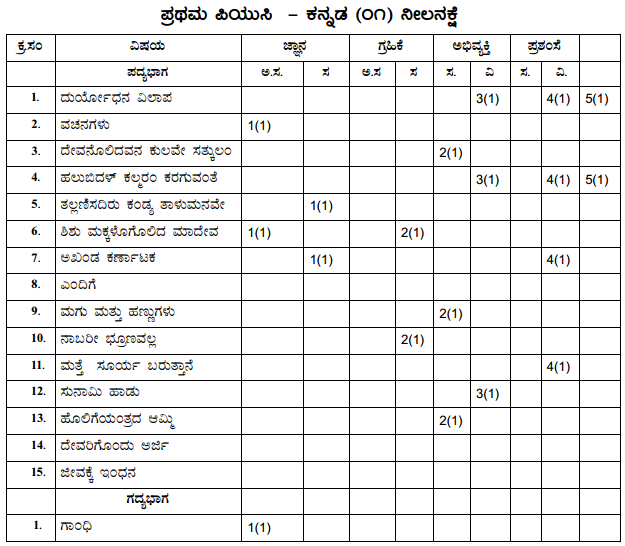
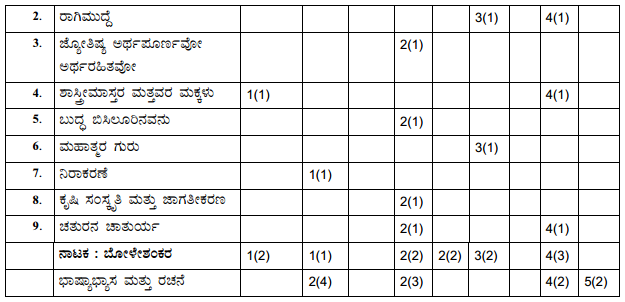
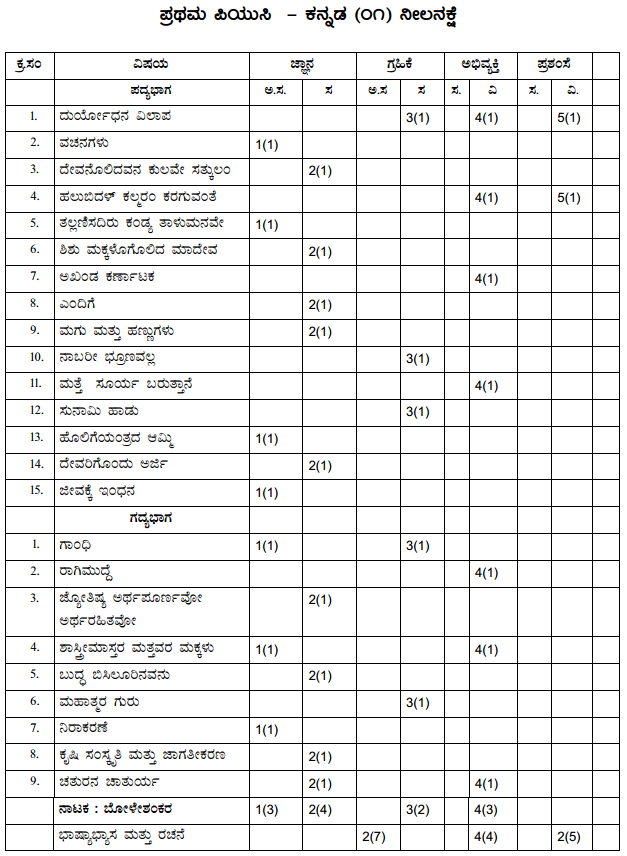
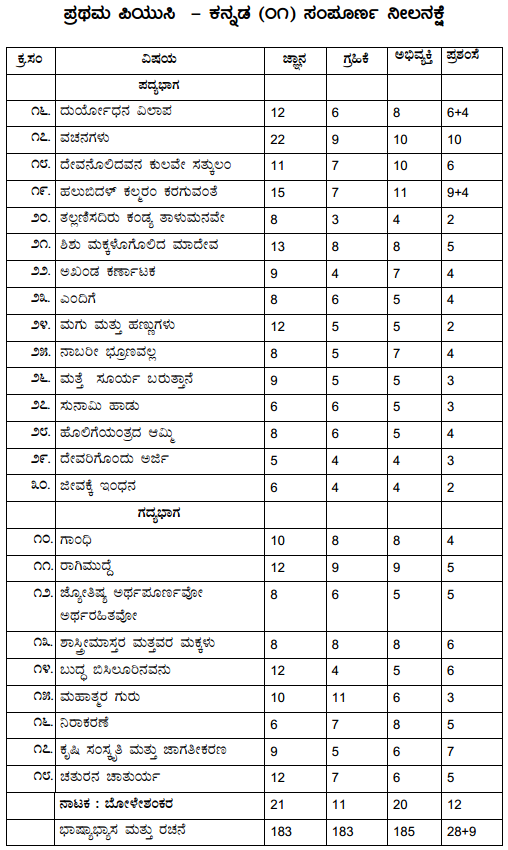
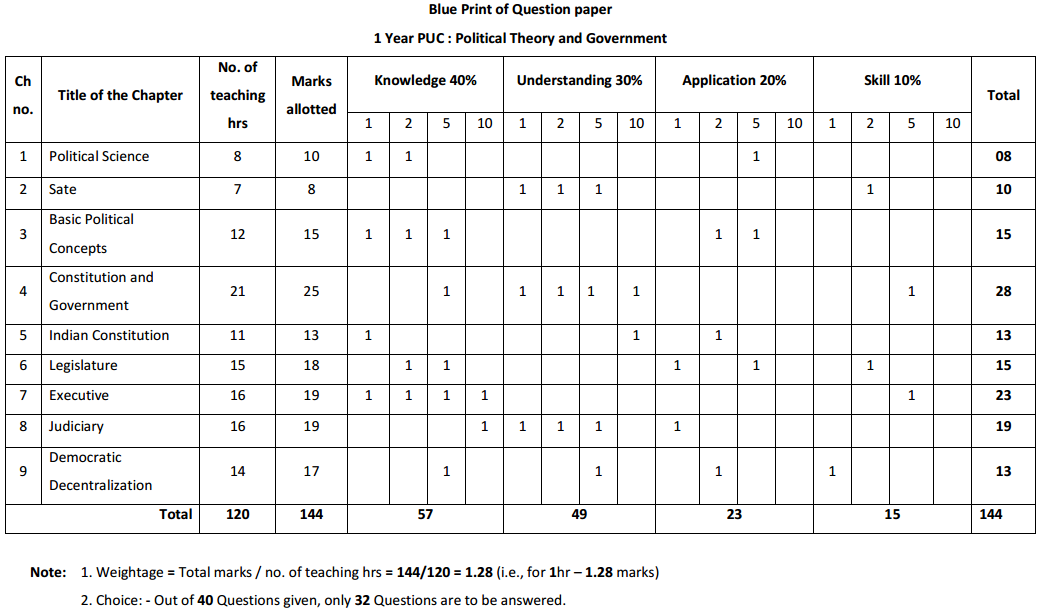
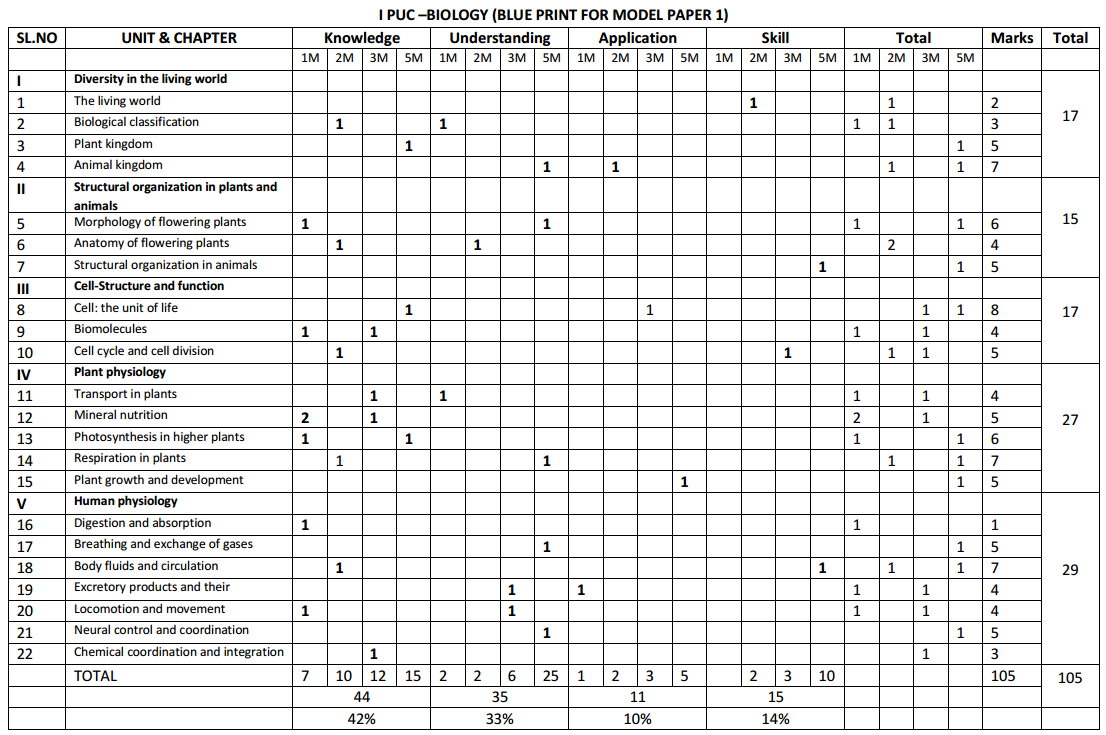
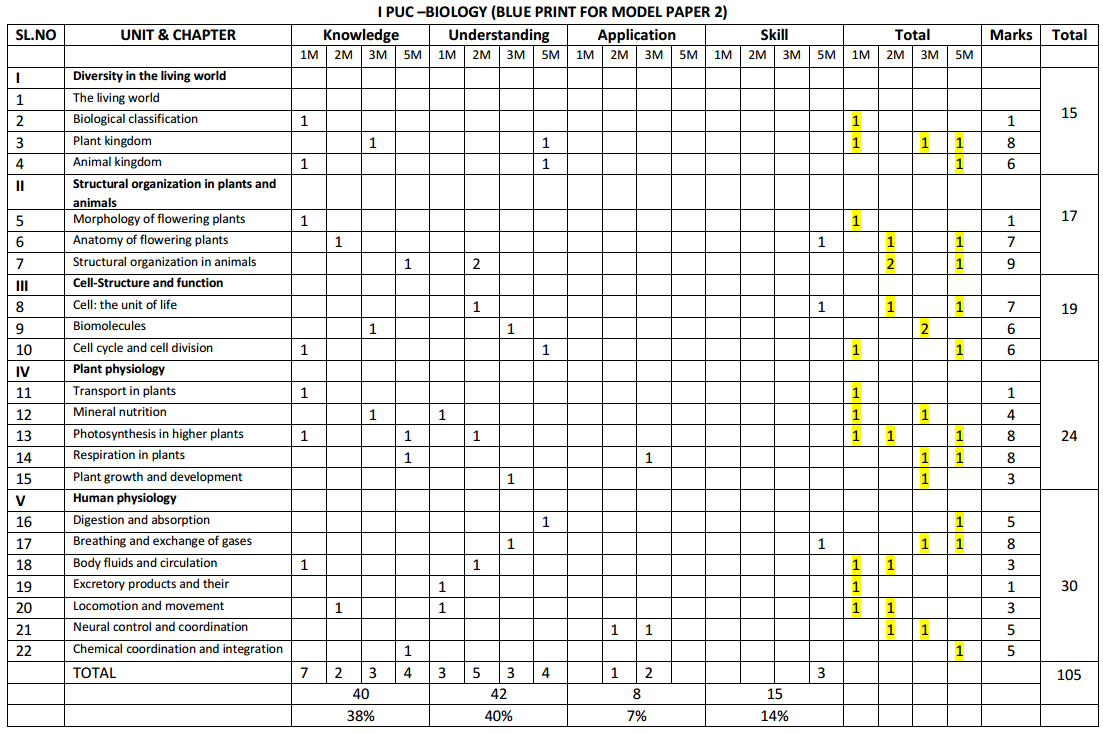
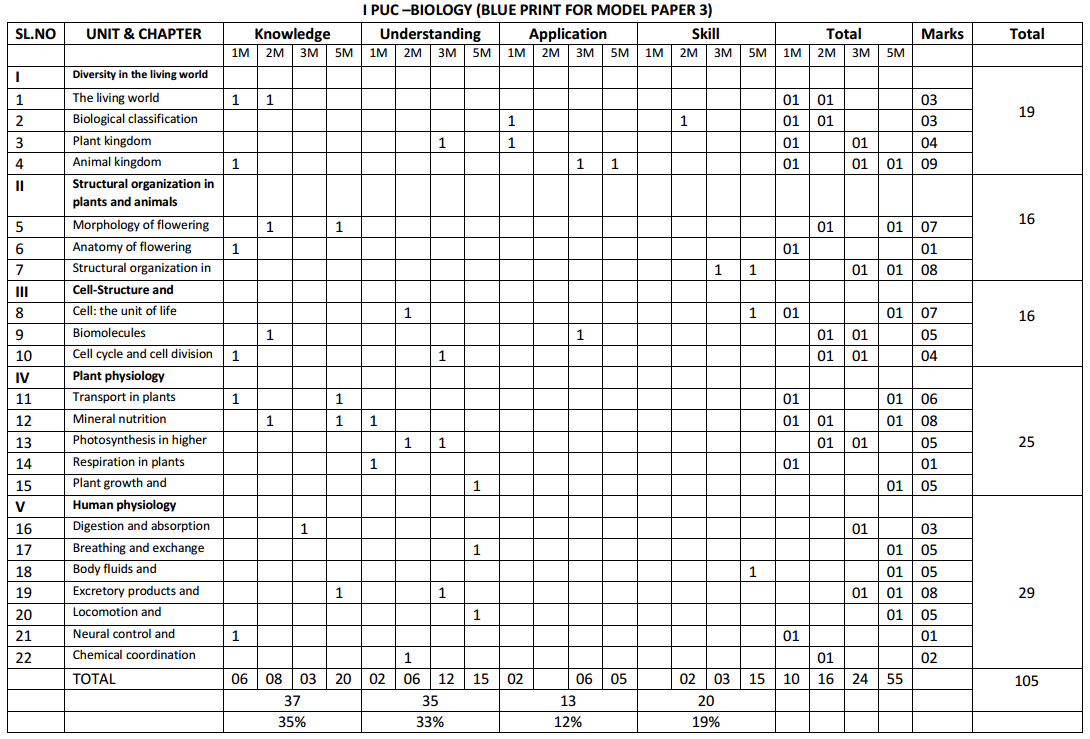
Students can Download 1st PUC Biology Previous Year Question Paper March 2015 (North), Karnataka 1st PUC Biology Model Question Papers with Answers helps you to revise the complete Karnataka State Board Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Karnataka 1st PUC Biology Previous Year Question Paper March 2015 (North)
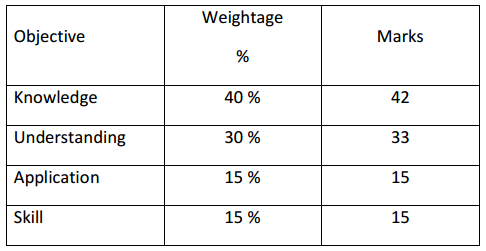
Time: 3.15 Hours
Max Marks: 70
General Instructions:
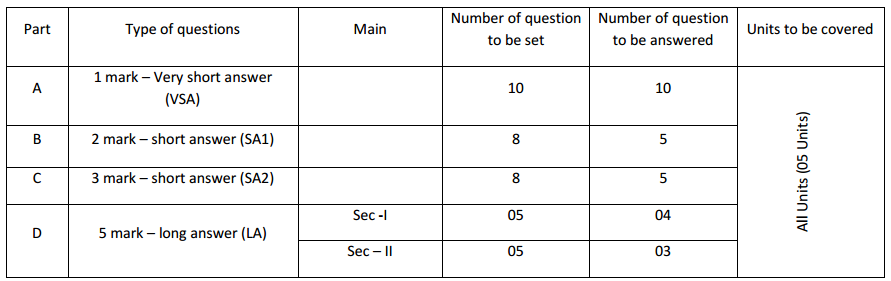
- The question paper consists of four parts A, B, C, and D.
- All the parts are compulsory.
- Draw diagrams wherever necessary. Unlabelled diagrams or illustrations do not attract any marks.
Part – A
Answer the following questions in one word / one sentence each: ( 10 × 1 = 10 )
Question 1.
Name the basic unit of classification.
Answer:
Species are the basic unit of classification.
Question 2.
Define Phyllotaxy.
Answer:
The mode of arrangement of leaves on the stem axis is known as phyllotaxy.
Question 3.
Mention the function of Nephridia.
Answer:
Excretion.
Question 4.
Name the bacterial Ribosome.
Answer:
70s Ribosome
![]()
Question 5.
Define Osmosis.
Answer:
It is a special type of diffusion in which only the solvent or water molecules move from a region of their higher concentration to a region of their lower concentration through a semi-permeable membrane.
Question 6.
Which is the non – digesting enzyme of Intestinal Juice?
Answer:
Enter Kinase.
Question 7.
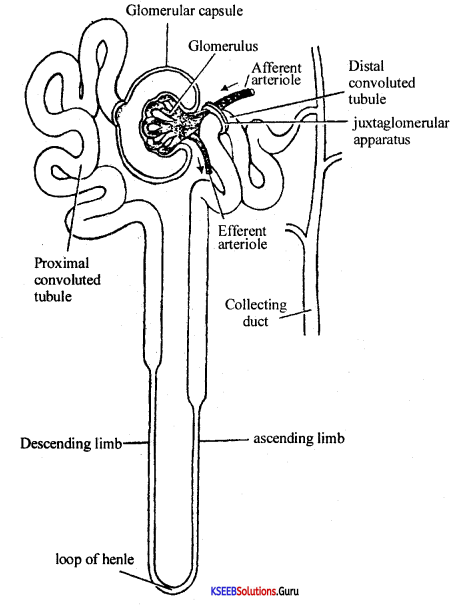
Name the structural and functional unit of the Kidney.
Answer:
Nephron.
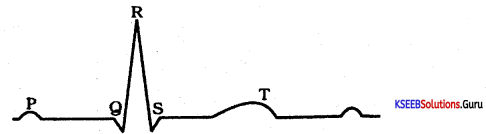
Question 8.
Expand ECG
Answer:
Electrocardiogram.
Question 9.
What is Transpiration?
Answer:
It is the phenomenon by which excess water is eliminated, in the form of vapors through the aerial parts of the plant body.
Question 10.
Mention any Inclusion bodies.
Answer:
Reserve food material in prokaryotic cells is stored in the cytoplasm in the form of inclusion bodies. These are not bound by any membranes.
Part-B
Answer any FIVE of the following questions in 3-5 sentences each, wherever applicable. (5 × 2 = 10)
Question 11.
Write any four characteristics of Fungi.
Answer:
Kingdom Fungi is divided into five classes, based on the following characters:
(a) Morphology of mycelium
(b) Mode of spore formation.
(c) Mode of sexual reproduction and
(d) Nature of fruiting bodies.
![]()
Question 12.
Mention the uses of Diatomaceous Earth.
Answer:
Diatomaceous Earth is used:
- as an absorbent for liquid nitroglycerin to make explosives.
- for filtering the liquids in sugar factories.
- as an inert extender in paints, as an insulator in boilers and blast furnaces.
- in the powdered form as abrasive in silver polish and in the manufacture of toothpaste.
Question 13.
Differentiate Bilateral and Radial Symmetry.
Answer:
Germ layers or germinal layers are primary layers that differentiate in the embryo at the time of gastrulation. Animals have a minimum of two germinal layers and a maximum of three germinal layers. All the tissues and organs of the body develop from germinal layers.
Types:
(a) Diploblastic Animals: Animals having two germinal layers viz, outer ectoderm and inner endoderm are called diploblastic animals.
(b) Triploblastic Animals: Animals having three germinal layers viz, outer ectoderm, middle mesoderm, and inner endoderm are called Triploblastic animals.
eg: Platyhelminthes, Aschelminthes, Annelida, Arthropoda, Mollusca, Echinodermata, and Chordata.
Question 14.
Write any four Biological significance of Carbohydrates.
Answer:
(a) Carbohydrates particularly cellulose, chitin, and pectin provide structural support and protection to plants and fungi.
(b) The major food storage molecules are starch in plants and glycogen in animals.
(c) Pentoses form an integral part of nucleic acids and thus help in heredity.
(d) Chitin is an important exoskeleton in arthropods.
Question 15.
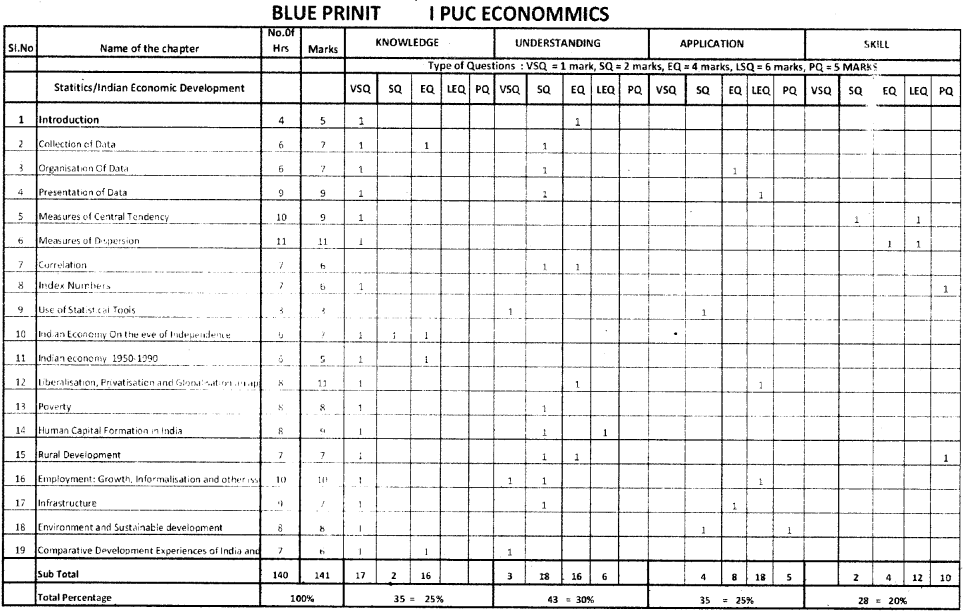
Draw a labeled diagram of Mitochondria.
Answer:
Question 16.
Mention the role of HCl in the Stomach.
Answer:
(a) It activates inactive pepsinogen into active pepsin.
(b) It converts inactive prorenin into active renin.
(c) It provides an acidic medium (pH 1.5 – 2.5) for the action of both pepsin, and renin.
(d) HCl kills harmful bacteria and loosens fibrous food.
(e) It inactivates the ptyalin.
Question 17.
Define Inspiration and Expiration.
Answer:
| Inspiration | Expiration |
| 1. It is a process of drawing air oxygen into the lungs from outside. | 1. It is a process of leaving out carbon dioxide from the lungs to the outside. |
| 2. Diaphragm and intercostal muscles contract. | 2. Diaphragm and intercostal muscles relax. |
| 3. Due to this the volume of the thorax, increases, and the lungs expand. | 3. Due to this the volume of the thorax, decreases, and bings get compressed. |
| 4. Pulmonary pressure falls. | 4. Pulmonary pressure increases. |
![]()
Question 18.
Briefly explain the transport of CO2 by blood.
Answer:
As carbon dioxide from the tissues enters into the blood, a small quantity of about 45% enters into RBCs. In the RBCs, carbon dioxide combines with hemoglobin and forms carbamino hemoglobin. The carbamino-hemoglobin on reaching the lungs dissociates into hemoglobin, and carbon dioxide.
CO2 + HbNH2 → HbNHCOOH.
PART-C
Answer any FIVE of the following questions in 40-80 words each, wherever applicable: (5 × 3 = 15)
Question 19.
Write any three economic importance of Cyanobacteria.
Answer:
Economic Importance:
Many of them are used as bio-fertilizers because. of their nitrogen-fixing capacity. e.g. Nostoc, Aulosira, Anabaena.
Spirulina is unicellular and spiral-like; ¡t is cultured and used as cattle-feed and human food, for it is rich in proteins. it is called a single called protein.
Question 20.
Mention briefly respiration in Frog.
Answer:
Respiratory System: Frogs respire on Land and in the water by two different methods. In water, their skin acts as the aquatic respiratory organ, and it is exchanged through the skin by diffusion.
Question 21.
List any three functions of Parenchyma.
Answer:
Parenchyma is defined as a living, simple, permanent, and storage tissue. It is the basic and packing tissue that occurs in all parts of the plant body such as cortex, pith, pericycle, etc.
Characters:
- Cells appear usually oval or spherical.
- Cells are compactly arranged without intercellular spaces except for the lacunar type.
- The cell wall is made up of cellulose and pectin.
- The cell walls show uneven thickening, especially at corners.
- Cells have cytoplasm and nucleus and hence are called living cells.
- Cells have large and prominent vacuoles.
Types:
Based on the pectin deposition, collenchyma is of the following three types.
(a) Angular collenchyma – Here pectin is deposited in the angles or intercellular spaces of cells, eg: Datura, Ficus, etc.
(b) Lamellar collenchyma – Here pectin is deposited in between the cellular layers in the form of sheets. eg: Radish, Sunflower, etc.
(c) Lacunar collenchyma – Here pectin is deposited along the sidewalls around the intercellular space leaving a small space in the center. eg: Malva, Althea, etc.
Functions:
- Collenchyma gives mechanical support.
- Cells possess chloroplasts in young stems and help in photosynthesis.
- Cells become meristematic and help in secondary growth.
- In young parts of dicot plants, it gives resistance against the pulling and bending actions of wind.
![]()
Question 22.
What is the Cell Cycle? Mention the phases of the cell cycle.
Answer:
The sequence of events that occur between the formation of a cell and its division into daughter cells is called a cell cycle.
It consists of 2 phases:
(a) Interphase
(b) Mitotic phase
Question 23.
Explain briefly Mass flow Hypothesis.
Answer:
The accepted mechanism used for the translocation of sugars from source to sink is called the pressure-flow hypothesis. The glucose prepared by photosynthesis is converted to sucrose and is then moved in the form of sucrose into companion cells and into sieve tube cells by active transport.
This loading creates a hypertonic condition in the phloem & water in the adjacent xylem moves into the phloem by osmosis. As osmotic pressure builds up the phloem sap will move to areas of lower pressure. Again by active transport sucrose is transported out of phloem sap into the cells where it is used to convert into energy, starch, or cellulose.
Question 24.
Mention the formed elements of Blood.
Answer:
(a) Erythrocytes
(b) Leucocytes
(c) Platelets
Question 25.
Explain the role of Saliva.
Answer:
It is secreted in an inactive form called prorenin. it is activated into rennin by HCl.
![]()
Rennin acts on the milk protein casein, and converts it into Para casein.
![]()
Para casein combines with calcium ions to form solid casein or curd.
Para casein + Ca2+ → Calcium paracaseinate (Solid Casein).
Calcium Para casemate is acted upon by pepsin and converted into protests, peptones, and polypeptides
![]()
Question 26.
What is Double Circulation? Mention the stages in double circulation.
Answer:
The human heart acts as a double pump.
The right side of the heart receives, and pumps deoxygenated blood and the left side of the heart receives and pumps oxygenated blood and hence both the routes are kept completely separate and there is no mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood. This type of circulation is said to be complete double circulation.
Double circulation involves shorter pulmonary circulation and longer systematic circulation.
Part-D (Section – I).
I. Answer any FOUR of the following questions in 200-250 words each. (4 × 5 = 20)
Question 27.
Write the general characters of the Phylum Annelida.
Answer:
General characters:
- Annelids are mostly aquatic-either marine or freshwater forms. Some are terrestrial burrowing, free-living, or sedentary forms. A few are ectoparasites.
- Annelids are bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic, coelomate, and segmented animals.
- The body is soft, cylindrical, or dorsoventrally flattened, uniform with cephalization at the anterior end.
- The body is protected by a thin cuticle which is secreted by the underlying epidermal cells.
- The body wall is dermo muscular (dermis with muscle cells or Libres), therefore can twist and turn or be highly contractile in nature.
- The body cavity is a true coelom fined by coelomic epithelium, the coelom is formed by splitting of embryonic mesoderm, and hence it is described as ‘schizócoetous’ or ‘Schizocoelic’ made of formation and the coelom as ‘Schizocoel’.
- The digestive system is a straight tubular structure and is complete with a mouth and anus. it also shows regional differentiation into parts like the buccal cavity, pharynx, esophagus, gizzard, intestine, and rectum.
The digestive system shows segmental specialization. - Annelids are the first group to have a blood vascular system. A definite circulatory system or blood vascular system is present which consists of blood and blood vessels. Blood flows only indefinite blood vessels, hence the circulatory system is described as the ‘closed type’ of the circulatory system. Blood is red in color due to the presence of hemoglobin in the plasma.
- Respiration occurs by simple diffusion through the body surfaõe or through respiratory structures called glib.
- The excretory system consists of coiled ectodermal tubes called nephridia, through which excretion takes place.
- The nervous system is well developed consisting of a nerve ring and a double ventral nerve cord.
- Characteristic locomotory structures are usually present, either in the form of chitinous setae or fleshly lateral extensions called parapodia.
- Reproduction is usually done in sexual mode. Members may be either bisexual or unisexual.
- Development may be direct or indirect, where the larval stage present is represented by a trochophore larva.
![]()
Question 28.
Enumerate any five characteristic features of Gymnosperms.
Answer:
1. The life cycle has a distinct, dominant, diploid, asexual phase represented by the well-differentiated evergreen woody plant, which is known as the sporophyte.
2. The sporophyte is heterosporous bearing microspores and megaspores within microsporangia and megasporangia respectively. These structures occur on leaf-like microsporophylls and megasporophylls. These are further organized into fertile structures called stroll or cones.
3. Sporophyte shows the presence of a taproot system which is well developed. The stein possesses branches that are dichotomies. Leaves are well developed and are dimorphic (two types of leaves): viz,
- Green photosynthetic leaves (Foliage).
- Brown-colored scale leaves.
4. Microspore develops into male gametophyte and megaspore produces female gametophyte.
These gametophytes represent the haploid phase and are highly inconspicuous in comparison with sporophytic generation.
5. Female gametophyte is enclosed within a megasporangium that in turn is covered by an integument. Such an integument megasporangium possessing the female gametophyte is called the ovule.
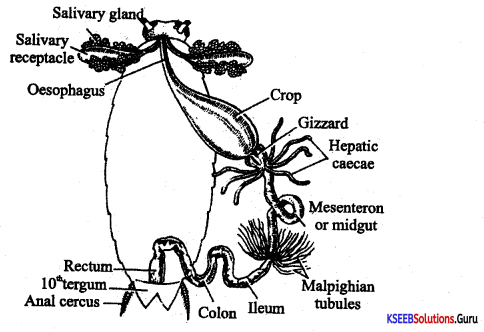
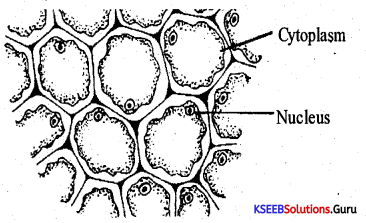
Question 29.
Draw a neat labeled diagram of the Digestive system of the Cockroach.
Answer:
Question 30.
Explain Fluid Mosaic Model? Mention the functions of the Plasma membrane.
Answer:
Fluid mosaic Model By Singer & Nicholson:
(a) According to this model, the plasma membrane consists of a double layer of lipid molecules and globular protein molecules and sterols distributed at random. In comparative terms, it can be said that the plasma membrane is formed of ‘protein icebergs in the sea of lipids’.
(b) The protein molecules are globular proteins and these proteins penetrate or lie at the periphery to form a mosaic pattern.
(c) Heads of the phospholipid molecuLes of the two layers are directed in the opposite directions while tails of the two layers face each other.
(d) In animal cells glycolipids and cholesterol are also present along with proteins.
Modifications of the plasma membrane.
To perform specific functions and exhibit flexibility, PM undertakes the following modifications:
- Microvilli: These are minute folding of the plasma membrane to increase surface area for absorption.
- Desmosomes: the inner surface of adjacent plasma membranes has thickened areas called desmosomes which help in cell adhesion.
- Pinocytic vesicles: Invaginations of the plasma membrane into cytoplasm and formation of fields that contain fluids.
- Mesosomes: In prokaryotes, invaginations of the plasma membrane are associated with the respiratory system enzymes and help in respiration and are called mesosomes.
The functions of the plasma membrane are:
- It maintains the size and shape of the cell.
- Osmosis: Osmosis is the process by which water molecules pass through a semi-permeable membrane (here it is the plasma membrane) from the region of its higher concentration- to one of lower concentration.
- Active transport: It is energy (from ATP) dependent transport of molecules or ions across a semi-permeable membrane against the concentration (electrochemical gradient). it can also be called “metabolically linked transport”.
e.g: Sodium – Potassium Pump: (Revolving door model):
The moving machinery of Na & K through active transport is called ‘Sodium – Potassium pump’.
Question 31.
Write the differences between Mitosis and Meiosis.
Answer:
| Mitosis | Meiosis |
| (a) occurs in all somatic cells and germ cells. | (a) occurs in germ cells of organisms that reproduce sexually. |
| (b) It is equational cell division. | (b) It is reductional cell division. |
| (c) Two daughter cells are produced. | (c) Four daughter cells are produced. |
| (d) Daughter cells have the same genetic constitution as the parent cells. | (d) Genetic constitution of daughter cells is different than parental cell due to crossing over |
| (e) Both the homologous chromosomes are present in daughter cells. | (e) The daughter cells contain one chromosome of each homologous pair |
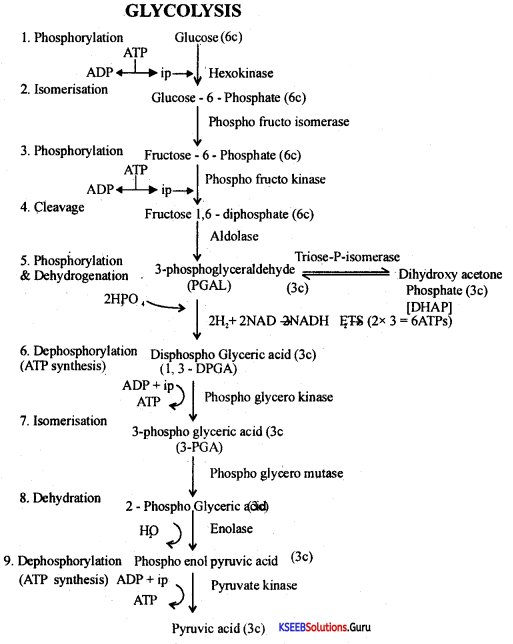
Question 32.
Give schematic representation of Kreb’s Cycle.
Answer:
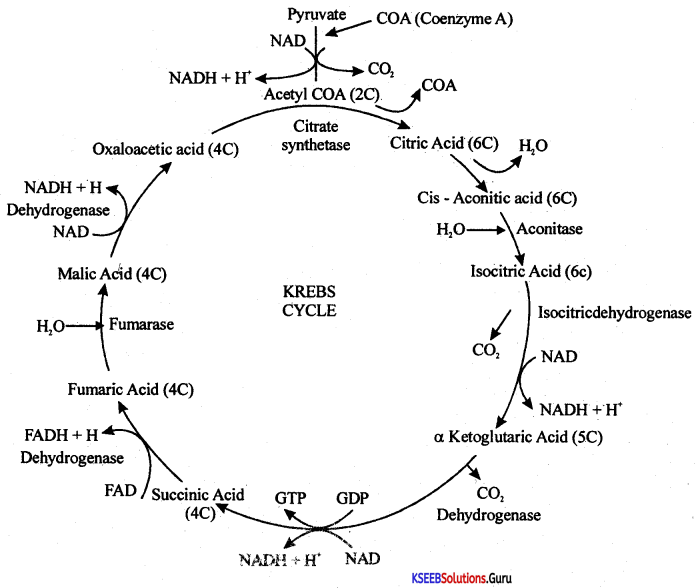
Note: To account for two molecules of acetyl CoA produced from 1 molecule of glucose the entire reaction has to be multiplied by two.
Bloenergetics:
1. Number of ArPs produced = 2 .
2. Number of NADH2 produced = 6 (6 × 3 = 18ATPs)
3. Number of FADH2 produced = 2 (2 × 2 = 4 ATPs)
The total yield of ATPs = 24.
Note: Efficiency of Krebs cycle along with its predatory reaction is 30 ATPs.
Section – II
II. Answer any THREE of the following questions in 200-250 words each, wherever applicable. (5 × 3 = 15)
Question 33.
Explain the physiological roles of Cytokinins.
Answer:
- Discovered by Skoog and Miller
- Chemically these are 6-fur furyl amino purine.
- Synthesized in young fruits, leaves, buds, rost tips and translocated through the xylem.
- Cytokinins stimulate cell division.
- Cytokinins prevent early aging or senescence by stabilizing proteins and chlorophyll. This
the phenomenon is called Richmond – Lang effect. - Cytokinins break seed dormancy and induce germination.
![]()
Question 34.
Write the Z scheme of Light reaction.
Answer:
Non-cyclic photophosphorylation is also called ‘Z’ scheme electron transport.
In this cycle, the electrons lost by chlorophyll pigment do not return to the same molecule.
Both PSI and PS II are utilized.
One molecule of ATP is formed.
Two molecules of NADPH2 are formed.
One molecule of O2 is formed.
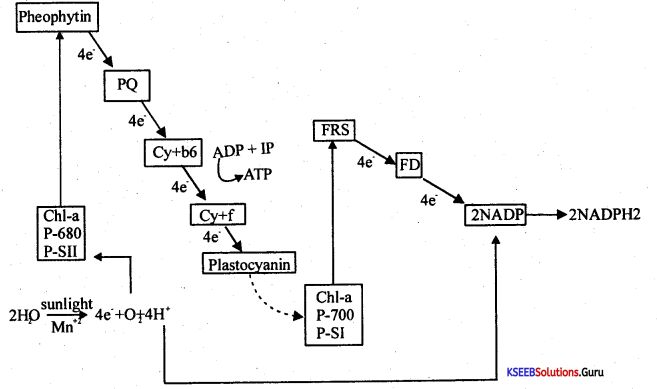
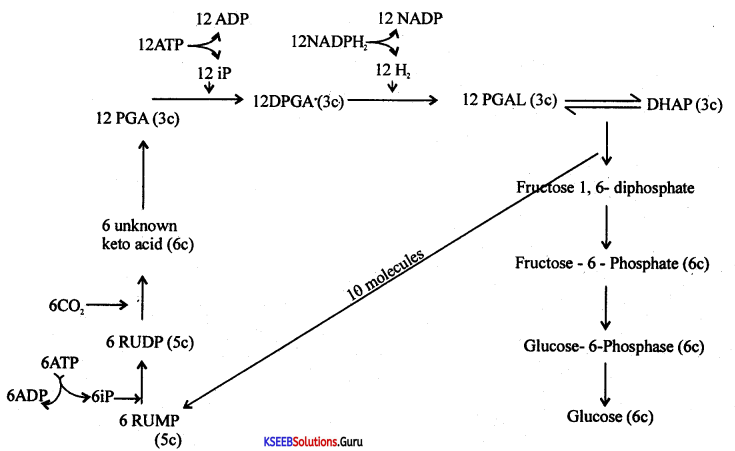
Question 35.
Explain the mechanics of Ascent of Sap.
Answer:
It is one of the most successful physical theories of the ascent of sap. Dixon and Jolly proposed this theory. According to this theory, the ascent of sap is due to three factors namely,
(a) Cohesive force of water.
(b) Adhesion of water molecules to the walls of the xylem vessel
(c) Transpiration pull
A strong intermolecular force of attraction exists between water molecules. Thus water molecules are bound to each other forming a continuous column of water.
There is a force of attraction between water molecules on the inner walls of xylem elements. Therefore water molecules are attached to the wall of the xylem. It ¡s called adhesion.
Due to the adhesive and cohesive properties of water, a continuous column of water is present in the xylem.
Transpiration at the leaf surface forces the mesophyll cells of the leaves to draw water from the neighboring xylem elements. This creates a suction force known as Transpiration pull.
This suction force pulls the water column ¡n the xylem upwards. This ascent of sap is due to the combined effect of adhesive, and cohesive properties of water and transpiration pull.
Merits:
- The ascent of sap is directly proportional to the rate of transpiration.
- It is a physical process and does not need energy.
- Strong cohesive, and adhesive forces are sufficient to prevent the rupture of the water columns in xylem vessels.
Demerits:
- The presence of an air bubble breaks the continuity of the water column.
- Ascent of sap continues even in the absence of transpiration, as at night times.
- The strength of the water column is thoughtful against two opposing forces such as gravitation force and transpiration tension.
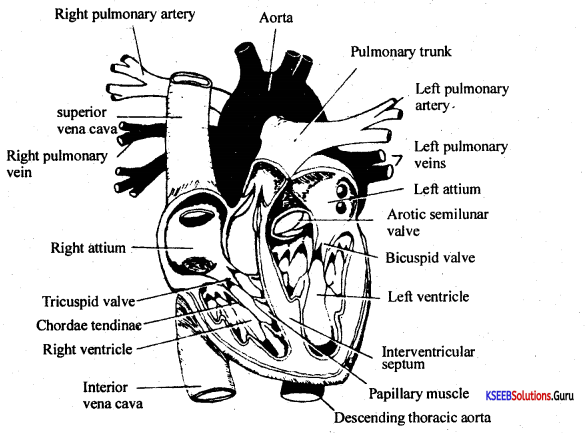
Question 36.
Draw a neat labeled diagram of V.S. of Human Heart.
Answer:
Question 37.
List any Five hormones of the Pituitary gland and write one function of each.
Answer:
The pituitary gland weighs about 0.5 gm and is a pea-sized endocrine gland that lies on the ventral surface of the brain attached to the hypothalamus by a nervous stalk called the infundibulum.
It is called the master gland or conductor of the endocrine orchestra as several of its hormones control other endocrine glands directly. The hormones of the pituitary that influence other endocrine glands are called tropins or trophic hormones. However, the pituitary gland itself works under the influence of the hypothalamus through releasing factors. The pituitary gland is called the master gland because it controls the functions of other endocrine glands by secreting hormones.
Based on origin, it is divided into two parts namely Adenohypophysis and Neurohypophysis.
I. Adenohypophysis (Anterior Pituitary): It accounts for nearly 75% of the total weight of the gland. It is derived from the buccal cavity in the form of a projection called Rathke’s pouch.
Adenohypophysis is further divided into three regions: Pars distalis, Pars intermedia, and Pars tubular. Pars intermedia degenerates .during fetal development and occurs only as a small strip in adults. Pars tubular has no functional significance. Adenohypophysis cells secrete seven major hormones.
1. Somatotrophic hormone or Human growth hormone (STH or HGH): Promotes the growth of muscles. It stimulates the uptake of amino acids by tissues and their synthesis into proteins.
- Hypo secretion in childhood causes Pituitary dwarfism. Such an individual will be abnormally dwarf and is called a midget.
- Hypersecretion in childhood causes Pituitary gigantism. Such an individual will be abnormally tall.
- Hypersecretion in adolescence causes acromegaly which is characterized by the formation of disproportionately large hands, feet, cheekbones, jaws, etc.
2. Thyroid-stimulating Hormone (TSH): Controls secretion of thyroid hormones by the thyroid gland and also regulates iodine intake by the thyroid gland.
- Hypo secretion leads to goiter, cretinism, and myxoedema.
- Hypo secretion leads to hyperthyroidism.
3. Adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH): It controls the( secretion of hormones (Cortisone) by the adrenal cortex.
- Hypersecretion of ACTH causes Cushing’s syndrome.
- Hypo secretion causes Addison’s disease.
4. Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH): In females the induces growth and maturation of Graffian follicle and stimulates follicular secretion of estrogen. In males, it stimulates the testis to produce sperm.
5. Luteinizing Hormone or Interstitial Cell Stimulating Hormone (LH or ICSH): In females, it stimulates ovulation and the formation of the corpus luteum. In males, it stimulates interstitial cells in the testis to secrete testosterone.