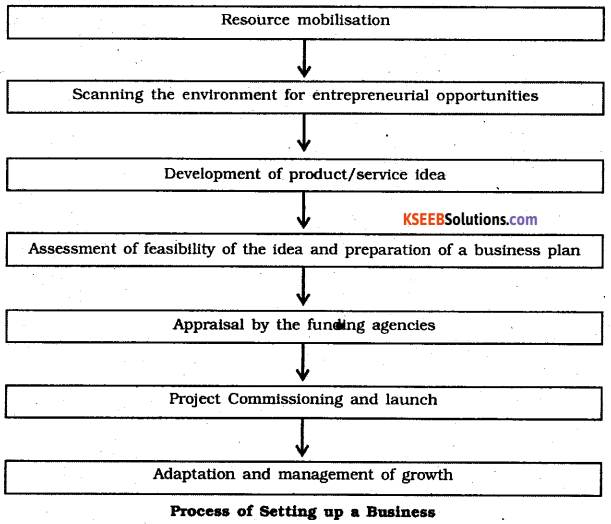
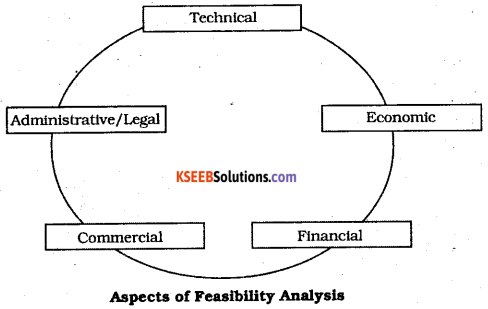
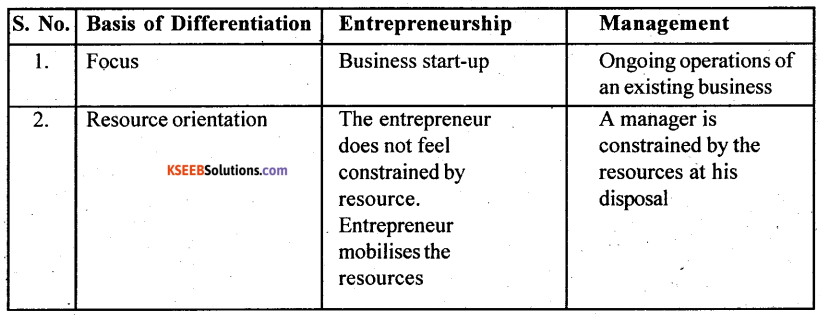
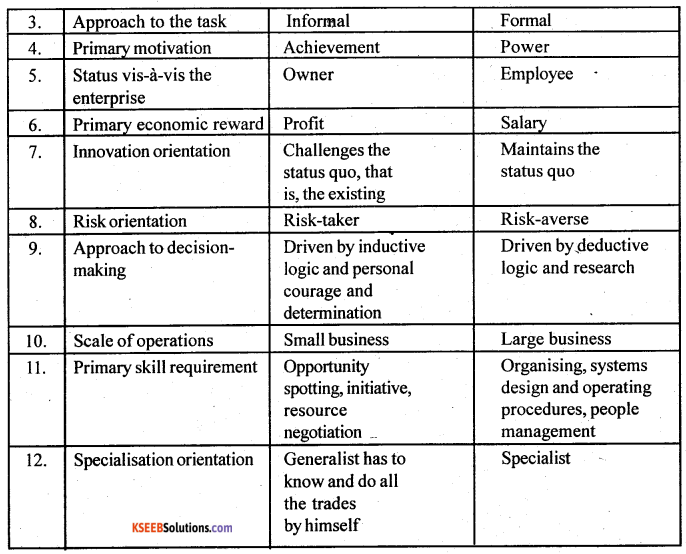
You can Download Chapter 18 Badakannu Pritisida Santa Questions and Answers Pdf, Notes, Summary, 2nd PUC Kannada Textbook Answers, Karnataka State Board Solutions help you to revise complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Karnataka 2nd PUC Kannada Textbook Answers Sahitya Sampada Chapter 18 Badakannu Pritisida Santa
Badakannu Pritisida Santa Questions and Answers, Notes, Summary