Karnataka 2nd PUC Business Studies Important Questions Chapter 13 Entrepreneurship Development
Exercises
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Write the meaning of the term ‘entrepreneur’.
Answer:
Entrepreneur: The owner of a business is known as Entrepreneur or we can say that the person who set-up his business. He is the co-ordinator, organizer of resources and gives shape to the business.
Question 2.
Write the meaning of the term of ‘entrepreneurship’.
Answer:
Entrepreneurship: It is the dynamic process of interaction between the person and the environment. It means starting up one’s own business concerned with strategic decisions of resource allocation and involved huge risk to create value and earn profit.
Question 3.
Write the meaning of the term of ‘Enterprise’.
Answer:
Enterprise: The output of the entrepreneurship process is known as the Enterprise. It is something attempted to be performed. It provides employment opportunities, professional opportunities and business opportunities which helps in building up the economy of a nation.
Question 4.
Why is entrepreneurship regarded as a creative activity?
Answer:
Entrepreneurship is a creative activity as an entrepreneur converts raw materials into useful goods and services; it involves creation of value, introduction of new products, discovery of new markets and technologies.
Successful entrepreneurs keep focusing on innovative ideas and skills to produce efficient and effective results. Thus, an entrepreneur is innovator and this process is creative.
![]()
Question 5.
“Entrepreneurs undertake moderate risk”. Elaborate this statement.
Answer:
“Entrepreneurs undertake moderate risks”. It implies that an entrepreneur assures various supply of the projects, he agreed to pay salaries, wages, rent whether the venture succeed or not. Secondly, the person who opted a career in entrepreneurship takes a bigger risk as there is no assured pay off. It is said that it is a 50:50 situation means loss and profit both are unpredictable. Success depends upon the observations, calculations of risk, skills and confidence. Risk is not centred to one problem it involves many issues like fluctuation in price, taste and preference fashion, risk of strikes, lock outs etc. It becomes the essential feature of the entrepreneurship which is to be focused more and more.
Question 6.
How entrepreneurship resulted in increasing the spectrum and scope of economic activities?
Answer:
Development does not mean only the betterment of existing but it means the overall betterment across the geographical, sectoral and technological scope. Entrepreneurship results in diversification of economic activities by creating employment, business opportunities, stabilizing the demand and supply factors as underdeveloped countries caught in the vicious cycle on the demand as well as supply side. Thus, it helps in overcome from this situation. GDP originates from industry and services increases. Entrepreneurs through their decisions to direct from the stale sectors and invest in green field sectors bring a virtual transformation of the economy from underdeveloped to developed status. Thus, we can say entrepreneurship result in increasing the spectrum and scope of economic activities.
Question 7.
What are the benefits and risks of becoming an entrepreneur?
Answer:
Benefits of an entrepreneur
- They are the owner of the business.
- No worries of job, compensation and reward.
- They earn profit.
- They have full authority to take decisions.
![]()
Question 8.
How can you guard against the risks?
Answer:
Risks of an Entrepreneur
- Market risk
- Financial risk
- Risk in product planning
- Risk of innovative technologies
In order to secure from the risk, an entrepreneur should analyse the market well, study about the innovative technologies, prepare the business plan so that financial institutions granted the fond, and adopt the best ideas for product planning.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Describe briefly the role of achievement motivation in entrepreneurship.
Answer:
Entrepreneurial motivation is important to learn as different individual motivated differently and for the success of an enterprise following needs are to be focused to motivate an entrepreneur
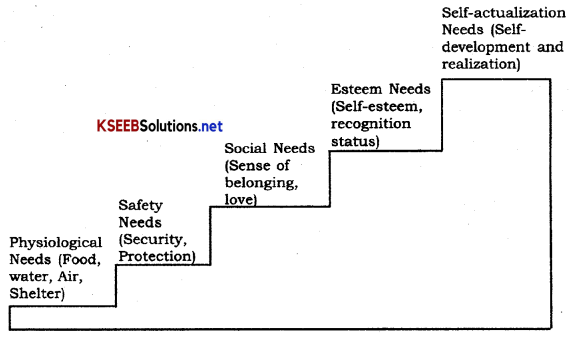
1. Need for Achievement: It implies a desire to accomplish something. In order to accomplish the task one can use the creativity, talent, organize physical resources, explore and use opportunities, overcome from the obstacles and attain a high standard.
2. Need for Power: It is concern with influencing people or the behaviour of others moving in the same direction to attain the objectives. Need for power means authority required to control the activities of an enterprise.
3. Need for Affiliation: It implies among other things a tendency of the people to conform to the wishes and norms of those whom they value. Entrepreneurs are believed to be low on affiliation buy they should focus and trace the elements of affiliation for a successful career and for the development of standardized goods and services for others.
4. Need for Autonomy: It means a desire for independence and being responsible and accountable to oneself rather than some external authority for performance. Everybody needs freedom to some extent as it is very difficult to take orders and work all the time as per the boss
![]()
Question 2.
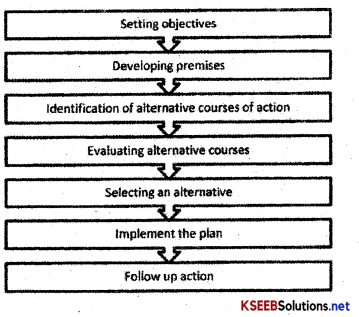
Describe briefly the steps involved in starting a new business.
Answer:
Setting up and running of business unit is a very crucial decision which Is taken by an entrepreneur. He performs several functions like assembling inputs, market analysis, sales strategy, risk factors, financial analysis and many more.
But in order to start a new business following steps are to be taken
1. Scanning the Environment: The complete awareness and understanding of business environment is known as Environment scanning. An entrepreneur scan business opportunities and risks involved. After the analysis, he use these opportunities and market them in much better way.
2. Development of Product: It is second step after scanning the environment an entrepreneur starts assessing scarce resources, assembling inputs and starts the production of goods and services.
3. Feasibility Analysis: It refers to the analysis which helps in knowing the practical possibility. An entrepreneur starts looking the feasibility like technical feasibility helps in knowing that the idea should be converted into reality using available technology, similarly economic feasibility helps in knowing the cost involved in production and after selling it will earn profit or not. The business plan starts after the feasibility report.
4. Funding Agencies: Finance is the backbone for the business activity. An entrepreneur needs finance to carry on the business that’s why they prepare a business plan which is to be submitted before the financial institutions and if they satisfy they fund the project.
5. Establishing of an Enterprise: After getting, the fund, an entrepreneur have to take legal permission and clearance from various agencies in order to establish an enterprise.
Question 3.
Examine the nature of relationship between entrepreneurship and economic development.
Answer:
There is a mutual relationship between economic development and entrepreneurship. Entrepreneurship development leads to economic development of the country by contributing in GDP and process of economic development gives an opportunity for expansion and growth
Following points explain the relationship between economic development and entrepreneurship
1. Contributing to Gross Domestic Product (GDP) Income is generated in the process of production. Entrepreneurs generate income via organization of production; it results in increasing the value of GDP directly.
2. Capital Formation: Entrepreneurs use their own funds and encourage various investment opportunities to invest in companies. This leads to capital formation.
3. Generation of Employment: Every new business gives the opportunity of employment to the people with different abilities, skills and qualifications. It becomes a source of livelihood to those who do neither have capital to earn interest or nor have the land to earn rent.
4. Improves Economic: Efficiency Entrepreneurs improve economic efficiency by improving the process, reducing waste, increasing yield and bring technical progress. In this way, entrepreneurship results in economic development.
On the other hand, economic development provides following opportunities for the growth and expansion of enterprise.
(a) Well-developed financial in the economy.
(b) Opportunities to raise and avail funds from various financial institutions.
(c) Lower rate of interest and moderate inflation.
(d) Availability of factors of production.
![]()
Question 4.
Clarify how motivation and abilities impact on individual’s decision to choose entrepreneurship as a career.
Answer:
Motivation and ability can positively reinforce each other. Persons having abilities search for the exposure and focus to start a new business. They take decisions logically with the personal courage and strive hard to acquire the necessary competencies to realize their dreams.
Following competencies contribute towards effective performance and success
- Entrepreneurs must take initiative to set up an enterprise.
- Recognize the opportunities and grab them as early as possible.
- Must strive for success.
- He must collect important information.
- Entrepreneurs must set up quality standards.
- Must be committed to the completion of task.
- Concern for conservation of time, money and effort.
- Entrepreneurs must have ability to do product planning.
- Must have ability to diagnose the problem and take required steps to solve it.
- Entrepreneur must be confident.
- Conveying one’s vision and convincing others of its values.
- He must seek the support of others.
- Providing leadership.
- Ensuring the progress of venture.
- Concern for employee’s welfare.
On the other hand, motivation is required to understand because entrepreneur’s objective is profit maximization and it can only be achieved when employees are motivated in such a manner that fulfilment of enterprise’s objective may also lead to satisfy employees basic needs. In this way, entrepreneurship career proves to be a success for an individual motivation and ability both goes hand to hand.
Question 5.
Anshuman was a very industrious sales executive with a small herbal cosmetic manufacturer. He earned a good salary and commission on the business he brought for the firm and had very good command over the -Delhi market for which he had virtually become indispensable. He was aware of the enviable position he held in the firm and thought aloud: “The key to success in any business is the sale of its products. The beginning and end of the business cycle is nothing but sale and “other” people working in the factory to manufacture products are mere cogs in the business machine set in motion by sales people. So why carry this burden and get only a tiny share of the prosperity of the firm? Instead others enjoying the fruits of my labour, why should I not start my own business?”
Should Anshuman take a leap? Give reasons for your answer.
Answer:
Yes, Anshuman can take a leap because:
- He has all the qualities of successful entrepreneur.
- He has the ability to bear the risk which is a prerequisite to capture a big share in the market.
- He has the calibre to do marketing of the product in an adventurous manner.
- He has the talent to face the competition posed by competitors in the market.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Entrepreneurs undertake
(a) Calculated risks
(b) High risks
(c) Low risks
(d) Moderate and calculated risks
Answer:
(b) High risks
![]()
Question 2.
In Economics, which of the following is not a function of the entrepreneur?
(a) Risk-taking
(b) Provision of capital and organization of production
(c) Innovation
(d) Day-to-day conduct of business
Answer:
(d) Day-to-day conduct of business
Question 3.
Which of the following statements does not clearly distinguish between entrepreneurship and management?
(a) Entrepreneurs found the business; managers operate it
(b) Entrepreneurs are the owners of their business; managers are employees
(c) Entrepreneurs earn profits; managers earn salaries
(d) Entrepreneurship is once for all activity; management is a continuous activity
Answer:
(d) Entrepreneurship is once for all activity.
Question 4.
In the roles and functions of the entrepreneur identified by Kilby, which of the following is not an aspect of ‘political administration’?
(a) Dealing with public bureaucracy
(b) Managing human relations within the firm
(c) Introducing new production techniques and products
(d) Managing customer and supplier relations
Answer:
(c) Introducing new production techniques and products
![]()
Question 5.
Which of the following attitudes is not generally associated with successful entrepreneurship?
(a) Investing in R&D
(b) Live your business day-by-day
(c) Innovate and improvise continually
(d) Produce as per customers requirements
Answer:
(b) Live your business day-by-day.
Case Problems:
Inspiring Feat: Dailywage Labourer Turns Entrepreneur
A landless woman from Bihar has been nominated among the top 25 farmers in Asia by a Mexican website.
Forty-five-year-old Lalmuni Devi was a daily wage labourer when she decided to take destiny into her own hands and transformed herself into a successful mushroom farmer. Today she manages to make Rs. 12,000 every year for an investment of only Rs. 600.
Her feat finds mention on a Mexican website that has grouped her as the top 25 inspirational farmers in its photo gallery.
”I am a poor woman. I thought that mushroom farming would profit henceforth I started it. Now I can earn a living for my family,” said Lalmuni Devi.
Successful enterprise
The success story has caught on with many women in the Azadpur village on the outskirts ofPatna.
’It is effortless farming, which we can even do in our village. Working in the scorching heat is very tiring. Mushroom farming generates more profit,” said Urmila Devi. Lalmuni and other landless women have been encouraged by the Indian Council for Agriculture Research to take up mushroom farming.
’It is to help the poorest ofthe poor through alternative livelihood support system For that we have chosen a village where people have no land and they have to share croppers,” said Dr A.R. Khan, Principal Scientist, ICAR, Patna.
Lalmuni’s efforts have paved the way for many other landless women to take up mushroom farming and earn a livelihood for their family with little effort.
Question 1.
What inspiring feat did Lalmuni Devi perform?
Answer:
Forty – five – years old Lalmuni Devi has become a part of top 25 inspirational farmers in one of the Maxican photo gallery because of her bold step in venture into mushroom farming. With this she has become able to earn Rs. 12,000 every year for an investment of only Rs.600. Prior to that she was a landless woman of Bihar. She has shown a great courage of starting her business and becoming a successful woman.
Question 2.
Do you feel that you can also become an entrepreneur? Elaborate.
Answer:
Yes, we feel that if one has the courage and desire to achieve something, he can become a successful entrepreneurs. Entrepreneurs are not born, they become with the passage of time and hardships of life. Thus, we can also become entrepreneur.
Question 3.
What qualities of an entrepreneur did Lalmuni Devi exhibit?
Answer:
Lalmuni showed the entrepreneurial qualities of initiative, sees and acts on opportunities, persistence and commitment to work contract.
![]()
Question 4.
What are the benefits and risks of becoming an entrepreneur? How can you guard against the risks?
Answer:
- It helps in economic development by accelerating the process of capital formation and providing employment opportunities.
- It helps in capitalisation of new opportunities.
- It brings wealth and new jobs,
- One become job provider.
Risks associated with this procedure:
- Entrepreneurship involves risks of failure,
- It bears threat from competitions.
- Fear of obsolescence.
Measures to overcome these risks:
Risks associated with the entrepreneurial process can be overcome by following the important steps:
- By making proper plans,
- By remaining innovative.
- Organizing resources should be done in a careful manner.
- Involving local people so that conflicts can be avoided.
- Keeping in view the government policy on the proposed subject matter.