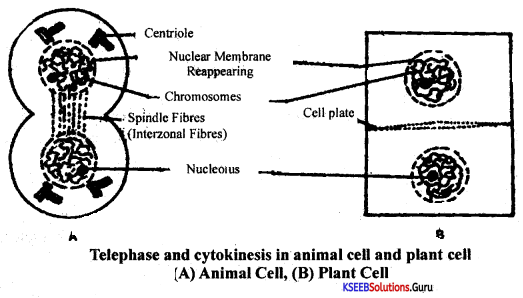
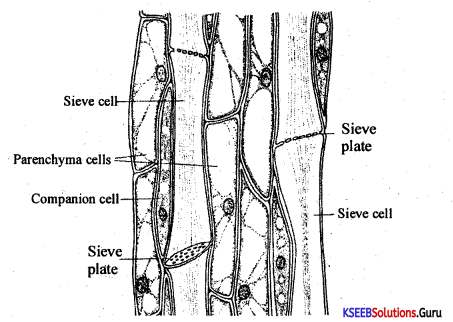
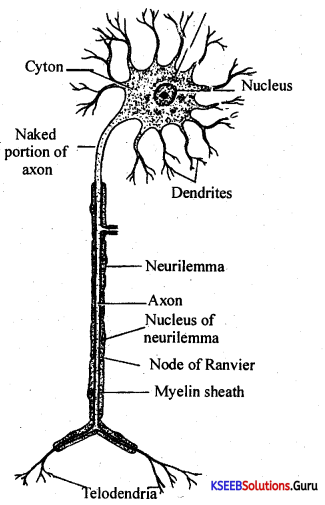
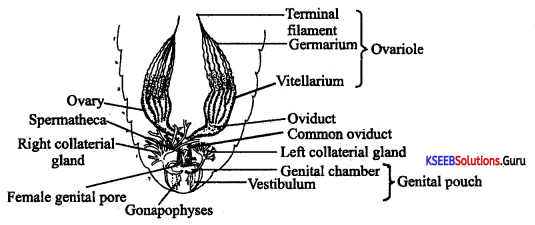
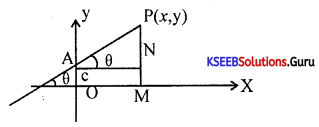
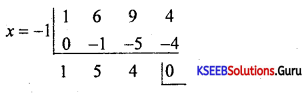
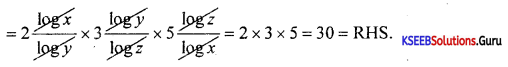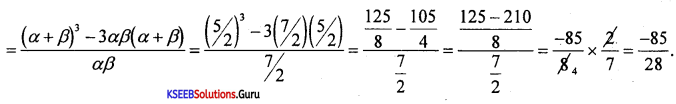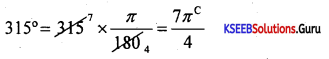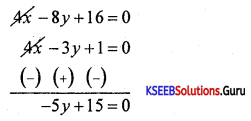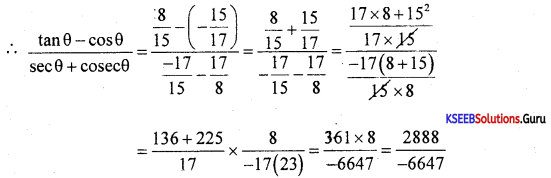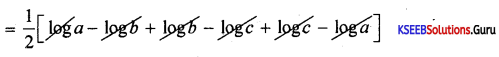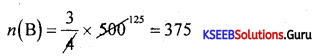Students can Download 1st PUC Biology Model Question Paper 8 with Answers, Karnataka 1st PUC Biology Model Question Papers with Answers helps you to revise the complete Karnataka State Board Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Karnataka 1st PUC Biology Model Question Paper 8 with Answers
Time: 3.15 Hours
Max Marks: 70
General Instructions:
- The question paper consists of four parts A, B, C, and D.
- All the parts are compulsory.
- Draw diagrams wherever necessary. Unlabelled diagrams or illustrations do not attract any marks.
Part – A
Answer the following questions in one word / one sentence each: ( 10 × 1 = 10 )
Question 1.
What is a herbarium?
Answer:
A herbarium is defined as a collection of plants, that have been dried, pressed, and preserved on a sheet.
Question 2.
Give an example for palmately compound leaf.
Answer:
Silk cotton tree.
Question 3.
Collenchyma is called a simple tissue. Why?
Answer:
Because it is made up of cells that are similar in structure and function.
Question 4.
What are mesosomes?
Answer:
Mesosomes are balloon or tubular ingrowths of plasma membrane formed in prokaryotes and contain enzymes for respiration.
Question 5.
Mention the significance of meiosis.
Answer:
Meiosis maintains the chromosome number constant in sexually reproducing organisms. It is essential since the chromosome number is doubled after fertilization.
![]()
Question 6.
Define root pressure.
Answer:
The hydrostatic pressure is created inside the xylem of the root due to the osmotic entry of water.
Question 7.
Name the oxygen scavenger molecule that protects nitrogenase in nodules.
Answer:
Leg – hemoglobin.
Question 8.
What is emphysema?
Answer:
The loss of elasticity of walls of alveoli resulting in their expansion is called emphysema. It is induced by cigarette smoke and other irritants.
Question 9.
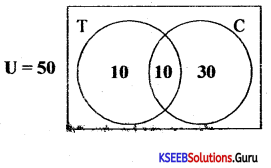
Which blood group is called a universal donor?
Answer:
‘O’ blood group.
Question 10.
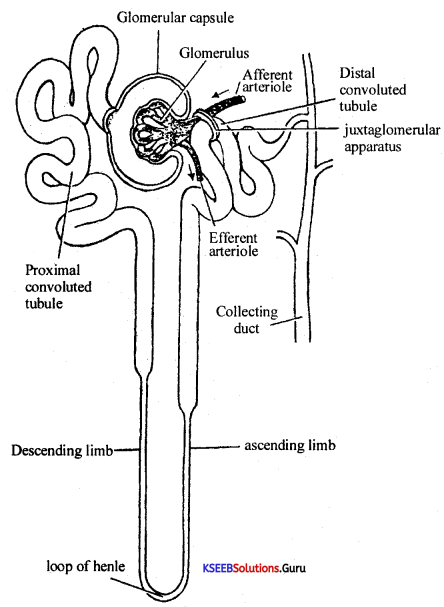
Why the filtration of blood in Bowman’s capsule is referred to as ultrafiltration?
Answer:
Because almost all the constituents of plasma except proteins are filtered into the lumen of the bow marks capsule due to the presence of micropores in the epithelial layer of Bowman’s capsule.
PART-B
Answer any FIVE of the following questions in 3-5 sentences each, wherever applicable: (5 × 2 = 10)
Question 11.
Write any four characters of fungi.
Answer:
Fungi are eukaryotic, achlorophyllous organisms that are but, generally multicellular a few are unicellular (yeast).
- The fungal body consists of long, slender, thread-like structures called hyphae, which form a network called mycelium.
- The hyphae have a cell wall made up of chitin.
- They may be aseptate and multi-nucleate i.e., coenocytic or septate.
- All fungi are heterotrophs -they are saprotrophs or parasites or live as symbionts in the roots of higher plants (mycorrhizae) and in lichens (mycobiont).
- They reproduce vegetatively by fragmentation, fission, or budding.
![]()
Question 12.
List any four salient features of phylum Coelenterata.
Answer:
- Coelenterates are all aquatic, most of them are marine and a few are freshwater forms.
- Members are multicellular and the cells are compactly arranged to form definite tissues.
- Coelenterates exhibit radial symmetry.
- These organisms have two germ layers viz. outer ectoderm and inner endoderm, and thus they are diploblastic. Between these two cellular germ layers, is a thick non-cellular gelatinous mesoglea.
- Two distinct types of individuals are seen in poly or hydra-like (hydroid) type and the medusoid type.
- Some forms exhibit polymorphism (eg: Obelia).
- Digestion is both extracellular and intracellular.
- Reproduction takes place by both sexual and asexual methods.
Question 13.
Give reasons for the following:
(a) The blood vascular system in cockroaches is considered as an open type.
(b) The vision in cockroaches is referred to as mosaic vision.
Answer:
(a) As blood flows in blood sinusoids which are open channels and in the hemocoel.
(b) As the eye contain several ommatidia to receive light signals instead of a single lens.
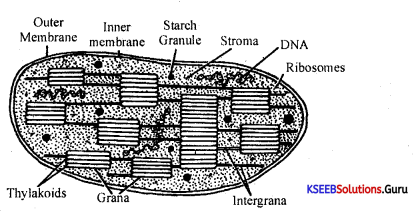
Question 14.
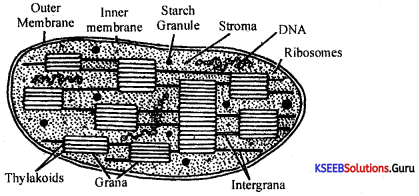
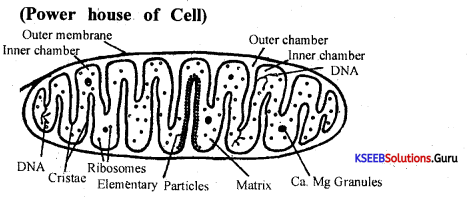
Draw a labeled diagram of a section of the chloroplast.
Answer:
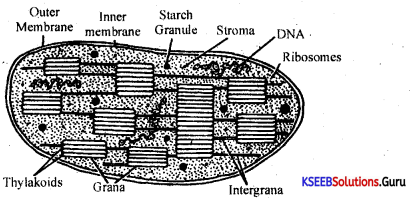
Electron microscopic structure of the chloroplast
Question 15.
What is vernalization? Mention any one of its importance.
Answer:
Some plants require low-temperature treatment for flowering. This treatment is known as vernalization.
Vernalization prevents precocious reproductive development late in the growing season and enables the plant to have sufficient time to reach maturity.
Significance: Subjecting the biennial plants like sugar best cabbage, carrot, etc to low temperature or cold treatment stimulates subsequent flowering.
Question 16.
Explain how the exchange of O2 and CO2 is achieved between alveoli and deoxygenated blood.
Answer:
Exchange of O2 and CO2 between alveoli and deoxygenated blood occurs by simple diffusion based on pressure/concentration gradient.
The PO2 in alveoli is 104 mm Hg and PO2 in deoxygenated blood is 40 mm Hg.
Due to the difference in partial pressure, the O2 from Alveoli diffuses into deoxygenated blood. The PCO2 in deoxygenated blood is 45 mm Hg and in the alveoli is 40 mm Hg. Due to this difference in partial pressure, the CO2 from deoxygenated blood diffuses into alveoli.
![]()
Question 17.
Explain the role of the Atrial Natriuretic factor in the regulation of kidney function.
Answer:
ANF is a peptide hormone secreted by the atrial wall. An increase in the blood flow to the atria of the heart can cause the release of ANF. ANF can cause vasodilation of blood vessels and thereby decrease blood pressure. ANF mechanism acts as a cheek on the renin-angiotensin mechanism.
Question 18.
What is osteoporosis? Mention the common cause that leads to osteoporosis.
Answer:
Osteoporosis is an age-related disorder characterized by decreased bone mass and increased chances of fractures.
The most common cause is the decreased levels of estrogen.
PART-C
Answer any FIVE of the following questions in 40-80 words each, wherever applicable: (5 × 3 = 15)
Question 19.
List the important rules of binomial nomenclature. Write the scientific name of a housefly.
Answer:
- Scientific names are, generally, written in Latin or derived from Latin, irrespective of their origin.
- The scientific names are written in italics or underlined. The first word denotes the name of the genus, and the second word denotes the species.
- The generic name starts with a capital letter, while the specific name starts with a small letter.
- The name of the author is written in an abbreviated form after the specific name e.g, Mangifera indica Linn.-indicates that this species was first described by Linnaeus.
- The name should be short, precise, and easy to pronounce.
The scientific name of housefly: Musca domestica.
Question 20.
defies the terms: (i) Monodelphous condition (ii) Apocarpous condition (iii) Zygomorphic flower.
Answer:
(i) Monoadelphous: The stamens are united into one bunch or one bundle.
(ii) Apocarpous condition: The carpels in an ovary are free.
(iii) Zygomorphic flower: When a flower can be divided into two similar halves only in one particular vertical plane, it is referred to as a zygomorphic flower.
Question 21.
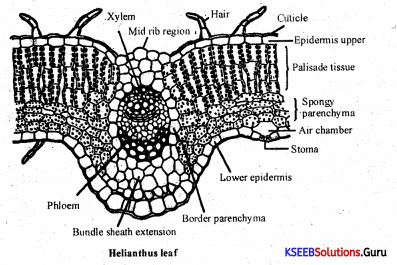
Write any three anatomical differences between the dicot leaf and the monocot leaf.
Answer:
| Isobilateral (Monocot) | Dorsiventral (Dicot) |
| 1. The upper epidermis has large bulliform cells. | 1. There are no bulliform cells. |
| 2. Stomata generally occur on both the epidermal layers. | 2. Stomata are generally found only on the lower epidermis. |
| 3. The mesophyll is not differentiated into palisade and spongy tissues. | 3. Mesophyll is well differentiated. |
| 4. The bundle sheath extensions are made up of sclerenchyma cells. | 4. The extensions are made up of collenchyma and parenchyma cells. |
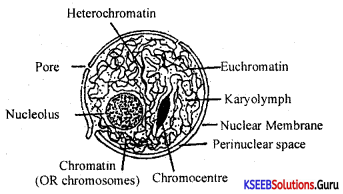
Question 22.
Write a note on the G0 phase of the cell cycle.
Answer:
G0 phase: Some cells in the adult animals exit the G1 phase and enter an inactive phase called quiescent state or G0 phase of the cell cycle.
Cells in this stage remain metabolically active. But these cells -do not exhibit cell division, unless called on to do so depending upon the requirement of an organism.
Therefore, they divide occasionally, as needed to replace cells that have been lost due to injury or cell death.
![]()
Question 23.
Draw the sigmoid growth curve. Write the formula to express, exponential growth.
Answer:
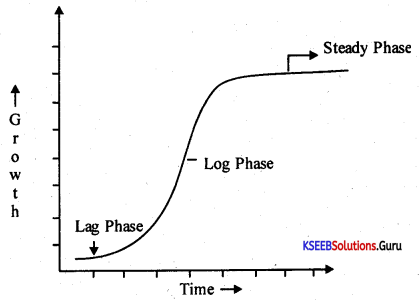
Formula to express exponential growth: W1 = WOert.
Question 24.
Give a brief account of the absorption of fatty acids and glycerol in the small intestine.
Answer:
Give a brief account of the absorption of fatty acids and glycerol in the small intestine.
Fatty acid and glycerol are insoluble, hence cannot be absorbed into the blood. They are first incorporated into small droplets called micelles. Micelles move to the intestinal mucosa, where they are reformed into very small protein-coated globules called chylomicrons.
Chylomicrons are transported into lymph vessels in villi and lymph vessels release these absorbed substances into the bloodstream.
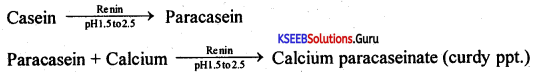
Question 25.
Explain the mechanism of coagulation of blood.
Answer:
Blood has a unique property. As long as circulating inside the body it retains the fluid state however as soon as blood comes out of the body as a result of a cut or an injury, blood is transformed from fluid state to gel state, preventing further loss. This self-regulating mechanism of the blood ¡s known as clotting of the blood.
The mechanism of blood clotting is explained by various theories out of these ‘Best and Taylor’s theory is one. According to this theory. four factors are responsible for blood clotting.
- Prothrombin: Produced by the liver and present in plasma.
- Thromboplastin: An enzyme released from damaged tissues, present ¡n the body tissues.
- Calcium ions: Present in the plasma of the blood.
- Fibrinogen: Produced by the liver and present in plasma.
Chemical events leading to the formation of b; od clot as suggested by ‘Best and Taylor’s theory can be represented as follows.
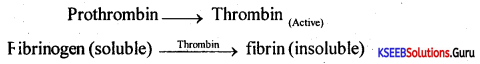
The reaction shown above indicates that the inactive Prothrombin is converted into active thrombin by the catalytic activity of the enzyme Thromboplastin in the presence of Ca2. The activated thrombin reacts with soluble fibrinogen, resulting in the formation of insoluble fibrin.
The fibrin threads form a mesh-like network in which the blood components get entangled and results in blood clots and thus prevents bleeding.
Best and Taylor’s theory doesn’t consider the role of platelets in the blood clotting mechanism.
Question 26.
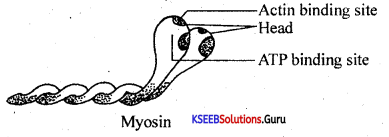
Write a note on myosin protein.
Answer:
- Myosin (Thick) Filament: length is about 1.6 nm and breadth the 15nm.
- Myosin ¡s a polymeric protein, whose monomeric proteins are called meromyosins.
- Each meromyosin has two important parts, a globular head with a short arm and a tail.
- The head with the short arm is called the heavy meromyosin (HMM) and the tail is called light meromyosin (LMM).
- The HMM component projects outwards at a regular distance at an angle from the surface of the polymeric meromyosin; it is known as a cross arm.
- The globular head functions as an ATPase enzyme and has the binding sites for ATP and active sites of actin.
PART-D (Section I)
Answer any FOUR of the following questions in 200-250 words each wherever applicable: (4 x 5 = 20)
Question 27.
Write the general characters of angiosperms.
Answer:
General characters:
- Plant body ¡s a diploid sporophyte and is well-differentiated into the underground root system and aerial shoot system.
- Plants produce special sexual reproductive structures called flowers.
- Flowers contain a male reproductive organ androecium and a female reproductive organ gynoecium.
- The androecium is composed of stamens which produce pollen grains. The gynoecium is composed of carpels that contain ovules.
- Pollen grain represents the male gametophyte and produces male gametes. The embryo sac in the ovule represents the female gametophyte and bears female gamete eggs and secondary nucleus.
- Fertilization is double fertilization where two male gametes involve in the process, one unit with the egg and the other with the secondary nucleus of the female gametophyte.
- After fertilization fertilized egg develops into an embryo. Ovule develops into a seed that is enclosed in the fruit structure developed from the ovary. Seed on germination gives rise to the sporophyte.
- The life cycle shows distinct heteromorphic alternation of generation between independent predominant diploid sporophytic phase and dependent reduced haploid gametophytic phase.
![]()
Question 28.
Differentiate between chordates and non-chordates.
Answer:
| Chordata | Non-Chordata |
| (a) Presence of a solid notochord or a vertebral column. | (a) Absence of chordadorsalis. |
| (b) Presence of a dorsal and tubules nerve chord. | (b) Presence of ventral and solid nervechord. |
| (c) Presence of pharyngeal gillslits. | (c) Absesnce of gilislits. |
| (d) Presence of ventral heart. | (d) Presence of dorsal heart. |
Question 29.
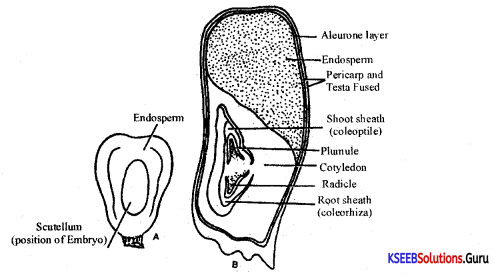
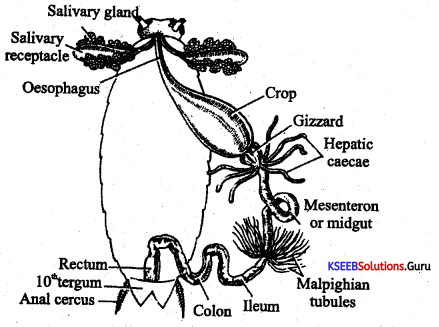
Draw a labeled diagram of the complete digestive system of the frog showing internal organs.
Answer:
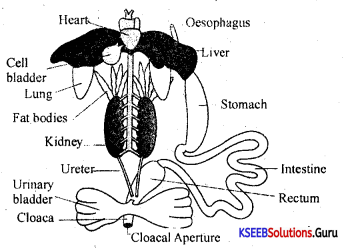
Question 30.
List the functions of the plasma membrane.
Answer:
The functions of the plasma membrane are:
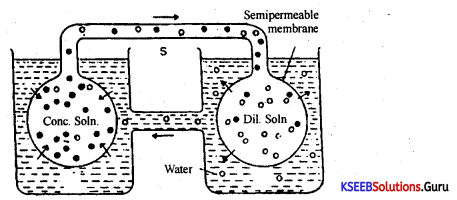
- It maintains the size and shape of the cell.
- Osmosis: Osmosis is the process by which water molecules pass through a semi-permeable membrane (here it ¡s the plasma membrane) from the region of its higher concentration- to one of lower concentration.
- Active transport: It is energy (from ATP) dependent transport of molecules or ions across a semi-permeable membrane against the concentration (electrochemical gradient).
- It can also be called “metabolically linked transport”.
e.g: Sodium – Potassium Pump: (Revolving door model) : - The moving machinery of Na & Kt through active transport ¡s called ‘Sodium – Potassium pump’.
Question 31.
Explain how the pH and concentration of substrate affect enzyme activity with graphical representation.
Answer:
Effect of PH on enzyme activity: Enzymes generally function in a narrow range of PH. Each enzyme shows its highest activity at a particular PH called optimum PH. Activity decreases both below and above optimum value.
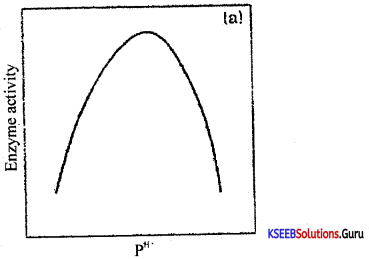
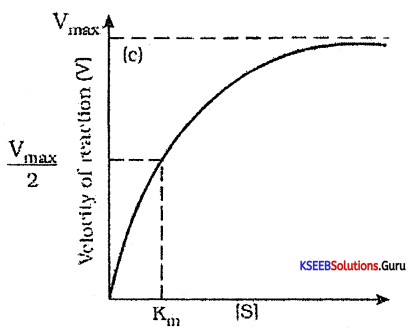
Effect of concentration of substrate on enzyme activity with the increase in substrate concentration, the velocity of enzymatic reaction raises at first. The reaction ultimately reaches a maximum velocity (Vmax) which is not exceeded by further raise in the concentrate of the substrate.
Question 32.
Explain the physical properties of water that govern the transpiration-driven ascent of sap. Explain how these properties help in the ascent of sap or transpiration pull and how a “pull” is achieved.
Answer:
It is one of the most successful physical theories of the ascent of sap. Dixon and Jolly proposed this theory. According to this theory, the ascent of sap is due to three factors namely,
(a) Cohesive force of water
(b) Adhesion of water molecules to the walls of the xylem vessel
(c) Transpiration pull
A strong intermolecular force of attraction exists between water molecules. Thus water molecules are bound to each other forming a continuous column of water.
There is a force of attraction between water molecules on the inner walls of xylem elements.
Therefore water molecules are attached to the wall of the xylem. It is called adhesion.
Due to the adhesive and cohesive properties of water, a continuous column of water is preserved in the xylem.
Transpiration at the leaf surface forces the mesophyll cells of the leaves to draw water from the neighboring xylem elements. This creates a suction force known as Transpiration pull.
This suction force pulls the water column in the xylem upwards. This ascent of sap is due to the combined effect of adhesive, and cohesive properties of water and transpiration pull.
Merits:
- The ascent of sap is directly proportional to the rate of transpiration.
- It is a physical process and does not need energy.
- Strong cohesive, and adhesive forces are sufficient to prevent the rupture of the water
columns in xylem vessels.
Demerits:
- The presence of an air bubble breaks the continuity of the water column.
- Ascent of sap continues even in the absence of transpiration, as at night times.
- The strength of the water column is thoughtful against two opposing forces such as gravitation force and transpiration tension.
Section-II
Answer any THREE of the following questions in 200-250 words each, wherever applicable: (3 × 5 = 15)
Question 33.
What are macronutrients? Describe the roles played by calcium and magnesium in plants.
Answer:
Macronutrients: Macronutrients are those elements, which are generally present in large amounts in the plant tissues, i.e., in excess of 10 m. mole kg-I of dry matter.
e.g., Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur, potassium, and magnesium.
Calcium:
Calcium is are obtained as calcium ions (Cat) from the soil.
Functions:
- It is necessary for the selective permeability of cell membranes.
- It occurs as calcium pectate in the middle lamella of the cell wall hence is necessary for cell enlargement.
- It is used in the formation of mitotic spindles during cell division, hence is required in meristematic, and differentiating tissues (root apex, and shoot apex).
- it activates certain enzymes in the metabolism.
Deficiency symptoms:
(i) Stunted growth.
(ii) Necrosis of meristematic regions.
Question 34.
Explain the events of the C4 pathway. Mention any two special features of C4 plants.
Answer:
- Pathway of CO2 fixation in which the first stable compound formed is a 4-carbon compound oxalic acetic acid in the presence of PEP carboxylase is called the C4 pathway.
- It was first observed by Hatch and Slack.
e.g: Monocots like maize, sugarcane, ragi, and dicots like euphorbia.
Mechanism:
- In mesophyll cells, CO2 is fixed by phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) to form the first stable carbon compound called oxalic acetic acid, a four-carbon sugar in the presence of PEP carboxylase.
- Oxalic acetic acid converts into malic acid.
- Malic acid is transferred to bundle sheath cells, where it is converted into pyruvic acid and CO2
- The released CO2 is used in the Calvin cycle and gets reduced to carbohydrates by the rubisco.
- Pyruvic acid is transported back to mesophyll cells.
Question 35.
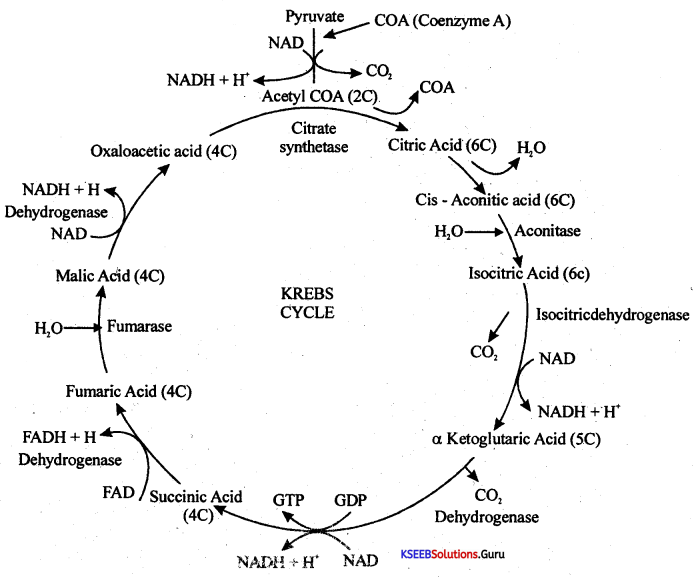
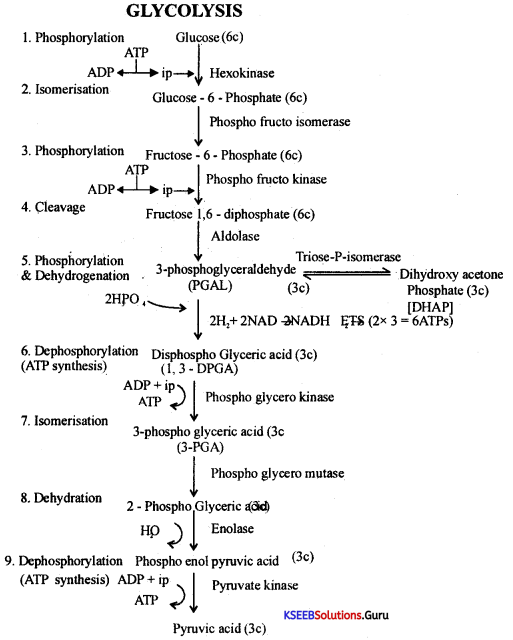
Write the schematic representation of the overall view of the Citric Acid cycle.
Answer:
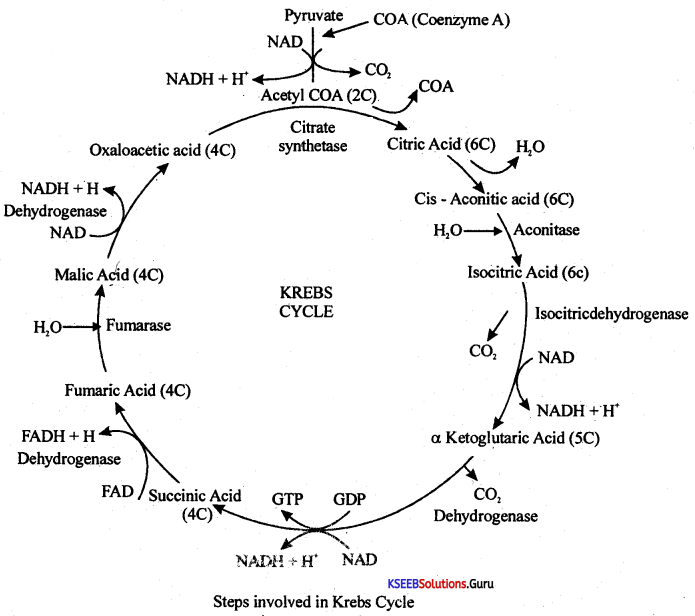
Note: To account for two molecules of acetyl COA produced from 1 molecule of glucose the entire reaction has to be multiplied by two.
Biocncrgetics:
1. Number of ÄTPs produced = 2
2. Number of NADH2 produced = 6 (6 × 3 = 18ATPs)
3. Number of FADH2 produced 2 (2 × 2 = 4 ATPs)
The total yield of ATPs = 24
Note:- Efficiency of Krebs cycle along with its predatory reaction is 30 ATPs.
![]()
Question 36.
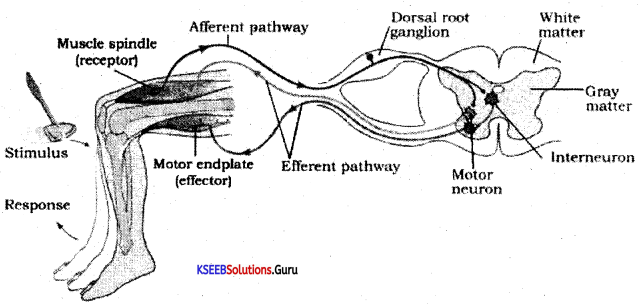
Describe the events of reflex action with a diagrammatic representation of the knee jerk reflex.
Answer:
The reflex action pathway comprises the following events.
The stimulus is received by a receptor (eg. muscle spindle). An afferent neuron receives signals from this sensory organ and transmits the impulse via a dorsal nerve root into the CNS (at the level of the spinal cord). The efferent neuron then carries the signals from CNS to the effectors.
The stimulus and response thus form a reflex arc.
Question 37.
What are hormones? Mention one function each for (i) ACTH (ii) Melatonin (iii) Parathyroid hormone (iv) Thymosin.
Answer:
Hormones are non-nutrient chemicals that act as intercellular messengers and are produced in trace amounts.
1. Adrenocorticotrophic hormone: ACTH stimulates the synthesis and secretion of steroid hormones called glucocorticoids from the adrenal cortex.
2. Melatonin: Melatonin plays a very important role in the regulation of the 24-hour (diurnal) rhythm of our body.
Melatonin helps in maintaining the normal rhythm of the sleep-wake cycle.
3. Parathyroid hormone: Parathyroid hormone increases the Ca2+ levels in the blood. Parathyroid hormone acts on bones and stimulates the process of bone resorption/ dissolution.demineralization.
Parathyroid hormone also stimulates the reabsorption of Ca2+ by the renal tubules and increases Ca2+ absorption from the digested food.
4. Thymosin: Thymosin plays a major role in the differentiation of T-lymphocytes which provide cell-mediated immunity.