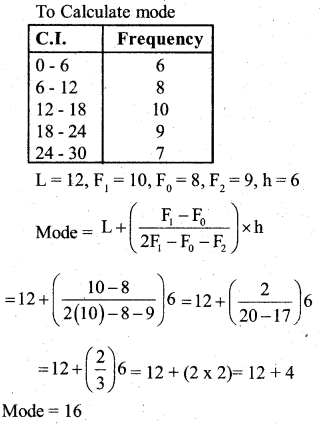
Answer:
Question 36.
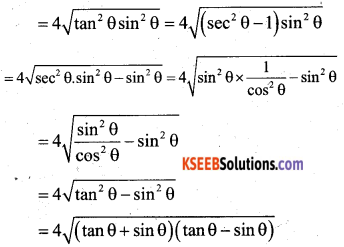
P.T \(\frac{\tan \theta}{1-\cot \theta}+\frac{\cot \theta}{1-\tan \theta}\) = 1+ secθ cosecθ
Answer:
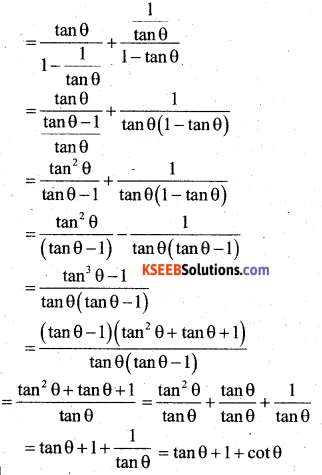
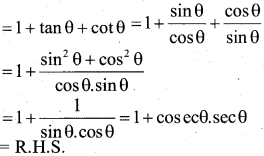
Question 37.
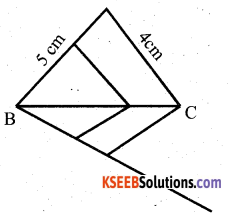
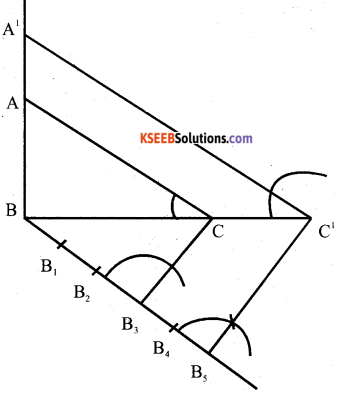
Draw a right triangle in which the sides (other than hypotenuse) arc of lengths 8cm and 6cm, then construct another triangle whose sides are 5/3 times the corresponding sides of given triangle.
Answer:
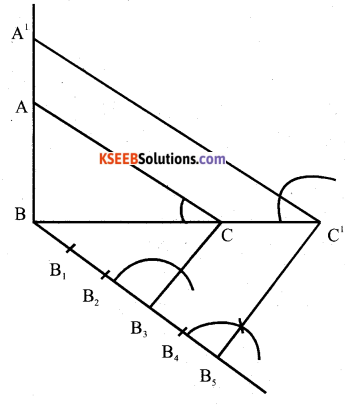
Verify
BC = 8cm
BC’= \(\frac{5}{3} \times 8=\frac{40}{3}\)
AB =6cms
A’B= \(\frac{5}{3} \times 6\)
=10cms.
VI. Answer the following : (5 x 1 = 5 )
Question 38.
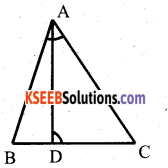
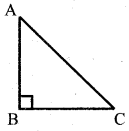
State and prove pythagoras theorem.
In a right angled triangle, square on the hypotenuse is equal to sum of A the squares on the other sides.
Answer:
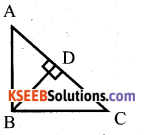
Data : ∆ ABC, ∠B = 90°
T.P.T : AC2 = AB2 + BC2
Construction : Draw BD ⊥ AC
Proof: In ∆ ABC and ∆ ABD
∠ ABC = ∠ADB = 90 [∵ Data & construction]
∠A = ∠A (∵ common Angle)
∠ACB =∠ ABD [ ∵ Re maining angle]
∴ ∆ ABC and ∆ ABD are equiangular
=> ∆ ABC ~ ∆ABD
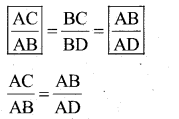
AB2= AC x AD ……… (1)
In ∆ABC and ∆ BDC
∠ ABC = ∠ BDC = 90 [∵ Data & construction]
∠C = ∠C (∵ common Angle)
∠BAC =∠ DBC [ ∵ Re maining angle]
∴ ∆ ABC and ∆ DBC are equiangular
∆ABC ~ ∆BDC
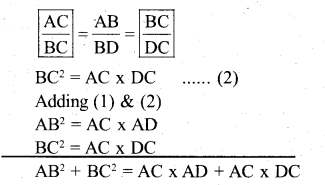
AB2 + BC2 = AC (AD + DC)
AB2 + BC2 = AC(AC)
AB2 + BC2=AC2
AC2 = AB2+ BC2