Students can Download Karnataka SSLC Maths Model Question Paper 2 with Answers, Karnataka SSLC Maths Model Question Papers with Answers helps you to revise the complete Karnataka State Board Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Karnataka State Syllabus SSLC Maths Model Question Paper 2 with Answers
Time: 3 Hours
Max Marks: 80
I. In the following questions, four choices are given for each question, choose and write the correct answer along with its alphabet: ( 1 × 8 = 8 )
Question 1.
For some integer n every odd integer is of the form
a) 2n + 1
b) n + 1
c) 2n
d) n
Answer:
2n + 1
Question 2.
The value of sin215° + sin225° + sin265° + sin275° is
a) 0
b) 1
c) 2
d) 3
Answer:
2
![]()
Question 3.
If chord AB subtends an angle 50° at the centre of a circle then the angle between the tangents at A and B is
a) 40°
b) 100°
c) 130°
d) 120°
Answer:
130°
Question 4.
The formula used to find the volume of a sphere
a) \(\frac{4}{3} \pi r^{3}\)
b) \(\frac{2}{3} \pi r^{3}\)
c) \(\frac{1}{3} \pi r^{3}\)
d) πr3
Answer:
a) \(\frac{4}{3} \pi r^{3}\)
Question 5.
α + β are the zeroes of the polynomial x2 – 6x + 4, then the value of \(\frac{(\alpha+\beta)^{2}-2 \alpha \beta}{\alpha \beta}\) is
a) 7
b) 8
c) -7
d) -8
Answer:
a) 7
Solution:
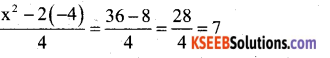
![]()
Question 6.
If 29th term of an A.P is twice its 19th term, then the 9th term is
a) -1
b) 0
c) 1
d) 2
Answer:
b) 0
Solution:
T29 = 2T19
a + 28d= 2(a + 18d)
a + 28d = 2a + 36d
0 = 2a + 36d-a-28d
0 = a + 8d
T9 = 0
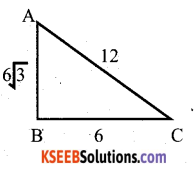
Question 7.
In ∆ ABC, AB = 6√3 cm, AC = 12 cm, BC = 6cm, The angle B is
a) 45°
b) 90°
c) 60°
d) 30°
Solution:
AC2 = AB2 + BC2
122= (6√3 )2 + 62
144= 108 + 36 144=144
∴ ∠B = 90°
![]()
Question 8.
If the probability of an event is P(A) then the probability of its complimentary event will be
a) 1+P(A)
b) 1 – P(A)
c) P(A) – 1
d) 1 / P(A)
Solution:
We know that for any two complimentary events A and Ā
P(A) + P(Ā) = 1 → P(Ā) = 1 – P(A)
II. Answer the following questions : ( 1 × 8 = 8 )
Question 9.
If α and β are the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial 2 – 3x – x2 then what is the value of α + β + αβ ?
Answer:
α + β = -b/a , αβ = c/a
= \(\frac{-(-3)}{-1}\) αβ = \(\frac{2}{-1}\) = – 2
= – 3
α + β + αβ = -3 -2 = -5
Question 10.
What are the roots of the quadratic equation x2 + (√3 + 1)x + √3 = 0?
Answer:
2 + (√3 + 1)x + √3 = 0 = 0
x2 + x + √3x + √3 = 0
x(x + 1)+ √3 (x + 1) = 0
(x + 1)(x + √3) = 0
x + 1 = 0, x + √3 = 0
x = -1, x = -√3
Question 11.
If the nth terms of the two AP 9, 7, 5, ….. and 24, 21, 18, ……… are same. Find n.
Answer:
9, 7, 5, …….
a = 9, d = 7-9 = -2 T = a + (n – 1)d
Tn = 9 + (n – 1) (-2)
Tn = 9 + (-2n + 2) ‘
Tn = 9 – 2n + 2
Tn = 11 – 2n
24,21,18,
a = 24, d = 21 – 24 = -3
Tn = a + (n – 1) d T=24 + (n – 1)(-3)
Tn = 24 – 3n + 3
Tn = 27 – 3n
Given : nth term of both A. P. is same.
∴ 11 – 2n = 27 – 3n
-2n +3n = 27 -11
n = 16
Question 12.
State A – A criterian theorem.
Answer:
“If two triangles are equiangular, then the corresponding sides are proportional.”
Question 13.
Find the H.C.F of 455 and 42 with the help of Euclid’s division algorithm.
Answer:
Step (1): a = 455 b = 42
a = bq + r
455 = 42 × 1 + 35
Step (2): a = 42, b = 35
a = bq + r
42 = 35 × 1 + 7
Step (3): a = 35, b = 7
a = bq + r
35 = 7 × 5 + 0
∴ H.C.F. (455, 42) = 7
Question 14.
Find θ if sin (θ + 56) = cosθ, where θ and ( θ + 56) are less than 90°.
Answer:
sin (θ + 56) = cos θ
sin (θ + 56) = sin (90 – θ)
θ + 56 = 90 – θ
θ + θ = 90 – 56
2θ = 34
θ = 34/2
θ = 17
Question 15.
If x = a sin θ and y = b tan θ, then find the value of \(\frac{a^{2}}{x^{2}}-\frac{b^{2}}{y^{2}}\)
Answer:
Consider


![]()
Question 16.
Calculate the height of a right circular cone where C.S.A. and base radius are 12320 cm2 and 56 cms. respectively.
Answer:

C.S.A of a cone = π rl
12320 = \(\frac{22}{7}\) x 56 x 1
1 = \(\frac{12320 \times 7}{22 \times 56}\)
1 = 70 cm
But 12 = r2 + h2
702 = 562 + h2
h22 = 702 – 562
h2 = (70 + 56) (70 – 56)
h2 =(126) (14)

III. Answer the following ( 2 × 8 = 16 )
Question 17.
Show that any positive odd integer is of the form 6q + 1 or 6q + 3 or 6q + 5 where q is an integer.
Answer:
Let nbe any positive, integer using division algorithm,
a = bq + r
Taking a = n, b = 6
n = 6q + r
If any number is divided by 6, then the possible remainders are 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5.
∴If n is odd, then r = 1, 3, 5
⇒ 6q + 1, 6q + 3, 6q + 5 are the positive odd integers.
Question 18.
Solve : 2x + 3y = 9
3x + 4y = 5
Answer:
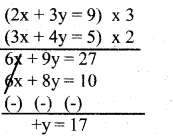
Substitute y = 17 in 2x + 3y = 9
2x + 3(17) = 9
2x + 51 =9
2x = 9 – 51
x = \(\frac{-42}{2}\)
= -21
Question 19.
Solve : (x – 2)2 + 1 = 2x – 3
Answer:
x2 + 4 – 4x + 1 = 2x – 3
x2 – 4x + 5 – 2x + 3 = 0
x2 – 6x + 8 = 0 x2 – 4x – 2x + 8 = 0
x(x – 4) -2(x – 4) = 0
(x – 4) (x – 2) = 0
x – 4 = 0, x -2 = 0
x = 4 or x = 2
Question 20.
Show that the points (-2, 1) (2, -2) and (5, 2) are the vertices of a right angled triangle.
Answer:
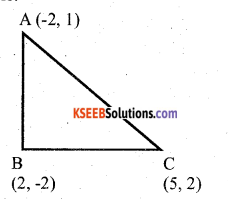
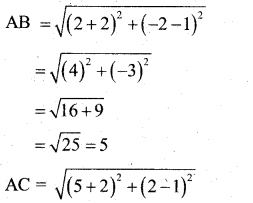

∴ ∆ ABC is a right angled triangle at B.
![]()
Question 21.
The equilateral triangles are drawn on the sides of a right triangle. Show that the area of the triangle on the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the areas of the triangles on the other two sides.
Answer:
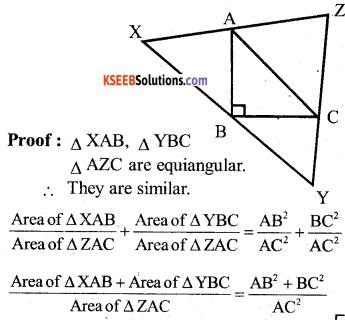

∴ Area of ∆ XAB + Area of ∆ YBC = Area of ∆ ZAC .
OR
In the given figure, PA, QB and RC are each perpendicular to AC. Prove \(\frac{1}{x}+\frac{1}{z}=\frac{1}{y}\)
Answer:

Question 22.
Two dice are thrown simultaneously. Find the probability that the sum of the numbers on the faces is neither divisible by 4 nor by 5.
Answer:
S = {(1, 1) (1,2) (1, 3) (1,4) (1, 5) (1, 6) (2, 1) (2, 2) (2,3) (2,4) (2, 5) (2,6) (3.1) (3, 2) (3, 3) (3, 4) (3, 5) (3,6) (4, 1) (4, 2) (4, 3) (4, 4) (4, 5) (4,6) (5, 1) (5, 2) (5, 3) (5, 4) (5, 5) (5,6) (6.1) (6,2) (6, 3) (6,4) (6, 5) (6,6)}
n(S) = 36.
An event of getting sum of the numbers neither divisible by 4 nor by 5.
A={ 1,1) (1,2) (1,5) (1,6) (2,1) (2, 4)
(2, 5) (3, 3) (3, 4) (3, 6) (4, 2) (4,3) (4, 5) (5,1) (5, 2) (5, 4) (5, 6) (6,1) (6, 3) (6, 5)} n(A) = 20
n(A) = 20
P(A) = \(\frac{\mathrm{n}(\mathrm{A})}{\mathrm{n}(\mathrm{S})}=\frac{20}{36}\)
Question 23.
Draw a circle of radius 3 cm. Take a point P outside the circle without using the centre of the circle, draw to tangents to the circle from an external point P.
Answer:
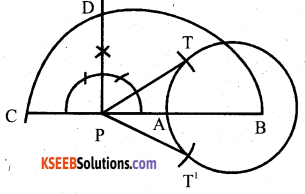
Question 24.
Prove that (cosecθ-cotθ)2 = \(\frac{1-\cos \theta}{1+\cos \theta}\)
Answer:
Consider LHS
(cosecθ-cotθ)2 = cosec2 θ +cot2 θ – 2cosecθ.cotθ
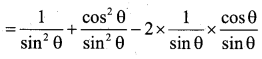

OR
If sinθ + cos θ = √2 sin (90 -θ) determine cot θ
Answer:
sin θ + cos θ = √2 sin (90 – θ)
sin θ + cos θ = √2 cos θ
sin θ = ypi cos θ – cos θ
sin θ = cos θ (√2 -1)
sinθ /cosθ = √2 -1
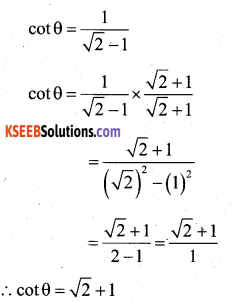
![]()
IV. Answer the following : ( 3 × 9 = 27 )
Question 25.
Asha is 5 times as old as her daughter Usha, 5 years later Asha will be 3 times as old as her daughter Usha. Find the present ages of Asha and Usha.
Answer:
Let the age of Asha be x years
Let the age of Usha be y years
According to question x=5y
x – 5y = 0 …….(1)
Five years later,
(x + 5) = 3(y + 5)
x + 5 = 3y + 15
x – 3y = 15 – 5
x – 3y = 15 – 5
x – 3y = 10 (2)
Substitute x = 5y in equation (2)
5y – 3y = 10
2y = 10
y = 10/2
y = 5
∴ x = 5y
= 5 × 5
x = 25
∴ The present age of Asha is 25 years.
The present age of Usha is 5 years.
OR
The sum of 2 digits of a 2 digit number is 12 the number obtained by interchanging the digits exceeds by the given number by 18. Find the number.
Answer:
Let the two digits be x and y
The 2 digit number will be 10x + y
The sum of digits = x + y – 12 ……..(i)
The number obtained by interchanging the digits =10y + x
= 10x + y + 18
10y + x – 10x – y = 18
9y – 9x = 18
Divide by 9
y – x = 2
y = x + 2 ….(ii)
Consider equation (1)
x + y = 12
Substitute y = x + 2
x + x + 2 = 12 .
2x =12 – 2
2x= 10
x= 5
y = x + 2
y = 5 +2
y = 7
∴ The number is : 10x +y
= 10(5)+7 = 50+ 7
= 57
Question 26.
Find the other two zeroes of the polynomial y4 + y3 – 9y2 – 3y + 18 if the
zeroes are √3 and -√3
Answer:
y = √3 and y = -√3
(y + √3) = o (y-V3) = o
(y + √3 )(y – √3 ) = o
y(y – √3 ) + √3 (y – √3 ) = 0
y2 – √3y + √3 y – 3 = o
y2 – 3 = 0

y2 + y – 6 = 0
y2 + 3y – 2y – 6 = 0
y(y + 3)-2(y + 3) = 0
(y + 3) = 0 & (y – 2) = 0
y=-3 & y = 2
The four zeros of polynomial are √3 , -√3 , -3 & 2
Question 27.
Solve for x.
\(\frac{1}{a+b+x}=\frac{1}{a}+\frac{1}{b}+\frac{1}{x}\) (Where a ≠ 0, b ≠ 0 x ≠ 0, x ≠ -a,-b
Answer:

(-a – b)ab = (a + b)x (a + b + x)
-a2b – ab2 = (a + b) (ax + bx + x2)
-a2b – ab2 = a2x + abx + ax2 + abx + b2x + x2b
-a2b – ab2= a2x + 2abx + ax2 + b2x + x2b
-ab(a+b) = ax(a+x) + xb(b+x)+2abx
=x[a(a+x)+b(b+x)+2ab]
=x[a2 + ax+b2 +bx + 2ab]
= x[(a+b)2 + x(a+b)]
-ab(a + b) = x(a+b)[a+b+x]
-ab = x(a + b + x)
-ab = ax + bx + x2
x2 + x (a + b) + ab = 0
x2 + ax + bx + ab = 0
x(x+a) + b(x + a) = 0
(x + a) (x +b) = 0
=>x + a = 0, x + b = 0
=> x = -a, x = -b
OR
The diagonal of a rectangular field is 60m more than the shorter side. If the larger side is 30m more than the shorter side, find the sides of the field.
Answer:
Let the shorter side of the rectangular field be x m.
Longer side is x + 30 and the diagonal is x+60
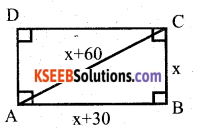
In ∆ ABC,
AC2 = AB2 + BC2
(x + 60)2 = ( x + 30)2+ x2
x2 + 3600 + 120x = x2 + 900 + 60x + x2
x2 + 900 + 60x – 3600 – 120x = 0
x2 – 60x – 2700 = 0
x2 – 90x + 30x – 2700 = 0
x(x – 90) + 30(x – 90) = 0
(x – 90) (x + 30) = 0
x – 90 = 0, x + 30 = 0
x = 90, x = – 30.
∴ The shorter side = x = 90m
The longer side = x + 30 = 90+30 = 120m.
![]()
Question 28.
If the points (7, -2) (5, 1) and (3, 5) are collinear. Find the value of k.
Answer:
Since the give points are collinear, the area of the triangle formed by them must be O i.e.
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) [x1(y2-y3) + x2(y3-y2) + x3(y1-y2)]
x1 = 7, x2 = 5, x3 = 3
y1 = – 2, y2 = 1, y3 = k
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) [7(1 – k) + 5 (k + 2) + 3(-2-1)] = 0
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) [7 – 7k + 5k + 10 – 9]-0
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) [7 – 2k + 1] = 0
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) [8 – 2k] = 0
8-2k = 0 or 2k=8
k = 8/2 = 4
k = 4
OR
Find the area of Rhombus if its vertices are (3, 0) (4, 5) (-1, 4) and (-2, -1) taken in order.
Answer:
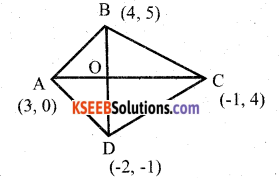
Area of rhombus = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) d1 × d2
Let A = (3, 0) B = (4, 5)
C = (-1, 4) D = (-2, -1)
Diagonal

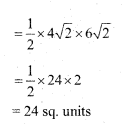
![]()
Question 29.
Prove the tangents drawn from an external point to a circle are equal.
Answer:
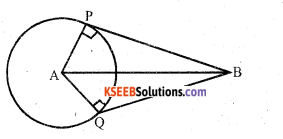
Data: A is the centre of the circle B is an external point.
BP and BQ are the tangents.
AP, AQ and AB are joined.
To prove that: a) BP = BQ
b) ∠PAB-∠QAB.
c) ∠PBA = ∠QBA
Proof: In ∆ APB and ∆ AQB
AP = AQ [Radii of same circle]
∠ APB – ∠AQB = 90°
AB = AB [common side]
∴ ∆ APB ≅ ∆ AQB [RHS]
a) PB = QB
b) ∠PAB = ∠QAB
c) ∠PBA = ∠QBA
Question 30.
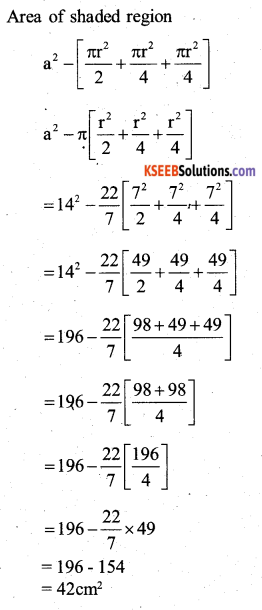
Find the area of the shaded region in the figure, where ABCD is a square of side 14 cm
Answer:

Area of square ABCD
= 14 × 14=196 cm2

Hence, area of the shaded region
= Area of square – Area of four circles
= 196 – 154
= 42cm2
OR
Find the area of the shaded regions. Given PQRS a square of sides 14cm. Soln: S R
Answer:
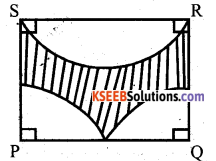
Question 31.
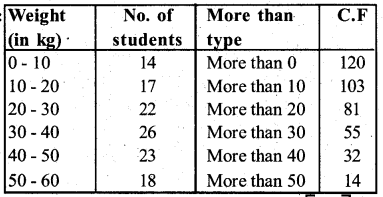
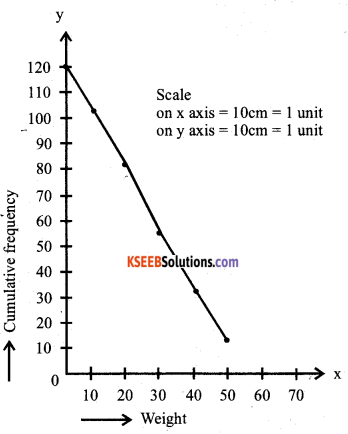
The following table gives the weight of 120 articles :

Change the distribution to a “more than type” distribution and draw its ogive.
Answer:
Question 32.
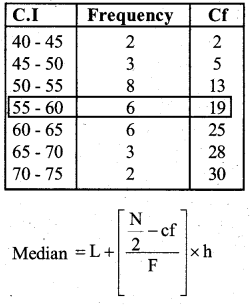
The distribution below gives the weights of 30 students of a class. Find the median weight of the students.
Weight (in kg)
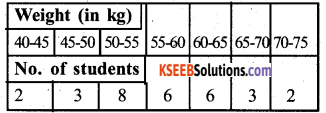
Answer:
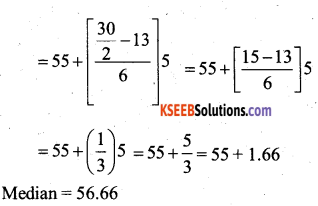
![]()
Question 33.
Construct a right triangle whose hypotenuse and one side measures 10cm and 8cm respectively. Then construct another triangle whose sides are 4/5 times the corresponding sides of the triangle .
Answer:
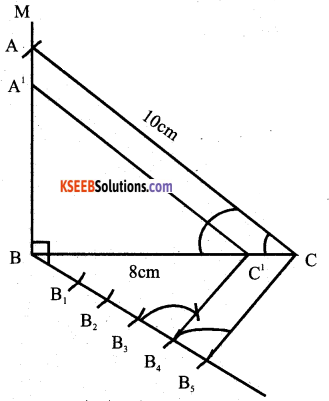
V. Answer the following ( 4 × 4 = 16 )
Question 34.
Solve the pair of equations graphically.
x + y = 8 and x – y = -2
Answe:
x + y = 8
y = 8 – x
x – y = -2
x = -2 + y

x = 6/2 = 3
x + y = 8
3 + y = 8
y = 8 – 3
y = 5
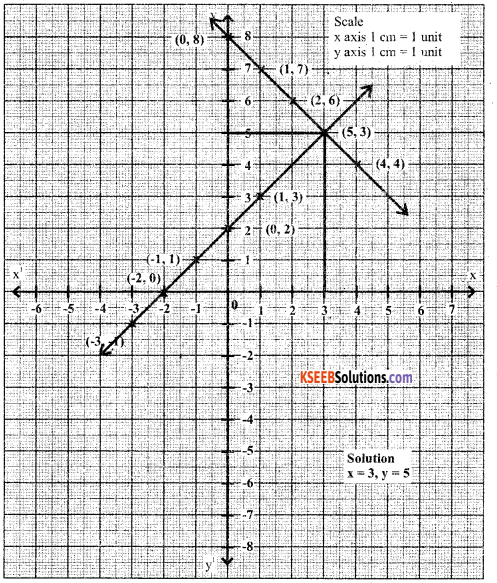
Question 35.
Devide 20 into four parts which are in arithmetic progression and such that the product of first and fourth is to the product of second and third in the ratio 2:3.
Answer:
Let the four parts in A.P be :
a – 3d, a – d, a +d, a + 3d
Their sum = (a – 3d) + (a – d) + (a + d) + (a + 3d) = 20
⇒ 4a = 20 or a = 5
Also, it is given that
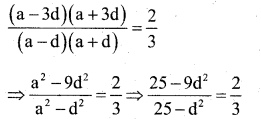
or 75 -27d2 = 50 – 2d2
25d2 = 25 .
⇒ d2 = 1 or d = +√1 = ±1
When a = 5, d = 1, the four parts are 2, 4, 6,8
When a = 5, d = -1; the four parts are 8, 6, 4,2
Hence the four parts are (2, 4, 6, 8) or (8, . 6,4,2)
OR
The angles of a quadrilateral are in AP such that the greatest is double the least calculate all the angles of the quadrilateral.
Answer:
Let the quadrilateral be ABCD
The angles of the quadrilateral are in AP.
∴ The four angles are A, B, C and D which are a -3d, a – d, a + d, a + 3d respectively.
⇒ The least angle is a – 3d and the greatest angle is a + 3d.
It is given that
a + 3d = 2(a – 3d)
a + 3d = 2a – 6d
2a – a – 6d – 3d = 0
a – 9d ……(1)
9d = a
But ∠A + ∠B+∠C + ∠D = 360°
a – 3d + a – d + a + d + a +.3d = 360°
4a = 360 / 4 = 90°
But 9d = a
d = \(\frac{a}{9}=\frac{90}{9}\) = 10°
∴ ∠A=a- 3d = 90 – 3(10) = 90 -30 = 60°
∠B = a – d = 90 – 10 = 80°
∠C = a + d = 90 + 10= 100
∠D = a + 3d = 9 + 3(10) = 90 + 30 = 120
![]()
Question 36.
A person on the lighhouse of height 100m above the sea level observes that the angle of depression of a ship sailing towards the light house changes from 30° to 45°. Calculate the distance travelled by the ship during the period of observation. (Take √3 ≈ 1.73)
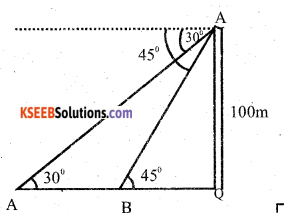
Answer:
P is the top of the light house PQ. We are given that its height PQ = 100m PX is horizontal line through P
∠APX = 30° and ∠BPX =45°
Then, ∠PAQ =30° and ∠PBQ = 45°
Suppose, AB = x metre and BQ = y metre
Karnataka SSLC Maths Model Question Paper 2 with Answers – 40
⇒ x + y =100√3 = 100√3 = 100× 1.732
⇒ x +y = 173.2
⇒ x + 100 = 173.2
⇒ x = 73.2
Therefore, the distance travelled = 73.2m
Question 37.
Prove that “the ratio of areas of two similar triangles is equal to the square of the ratio of their altitudes.
Answer:
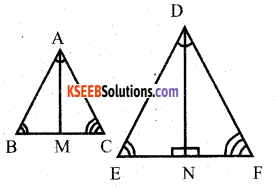
Data : ∆ABC ∼ ∆DEF
∠A = ∠D
∠B = ∠E
∠C = ∠F
\(\frac{A B}{D E}=\frac{A C}{D F}=\frac{B C}{E F}\)
T.P.T : \(\frac{\text { Area of } \Delta \mathrm{ABC}}{\text { Area of } \Delta \mathrm{DEF}}=\frac{\mathrm{AB}^{2}}{\mathrm{DE}^{2}}=\frac{\mathrm{AC}^{2}}{\mathrm{DF}^{2}}=\frac{\mathrm{BC}^{2}}{\mathrm{EF}^{2}}\)
Construction:Draw AM ⊥ BC and AN ⊥ EFim
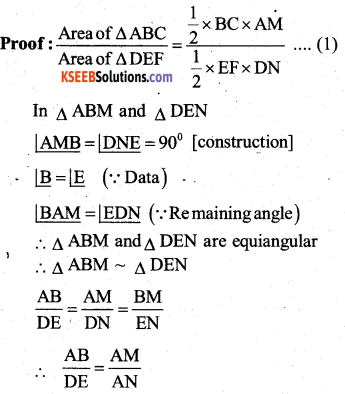
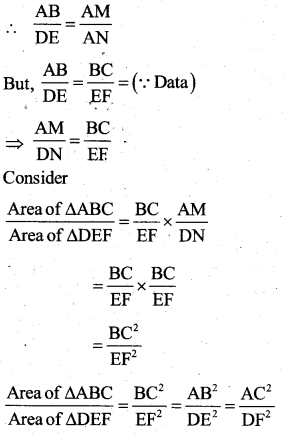
![]()
VI. Answer the fallowing : ( 5 × 1 = 5 )
Question 38.
The radii of the circular ends of the frustrum of height – 6cm are 14 cm and 6cm respectively. Find the lateral surface area and total surface area of frustrum.
Answer:
R = 14cm, r = 6cm and h =6cm
Now, let 1 be the slant height of the frustrum;
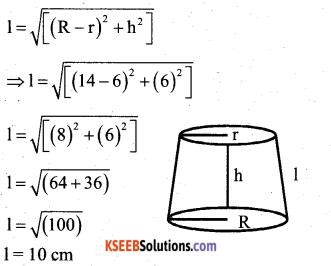
Now, lateral surface area of the frustrum
= π(R + r)l
= π (14 + 6) 10
= 628.57 cm2
And total surface area of the frustrum = π[(R+r)l + R2+ r2]
= π [(14 + 6)10 + (14)2 + (6)2]
= π(200 + 196 + 36)
= π(432)
= 1357.71 cm2.