You can Download Chapter 6 Staffing Questions and Answers, Notes, 2nd PUC Business Studies Question Bank with Answers Karnataka State Board Solutions help you to revise complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Karnataka 2nd PUC Business Studies Question Bank Chapter 6 Staffing
2nd PUC Business Studies Staffing Text Book Exercises
2nd PUC Business Studies Staffing Short Answer Type Questions With Answers
Question 1.
Briefly enumerate the important sources of recruitment.
Answer:
The various sources of recruitment are classified into two broad categories:
Internal sources:
- Promotions: It implies upgrading of an employee to a higher position carrying higher status, higher responsibility and higher salary. It is a vertical movement of an employee within the organization.
- Transfers: It means lateral movement of employee in the same grade, from one job to another, without any change in his status, responsibility and’salary.
Question 2.
What is meant by recruitment? How is it different from selection?
Answer:
Recruitment refers to the process of finding possible candidates for a job. It can be defined as the process of motivating and encouraging people to come and apply for a job in an organisation. Selection is the process of identifying and choosing the best person out of a number of prospective candidates for a job.
If recruitment is positive, selection is negative. Recruitment helps in creating a pool of prospective workforce whereas selection helps in finding the best out of them.
Question 3.
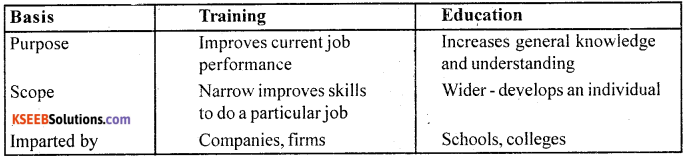
Define training. How is it different from education?
Answer:
Training is the systematic development of knowledge, skills and attitudes required by an individual to perform adequately a given task or job.
Question 4.
Distinguish between training and development.
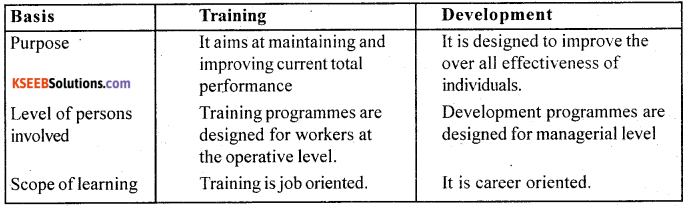
Answer:
Difference between training and development
Question 5.
Why arc internal sources of recruitment considered to be more economical?
Answer:
Filling of jobs internally is cheaper as compared to getting candidates from external sources because only transfer or promotion has to be done. It does not involve the long process of staffing or selection which increases the cost in the form of more time, money and efforts in recruiting.
![]()
Question 6.
What is the importance of staffing function in today’s environment?
Answer:
Staffing is considered to be a key function because it deals with human resource, which is regarded as one of the most valuable resource of any organisation. Once an organisation could place the right man at the right Job, it is easy to plan, organise, coordinate, direct and control the human activities to get the desired results.
It helps in discovering and obtaining competent personnel, ensures the continuous survival and growth, helps to ensure optimum utilisation of resources and improves Job satisfaction as well.
2nd PUC Business Studies Staffing Long Answer Type Questions With Answers
Question 1.
Define the staffing process and the various steps involved in it.
Answer:
Staffing process of the management is concerned with acquiring, developing, employing, remuneration and retaining people or we can say it is the timely fulfilment of the manpower requirements within an organisation.
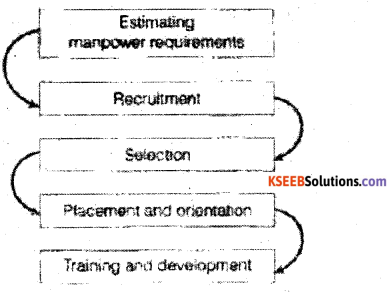
The following steps are involved in the staffing process
1. Estimating the Manpower requirements : The first step in the staffing process is determining the present manpower inventory and assessing the present and future manpower requirements of the organisation keeping in mind the production schedule, demand etc.
2. Recruitment: Recruitment may be defined as the process of searching for prospective employees and stimulating them to apply for jobs in the organisation. For this various sources can be used like transfer, promotion, advertising, job consultants etc
3. Selection: Selection of the prospective is the process of choosing from among the pool job candidates developed at the stage of recruitment. It Involves a host of tests and interviews
4. Placement and Orientation: Orientation is introducing the selected employee to other employees and familiarising them with the rules and policies of the organisation. They are taken around the work place and given the charge of the job for which they have been selected. Placement refers to the employee occupying the position or post for which they have been selected.5.
5. Training and Development: All organisations have either in-house training centres or have forged alliances with training and educational institutes to ensure continued learning of their staff. By offering the opportunities for career advancement to their members, organisations are not only able to attract but also retain their talented staff.
6. Performance Appraisal: After the employees have undergone a period of training and they have been on the job for some time, there is a need to evaluate their performance. The employee is expected to know what the standards are and the superior is to provide the employee feedback on his/her performance. The performance appraisal process therefore, will include defining the job. appraising performance and providing feedback.
7. Promotion and Career Planning: It is very important for all organisations to address career related issues and promotional avenues for their employees. They must provide opportunities to every one to show their potential and in return promotions can be provided.
8. Compensation: All organisations need to establish wage and salary plans for their employees. There are various ways to prepare different pay plans depending on the worth of the job. Compensation therefore, refers to all forms of pay or rewards going to employees.
Question 2.
Explain the procedure for selection of employees.
Answer:
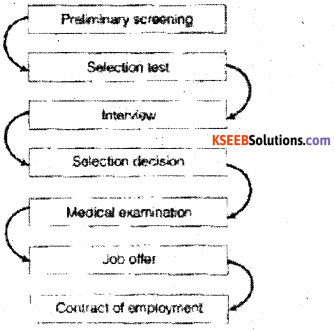
Selection is the process of differentiating between applicants in order to identify and select the best and eliminating the rest. The follow ing steps are followed in selection process:
- Preliminary Screening: After receiving the application from candidates , the same must be examined and decided to be considered and followed up. Screening includes checking the contents of the applications and to prepare a list of eligible candidates who are to be evaluated further.
- Selection Tests: After screening the applications, eligible candidates are asked to appear for selection tests. These tests are made to measure the skill and abilities of the candidates in the terms of the requirement of the job. The following tests are conducted:
(a) Intelligence tests: These tests are used to judge, the mental capacity of the applicant.These tests evaluate the ability of an individual to understand instructions and make decisions.
(b) Trade or proficiency tests: Trade tests are designed to measure the skills already acquired by the individuals. They measure the level of knowledge and proficiency in the area of profession or technical training.
(c) Personality tests: These tests probe for the overall qualities of a person as a whole. They provide clues to a person’s emotional reactions, maturity level etc.
(d) Interest tests: It identifies the areas in which a candidate has special concern, fascination, involvement etc. These test suggest the nature of job liked by a candidate which may bring him job satisfaction.
- Interview: It s considered as a method of personal appraisal , through face to face conversation and observation. Some of the methods are:
(a) Direct Interview: Under this method, direct questions are asked to the applicant, to identify his skills, character, area of interest, attitudes etc.
(b) Indirect interview: Under this method, the applicant is asked to express his opinion on any topic he likes and the interviewer listens to the views of the applicant without any intervention. This helps o assess the personality of the applicant.
(c) Patterned or structural interview: In this type of interview, the interviewer is looking for information in a particular area of interest in the organization. A number of standard questions are framed which focuses on experience, skills and personality which is to be answered by the applicant.
(d) Stress Interview: In this interview, the interviewer will intentionally try to upset the applicant, to see his reactions under pressure. This type of interview is common in high stress jobs.
(e) Board or Panel interview: In this interview a group of persons called Board or Panel asks the applicant, questions in different subjects. Immediately after the interview, they meet and discuss and evaluate the performance of the applicant on the basis of answers given by him.
- Reference and Background checks: The information is to be obtained and verified from the heads of educational institutions where the candidates have studied or from the persons names are given by the candidates as reference or from their previous employers.
- Selection Decision: After a candidate has cleared all the hurdles in the selection procedure the employer may take a decision of selection after consulting the concerned manager who is responsible for the performance of the new employee.
- Medical Examination: Candidates finally selected for the job are asked to undergo medical examination to see whether they are physically fit for the job.
- Job Offer: Candidates finally selected are offered to join the organization for which a formal appointment order is issued by the organisation which contains the nature of the job, pay scale and other terms and conditions.
- Contract of Employment: If the selected candidate decides to join the organization, he has to report to the concerned authority and formally join the organization by giving his consent in writing.
![]()
Question 3.
What are the advantages of training to the individual and to the organisation?
Answer:
Training helps both the organisation and the individual.
Benefits to the Organisation
- Training is a systematic learning which reduces the wastage of efforts and money.
- Enhances employee productivity
- Training helps a manager to handle an emergency situation.
- Training motivates workers and thus reduces absenteeism.
- Helps in adjusting to the changing environment (technological).
Benefits to the Employee
- Better career opportunities due to improved skills and knowledge.
- Earnings can be increased due to improved performance.
- Trained workers can handle machines more efficiently.
- Employees always remain motivated and satisfied.
Question 4.
The staffing function is performed by every manager and not necessarily by a separate department. Explain.
Answer:
Staffing is a function which all managers need to perform. It is the responsibility of all managers to directly deal with and select people to work for the organisation. When the manager performs the staffing function his role is slightly limited. In small organisations, managers may perform all duties related to employees salaries, welfare and working conditions but as organisations grow and number of persons employed increases, a separate department called the Human Resource Department is formed which has specialists in managing people.
2nd PUC Business Studies Staffing Application Type
Question 1.
The workers of a factory are unable to work on new machines and always demand for help of supervisor. The supervisor is overburdened with their frequent calls. Suggest the remedy.
Answer:
Since the workers of a factory are unable to work on new machines, training should be imparted in this case as it is the process of learning new skills and application of knowledge. Whenever the new machines are installed in business, it is the duty of management to provide training in order to achieve the desired goal.
As per the case it is mentioned that supervisors are overburdened with the calls for help. Supervisor have other duties also and if he is involved in imparting training, then his work suffers. Thus, the management should provide the apprenticeship training programme. Under this, trainee is put under the guidance of a master worker.
These are designed to acquire a higher level of skill. The master worker performs the job and the trainee observes him performing. When the learner learns all the skills, then slowly they can start taking up the job step by step and get full charge on job after some time.
![]()
Question 2.
The workers of a factory remain idle because of lack of knowledge of hi- tech machines. Frequent visit of engineer is made which causes high overhead charges. How can this problem be removed?
Answer:
The workers of a factory are not performing because of lack of knowdedge of hi- tech machines. Technological change arises the need for employees to upgrade or alter their skills. Thus, in this case training should be provided by the engineer to one of their supervisor so that they will guide the other workers and able to enhance their productivity.
Frequent visit of engineer results in high overhead charges When training is imparted to the supervisor, then they can handle the situation in the absence of engineer or in case of emergency.
Question 3.
The quality of production is not as per standards. On investigation, it was observed that most of the workers were not fully aware of the proper operation of the machinery. What could be the way to improve the accuracy?
Answer:
Workers should be provided off the job training methods where they can be taught how to maintain accuracy related to the proper operations of the machinery. Training makes the employee more efficient and results in high productivity.
Question 4.
An organisation provides security services. It requires such candidates who are reliable and don’t leak out the secrets of their clients. What step should be incorporated in selection process?
Answer:
‘Reference check’ – this step should be done very carefully. Previous employer can be contacted to check for his moral behaviour or conduct, sincerity etc. The new candidates should be made to sign a contract of employment which clearly states that strict action will be taken If found guilty
Question 5.
A company is manufacturing paper plates and bowls. It produces 1,00,000 plates and bowls each day. Due to local festival, it got an urgent order of extra 50,000 plates and bowls. Advise how the company will fulfill its order and which method of recruitment would you suggest?
Answer:
There are two sources; internal and external. If internal source is used then existing workforce can be asked to work overtime. If external source is used then either of the following has to be done:
- Existing employees can be asked to recommend names of their friends and relatives.
- Recruitment through labour contractors can also be done.
2nd PUC Business Studies Staffing Case Problems
(i) A company X limited is setting up a new plant in India for manufacturing auto compo-nents. India is a highly competitive and cost effective production base in this sector. Many reputed car manufacturers source their auto components from here. X limited is planning to capture about 40% of the market share in India and also export to the tune of at least $ 5 million in about 2 years of its planned operations. To achieve these targets it requires a highly trained and motivated work force. You have been retained by the coippany to advise it in this matter. While giving answer keep in mind the sector, the company is operating.
Question 1.
Outline the process of staffing the company should follow.
Answer:
X Ltd is planning to set up new plant in India for manufacturing auto components. The prime concern of the company is to hire the manpower who are highly trained and motivated. In order to achieve the targets, the company should follow the staffing process in this manner.
Question 2.
Which sources of recruitment the company should rely upon? Give reasons for your recommendation,
Answer:
The company is establishing a new unit in India, Thus, they should rely on external sources of recruitment. They should adopt this source and through employment exchange and placement agencies, labour contractors they will able to get the good staff for the company. This recommendation is fruitful because through these sources, the company will get a wide choice of candidates. They can get qualified personnel and bring new blood in the organisation who are highly competitive, who will work harder to show better performance.
![]()
Question 3.
Outline the process of selection the company should follow with reasons.
Answer:
Through recruitment process the organisation will receive a large number of applications. In order to select the most suitable candidates to perform the job, selection process is to be considered. Following steps are to be taken ‘
Company should follow these steps in series. As the
- first step, preliminary screening helps the manager to select from among those candidates whose applications are shortlisted.
- Second step is selection test: It is to be conducted to check the practical knowledge of the candidates.
- Third step: interview: This is to be taken for those candidates who have cleared the test. A panel of experts is set to identify the best among hundreds.
- Fourth step is selection decision. The candidates who pass the test, interview included In selection list are critically examined whether they are best or not.
- Fifth step is examining their medical fitness and if they are efficient or not.
- Sixth step is to offer the job, providing them a letter of appointment in which terms and conditions are mentioned.
- The final step is the contract of employment when the candidate accepts the job offer and they sign the contract of employment, the employer and candidate exchange certain documents.
Question 4.
Which methods of training and development should the Company initiate? Explain giving reasons.
Answer:
The company can use ’On the job’ and ‘Off the job’ training methods. The merits or benefits of ‘On the job’ are
- It is a practical method.
- The trainee can contribute towards the real/actua! work, (iii) Separate arrangements need not be done.
If the ‘Off the job’ methods are used, then the benefits derived are the following :
- Vestibule training helps in avoiding modern and expensive equipment from being damaged.
- Conference helps to develop conceptual knowledge reduce, resistance to change etc.
(ii) A major insurance company handled all recruiting screening and training processes for data entry/customer service representatives. Their competitor was attracting most of the qualified, potential employees in their market. Recruiting was made even more difficult by the strong economy and the ‘job seeker’s market: This resulted in the client having to choose from candidates who had the ‘soft’ skills needed for the job, but lacked the proper ‘hard’ skills and training.
Question 1.
As an HR manager, what problems do you see in the company?
Answer:
The human resource manager may face the following problems
- Lack of trained workforce
- Lack of sufficient personnel to provide customer services.
- Inefficient maintenance of data.
Question 2.
How do you think it can be resolved?
Answer:
Following steps can be taken to resolve these problems
- Proper training of the personnel.
- Provision of incentive based schemes.
- Proper data base should be maintained by the company in order to provide efficient services.
(iii) A public transport corporation has hired 1,000 buses for the different routes for the
passengers of metropolitan city. Most of the 3,000 crewmen (drivers, conduct, helpers etc) of these buses have been found to be wanting in satisfactorily dealing with public and daily commuters. They seem to be little interested in the job and the job seem to have lost all meaning to them.
Question 1.
As manager of the public transport company what measures do you suggest to improve the working of crewman in question?
Answer:
The following measures can be taken to improve the working of crewmen.
- Along with wages/salary, various other facilities should be provided to them like education for their children, insurance etc.
- Working hours should be between 7 to 8 hours only per day
- Rest periods should be provided.
Question 2.
Is it possible to modify their behaviour by planning a suitable type of training? Suggest one.
Answer:
Yes, it is possible to modify their behaviour by planning ‘coaching’ training programme as in this programme, a superior guides and instructs the trainees as a coach. He suggests the changes required in behaviour and performance of the employees. Coach gives due importance to the objective of individuals and objectives of organisation. Thus, effective coaching motivates the employees to perform to their best ability.
![]()
(iv) Ms Jayshree recently completed her post graduate diploma in human resource management. A few months from now a large steel manufacturing.company appointed her as its human resource manager. As of now, the company employs 800 persons and has an expansion plan in hand which may require another 200 persons for various types of additional requirements. Ms Jayshree has been given complete charge of the company’s human resource department.
Question 1.
Point out what functions is she supposed to perform?
Answer:
Ms Jayshree as HR manager is required to perform the following functions
- Recruitment
- Prepare job description
- Preparing compensation and incentive plans
- Arranging training programmes
- Making welfare schemes for employees
- Handling grievances of employees
- Handling labour dispute
Question 2.
What problems do you foresee in her job?
Answer:
She may face the following problems.
- Properly qualified candidates may not be available.
- Demand for wages may go higher. ‘
- After providing training, the workers may leave the organisation.
- Trade unions may bring unreasonable demands.
Question 3.
What steps is she going to take to perform her job efficiently?
Answer:
Following steps can be taken by her to perform her job efficiently
- She should make use of all the possible sources of recruitment.
- She should frequently consult the experts and also observe the policies followed by competitors to recruit and retain the workforce.
- Maintaining cordial relationship with trade unions and encouraging them to act as one big family.
Question 4.
How significant is her rote in the organisation?
Answer:
Her role n very significant in the organisation. She is a human resources manager and concerned with timely procurement of competent manpower and ensuring its effective and efficient utilisation so as to survive along with the three main objectives; organisational, individual and societal.
2nd PUC Business Studies Staffing Additional Questions
2nd PUC Business Studies Staffing One Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What is staffing?
Answer:
Staffing is the process through which competent employees are selected, trained, developed, rewarded and integrated towards the achievement of business goals.
Question 2.
What is manpower planning?
Answer:
It refers to the process of estimating the manpower requirement of an organization.
Question 3.
What do you mean by recruitment?
Answer:
Recruitment is the process of searching candidates for employment.
Question 4.
What is selection?
Answer:
It is procedure of matching organizational requirement with the skills & qualification of the people.
Question 5.
What do you mean by placement?
Answer:
In urban area a number of private organizations have started functioning as employment exchanges. These agencies are called as placement agencies.
![]()
Question 6.
Give the meaning of orientation.
Answer:
It means introducing the selected employee to the other employees and familiarizing him with the rules & regulation of the organization
Question 7.
What is training?
Answer:
Training is the organized procedure in which people learn knowledge & skill for definite purpose.
Question 8.
Give the meaning of development.
Answer:
It refers to the process of not only building up the skills and abilities for a specific purpose but to undertake more difficult & challenging tasks.
Question 9.
Give the meaning of performance appraisal.
Answer:
It is the systematic evolution of the individual with respect to his performance on the job
Question 10.
What is promotion?
Answer:
It is upward movement of an employee from one job to the higher one within the organization. It Increases salary, status & responsibilities.
Question 11.
What is the purpose of preliminary screening?
Answer:
The purpose of screening is to prepare a list of eligible candidates who are to be evaluated further.
Question 12.
Name any one type of selection test
Answer:
Aptitude test
Question 13.
What is the purpose of conducting stress interview.
Answer:
In this interview, the interviewer will intentionally try to upset the applicant, to see his reaction under pressure.
Question 14.
Give the meaning of on the job training.
Answer:
On the job the training is a method, where workers learn by doing the work. Workers work under the guidance & supervision of supervision or certain trained employees.
Question 15.
Give the meaning of off the job training.
Answer:
Off the job training method are methods are those in which training is provided away from the actual working condition.
![]()
Question 16.
State any one method of on the Job training.
Answer:
Job rotation
Question 17.
State any one method of off the job training.
Answer:
Class Room Lecture.
Question 18.
State any’one importance of staffing.
Answer:
Higher Job satisfaction
Question 19.
State any one internal source of recruitment.
Answer:
Internal Transfers
Question 20.
Mention any one external source of recruitment.
Answer:
Direct Recruitment
Question 21.
State any one importance of training.
Answer:
Training improves in employees performances both in quality & quantity
Question 22.
State any one method of training.
Answer:
On the job training & off the job training
Question 23.
What is job rotation.
Answer:
It is the method of training which serves the purpose of employee’s development through provision of diversified training. Here, an employee has to rotate from one job to another, and from one section to another.
Question 24.
Give the meaning of aptitude test.
Answer:
Aptitude means the potential which an individual has for learning new skills.
Question 25.
Define training.
Answer:
Training is the process which is done to increase the knowledge and skills of an employee to perform the present job accurately.
![]()
2nd PUC Business Studies Staffing Two Marks Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Define Staffing
Answer:
“Staffing is a function which is concerned with the placement, growth & development of all those members of the organization, whose function is to get the things done through others.
Question 2.
State the two activities of staffing.
Answer:
Training & Development, Human Resource Planning
Question 3.
State any two steps in staffing.
Answer:
Man Power Planning & Recruitment.
Question 4.
What is manpower planning?
Answer:
It refers to the process of estimating the man power requirement of an organization.
Question 5.
What do you mean by recruitment?
Answer:
Recruitment is the process of searching candidates for employment. And encouraging them to for jobs in an organization
Question 6.
Give the meaning of selection
Answer:
It is procedure of matching organizational requirement with the skills & qualification of the people. It is the process of selecting the best & eliminating the rest.
Question 7.
What is placement?
Answer:
It means assigning the jobs to the selected candidate. Thus it may include initial assignment of job to new employee & on transfer promotion or demotion of the employee.
Question 8.
Give the meaning of orientation
Answer:
It means introducing the selected employee to the other employees and familiarizing him with the rules & regulation of the organization
Question 9.
What is training & development?
Answer:
Training: Training is the organized procedure in which people learn knowledge & skill for definite purpose.
Development: It refers to the process of not only building up the skills and abilities for a specific purpose but to undertake more difficult & challenging tasks
Question 10.
What is performance appraisal?
Answer:
It is the systematic evolution of the individual with respect to his performance on the job.
![]()
Question 11.
What is promotion?
Answer:
It is upward movement of an employee from one job to the higher one within the organization. It Increases salary, status & responsibilities.
Question 12.
Define recruitment.
Answer: According to werther and Davis: It is the process of finding & attracting capable applicants for employment. The process begins when new recruits are sought and ends when their applications are submitted.
Question 13.
State any two internal sources of recruitment
Answer:
Promotions: It is upward movement of an employee from one job to the higher one within the organization. It Increases salary, status & responsibilities.
Transfer: It means lateral movement of employee in the same grade from one job to another without any changes in his status.
Question 14.
What is transfer?
Answer:
It means lateral movement of employee in the same grade
Question 15.
State any two external sources of recruitment
Answer:
Casual Callers: They are also called as unsolicited application. Here many qualified persons apply for employment to the reputed companies on their own initiative.
Advertisement: Employment advertisement refers to the details about the company, job specification given in the news paper, journals, bulletins etc. which brings response from the . suitable candidates.
Question 16.
Give fhe meaning of campus interview.
Answer:
Selection of suitable candidates from the universities, Colleges and institutes are popularly known campus recruitment.
Question 17.
Define selection
Answer:
According to yoder it is a process by which candidates for employment are divided into two classes those who will be offered employment & those who will not
Question 18.
What are selection test?
Answer:
These tests are made to discover & measure ,the skills abilities of the candidates in terms of the requirement.
Question 19.
What are patterned or structural interview?
Answer:
In this type interviewer is done while looking for information in a particular area of interest. A number of standard question are framed by the interviewer, to focus on the skills & personality of the candidate.
Question 20.
Give the meaning of board or panel interviews.
Answer:
In this interview a group of persons ask the applicant question on different subjects. This type of interview is common in case of professional jobs.
Question 21.
What is Group interview?
Answer:
A common topics presented before the candidates for discussion. It offers candidates to express their style, which allows interviewers to assess a candidates skills
Question 22.
What is Apprenticeship training?
Answer:
It is the formalized method of training with, on the job work under supervision.
Question 23.
What is Internship training?
Answer:
Internship is a system of on the job training, that allows learners to gauge their chosen profession area.
Question 24.
Give the meaning of Job Rotation
Answer:
It is a method of training of employees’ development through provision of diversified training. Here the employee has to, rotate from one job to another, one department to another department.
Question 25.
What is case study method of training
Answer:
It is written description of an actual situation in the past in the same organization. Trainees are supported to analyze and give their conclusion.
Question 26.
What is vestibule Training?
Answer:
This method of training is used mostly to train technical staff and office employees who deals with the tools, equipments and machines.
![]()
2nd PUC Business Studies Staffing Four Marks Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Explain the importance of staffing.
Answer:
The importances of staffing are as follows:
1. For implementing managerial functions: Staffing brings life into organization by manning right people for right jobs. The success of all management functions depends on staffing.
2. Higher Job Satisfaction: The staffing function helps in building in a sound human organization in which the employee’s performance and the job satisfaction is very high.
3. Increased productivity and profitability: Training and development of employees are most important staffing functions, which increases productivity and profitability of the organization.
4. Effective use of resources: The right of selection of employees for the right jobs, is instrumental in the effective utilization of capital, materials, technology etc., in the organization which will ensure minimum wastage and improved quality in work and products.
5. Right people for right jobs: The staffing function helps the organization in discovering and selecting competent personnel for various positions in the organization which increases efficiency and strengthens the organization to face the challenges.
Question 2.
“Staffing is a part of Human Resource Management”- Give reasons.
Answer:
1.Staffing is a part of Human Resource Management can be justifies by the following reasons:
2. Staffing is a function which brings together the human assets and physical assets of the organization
3. Staffing involves knowledge and approaches to the concept of hiring, retaining and firing of personnel in the organization.
4. Staffing is continuous and found at every level of management – Lower level, Middle level and higher level.
5. Staffing should be treated as a part of human resource management – justified by human resource accounting.
6. Human relations approach recognizes human factor as the most important instrument of success in an organization.
7. Staffing as a part of human resource management gives more importance for staffing concepts viz., selection, development, training, orientation etc.
Question 3.
State the steps in Staffing process.
Answer:
Staffing involves the following process:
Man power planning: It refers to the process of estimating the man power requirement of an organization by considering infrastructure, technology, production schedule, market fluctuation, demand forecasts etc.
- Recruitment: It is the process of finding and attracting suitable applicants for employment.
- Selection: It is the process of picking the suitable candidate form the pool of job applicants to fill in various jobs in the organization.
- Placement: It means assigning jobs to the selected candidates. It may be assigning a new job or a different job to an old employee.
- Orientation: Means introducing the selected new employee to other employees and familiarizing him with the rules and policies of the organization.
- Training: Training is the process which is done to increase the knowledge and skills of an employee to perform the present job accurately.
- Development: refers to the process of not only building up the skill, but also the overall competence of managerial executives to undertake challenging tasks.
- Performance appraisal: It is the systematic evaluation of the individual with respect to his performance on the job and his potential for development.
- Promotion and Career planning: Promotion is the vertical movement of an employee within the organization, with an increase in salary, status and responsibilities.
- Compensation: Workers tender their services for wages or salary. The term compensation comprises cash payments which is in addition to wages and salary and includes bonus, share in profit, pension etc.
![]()
Question 4.
Briefly explain any five external sources of Recruitment.
Answer:
The various external sources of Recruitment are as follows:
1. Direct Recruitment: This is a source of external recruitment in which the application for vacancies are presented on bulletin boards outside the factory or at the gate. A written application is submitted by the candidates and they have to take up tests and interviews. If they are suitable for the job, they are immediately selected.
2. Casual Callers (Unsolicited applications): Many qualified persons apply for employment to reputed companies on their own initiative. Such applications are known as unsolicited applications. By keeping a proper record of these applications the candidates may be called for an interview whenever the need arises.
3. Advertisement: This is the most effective means to search potential employees from outside the organization. The necessary information about the company, job descriptions and job specifications given in the advertisement brings response from suitable candidates spread over different parts of the country.
4. Employment exchange: In India, Employment exchanges have been set up by the Government for bringing together job seekers and employers who are looking for employees. Those who are search of a job register themselves with the local employment exchanges which keep a record of all such persons. The employer informs about the vacancies to his nearest employment exchange. Most of the Government undertakings employ people through such exchanges.
5. Placement agencies: In Urban areas, a number of private organizations have started functioning as placement agencies. They register the names of job seekers and arrange interviews and send them for different companies who have suitable openings.
Question 5.
Explain the different types of Selection tests.
Answer: Selection tests are often conducted to measure the intelligence, aptitude, proficiency, personality of the candidates. The different types of selection tests are:
1. Intelligence tests: These tests are used to judge the mental capacity of the applicant. These tests evaluate the ability of an individual to understand instructions and make decisions.
2. Trade or proficiency tests: Trade tests are designed to measure the skills already acquired by the individuals. They measure the level of knowledge and proficiency in the area of profession or technical training.
3. Personality rests: These tests probe for the overall qualities of a person as a whole. They provide clues to a person’s emotional reactions, maturity level etc.
4. Interest tests: It identifies the areas in which a candidate has special concern, fascination, involvement etc. These test suggest the nature of job liked by a candidate which may bring him job satisfaction.
Question 6.
Briefly explain any five types of Selection interview.
Answer:
Interview is considered as a method of personal appraisal, through face to face conversation and observation. Some of the interview methods are given below:
1. Direct Interview: Under this method, direct questions are asked to the applicant, to identify his skills, character, area of interest, attitudes etc.
2.Indirect interview: Under this method, the applicant is asked to express his opinion on any topic he likes and the interviewer listens to the views of the applicant without any intervention. This helps of assess the personality of the applicant.
3.Patterned or structural interview: In this type of interview, the interviewer is looking for information in a particular area of interest in the organization. A number of standard questions are framed which focuses on experience, skills and personality which is to be answered by the applicant.
4. Stress Interview: In this interview, the interviewer will intentionally try to upset the applicant, to see his reactions under pressure. This type of interview is common in high stress jobs.
5.Board or Panel interview: In this interview a group of persons called Board or Panel asks the applicant, questions in different subjects. Immediately after the interview, they meet and discuss and evaluate the performance of the applicant on the basis of answers given by him
![]()
Question 7.
Explain the benefits of Training.
Answer:
Benefits of training are as follows:
- Training improves employee’s ability and skills and in turn improve their performance both in quality and quantity.
- A well planned and systematically organized training progamme reduces the time and cost involved in learning the work.
- Training also changes attitude from negative to positive Higher performance, Job security, promotional avenue etc. and leads to high morale among the employees.
- A well trained employee will be well acquainted with the job and will need less supervision.
- Training improves employee’s ability, knowledge and skills and makes him eligible for promotion.
Question 8.
Explain the different methods of on-the-job training.
Answer:
Some of the methods of on-the-job training are:
1. Apprenticeship training: It is the formalized method of training curriculum program that combines classroom education with on the job work under supervision. It is also called ‘Understudy’ in which a trainee is put under the supervision and guidance of an experienced expert. This method is best suited for training in crafts, trades and technical areas.
2. Coaching: In this method, the trainee is placed under a particular supervisor, who functions as a coach in training the employee. This helps the learner to pick up the skill in speed. The supervisor provides feed back to the trainee on his performance and offers him some suggestions for improvement.
3. Internship Training: It is the system of on the job training that allows learners to gauge their interest in their chosen professional area. This method is usually meant for such vocations, where advanced theoretical knowledge is to be backed up by practical experience on the job.
4. Job – Rotation: It is the method of training which serves the purpose of employee’s development through provision of diversified training. Here, an employee has to rotate from one job to another, and from one section to another.
Question 9.
Explain the different methods of off-the-job training.
Answer:
The following are the important methods of off-the-job training:
1. Classroom lecture: This method is well known to train white collar or managerial executives in the organization. Under this method, the trainees are called to the room like that of a classroom, to get training in the form of lecture.
2. Case study: It is a written description of an actual situation in the past in the same organization and the trainees are supposed to analyze and give their conclusions. Case is later discussed by instructor with all the pros and cons of each option.
3.Vestibule training: This method is used mostly to train technical staff office employees who deal with tools, equipments and machines. Here, the employees learn their jobs on the equipment or tool they will be using in their workplace.
4.Computer modeling: Computer simulation modeling is the technique of representing the real world by a computer program or software. It can assist in the design, creation and evaluation of complex systems. It is useful when change to the actual system is : difficult to implement and impractical.
2nd PUC Business Studies Staffing Eight Marks Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Briefly explain the different methods of on-the-job training and off-the-job training, j Answer: Some of the methods of on-the-job training are:
Answer:
1. Apprenticeship training: It is the formalized method of training curriculum program that combines classroom education with on the job work under supervision. It is also called ‘Understudy’ in which a trainee is put under the supervision and guidance of an experienced expert. This method is best suited for training in crafts, trades and technical areas.
2. Coaching: In this method, the trainee is placed under a particular supervisor, who functions as a coach in training the employee. This helps the learner to pick up the skill in speed. The supervisor provides feed back to the trainee on his performance and offers him some suggestions for improvement.
3. Internship Training: It is the system of on the job training that allows learners to gauge . their interest in their chosen professional area. This method is usually meant for such vocations, where advanced theoretical knowledge is to/be backed up by practical experience on the job.
4. Job – Rotation: It is the method of training which serves the purpose of employee’s development through provision of diversified training. Here, an employee has to rotate . from one job to another, and from one section to another
![]()
Some of the methods of off-the-job training are:
1. Classroom lecture: Classroom lecture: This method is well known to train white collar or managerial executives in the organization. Under this method, the trainees are called to the room like that of a classroom, to get training in the form lecture.
2. Case study: It is a written description of an actual situation in the past in the same organization and the trainees are supposed to analyze and give their conclusions. Case is later discussed by instructor with all the pros and cons of each option.
3. Vestibule training: This method is used mostly to train technical staff office employees who deal with tools, equipments and machines. Here, the employees learn their jobs on the equipment or tool they will be using in their workplace.
4. Computer modeling: Computer simulation modeling is the technique of representing the real world by a computer program or software. It can assist in the design, creation and evaluation of complex systems. It is useful when change to the actual system is difficult to implement and impractical.
2nd PUC Business Studies Staffing Five Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Assuming that you are the HR manager Of an organization state any few your would look into while recruiting employees.
Answer:
As an HR manager sources of recruitment chosen will be:
- Internal Sources: Promotions and Transfer.
- External Sources: Direct Recruitment
- Casual callers
- Advertisement.
- Employment Exchange.
- Placement agencies.
- Campus Recruitment.