Indian Position and Extension Location and Extent of India Class 10 Questions and Answers KSEEB 10th Social Science
I. Fill in the blanks with suitable answers:
Question 1.
The total area of India is ______________ Sq km.
Answer:
32,87,263
Question 2.
The country to the south – east of India is ______________.
Answer:
Sri Lanka
![]()
Question 3.
The ______________ latitude passes through the middle of India.
Answer:
23\(\frac {1}{2}\)°N
Question 4.
The newly formed state of India is ______________
Answer:
Telangana
II. Discuss in groups and answer the following
Question 1.
Give the latitudinal and longitudinal extent of India.
Answer:
The mainland of India extends from 8.4 deg to 37.6 deg North Latitude and from 68.7 deg to 97.25 deg East Longitude.
Question 2.
Which is the southern most point of Indira?
Answer:
The Indira Point is the southern most point of India which is located in Nicobar Island at 6.45 deg N Latitude.
Question 3.
Name India’s neighbouring countries situated in north west.
Answer:
Pakistan & Afghanistan
Question 4.
Write a short note on the frontiers of India.
Answer:
Frontiers : India has both land and water frontiers. The land frontiers of the country is about 15,200 km. Except in some places India has natural frontiers almost on all side. The Himalayan ranges form a natural frontier in the north between India and China.
The mainland of India has water frontier of about 6100 km. The total length of India’s coast line including the Andaman and Nicobar islands as well as Lakshadweep islands, is 7516.5 km. The Arabian Sea in the west, the Indian Ocean in the south and the Bay of Bengal in the east form the water frontiers. They are also natural frontiers.
![]()
Additional Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Describe the geographical location of India?
Answer:
Geographically India is located in the Northern Hemisphere and is at the centre of the Eastern Hemisphere. It is a peninsula situated in South-East Asia. The mainland of India extends from 8°.4’ to 37°.6’ North latitude and from 68°.7’ to 97°.25’. East longitude. The Andaman and Nicobar islands extend further southward and add to India’s latitudinal extent. The Indira Point, the southern most point is located in the Nicobar island at 6°.45’ N. Latitude. The northern tip of India is Indiracol in Jammu and Kashmir.
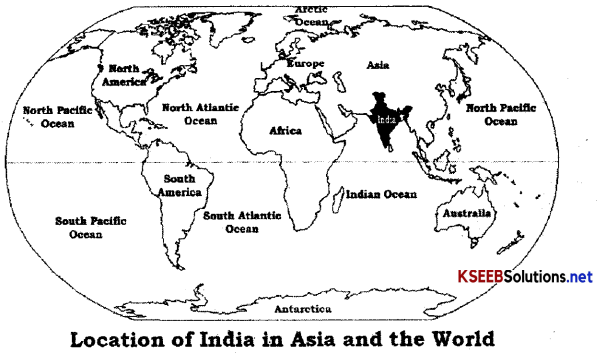
The Tropic and cancer \(\left(23 \frac{1^{0}}{2} \mathrm{~N}\right)\) passes through the middle of the country and E. longitude is the central meridian of India. The Indian Standard Time (1ST) is based on this longitude.
Question 2.
Which is the seventh largest country in the world?
Answer:
India
Question 3.
What is the east to west extent of India?
Answer:
2933 km
Question 4.
What is the north to south extent of India?
Answer:
3214 km
Question 5.
What is the total land frontiers of India?
Answer:
15200 Km
![]()
Question 6.
Which land frontier forms a natural frontier between India and China?
Answer:
The Himalayan ranges
Question 7.
What is the total water frontier of Indian main land?
Answer:
6100 km
Question 8.
Which natural waterbodies separates India and Srilanka?
Answer:
Palk Strait and Gulf of Munnar
Question 9.
Which is the name of the northern most tip of India?
Answer:
Indira Col
Question 10.
Which boundary Sine separates India and Pakistan?
Answer:
The Rad-Cliff line
Question 11.
Which boundary line separates India and Afghanistan?
Answer:
The Durand line
Question 12.
Which boundary line separates India and China?
Answer:
McMohan Line
Question 13.
How many States and Union Territories is India divided into?
Answer:
29 States and 7 Union Territories
![]()
Question 14.
Which are the largest and smallest States of India?
Answer:
Rajasthan is the largest State and Goa is the smallest State and Goa is the smallest state of India.
Multiple Choice Questions and Answers
Question 1.
The north south extent of India is
a. 3214 Kms.
b. 15200 Kms.
c. 6100 Kms.
d. 2933 Kms.
Answer:
a. 3214 Kms.
Question 2.
The latitudinal extent of India is:
a. 6° .8′ N to 9° .7 N’
b. 8° .4′ N to 37° .6 N’
c. 7° .4′ N to 73° .6 N’
d. 4° .7′ N to 63° .7 N’
Answer:
b. 8° .4′ N to 37° .6 N’
Question 3.
The norther tip of India is called:
a. Indira Point
b. Nehru Point
c. Indira Col
d. Indira Tip
Answer:
c. Indira Col
![]()
Question 4.
The countries which share its boundaries with India in the north are:
a. Nepal and Bhutan
b. Bangladesh and Myanmar
c. Pakistan and Afganisthan
d. Nepal, Bhutan and China
Answer:
d. Nepal, Bhutan and China
Question 5.
India lies in the Hemisphere:
a. Northern
b. Southern
c. Western
d. Eastern
Answer:
a. Northern
Question 6.
The central meridian of India is:
a. 23 \(\frac {1}{2}\)° North
b. 82 \(\frac {1}{2}\)° East
c. 68.5° East
d. 97.50° East
Answer:
b. 82 \(\frac {1}{2}\)° East
Question 7.
The Indian Standard Time (IST) is based on:
a. 82.-5° E Longitude
b. 88.5° E longitude
c. 97° 7 ‘ E longitude
d. 68° r E longitude
Answer:
a. 82.5° E Longitude
Question 8.
Lately a new State was created in India. Which is it?
a. Jharkand
b. Chattisgarh
c. Telangana
d. Delhi
Answer:
c. Telangana
Question 9.
7th largest country in the world is :
a. China
b. Russia
c. Canada
d. India
Answer:
d. India
![]()
Question 10.
The natural frontier towards the west of India is:
a. Bay of Bengal
b. Indian Ocean
c. Himalayas
d. Arabian Sea
Answer:
d. Arabian Sea
