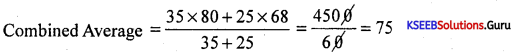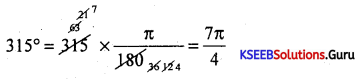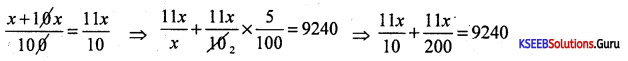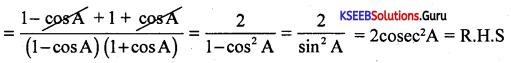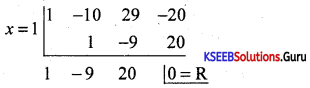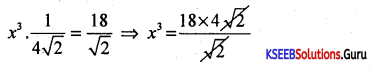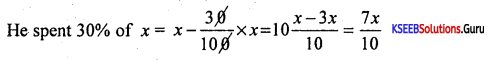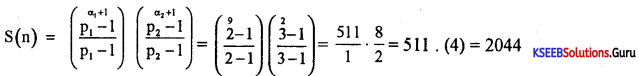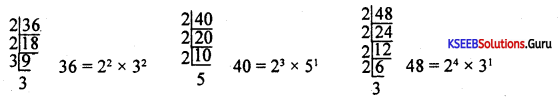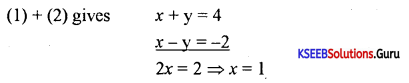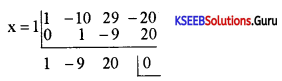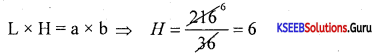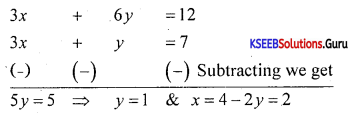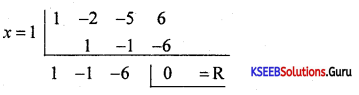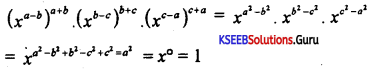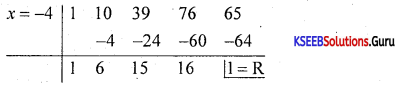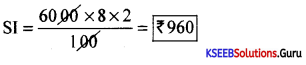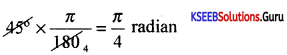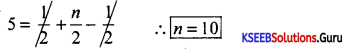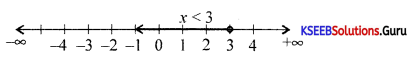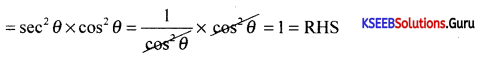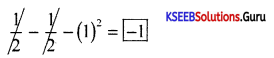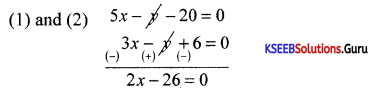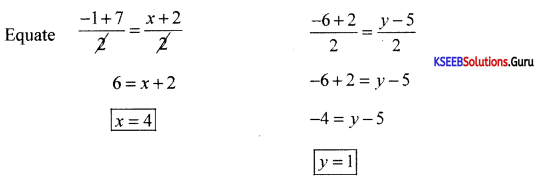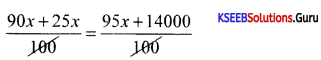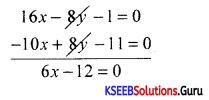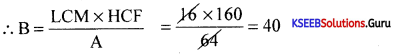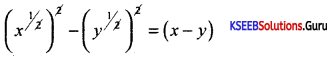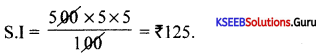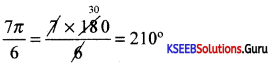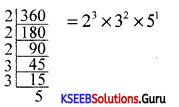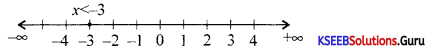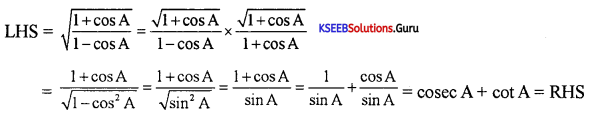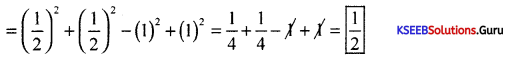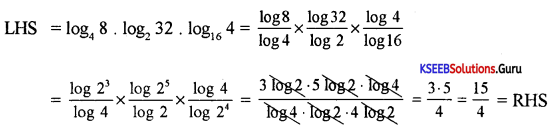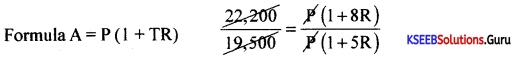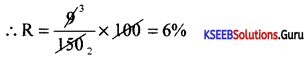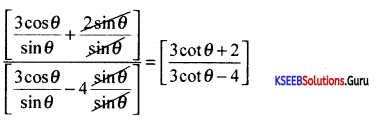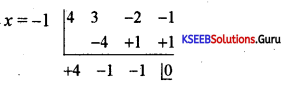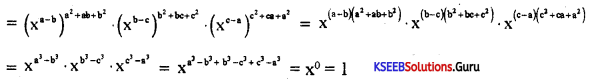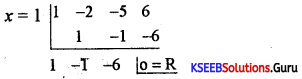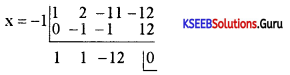Students can Download 1st PUC Basic Maths Previous Year Question Paper March 2017 (North), Karnataka 1st PUC Basic Maths Model Question Papers with Answers helps you to revise the complete syllabus.
Karnataka 1st PUC Basic Maths Previous Year Question Paper March 2017 (North)
Time: 3.15 Hours
Max. Marks: 100
Instructions:
- The questions paper consists of five parts A, B, C, D, and E.
- Part – A carries 10 marks, Part – B carries 20 marks, Part – C curries 30 marks, Part – D carries 30, and Part – E carries 10 marks.
- Write the question numbers properly as indicated in the questions paper
PART-A
I. Answer any TEN questions. (10 × 1 = 10)
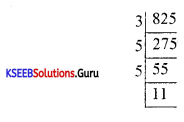
Question 1.
Give the canonical representation of 825.
Answer:
825 = 31 × 52 × 11.
Question 2.
Convert the set A = {a, e, i, o, u} from roster form into rule form.
Answer:
A = {x/x is a vowel in English alphabet}
Question 3.
If A = {a, b, c}; B = {c, d}. Find B × A.
Answer:
B × A = {c, d) x {a, b, c}
= c, a) (c, b) (c, c) (d, a) (d, b) (d, c)}.
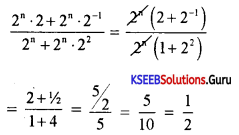
Question 4.
Simplify: \(\frac{a^{m+n} \cdot a^{2 m-n}}{a^{m-n}}\)
Answer:
![]()
Question 5.
Express Y = 27 in the .Lograrithmic Form.
Answer:
log3 27 = 3
![]()
Question 6.
Find the 8th term of an A.P -2, -4, -6 ………..
Answer:
T = a + (n – 1)d
T8 = -2 + (8 – 1)(-2)
T8 = -2 – 14 = -16
Question 7.
Solve: \(\frac{x+2}{x-2}=\frac{5}{2}\)
Answer:
2(x + 2) = 5(x – 1)
2x + 4 = 5x – 5
4 + 5 = 5x – 2x ⇒ 3x = 9 ⇒x = 3.
Question 8.
Define perpetuity.
Answer:
An annuity that is payable forever is called a perpetuity.
Question 9.
Convert 42% into a decimal.
Answer:
42% = \(\frac{42}{100}\) = 0.42.
Question 10.
The average score of 35 girls is 80 and the average score of 25 boys is 68. Find the average score of both boys and girls together.
Answer:
X̄12 = \(\frac{35 \times 80+25 \times 68}{35+25}=\frac{2800+1700}{60}\) = 75
Question 11.
Convent 75° into radians.
Answer:
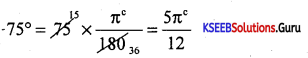
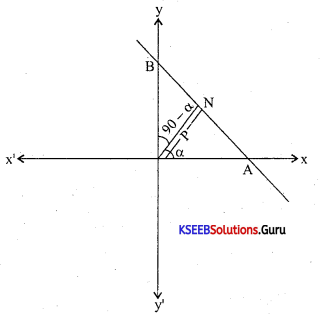
Question 12.
If the distance between the points (3, -2) and (-1, a) is 5 units. Find the values of
Answer:
\(\sqrt{(3+1)^{2}+(-2-a)^{2}}\) = 5
42 + 4 + a2 + 4a = 5
a2 + 4a + 15 = 0
Using formula method we get the values of a.
Part – B
II. Answer any TEN questions. (10 × 2 = 20)
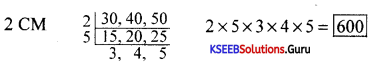
Question 13.
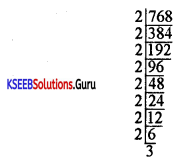
Find the L.C.M of 12, 21 and 24.
Answer:

∴ L.C.M = 23 × 3 × 7 = 24 × 7 = 168
Question 14.
Find the H.C.F of 18 and 24.
Answer:
18 = 2 × 32, 24 = 23 × 3
H.C.F = 2 × 3 = 6
![]()
Question 15.
If A = {a, b,c, d}\ B = {d, e, f, g, h, i}. Find A – B & B – A.
Ans.wer:
A – B = {a, b, c}, B – A = {e, f g, h, i}
Question 16.
Find the value of x so that the slope of the line joining the points (2, 5) and (x 13) is 20.
Answer:
Slope = \(\frac{y_{2}-y_{1}}{x_{2}-x_{1}}\)
\(\frac{13-5}{x-2}\) = 20 ⇒ \(\frac{8}{x-2}=\frac{20}{1}\)
⇒ 20x – 40 = 8 ⇒ 20x = 48
⇒ x = \(\frac{48}{20}=\frac{12}{5}\) = 2.4
Question 17.
Find the common difference of an A.P. whose first term is 6 and 12th term is 72.
Answer:
Given a = 6 and T12 = a + 11d = 72
6 + 11d = 72,
11d = 72 – 6 = 66 ⇒ d = 6.
Question 18.
The sum of two consecutive numbers is 23. Find them.
Answer:
Let the 2 consecutive numbers be x and x + 1
Given sum = 23
x + x + 1 = 23
2x = 22 ⇒ x = 11
∴ The 2 consecutive numbers are 11 & 12.
Question 19.
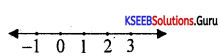
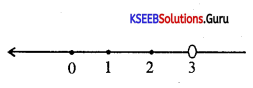
Solve 2x + 6 < 0; x ∈ Z inequalities in one variable and represent the solution on the number line.
Answer:
Answer:
Given 2x + 6 < 0
∴ 2x ≤ -6 ⇒ x ≤ -3

Solution set is [-∞, -3].
![]()
Question 20.
Find the interest on Rs. 1,500 at 4% pa. for 145 days.
Answer:
S.I.= 1500 × \(\frac{145}{365} \times \frac{4}{100}=\frac{870000}{36500}\) =23.836.
Question 21.
If x = a secθ; y = btanθ prove that \(\frac{x^{2}}{a^{2}}-\frac{y^{2}}{b^{2}}\) = 1
Answer:
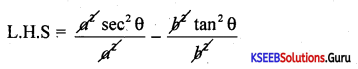
⇒ sec2 θ – tan2 θ = 1 = R.H.S
Question 22.
The weight of 6 men is 90 Kg, 70.5, 56 Kg, 45.5Kg, 85 Kg, and 78 Kg. Find average weight.
Answer:
X̄ = \(\frac{90+70.5+56+45.5+85+78}{6}=\frac{425}{6}\) = 70.83
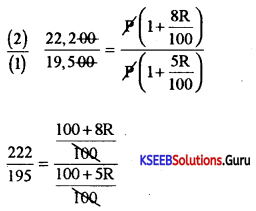
Question 23.
Karthik received a scholarship of ₹ 5,000 in 2011 and ₹ 8,000 in 2012. Find the percentage increase.
Answer:
Diff in the amount = 8000-5000 = 3000₹
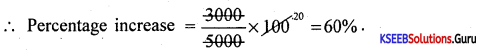
![]()
Question 24.
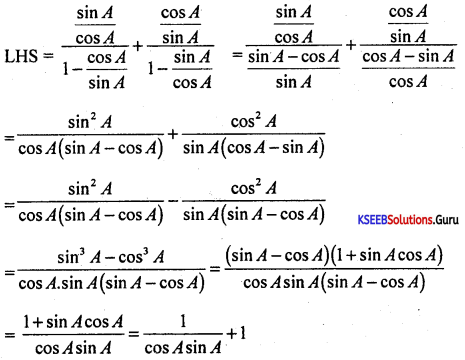
Prove that tan2 A(1 – sin2A) = sin2 A
Answer:
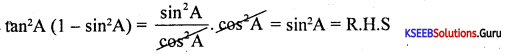
Question 25.
Find the area of the triangle whose vertices are A(3, 4); B(2, -1), and C(4, -6).
Answer:
Area of ∆ABC = \(\frac{1}{2}\)[x1(y2 – y3) + x2 (y3 – y1) + x3 (y1 – y2)]
= \(\frac{1}{2}\)[3 (-1 + 6) + 2 (-6 – 4)+4 (4 – (-1)].
A = \(\frac{1}{2}\)[3(5) + 2(-10) + 4(5)]
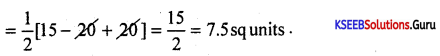
Part – C
III. Answer any TEN questions. (10 × 3 = 30)
Question 26.
If the product of two numbers is 216 and their L.C.M is 36. Find their H.C.F.
Answer:
Given L.C.M of 36 and Product = 216, H.C.F = ?
H.C.F = \(\frac{a \times b}{L . C . M}=\frac{216}{36}\) = 6
Question 27.
If A= {1, 2}; B = {2, 3}; C = {3, 4}. Find (A × B) ∩ (A × C).
Answer:
A × B = {1,2} × {2,3}{(1,2) (1, 3) (2,2) (2, 3)}
A × C = {1, 2} × {3, 4} – {(1,3) (1, 4) (2,3) (2,4)}
(A × B) ∩ (A × C) = {(1, 3) (2, 3)}.
Question 28.
If A = {2, 3, 4} write ail the proper subsets of ‘A’.
Answer:
Proper subsets of A
X = P(A) = {{Q} (2) (3) (4) (2, 3) (3, 4) (4, 2)}.
![]()
Question 29.
Prove that (xb-c)a . (xc-a)b . (xa-b)c = 1.
Answer:
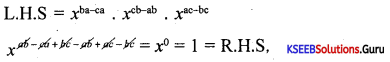
Question 30.
If the second term of the G.P is 6 and 5th term is 162. Then find the GP.
Answer:
T2 = ar = 6 ….(1), T5 = ar4 = 162 ….(2), G.P. = ?
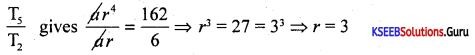
ar = 6 ⇒ 3a = 6 ⇒ a = 2
Terms of G.P are a, ar ar2, ar3
2, 2 × 3, 2 × 32, 2 × 33………….
2, 6, 18…………..
Question 31.
The sum of 6 times a number and 5 times the number is 55. Which is that number?
Answer:
Let the number be x
Given 6x + 5x = 55
11x = 55 ⇒ x = 5
∴ The number is 5.
Question 32.
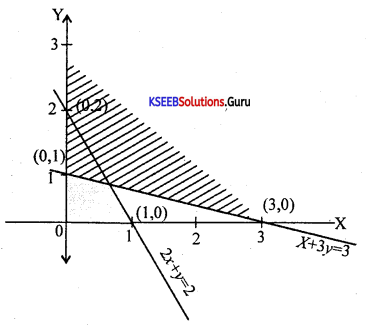
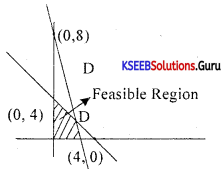
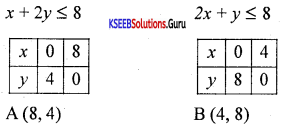
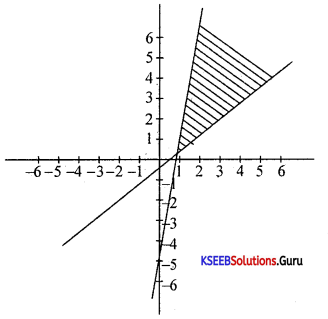
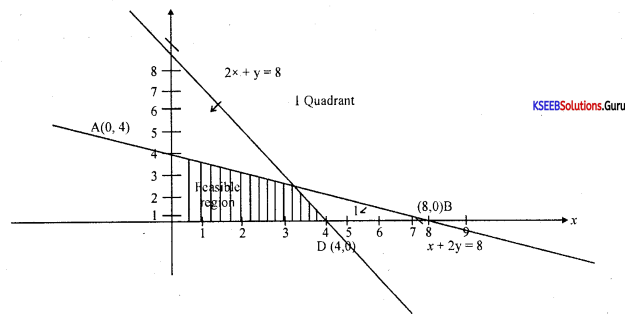
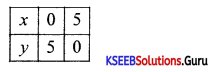
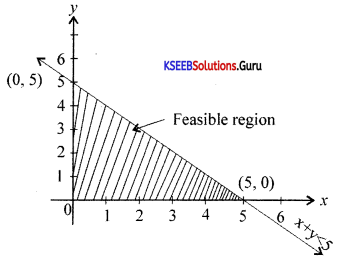
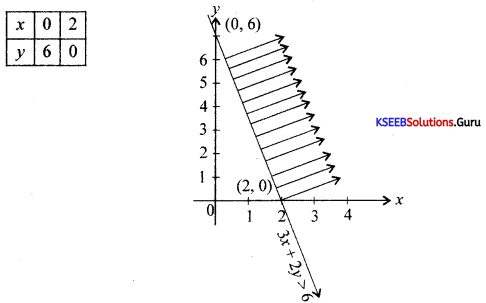
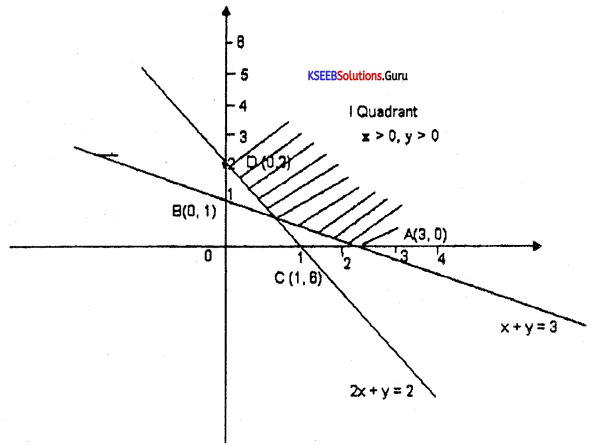
Solve graphically:
3x – 7 > 2(x – 6) and 6 – x > 11 – 2x; x∈R
Answer:
3x – 7 > 2x – 12
3x – 2x > -12 + 7
x > -5
6 – x > 11 – 2x
-x + 2x >11 – 6
x > 5
Question 33.
Find the present value of an annuity due of 8000 for 5 years at 5% p.a.
Answer:
P = \(\frac{a\left[(1+i)^{n}-1\right]}{i(1+i)^{n}}\)(1 + i)
P = \(\frac{8000\left[(1+0.05)^{5}-1\right]}{0.05(1+0.05)^{5}}\) × (1 + 0.05)
= \(\frac{8000\left[(1.05)^{5}-1\right](1.05)}{0.05 \times(1.05)^{5}}=\frac{8000[(1.2763-1)](1.05)}{0.05 \times 1.2763}\) = ₹ 36369.50
Question 34.
Calculate the arithmetic average mark from the following data.
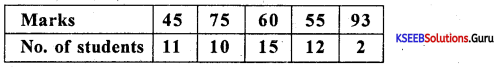
Answer:
X̄w = \(\frac{45 \times 11+75 \times 10+60 \times 15+55 \times 12+93 \times 2}{11+10+15+12+2}\)
= \(\frac{495+750+900+660+186}{50}=\frac{2991}{50}\) = 59.82 ≈ 60
Question 35.
In an election, the winning candidate got 4,800 votes which are 80% of the total votes. Calculate the total number of votes.
Answer:
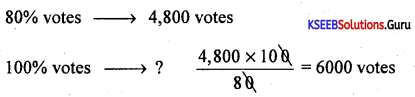
∴ Total number of votes = 6000
Question 36.
If tan θ = \(\frac{a}{b}\) show that \(\frac{a \sin \theta-b \cos \theta}{a \sin \theta+b \cos \theta}=\frac{a^{2}-b^{2}}{a^{2}+b^{2}}\)
Answer:
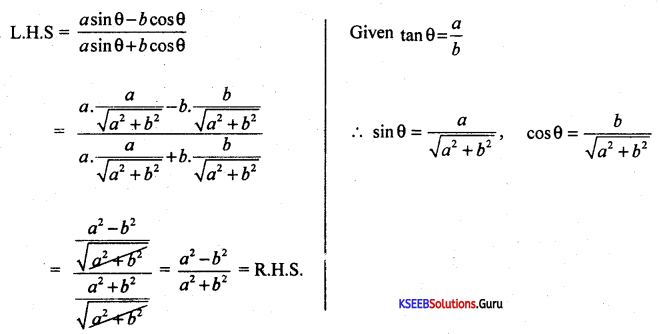
Question 37.
A point ‘P’ moves such that PA2 = 3PB2. If A = (5, 0) and B = (-5, 0). Find the equation of the Locus of ‘P’
Answer:
Let P(x, y) be the point on the locus
Given PA2 = 3PB2 and A = (5, 0), B = (-5, 0)
(x – 5)2 + (y – 0)2 = 3[(x + 5)2 + (y – 0)2]
x2 + 25- 10x + y2 = 3[x2 + 25 + 10x + y2]
3x2 + 75 + 30x + 3y2 = x2 + y2 – 10x + 25
2x2 + 2y2 + 40x + 50 = 0 is the required equation.
![]()
Question 38.
Find the point of intersection of the lines 3x = 2y – 5 = 0 and 4x – y – 3 = 0.
Answer:
3x + 2y – 5 = 0
4x – y – 3 = 0 → Multiplying by 2

11x – 11 = 0 ⇒ x = \(\frac{11}{11}\) = 1
y = 4x – 3 = 4 – 3 = 1.
∴ Point of intersection is (1,1).
Part – D
IV. Answer any SIX questions. (6 × 5 = 30)
Question 39.
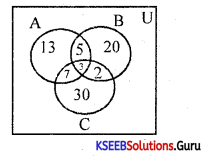
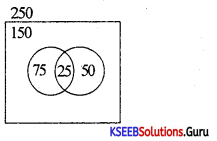
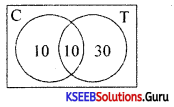
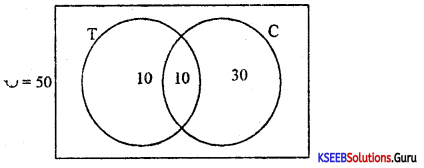
Out of 50 people, 20 people drink tea, 10 take both tea and coffee. How many take at least one of the two drinks.
Answer:
Given n(T) = 20, n(T∪C) = 50, n(T∩C) = 10, n(C) = ?
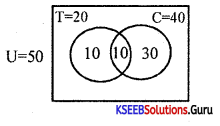
n(T∪C) = n(T) + n(C) – n(T∩C)
50 = 20 + n(C)-10
n(C) = 40
∴ No. of people taking atleast one of the two drinks = 10 + 10 + 30 = 50.
Question 40.
If log\(\left(\frac{a-b}{4}\right)\) = log\(\sqrt{a}\) + log\(\sqrt{b}\) show that (a + b)2 = 20ab.
Answer:
Given log\(\left(\frac{a-b}{4}\right)\) = log\(\sqrt{a}\) + log\(\sqrt{b}\)
log\(\left(\frac{a-b}{4}\right)\) = log\(\sqrt{ab}\)
\(\frac{a-b}{4}=\sqrt{a b}\) S.B.S
(a – b)2 = 16ab
a2 + b2 – 2ab = 16ab (Add 4ab both sides)
a2 + b2 + 2ab = 20ab,
(a + b)2 = 20ab.
Question 41.
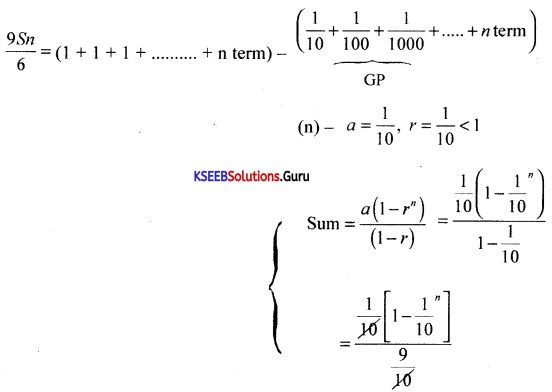
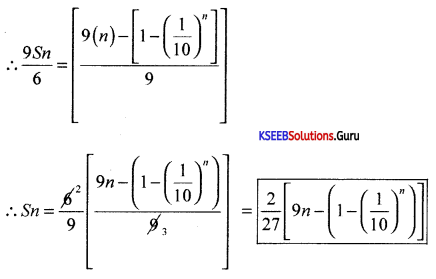
Find the sum of n terms of GP. 5 + 55 + 555 +……………
Answer:
Let S = 5 + 55 + 555 +…………… to n terms
\(\frac{\mathrm{S}}{5}\) = 1+ 11 + 111+………..to n terms
\(\frac{9 \mathrm{~S}}{5}\) = 9 + 99 + 999 +…………… to n terms
=(10 – 1) + (100 – 1) + (1000 – 1) +……….. to n terms
= (10 + 100 + 1000 +………… to n terms) – (1 + 1 + 1………. to n ternis)
= \(\frac{10\left(10^{n}-1\right)}{9}\) – 1 × n
S = \(\frac{5}{9}\left[\frac{10\left(10^{n}-1\right)}{9}-n\right]\)
Question 42.
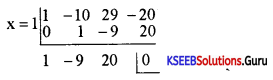
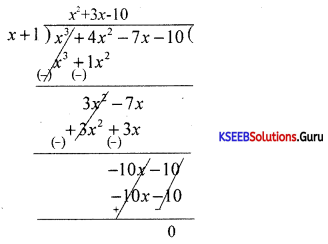
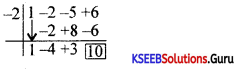
Find the integral root between -3 and 3 by inspection and then using synthetic division, solve the equation x3 – 2x2 – 5x + 6.
Answer:
Let f(x) = x3 – 2x2 – 5x + 6,
f(1)= 1 – 2 – 5 + 1 = 0
∴ x = +1 is a root of the given equation. Let us remove this root by synthetic division.
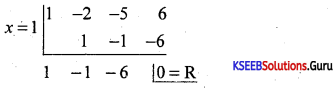
∴ The resulting equation is x2 – x – 6 = 0 is the quotient and remainder is 0.
x2 – x – 6 = 0
(x – 3) (x + 2) = 0 ⇒ x = -2 or 3
Thus x = 1, -2, 3 are the roots of the given equation.
Question 43.
At what time a sum of ₹1,200 will earn ₹573 as compound interest at the rate of 5% p.a. if the interest is added annually?
Answer:
Given P=1200, C.I = 573, A = 1200 + 573 = 1773
i = \(\frac{5}{100}\) = 0.05, n = ?
A = P(1 + i)n
1773 = 1200(1 +0.05)n
\(\frac{1773}{1200}\)1.4775 = (1.05)n
(1.05)n = (1.05)8 ⇒ n = 8.
![]()
Question 44.
Preritha wants to buy a house after 5years when it is expected to cost 50 lakhs. How much should she save annually if her savings earn a compound interest of 12 percent?
Answer:
Given F = 50,00,000, n = 5, i = 0.12, a = ?
F = \(\frac{a\left[(1+i)^{n}-1\right.}{i}\) ⇒ 50,00,000 = \(\frac{a\left[(1+0.12)^{5}-1\right]}{0.12}\)
50,00,000 = 6.3528a ⇒ a = \(\frac{50,00,000}{6.3528}\) = ₹ 787054.5
Question 45.
If θ = \(\frac{5}{2}\) and θ is acute then prove that \(\frac{3 \cos \theta+2 \sin \theta}{3 \cos \theta-4 \sin \theta}=\frac{19}{7}\)
Answer:
Given cotθ = \(\frac{5}{2}=\frac{a d j}{o p p}\)
∴ Hyp = \(\sqrt{5^{2}+2^{2}}=\sqrt{29}\)
cosθ = \(\frac{5}{\sqrt{29}}\), sinθ = \(\frac{2}{\sqrt{29}}\)
L.H.S = \(\frac{3 \cos \theta+2 \sin \theta}{3 \cos \theta-4 \sin \theta}\)
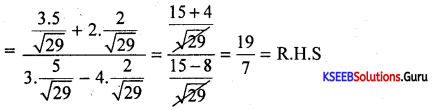
Question 46.
The price of a pair of trousers was decreased by 22% to 390. Whast was the original price of the trousers?
Answer:
Let the price of trouser = x
It was decreased by 22% to ₹ 390
∴ x – \(\frac{22 x}{100}\) = 390
\(\frac{100 x-22 x}{100}\) = 390 ⇒ 78x = 390 × 100
x = \(\frac{39,000}{78}\) =500
∴ Original price of the trouser = ₹500.
Question 47.
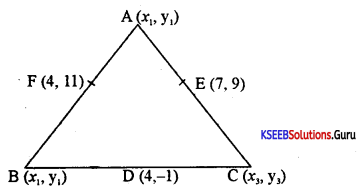
Find the coordinates of the vertices of the triangle. Given the midpoints of the sides as (4, -1); (7, 9) & (4, 11).
Answer:
Let A, B, C be the vertices of the A,e, and D, E, and F be the mid-points of the sides BC, CA, and AB respectively.
D = Midpoint of BC
(4, -1) = \(\left(\frac{x_{2}+x_{3}}{2}, \frac{y_{2}+y_{3}}{2}\right)\)
⇒ x2 + x3 = 8, y2 + y3 = 2 …………….(1)
E = Mid point of CA
(7, 9) = \(\left(\frac{x_{3}+x_{1}}{2}, \frac{y_{3}+y_{1}}{2}\right)\)
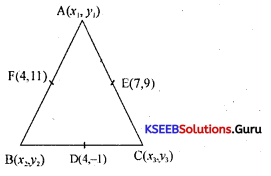
⇒ x3 + x1 = 14, y3 + y1 = 18 ……………..(2)
F = Mid point of AB
(4,11) = \(\left(\frac{x_{1}+x_{2}}{2}, \frac{y_{1}+y_{2}}{2}\right)\)
⇒ x1 + x2 = 8, y1 + y2 = 22 ………………..(3)
Solving equations 1,2 and 3 we get
x1 = 7, x2 = 1, x3 = 7
y1 =21, y2 = 1, y3 = -3
Thus A = (7, 21), B = (1, 1) and C = (7, -3).
![]()
Question 48.
Find ‘a’ so that the lines x – 6y + a = 0; 2x + 3y + 4 = 0 and x + 4y + 1 = 0 concurrent.
Answer:
Given 2x + 3y + 4 = 0 ………….. (1)
x + 4y + 1 = 0 …………. (2) × 2
x – 6y + a = 0 …………. (3)
Solving 1 and 2 we get
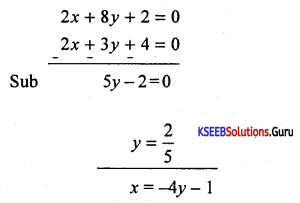
= \(\frac{-8}{5}\) – 1 = \(\frac{-8-5}{5}=\frac{-13}{5}\)
Put x = \(\frac{-13}{5}\) and y = \(\frac{2}{5}\) in equation 3
We get x – 6y + a = 0
a = 6y – x
a = 6.\(\frac{2}{5}-\left(\frac{-13}{5}\right)\)
= \(\frac{12}{5}+\frac{13}{5}=\frac{25}{5}\) = 5
∴ a = 5
Part – E
V. Answer any ONE question. (1 × 10 = 10)
Question 49.
(a) If U = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9} A = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} B = {3, 4, 5, 6, 7}
Show that (A ∩ B)’ =A’∪B’
Answer:
A ∩ B = {3,4, 5}
(A ∩ B)’ = {1,2, 6, 7, 8,9} ………….(1)
A’∪B’ = {6,7, 8,9} ∪ {1,2, 8, 9}
= {1,2, 6,7, 8, 9} ………………(2)
From 1 and 2 we get A’∪B’ = (A ∩ B)’.
(b) Insert G. Means [Geometric Mean] between \(\frac{1}{4}\) and \(\frac{1}{64}\).
Answer:
G.M = \(\sqrt{\frac{1}{4} \times \frac{1}{64}}=\sqrt{\frac{1}{4^{4}}}=\frac{1}{4^{2}}=\frac{1}{16}\)
(c) If ax = b; & by = c; cz = a. Show that xyz = 1.
Answer:
Consider ax = b’
(cz)x = b
czx = b
(by)zx = b’ ⇒ & bxyz = b’⇒ xyz = 1.
![]()
Question 50.
(a) Find the equation of the locus of the point which moves such that its distance from 3x – 4y + 1 = 0 is equal to its distance from (1, -1).
Answer:
Let A = (1, -1) and P(x, y) be any point on the locus, then PA = distance from the line 3x – 4y +1 = 0
\(\sqrt{(x-1)^{2}+(y+1)^{2}}=\left|\frac{3 x-4 y+1}{\sqrt{9^{2}+16^{2}}}\right|\) S.B.S
(x – 1)2 + (y + 1)2 = \(\frac{(3 x-4 y+1)^{2}}{25}\)
25(x2 – 2x + 1 + y2 + 2y + 1) = 9x2 + 16y2 + 1 – 24xy – 8y + 6x
16x2 + 24xy + 9y – 56x + 58y + 49 =0 is the required equation of the locus.
(b) A manufacturer produced and sells balloons at 8 per unit. His fixed cost is ₹6,500 and the variable cost per balloon is ₹3.50. Calculate
(i) Revenue Function (ii) Cost Function
(iii) Profi Function (iv) Break even point.
Answer:
i.e. (i) R(x) = 8x
(ii) C(x) = 3.5x + 6500
(iii) P(x) = 4.5x – 6500
i.e.,P(x) = 6500 = 0
(iv) At BEP P(A) = 0
4.5x – 6500 = 0
4.5x = 6500
x = 144.4 units
(c) What is the present value of an income of 3000 to be received forever if the interest rate if 14% p.a.
Answer:
P∞ = \(\) = ₹21428.5